IJCRR - 13(20), October, 2021
Pages: 113-118
Date of Publication: 24-Oct-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
An Observational Study on the Effects of Antidepressant Treatment on Salivary Cortisol Secretion in Patients of Major Depressive Disorders
Author: Kavita, Ravi Kant Tiwari, Usha Joshi, Manoj Kumar Sahu
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Altered cortisol secretion in the form of Cortisol Awakening Response (CAR) is one of the consistent features in patients with depression. Evidence suggests that antidepressant treatment might alter cortisol indicators in patients with depression. Aim and Objectives: This study was aimed to evaluate the changes in morning and evening salivary cortisol indicators in patients with major depressive disorders, who had received antidepressant treatment. Methods: The participants were sixty-four diagnosed cases of major depressive disorders according to Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM IV) criteria, who were taking antidepressant medications from different groups for at least one month. The salivary cortisol values were taken as morning and evening samples at baseline and two follow up at two months intervals and compared by student's t-test. Results: A significant difference (p< 0.0001) was noted in the mean salivary cortisol levels (morning and evening)at baseline and subsequent follow-up. Conclusions: Morning and evening salivary cortisol concentrations were increased in patients with MDD. Antidepressant treatment resulted in the alteration of cortisol indicators.
Keywords: Cortisol Awakening Response (CAR), Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs), Serotonin Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, Neurotransmitter
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION:
Depression is a leading medical contributor to the global burden of disease. It can become long-lasting with frequent recurrences. Females of the middle age group (between the ages of 25 and 45 years) are the major sufferers and are affected almost twice as likely (10%-25%) as males (5%-12%) to experience depression. Genetic predisposition is one of the important risk factors. Individuals with first-generation relatives with major depression have about 2 to 3 times greater chance of experiencing depression compared with individuals without a similar family history. 1In the pharmacotherapy of depression several novel classes of antidepressants have been introduced, but still only about 60-65%of patients with depression respond to antidepressant therapy. Depression is also responsible for 60%-70% of all suicides and about 10%-20% of cases with major depression eventually commit suicide.2 Despite the completion of multiple antidepressant drug treatments and aggressive treatment regimens, about 15% of the patients diagnosed with major depressive disorders (MDD) will continue to suffer from depression. Even among the patients who initially responded to antidepressant treatment as indicated by the reduction in their depressive symptoms, about 2/3rd of these patients fail to achieve complete remission of depressive symptoms.3
Among the neurotransmitters (NT) of monoamine systems, reuptake is the principal mechanism by which the action of NT is terminated. The first-generation antidepressants include monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs). The MAOIs enhance monoaminergic neurotransmission by inhibiting monoamine metabolism and thereby enhancing neurotransmitter storage in secretory granules, while the TCAs act by inhibiting 5-HT and norepinephrine reuptake. While efficacious, these first-generation agents exhibit side effects and drug and food interactions that limit their use relative to the newer drugs. The newer second-generation antidepressants include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and the serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)are the preferred initial choice to treat depression because of their safety, tolerability and overall efficacy.4
Cortisol participates in complex interactions with the hormonal and immune systems in humans as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. Hyperactivity of the HPA axis is considered an important mechanism explaining the pathophysiology of depression. However, the association may not be entirely reproducible and consistent. The recent reviews indicated that the morning and evening cortisol concentrations are increased in patients with depression, and this increase was more pronounced in older patients with either melancholic or psychotic depression. Furthermore, HPA hyperactivity has been shown in patients who have recovered from depression, in non-depressed people with a parental history of depression, and people at increased risk of depression due to a personality characterized by neuroticism.5
Salivary cortisol which is a well-known stress hormone has a half-life of approximately 1 hour. Salivary cortisol represents the biologically active free cortisol in plasma. The therapeutic benefit of antidepressants takes about 2–4 weeks of treatment and their antidepressant effects might be due to alteration of the HPA axis.6
Keeping the above facts in mind, this study was aimed to evaluate the alterations in salivary cortisol level as morning and evening concentrations and to assess the effects of antidepressant treatment on these parameters.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
The present prospective cohort study was carried out in the Department of Pharmacology and Psychiatry at Pt. J. N. M. Medical College & Dr. B. R. A. M. Hospital Raipur (C.G) over one year from June 2015 to June 2016. The study included the patients attending the psychiatry OPD with the diagnosis of Major Depressive Disorders (MDD) as per the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV). The sample size for this study was calculated by using the formula {n=z2.pq/d2} where q=1-p. By applying the values of z, d (absolute precision) and p (expected proportion in the population which was found from previous studies), to the above formula as 1.96, 5% and 5% respectively, the calculated sample size was found to be 73.7Total 90 subjects were recruited over one year of which 26 subjects loss to follow up and total 64 subjects came for regular follow up. The study had clearance from the Institutional Ethical committee.
Study population:
The selection of patients was done on the following inclusion and exclusion criteria-
Inclusion criteria-
-
-
Patients diagnosed with a case of major depression who were taking antidepressant medications for at least one month.
