IJCRR - 13(20), October, 2021
Pages: 179-185
Date of Publication: 24-Oct-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
To Access the Effects of Cigarettes Smoking and Nicotine Dependency in Lung Function of Healthy Smokers Using Fagerstorm's Questionnaire and Spirometry
Author: Mani Sathish Kumar, Ganesh Gayathri, Mani Anbumaran, Vadivelu Gangadharan
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Globally, India stands second to China in the total number of smokers. Recent findings showed huge growth in adult male smokers in the country. One out of five adults i.e 20% adults smoke all over the world, With over the 20th century it killed around 100 million people. Objective and Methodology: The purpose of this study is to analyse the effects of cigarette smoking and nicotine dependency on lung function of healthy smokers using Fagerstrom's questionnaire and spirometry. Where along with the history, spirometry and Fagerstrom's questionnaire is asked. The test is performed on 76 patients who are divided into four categories based on Fagerstrom's questionnaire namely low nicotine dependence, low \? moderate nicotine dependence, moderate nicotine dependence, and high dependence. The differences in the mean value of each parameter between the four categories of smokers based on the duration of smoking and also on the number of cigarettes smoked per day were analyzed and discussed. Result: The mean FVC of the patients with high dependence (54.12\? 18.893) is lesser and the mean FVC of the patients with low dependence (72.85\?14.072) is greater. This concludes higher nicotine dependence has reduced FVC and there is near significance between each category and the mean FEV1 of the patients with high dependence (42.12\? 21.437) is lesser and the mean FEV1 of the patients with low dependence (67.58\?18.322) is greater. Conclusion: This concludes the high dependence on nicotine has reduced FEV1 and there is near significance between each category. An increase in Nicotine dependence level decreases the BMI moderately.
Keywords: Smoking, Nicotine, Dependency, Spirometry, Fagerstrom’s, Lung capacity, BMI
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Recent findings showed huge growth in adult male smokers in the country. Within 17 years the statistics have grown high from 79 million’s to 108 million.1This problem is compounded by the fact that the rate of cigarette smoking in young people continues to steadily increase.2
Smoking is a known risk factor for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases 3 and a cause of different cancers.3Cigarette smoke can trigger exacerbations of asthma, reduce lung function and increase health care utilization including hospital admissions.4,5
Smoking behaviours in India are also peculiar with a large number of people using non-conventional forms of tobacco in hookah, bidi, or chillum.6,7 Lung cancer is nearly 6-times common in hookah smokers compared to non-smokers,6 and Chillum smoking has been demonstrated to result in a much higher increase in end-tidal carbon monoxide levels than cigarette smoking.7
As cigarettes are costlier compared to other tobacco products like bides and dipping tobacco, the young male population is shifting from costly cigarettes to these cheaper products landing themselves in more trouble. We used Fagerstrom’s nicotine dependency test (FTND) score to categorize the smokers into low, low to moderate, moderate and high nicotine dependents.8 However the number of cigarettes per day in the FTND itself is found to be a better item than the whole of the FTND questionnaire.9
AIMS AND OBJECTIVES
AIM:
The purpose of this study is to analyse the effects of cigarette smoking and nicotine dependency in lung function of healthy smokers using Fagerstrom’s questionnaire and spirometry.
OBJECTIVES:
The relationship between nicotine dependence level and lung functions among cigarette smokers.The relationship between Age and BMINicotine dependence level among the cigarette smokers
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This Prospective observational study was conducted upon 76patients, who presented to the department of TB and Respiratory Medicine from JAN 2019 – JAN 2020 at Saveethamedical college and hospital, after ethical committee clearance
Inclusion criteria:
Only male patients, Age >18 yrs, Patients with chief complaints and history of smoking, active smokers and ex-smokers.
Exclusion criteria:
Non-smokers, Patient unable to perform PFT, Test not reaching 6-second, expiration time, Active pulmonary tuberculosis, Active haemoptysis, Presence of pleural disease, Cor-Pulmonale, Resting heart rate >120/ min, Systolic blood pressure > 180mm Hg, Diastolic blood pressure > 100mm Hg, female patients.
