IJCRR - 13(21), November, 2021
Pages: 27-33
Date of Publication: 09-Nov-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
High-Risk Pathological Features in Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy Specimens
Author: Anuradha Sekaran, Harika Methuku, C. Mallikarjun, Purna Chandra Reddy, Narrendran AP, Rajesh Kumar Reddy Adapala
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Radical prostatectomy is the treatment of choice for localized prostate cancer. Minimally invasive surgery such as robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (RALRP) is the new gold standard. RALRP has many advantages like visualisation of the surgical field, better instrument control, refined dissection and better assessment of high-risk pathological features. Detection of high-risk pathological features is important since they determine biochemical recurrence after prostatec�tomy. This study evaluates oncological outcomes in patients undergoing RALRP. Materials and Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 88 patients who have undergone RALRP over 3 years (2018-2020). The appropriate data was statistically analysed and interpreted. Results: The mean patient age in our study was 68.3 years. Mean PSA was 18.5ng/ml. The majority of the patients in our study had the organ-confined disease (T2). 28% had extraprostatic extension (EPE), 20% showed seminal vesicle invasion. The right lateral margin was the most common positive surgical margin in our study. Pelvic lymph node dissection was done in 33 out of 88 patients out of which 6 patients showed lymph node metastasis. Conclusion: RALRP evolved as the most common treatment modality for prostatic cancers in recent years. Our study attempts to assess the pathological features in RALRP specimens.RALRP in our study provided a lesser positive surgical margin rate, improved visualization of apex, higher lymph node yield. This is in concordance with few studies published in the literature, which have compared RALRP with RRP.
Keywords: Prostate carcinoma, Robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy, Positive surgical margins, Extraprostatic extension, Seminal vesical invasion, Biochemical recurre
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION:
Prostate carcinoma is the most common cancer in men. A common treatment modality is a radical prostatectomy. After radical prostatectomy, patients with high-risk pathological features have an increased risk of developing biochemical recurrence in the future. Any inaccurate risk assessment in prostate carcinoma is likely to result in improper treatment. It can lead to indiscriminate administration of androgen deprivation therapy or unnecessary exclusion of cases from the same. Histopathological features provide indicators of PSA recurrence-free survival. The high-risk pathological factors include grade group, positive surgical margins, EPE, lymph node metastasis, seminal vesicle invasion (SVI) and higher grade of disease. After radical prostatectomy, the probability of disease-free survival at 5 years is around 80% for tumours with negative margins, whereas it is only 58% to 64% for tumours with positive margins1. EPE and lymph node metastasis are important factors that correlate with biochemical recurrence and disease-free survival. SVI is also a predictive pathological factor of local recurrence and distant metastases2. Radical Prostatectomy can be performed either through retropubic, laparoscopic or robotic-assisted laparoscopic techniques. With the introduction of advanced robotic devices such as the Da Vinci Surgical System, RALRP has been widely accepted as a new gold standard in the treatment of prostate cancer3. Advantages of RALRP over RRP are minimally invasive procedure, high precision, greater 3-dimensional visualization of the surgical area, better functional and oncologic outcomes with less operative blood loss, higher continence and potency rates. RALRP shows a lower positive surgical margin rate and maintenance of larger amounts of residual surface adipose tissue in RALRP specimens3. Maintained larger amounts of residual surface adipose tissue indicates better-preserved prostate capsules and diagnosis of EPE also depends on the presence of surface adipose tissue, RALRP usually provides better specimens for accurate pathologic staging than RRP3. The probability of disease-free survival depends on accurate pathologic assessment which is therefore very important.