-
Patients diagnosed with a case of major depression were taking antidepressant medications from different groups such as TCAs, SSRIs, SNRIs and atypical antidepressants.
-
Age group18 years and above.
Exclusion criteria-
-
Patients having hormonal disorders.
-
Patients having other psychiatric illnesses.
-
Pregnant and lactating mothers.
-
Patients having substance abuse disorders.
Methods and statistical analysis: All the subjects were informed in detail about the purpose of the study and gave their written consent. Detailed clinical history, drug history and other relevant information were taken from the patients. The levels of the salivary cortisol were measured as morning and evening samples, by the salimetric salivary cortisol ELISA kit, and taken as a baseline and then the two follow up done at the interval of 2 months. The changes in salivary cortisol levels were noted and these values were compared by student’s t-test. Statistical significance was set at P<0.05. The SPSS 16.0 software was used for data analysis (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences version 16.0; SPSS, IBM Corporation, Chicago, Illinois, USA).
RESULTS:
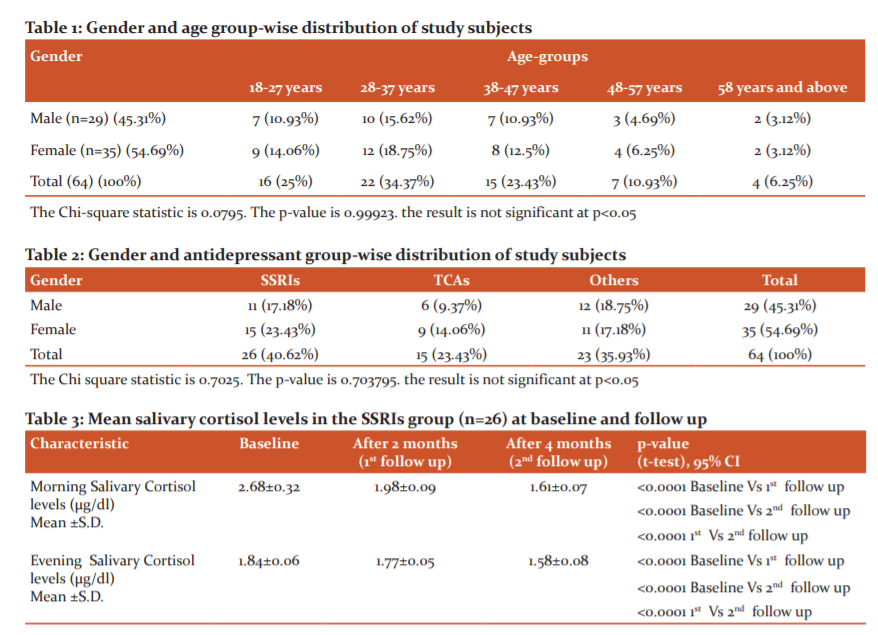
The gender and age-group wise distribution of study subjects showed that out of the 64 subjects included in this study, the majority (54.69%) were females and aged between 18-37 years of age (32.81%). In the same age range, the percentage of male subjects was 26.55% (table-1). The mean age in the study group was found to be 36.2±5.3 years. The mean duration of illness in the study group was found to be 14.1±1.5 months and the mean duration of treatment was found to be 8.7±2.9 months.
Based on the antidepressant group taken by the patients, they were divided into three groups, i.e. SSRIs group, TCAs group and other antidepressants group which included the drugs from other antidepressant classes or using more than one group. The majority of the study participants belonged to the SSRIs group (40.62%), followed by other antidepressants group (35.93%) (Table-2).
Among the SSRIs group, the baseline means morning salivary cortisol level was 2.68±0.32 µg/dl which was subsequently reduced to 1.98±0.09 µg/dl and 1.61±0.07 µg/dl after 2 months (first follow up) and 4 months of therapy (second follow up) respectively. Similarly, the baseline means evening salivary cortisol level was 1.84±0.06 µg/dl which was subsequently reduced to 1.77±0.05 µg/dl and 1.58±0.08 µg/dl at first and second follow up respectively (table-3).
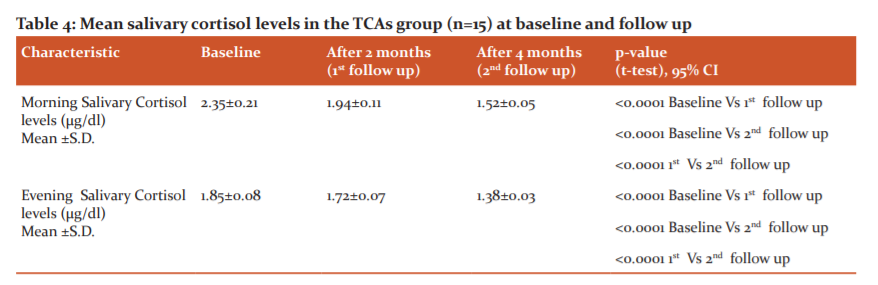
The baseline means morning salivary cortisol level in the TCAs group was 2.35±0.21 µg/dl which was subsequently reduced to 1.94±0.11 µg/dl and 1.52±0.05 µg/dl at first and second follow up respectively, while the baseline means evening salivary cortisol level was 1.85±0.08 µg/dl which was subsequently reduced to 1.72±0.07 µg/dl and 1.38±0.03 µg/dl at first and second follow up respectively (table-4).