Considering the prevalence rate of 14.2% daily smokers in Tamil Nadu as reported in the Global adult tobacco survey (GATS India,2010) report and with a power of 80% and a 5% alpha error, the sample size calculated was 76. The study participants were recruited from the chest medicine OPD. After taking an informed consent on explaining the risk and benefit of the study, smokers patients will, undergo a pulmonary function test (spirometry). Spirometry is done using a standard spirometer (flow-based spirometer). Basic anthropometric data like age, weight to the nearest kilograms and height to the nearest centimetres, were recorded. Pulmonary function testing was performed according to the standards of the American Thoracic Society/European respiratory society task force guidelines. Each study participant performed 2 to 3 forced expiratory manoeuvres. The best attempt was saved. FVC, FEV1, FEV1/FVC, FEF 25-75%, PEF are noted.
The subjects were explained about the study protocol and questions raised by them were cleared. Based on their FTNDquestionnaire.9
RESULTS
Out of 76 patients who participated in the study, 64.5% of patients are current smokers and 35.5% of the patients are Ex-smokers.
It is observed that from (Table-1) 15.79% of the patients are having smoking habit for up to 5 years, 28.94 % of the patients have 6-15 years of smoking habit, whereas 32.9% and 28.94% of the patients are having smoking habits for 16-25 years and more than 26 years respectively.
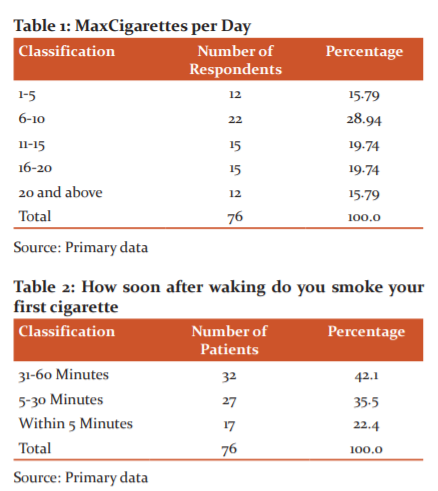
It is noted that From(Table-2) 42.1% of the patients agreed that the take within 31-60 minutes smoke the first Cigarette, 35.5% of the patients took 5-30 minutes for them to smoke the first Cigarette and 22.4% of the patients agreed that they took less than five minutes for smoking first Cigarette after waking(Figure-2).10,11
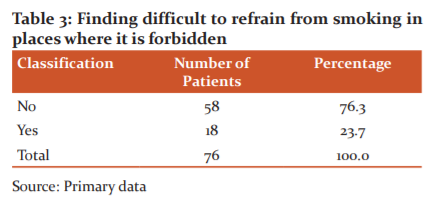
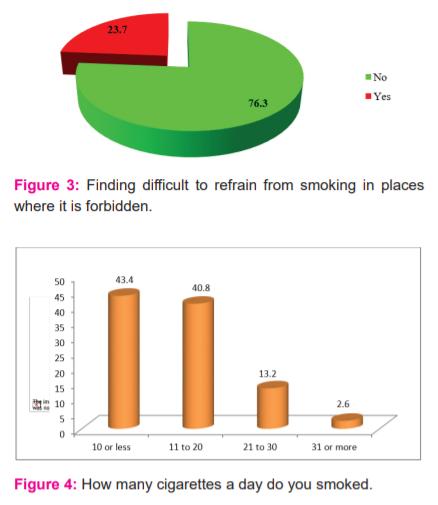
It is observed from (Table -3) that 76.3% of the patients denied that they are finding it difficult to refrain from smoking in places where it is forbidden (Figure-3). However, 23.7% of patients agreed with the same.12
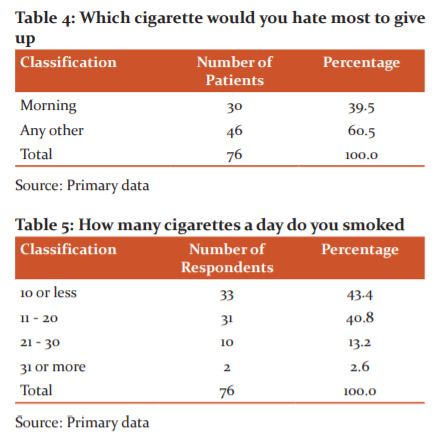
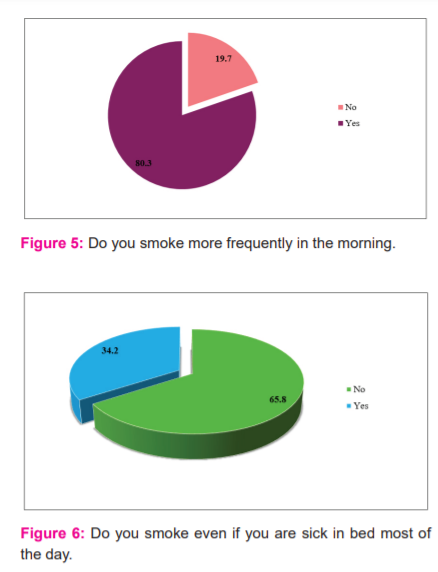
43.4 % of the patients agreed that they use to smoke 10 or fewer cigarettes, 40.8 % of the patients accepted that they use to smoke 11-20 cigarettes (Figure-4),14 13.2 % of the patients honestly agreed that they use to smoke 21-30 cigarettes and only 2.6 % of the patients use to smoke more than 30 cigarettes (Table-5).15
It is noted from the above table that 65.8 % of the patients agreed that they won’t smoke if they are sick in bed most of the day (Table-4). 34.2 % of the patients honestly agreed that they use to smoke even if they are sick in bed most of the days.13