OBJECTIVE:
Prediction of oncological outcomes with an emphasis on high-risk pathological factors including biochemical recurrence in post-RALRP patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
We retrospectively reviewed 88 patients who had undergone RALRP over 3 years. Prostatectomy and lymph node excision specimens were examined by the pathologists according
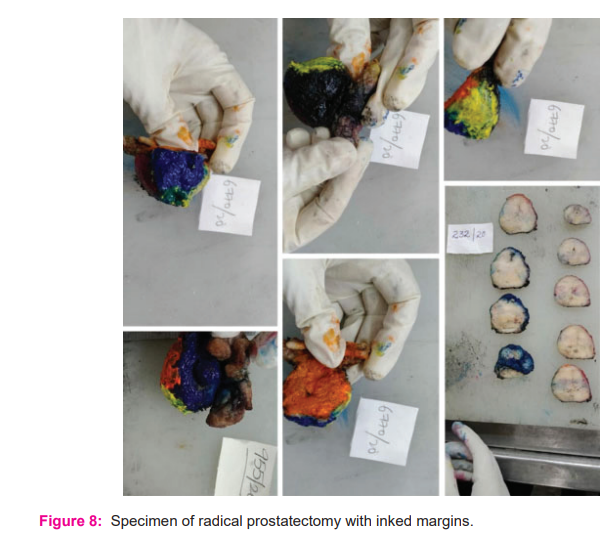
to standard protocols. These specimens received were oriented, and inked with different colours on apex, base, anterior, posterior, right and left sides. The vas resection margins were sampled and the seminal vesicles were cut close to the prostate. The apex and base are cut perpendicular to the urethra and then sectioned sagitally. The remaining prostate was sliced into 4 mm sections (figure 8). Tumours were graded and grouped according to the revised Gleason score as per the 2016 World Health Organization (WHO) classification of Tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs. The pathologic staging was done according to the 2018 pTNM classification.
Parameters analysed in the present study are the age of the patient, preoperative and post-operative serum Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA), Gleason score in preoperative Transrectal ultrasound-guided biopsy (TRUS) or Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Gleason score in radical prostatectomy specimen, extraprostatic extension (EPE), lymphovascular invasion(LVI), Seminal vesicle invasion (SVI), positive surgical margins (PSM) and pelvic lymph node dissection. Prospectively, post-operative PSA levels at the last follow up visit were noted.
RESULTS:
Preoperative characteristics of patients undergone RALRP are shown in table 1.
The final report was signed out after being reviewed by two pathology consultants
Patients ages ranged between 51 to 83 years. Preoperative PSA was available in 83 patients which ranged between 5.24 to >100 ng/mL with a mean of 18.5ng/mL. Preoperative Gleason scores were available in 83 out of 88 patients. 31%, 55%, 13% of patients had preoperative Gleason pattern 6,7, 8-10 respectively.
Final Gleason score in radical prostatectomy – Gleason score 6 in 10% of patients, Gleason score 7 in 74 % of patients, Gleason score 8-10 in 16% of patients. The discordance between initial core needle biopsy GS and RALRP GS was observed to be ~4.8 % in the current study (calculated using paired Student t-test).
Any poorly differentiated foci on both biopsies and prostatectomy specimens were confirmed by immunostaining with alpha-methyl acyl-CoA racemase(AMACR) as and when required.
Extraprostatic extension is seen in 28% of patients. LVI is seen in 12% of patients. Seminal vesicle invasion is seen in 20% of patients. Surgical margin apex was involved in one patient. The surgical margin base and anterior were uninvolved in all patients. The surgical posterior margin was involved in one patient. The surgical right lateral margin was involved in 5 out of 88 patients. The surgical left lateral margin was involved in one patient. Bladder neck margin was involved in one patient. Pelvic lymph node dissection was done in 37% (33 out of 88) patients out of which lymph node metastasis was found in 6 out of 33 patients. Final pathologic stage classification of T2 in 67 % patients, T3a in 13% patients, T3b in 20% patients.
To analyse the frequency of biochemical recurrence, patients were followed –up with postoperative serum PSA determinations. The values were analysed in 44 out of 88 patients, with the cut-off value being less than or equal to 0.2ng/ml. Around 62% of patients were found to have values less than 0.2ng/ml and the remaining (38%) had more than 0.2ng/ml.