It is noted that 19.7% of the patients agreed that they can smoke more frequently in the morning and 80.3 % of the patients accepted that they are not frequent smokers in the morning (figure-5).16,17
The difference in nicotine dependency on lungs function
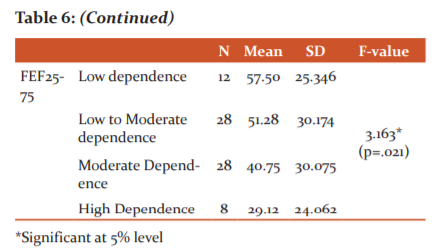
This section presents the Comparison of nicotine dependence levels on lung functions among cigarette smokers. To compare the nicotine dependence level on lung functions one way ANOVA is used. The results are shown in the following (Table-6).
Null hypothesis H01: There is no significant difference between nicotine dependence levels concerning the lungs function.

The F-value of 3.243 indicates that the null hypothesis H01 is rejected at a 1% level. It is noted that the mean FVC of the patients with high dependence (54.12) is lesser and the mean FVC of the patients with low dependence (72.85) is greater. This concludes the high nicotine dependence has reduced FVC.
F-value of 3.090 indicates that the null hypothesis H01 is rejected at a 1% level.18 It is noted that the mean FEV1 of the patients with high dependence (42.12) is lesser and the mean FEV1 of the patients with low dependence (67.58) is greater. This concludes the high dependence on nicotine has reduced FEV1.19
F-value of 3.225 indicates that the null hypothesis H01 is rejected at a 1% level. It is noted that the mean FEV1/FVC of the patients with high dependence (74.75) is lesser and the mean FEV1/FVC of the patients with low dependence (94.00) is greater. This concludes the high nicotine dependence has reduced FEV1/FVC.
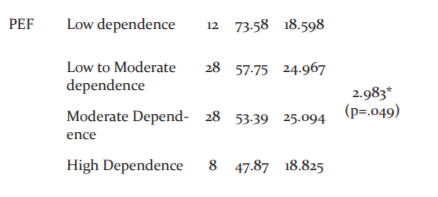
F-value of 2.983 indicates that the null hypothesis H01 is rejected at a 1% level. It is noted that the mean PEF of the patients with high dependence (47.87) is lesser and the mean PEF of the patients with low dependence (73.58) is greater.20 This concludes the high nicotine dependence has reduced PEF.
F-value of 3.163 indicates that the null hypothesis H01 is rejected at a 1% level. It is noted that the mean FEF25-75 of the patients with high dependence (29.12) is lesser and the mean FEF25-75 of the patients with low dependence (57.50) is greater. This concludes the high nicotine dependence has reduced FEF25-75.
Influence of cigarettes smoked on nicotine dependency
This section presents the Influence of cigarettes smoked on nicotine dependency among cigarette smokers. A sample of 76 patients was selected for the study. To study the Influence of cigarettes smoked on nicotine dependency, one way ANOVA is used. The results are shown in the following table.
Null hypothesis H02: There is no influence of cigarettes smoked on nicotine dependency
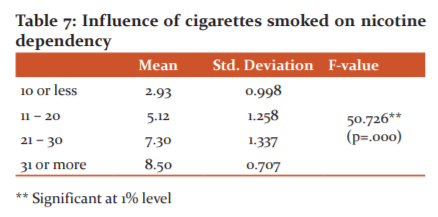
From the above (Table-7) the F-value of 50.726 indicates that the null hypothesis H02 is rejected at a 1% level. It is noted that the mean nicotine dependence of the patients who smoke more than 30 cigarettes (8.50) is higher and the dependence level of patients smoking less than 10 cigarettes (2.93) is less. This concludes the increase in smoking more cigarettes have improved the nicotine dependency level.
Relationship between age, BMI and Nicotine dependence level
This section gives clarity about the relationship between age, BMI and Nicotine dependence level among cigarette smokers. Karl Pearson’s correlation coefficient is obtained and the results are shown in the following table.
Null hypothesis H03: There is no significant relationship between age and Nicotine dependence level
Null hypothesis H04: There is no significant relationship between BMI and Nicotine dependence level
It is observed that the correlation coefficient (0.315) between age and Nicotine dependence level is positive and significant at 1% level; in this case, the null hypothesis H03is rejected. It is concluded that as age increases the Nicotine dependence level increases moderately.
It is observed that the correlation coefficient (-0.265) between BMI and Nicotine dependence level is negative and significant at 5% level; in this case, the null hypothesis H04is rejected. It is concluded that an increase in Nicotine dependence levels decreases the BMI moderately among cigarette smokers.

DISCUSSION:
The differences in the mean value of each parameter between the four categories of smokers based on the duration of smoking and also on the number of cigarettes smoked per day were analyzed and discussed.21
Out of 76 patients who participated in the study, 64.5% of the patients are current smokers and 35.5% of the patients are Ex-smokers there predominant chief complaints discussed in (Figure-1).22
The findings resulted in 9.22% of the patients are having smoking habits up to 5 years, 28.94 % of the patients have 6-15 years of smoking habit,23 whereas 32.9% and 28.94% of the patients are having smoking habits for 16-25 years and more than 26 years respectively.24
It is understood that 15.79% of the patients are smoking 1-5 cigarettes per day, 28.94% of the patients are smoking 6-10 cigarettes per day,25 19.74% of the patients are smoking 11-15 cigarettes per day,26 another 19.74% of the patients are smoking 16-20 cigarettes per day and 15.79% of the patients agreed that they smoke 20 and more Cigarettes per day.27
The sample test was performed to find the significant difference between the four categories having nicotine dependency levels concerning PFT observations.
The result showed that the F-value of 3.243(P=0.015) and the mean FVC of the patients with high dependence (54.12± 18.893) are lesser and the mean FVC of the patients with low dependence (72.85±14.072) is greater. This concludes the high dependence on nicotine has reduced FVC and there is near significance between each category.28
The result showed that the F-value of 3.090(P=0.032)and the mean FEV1 of the patients with high dependence (42.12± 21.437) are lesser and the mean FEV1 of the patients with low dependence (67.58±18.322) is greater. This concludes the high dependence on nicotine has reduced FEV1 and there is near significance between each category.29
The result showed that the F-value of 3.225(P=0.023)and the mean FEV1/FVC of the patients with high dependence (74.75±17.161) are lesser and the mean FEV1/FVC of the patients with low dependence (94.00±13.724) is greater.30 This concludes the high nicotine dependence has reduced FEV1/FVC and there is near significance between each category.
The result showed that the F-value of 2.983(P=0.049)and the mean PEF of the patients with high dependence (47.87±18.825) are lesser and the mean PEF of the patients with low dependence (73.58±18.598) is greater. This concludes the high dependence on nicotine has reduced PEF and there is near significance between each category.31
The result showed that the F-value of 3.163(P=0.021)and the mean FEF25-75 of the patients with high dependence (29.12±24.062) are lesser and the mean FEF25-75 of the patients with low dependence (57.50±25.346) is greater. This concludes the high nicotine dependence has reduced FEF25-75 and there is near significance between each category.
The correlation coefficient (0.315) between age and Nicotine dependence level is positive and significant at a 1% level.32 It is concluded that as age increases the Nicotine dependence level increases moderately.