DISCUSSION:
RALRP has changed the treatment of prostate cancer with marked improvement in functional outcome and reduced technical limitations4. India saw exceptional growth in robotic surgery from 2006 onwards. There are currently 66 centres and 71 robotic installations as of July 2019, with more than 500 trained robotic surgeons in our country. The trend suggests that the rise of robotic surgery in India has been, and is going to be a rapid and huge one. Different surgical procedures have varying incidences of positive surgical margins which play an important role in the evaluation of oncologic outcomes. Capsular incision during surgery indicates damage to the prostate capsule and may contribute to a positive surgical margin if the tumour is present at the site of the capsular incision. The presence of residual surface adipose tissue suggests an undamaged prostate capsule. Rajan et al. showed that preoperative PSA, GS, clinical T stage, pT stage, and >3mm multifocal PSMs were predictive factors of Biochemical recurrence (BCR)5. Preoperative serum PSA levels also affect BCR6. Therefore this study is to scrutinize RALRPand its outcomes on positive surgical margin status, EPE and other histologic variables which define patient outcomes.
GLEASON SCORE:
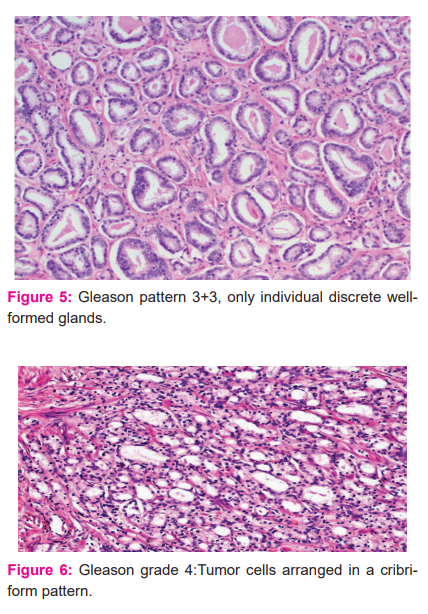
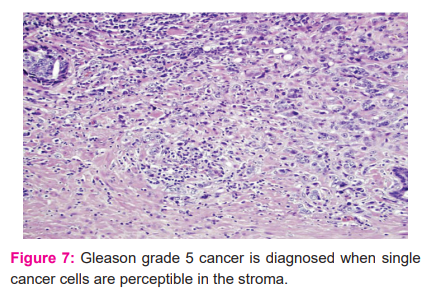
Appropriate treatment modalities for prostate cancer are mainly based on pathologic information obtained from needle biopsies, that should correlate with that obtained from Radical prostatectomies. GS is associated with tumour prognosis and the new WHO grading system is composed of five prognostic grades. Inconsistency rates of Gleason score between needle biopsy and radical prostatectomy were around 23% to 56%7. Increasing the number of needle biopsies strengthens the accuracy of GS for accurate prediction of final cancer grade. The other reasons for GS discrepancies comprise grading errors by pathologists, borderline grades, sampling errors and the fact that prostate cancer is multifocal, with a heterogeneous population of tumour cells. This may result in inadequate sampling and that is over-represented with high-grade disease or, conversely, over-represented with the low-grade disease compared with histological grade in the resected prostate. In our study, discordant states were only around ~4.8%. Examples of fewGleason patterns are shown in Figures 5,6 and 7.
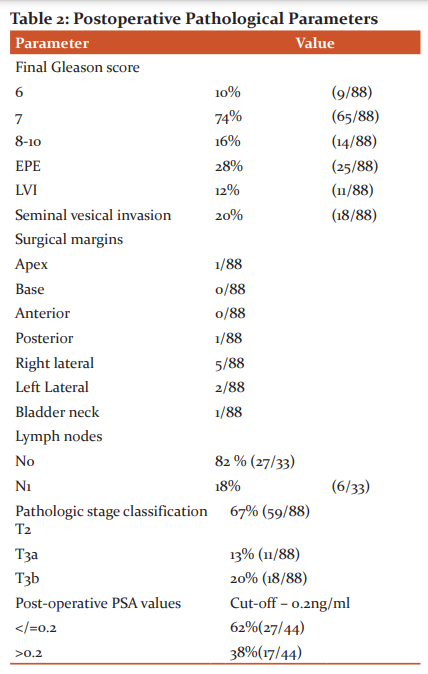
POSITIVE SURGICAL MARGIN IN RALRP:
The Independent predictive factor of biochemical recurrence, local recurrence and development of distant metastasis is found to be PSM after RP8. Figure 4 depicts a positive surgical margin. Factors such as cancer volume, surgical technique, artefacts, experience and pathological evaluation affect surgical margins6. Also, the rate of PSMs significantly increased with
Preoperative PSA, Pathological tumour stage and grade6. Coelho et al. compared the data from 11 published studies of RALRP (8,472 cases) in high-volume centres which showed weighted mean positive surgical margin rates of 13.6% which was lower compared to RRP specimens where PSM of 24% was observed 8,3. When Coelho et al. compared PSM rates in different T stages PSM rates for pT2 tumours were also lowest (9.6% for RARP) when compared to PSM rates in RRP and laparoscopic radical prostatectomy(LRP)8. A study done by Henghonget al. noted that the positive surgical margin rate in RALRP group was 28.6% which was comparable with the published data (9.3-33.3%)3. However all of the reports cited above were non-randomized studies, so definitive conclusions cannot be reached8. PSM in our study was 11.3 % which was comparable to the above-mentioned studies.
PSM for organ-confined disease (pT2) varies from 4.5 to 10.6%, whereas the same for pT3 disease ranges from 20 to 47%9. In our study, the PSM for cases with pT2 and pT3 were 10.5% and 10% respectively.
Few studies showed that PSM at apex reduced in RALRP when compared to RRP due to improved visualization of apex10, however other studies showed no statistical difference between different PSM sites in RALRP vs RRP11. In our study, posterior and lateral margins are more involved than apex which was comparable to few other studies in literature10. In the study of 500 cases done by Patel et al. apex was involved in 8.5% of all patients with positive surgical margin and posterolateral was involved in 56% whereas those rates are 10% and 80% in our study respectively10.
EPE IN RALRP:
EPE in simpler terms is defined as the presence of a tumour beyond the confines of the prostate gland (figure 1). Identifying boundaries of the prostate gland is difficult at times especially when the desmoplastic reaction is induced by a tumour at the periphery and also due to the fact prostate lacks a true histological capsule12. Hence Diagnostic criteria for EPE will vary with different regions and also diagnosis of EPE can be made in several different situations12.EPE is a well-established adverse prognostic factor of prostatic carcinoma12. Over some time, it was observed that about 50% of patients with EPE did not show 10-year tumour progression, hence studies have been done to quantify EPE in a manner by which it can predict tumour progression12. In our study, EPE was found in 28 % of patients.
LYMPH NODE DISSECTION AND METASTASIS:
In intermediate and high-risk localized prostate cancer, pelvic lymph node dissection(PLND) is performed along with radical prostatectomy13. Improvement of cancer-specific survival is noted with excision of at least 4 lymph nodes as demonstrated by the Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) database study13. With the increase in the number of lymph nodes removed during Radical prostatectomy (RP) and PLND, improvement in cancer-specific survival was noted in a study done by Abdollah et al13. Several lymph nodes dissected are more in RALRP than RRP as more meticulous dissection with the help of 3D vision and less intraoperative blood loss14. In the study of 100 patients who had undergone extended pelvic lymphadenectomy by Batra et al., 17% were detected with lymph node?positive disease13. This finding is comparable to findings in our study. In our study out of 33 patients who had undergone lymphadenectomy 18% of patients had lymph node positive disease. Extended PLND was an independent prognostic factor for biochemical progression?free survival when adjusted for other clinical and pathologic features13.