The correlation coefficient (-0.265) between BMI and Nicotine dependence level is negative and significant at a 5% level. It is concluded that an increase in Nicotine dependence levels decreases the BMI moderately among cigarette smokers.
CONCLUSION:
To conclude, our study suggests that nicotine dependency is the indirect root cause for the declined lung functions of a healthy smoker. The statistical significance of the results confirms the decrease in lung function with an increase in nicotine dependency. And also Age and BMIreduce lung function in nicotine dependency of healthy smokers. Nicotine craving causes the smoker to smoke more and more.34 Smoking cessation is the only way to prevent further decline in lung function and recovery of damaged lungs to a certain extend.
Fagerstrom’squestionnaire playing an important role in detecting nicotine dependency. Hence it higher scores more in nicotine dependence and it accelerates the lung function capacity declined quicker.35
Early intervention with counselling and adequate treatment using this questionnaire prevent schronic lung diseases.
Acknowledgement: I thank the department and my colleagues and the authors who contributed to the work and special mention to all the patients who have participated in the study without hesitance and I also thank our management and the Journal committee for accepting and publishing the study.
Source of Funding: None
Authors Contribution: Data Collection, Statistics and article writeup.
Conflict of Interest: None
IEC Letter No: SMC/IEC/2020/02/112
References:
1. Mishra S, Joseph RA, Gupta PC, Pezzack B, Ram F, Sinha DN, et al. Trends in bidi and cigarette smoking in India from 1998 to 2015, by age, gender and education. BMJ Glob Heal. 2016;1:e000005:1–8.
2. Academic Development: Office of Tobacco Control, Department of Disease Control, Ministry of Public Health: Tobacco smoking among Thai youth (in Thai). Thailand, 2010
3. CDC. Preventing Tobacco Use Among Young People, A Report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services 1994.
4. Joad JP. Smoking and pediatric respiratory health.Clin Chest Med. 2000;21:37–viii.
5. Ulrik CS, Lange P. Cigarette smoking and asthma. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2001;56:349–53.
6. Gupta D, Agarwal R, Aggarwal AN, Maturu VN, Dhooria S, Prasad KT, et al. Guidelines for diagnosis and management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Joint ICS/NCCP (I) recommendations. Lung India.2013; 30:228–67. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
7. Koul PA, Hajni MR, Sheikh MA, Khan UH, Shah A, Khan Y, et al. Hookah smoking and lung cancer in the Kashmir valley of the Indian subcontinent. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011; 12:519–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
8. Heatherton TF, Kozlowski LT, Frecker RC, Fagerstrom KO. The Fagerstrom Test for Nicotine Dependence: a revision of the Fagerstrom Tolerance Questionnaire. Br J Addict. 1991;86(9):1119–27.
9. Breslau N, Johnson EO. Predicting smoking cessation and major depression in nicotine-dependent smokers. Am J Public Health. 2000;90(7):1122–7.
10. Miller MR, Hankinson J, Brusasco V. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir J, 2005, 26: 319–338. [Medline] [CrossRef]
11. Kuperman AS, Riker JB: The variable effect of smoking on pulmonary function. Chest, 1973, 63: 655–660. [Medline] [CrossRef]
12. Anthonisen, N.R. Effects of smoking intervention and the use of an inhaled anticholinergic bronchodilator on the rate of decline of FEV1: the Lung Health Study. J Am Med Asss. 1994. 272(19): p. 1497-1505.
13. Bach, P.B. Variations in lung cancer risk among smokers. Journal of the National Cancer Institute (JNCI), 2003. 95(6): p. 470-478.
14. Stewart, B.W., KleihuesP., and I.A.f.R.o. Cancer, World cancer report. Vol. 57. 2003: IARC press Lyon.
15. Hirayama, T. Non-smoking wives of heavy smokers have a higher risk of lung cancer: a study from Japan. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 2000. 78(7): p. 940-942.
16. Health, U.D.o. and H. Services, The health consequences of involuntary exposure to tobacco smoke: a report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Coordinating Center for Health Promotion, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health, 2006. 709.
17. D'Souza MS, Markou A . Neuronal mechanisms underlying the development of nicotine dependence: implications for novel smoking-cessation treatments. Addict SciClinPract. 2011; 6 (1): 4–16. PMC 3188825. PMID 22003417
18. Stratton 2018, p. Dependence and Abuse Liability, 256.
19. Piper M, McCarthy D, Timothy S. Assessing tobacco dependence: A guide to measure evaluation and selection. Nicot Tobac Res. 2006; 8 (3): 339–351. doi:10.1080/14622200600672765. ISSN 1462-2203.PMID 16801292.