The preoperative clinical stage was found to be the only significant criteria for pelvic lymph node involvement in the study done by Batra et al.13Lymphnode with tumour deposit is depicted in figure 2.
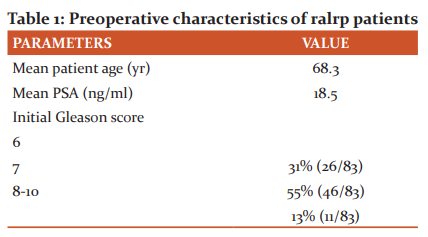
SEMINAL VESICLE INVASION (SVI):
SVI is defined as a tumour invading the muscular wall of seminal vesicles (figure 3). In patients, without lymph node metastasis SVI route is not of prognostic importance15. Despite earlier detection and stage migration in the PSA era, the SVI rate decreased from >10% to 6% of all RP specimens15. SVI is a poor prognostic indicator despite lower PSM rate, lymph node-positive rate, frequency of T3b disease and is believed to be associated with occult micrometastatic disease, earlier biochemical recurrence and disease progression15. Advanced clinical stage, intermediate or high-risk Gleason score at pathological evaluation and positive surgical margins predict biochemical recurrence15. In our study, SVI is seen in 20% of the patients.
POST-OPERATIVE PSA VALUES AND ASSOCIATION WITH BCR:
The most appropriate definition of BCR after a RALRP is uncertain. In general, PSA should reach undetectable levels within 4 weeks after surgery. However, a detectable PSA level after this time does not necessarily represent a clinically significant recurrent disease. Some patients with detectable PSA levels do not progress because of the presence of a benign prostate gland at the margin of resection or from a dormant residual focus of prostate cancer at a local or distant site16.
Like that reported by others, 17BCR is defined by single post-op PSA value of less than or equal to0.2ng/ml. This shows that RALRP confers effective BCR control, however, long-term oncological safety still needs to be established.
LIMITATIONS:
We were able to analyze the postoperative PSA values of only 50% of patients (44/88) since the remaining did not present themselves for follow-up. And the comparison between RRP and RALRP was not done.
CONCLUSION:
In summary, the risk assessment of disease recurrence and progression after prostatectomy is based on specific serological and histopathological findings. These findings should be analysed precisely for the optimal administration of adjuvant therapy and follow-up. Among surgical options, RALRP has evolved as the most promising treatment modality for prostatic carcinoma. It has advantages such as high lymph node yield, better visualization of apex, less PSM rate and therefore may have good long term oncologic outcomes.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS:
The authors would like to thank the technical staff of AIGHospitals and Consultants of AINU Hospitals for providing material for publication and Dr Juhi Khanna for her help in drafting of the manuscript.
DECLARATIONS:
Funding: No funding sources
Conflict of interest: None declared
Ethical approval: Not required
Author’s contribution statement:
-
Dr AnuradhaSekaran – Conception of study, data analysis, interpretation and critical revision
-
Dr Harika Methuku – Data collection, Analysis and Interpretation
-
Dr Mallikarjuna C – Conception of study and revision of the manuscript
-
Dr Purna Chandra Reddy K– Manuscript revision
-
Dr Narendra A.P – Data analysis
-
Dr Rajesh Kumar Reddy Adapala - Critical revision


References:
|
1.
|
Epstein JI. Pathologic assessment of the surgical specimen. Urol Clin North Am.2001;28(3):567–94.
|
|
|
|
|
2.
|
Pierorazio PM, Ross AE, Schaeffer EM, Epstein JI, Han M, Walsh PC, et al. A contemporary analysis of outcomes of adenocarcinoma of the prostate with seminal vesicle invasion (pT3b) after radical prostatectomy. J Urol.2011;185(5):1691-7.