20. Akerman, Sarah C, Brunette MF. Green, Alan I. et al. "Treating Tobacco Use Disorder in Pregnant Women in Medication-Assisted Treatment for an Opioid Use Disorder: A Systematic Review".J Subst Abuse Treat. 52: 40–47. doi:10.1016/j.jsat.2014.12.002. ISSN 0740-5472.PMC 4382443.PMID 25592332.
21. Falcone Ma, Lee B, Lerman C, Blendy JA. Translational Research on Nicotine Dependence.TranslationalNeuropsychopharmacology.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2015;28. pp. 121–150. doi:10.1007/7854_2015_5005. ISBN 978-3-319-33911-5.ISSN 1866-3370.PMC 3579204.PMID 26873019.
22. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (1988). The health consequences of smoking: Nicotine addiction: A report of the Surgeon General (PDF). U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Centers for Disease Control, Center for Health Promotion and Education, Office on Smoking and Health. DHHS Publication No. (CDC) 88-8406.
23. Rachid F. Neurostimulation techniques in the treatment of nicotine dependence: A review. Am J Addict. 25 (6): 436–451. doi:10.1111/ajad.12405. ISSN 1055-0496.PMID 27442267.
24. MacDonald K, Pappa K . "WHY NOT POT?: A Review of the Brain-based Risks of Cannabis". InnovClinNeurosci. 13 (3–4): 13–22. PMC 4911936.PMID 27354924.
25. Ng M, Freeman MK, Fleming TD, Robinson M, Dwyer-Lindgren L, Thomson B, et al. Smoking prevalence and cigarette consumption in 187 countries, 1980-2012.J Am Med Ass. 311 (2): 183–92. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.284692. PMID 24399557.
26. Moylan S, Jacka FN, Pasco JA, Berk M. Cigarette smoking, nicotine dependence and anxiety disorders: a systematic review of population-based, epidemiological studies. BMC Med. 10 (1): 123. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-10-123. ISSN 1741-7015.PMC 3523047.PMID 23083451.
27. Richard B, Jeff M. Professional Paramedic, Volume I: Foundations of paramedic Care. Cengage Learning. pp. 640–.ISBN 978-1-133-71465-1.
28. Bullen C. Electronic Cigarettes for Smoking Cessation. Curr Card Rep.2014; 16 (11): 538. doi:10.1007/s11886-014-0538-8. ISSN 1523-3782.PMID 25303892.
29. Saccone NL, Culverhouse RC, Schwantes AN, Cannon DS, Chen X, Cichon S, et al. Multiple independent loci at chromosome 15q25.1 affect smoking quantity: a meta-analysis and comparison with lung cancer and COPD. PLOS Genetics.2010; 6 (8): e1001053. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1001053. PMC 2916847.PMID 20700436.
30. Fiore MC, Jaen CR, Baker TB . Treating tobacco use and dependence: 2008 update (PDF). Rockville, MD: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, U.S. Public Health Service. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-27. Retrieved 2016-09-02.
31. "Anyone Can Become Addicted to Drugs". National Institute on Drug Abuse. July 2015.
32. "E-Cigarette Use Among Youth and Young Adults: A Report of the Surgeon General" (PDF). United States Department of Health and Human Services.Surgeon General of the United States. 2016. This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
33. Camenga DR, Jonathan D. Tobacco Use Disorders Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America.2016; 25 (3): 445–460. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2016.02.003. ISSN 1056-4993.PMC 4920978.PMID 27338966.
34. Pistillo F, Clementi F, Zoli M, Gotti C. Nicotinic, glutamatergic and dopaminergic synaptic transmission and plasticity in the mesocorticolimbic system: Focus on nicotine effects. Progr Neurobio. 2015; 124: 1–27. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2014.10.002. ISSN 0301-0082.PMID 25447802.
35. Shaik SS. "Tobacco Use Cessation and Prevention – A Review. J Clin Diagn Res.2014; 10 (5): ZE13-7. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2016/19321.7803. ISSN 2249-782X. PMC 4948554.PMID 27437378.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License