|
|
|
|
|
3.
|
Hong H, Mel L, Taylor J, Wu Q, Reeves H.Effects of robotic-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy on surgical pathology specimens. Diagn Pathol. 2012;7(1):24.
|
|
|
|
|
4.
|
Binder J, Kramer W.Robotically?assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy.Bri J U Int. 2001;87(4):408-10.
|
|
|
|
|
5.
|
Kang JK, Chung JW, Chun SY, Ha YS, Choi SH, Lee JN, et al. Oncological and functional outcomes following robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy at a single institution: a minimum 5-year follow-up. YeungnamUniv J Med.2018;35(2):171–8.
|
|
|
|
|
6.
|
Pfitzenmaier J, Pahernik S, Tremmel T, Haferkamp A, Buse S, Hohenfellner M. Positive surgical margins after radical prostatectomy: do they have an impact on biochemical or clinical progression? Bri J U Int.2008;102(10):1413–8.
|
|
|
|
|
7.
|
Camtosun A, Gökçe H. Comparison of prostate biopsy pathology and radical prostatectomy pathologies. Dicle T?p Dergisi.2019;46(1):133-9.
|
|
|
|
|
8.
|
Coelho RF, Rocco B, Patel MB, Orvieto MA, Chauhan S, Ficarra V, et al. Retropubic, laparoscopic, and robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a critical review of outcomes reported by high-volume centres. J Endourol.2010;24(12):2003–15.
|
|
|
|
|
9.
|
Kaler KS, Vernez SL, Skarecky DW, Ahlering TE. Outcome Measures After Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy. In: Robotic Urology. Cham: Springer International Publishing;2018.p.421-37.
|
|
|
|
|
10.
|
Patel VR, Shah S, Arend D. Histopathologic outcomes of robotic radical prostatectomy. Sci World J.2006;6:2566–72.
|
|
|
|
|
11.
|
Fujimura T, Fukuhara H, Taguchi S, Yamada Y, Sugihara T, Nakagawa T, et al. Robot-assisted radical prostatectomy significantly reduced biochemical recurrence compared to retropubic radical prostatectomy. Bri Med Cancer Res. 2017;17(1):1-7.
|
|
|
|
|
12.
|
Magi-Galluzzi C, Evans AJ, Delahunt B, Epstein JI, Griffiths DF, van der Kwast TH, et al. International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Handling and Staging of Radical Prostatectomy Specimens. Working group 3: extraprostatic extension, lymphovascular invasion and locally advanced disease. Mod Pathol.2011;24(1):26–38.
|
|
|
|
|
13.
|
Batra V, Gautam G, Jaipuria J, Suryavanshi M, Khera R, Ahlawat R. Predictive factors for lymph node positivity in patients undergoing extended pelvic lymphadenectomy during robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Indian J Urol.2015;31(3):217–22.
|
|
|
|
|
14.
|
Tang K, Jiang K, Chen H, Chen Z, Xu H, Ye Z. Robotic vs. Retropubic radical prostatectomy in prostate cancer: A systematic review and a meta-analysis update. Oncotarget.2017;8(19):32237–57.
|
|
|
|
|
15.
|
Pierorazio PM, Ross AE, Schaeffer EM, Epstein JI, Han M, Walsh PC, et al. A contemporary analysis of outcomes of adenocarcinoma of the prostate with seminal vesicle invasion (pT3b) after radical prostatectomy. J Urol.2011;185(5):1691–7.
|
|
|
|
|
16.
|
Ravery V. The significance of recurrent PSA after radical prostatectomy: benign versus malignant sources. Semin Urol Oncol.1999;17(3):127–9.
|
|
|
|
|
17.
|
Amling CL, Bergstralh EJ, Blute ML, Slezak JM, Zincke H. Defining prostate-specific antigen progression after radical prostatectomy: what is the most appropriate cut point? J Urol.2001;165(4):1146–51.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License