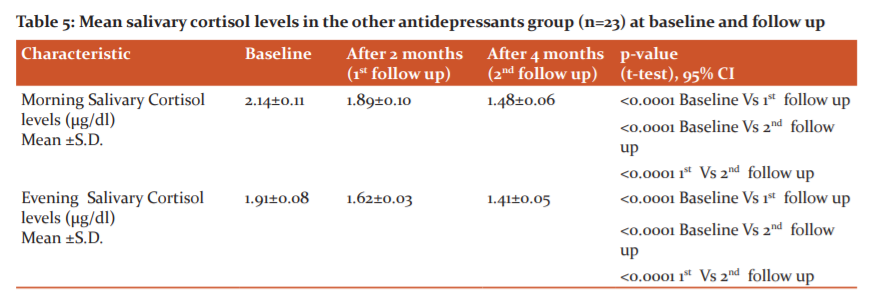
In the patients treated with other groups of antidepressants, such as SNRIs, atypical antidepressants or combinations, the baseline means morning salivary cortisol level was 2.14±0.11 µg/dl which was subsequently reduced to 1.89±0.10 µg/dl and 1.48±0.06 µg/dl at first and second follow up respectively, while the baseline means evening salivary cortisol level was 1.91±0.08 µg/dl which was subsequently reduced to 1.62±0.03 µg/dl and 1.41±0.05 µg/dl at first and second follow up respectively (table-5).
In all the three groups of patients, i.e. the SSRIs group, the TCAs group and other antidepressants group, there was a statistically significant difference (p<0.0001) between the baseline and subsequent follow up values of mean morning and evening salivary cortisol levels.
DISCUSSION:
This study aimed to evaluate the changes in salivary cortisol parameters as morning and evening cortisol levels in the patients of MDD and to observe the effects of antidepressant treatment on these parameters. Among the total 90 patients recruited in this study, only 64 came to regular follow up, hence included in the data analysis. These patients were divided into three groups, i.e., SSRIs group (n=26), TCAs group (n=15) and another group (n=23) who had received antidepressants apart from SSRIs/ TCAs or a combination of antidepressants.
In this study, we found that in all three groups of patients, the morning and evening salivary cortisol levels were above the reference range of normal. 7 In a study conducted by Khan QU, et al.(2019), the mean salivary cortisol level was found significantly higher (p=0.031) in depressive patients (2.23±1.69 µg/dl) as compared to normal subjects (1.46±0.91 µg/dl).8 The results of our study were also consistent with the studies conducted by Herbert J, et al. (2012) and Yonekura T, et al. (2014), where they observed higher salivary cortisol levels in the patients of MDD.9,10 The Pathophysiological basis for this observation could be the hyperactive hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. Few studies observed the reverse findings, i.e. decreased salivary cortisol levels instead of rising, in the patients of major depression.11,12 In some studies, the short and long term administration of SSRIs had resulted in varied results on cortisol levels. These findings suggest that though the hyperactive HPA axis is at the centre of depressed mood and the alterations in cortisol parameters, these observations (rise or fall of cortisol levels) are not exclusively consistent and reproducible.13, 14In a recent meta-analysis it has been observed that the changes in cortisol parameters largely depend on the timing and method of cortisol measurement, i.e. methodological quality of the study.15 Cortisol secretion is at a high level on waking in the morning, followed by a peak rise, 30 min after waking (known as CAR, Cortisol Awakening Response) and then subsequent decline across the day with reaching its nadir around midnight.16 In this study, we have seen the effects of different groups of antidepressants such as SSRIs, SNRIs, TCAs and atypical antidepressants on both morning and evening cortisol levels to allow for the measurement of diurnal cortisol profile and more detailed investigation to see the involvement of HPA axis. Hinkelmann K, et al. and Knorr U, et al. observed that long term administration of SSRIs had been found to decrease waking cortisol levels.17, 18 In our study, we found similar results with all the major groups of antidepressants such as SSRIs, SNRIs and TCAs to decrease the morning and evening salivary cortisol levels. The serotonergic system and HPA axis functioning have a deep-rooted relationship with each other. Measuring the increase in the levels of salivary cortisol following awakening could be used as a simple and reliable means of assessing HPA-axis activity. Though the literature review showed that there were both animal and human studies on the effects of antidepressants on cortisol parameters, the comparative studies between different groups of antidepressants were few. A better understanding of the biological mechanisms of actions of antidepressants could explore improved treatment outcomes in patients with depression and anxiety. The biological effects of different groups of antidepressants on the HPA axis activity as manifested by cortisol parameters have shown that the TCAs group of antidepressants resulted in more strongly suppressed cortisol levels as compared to SSRIs and other groups of antidepressants.19 In some studies it was found that short term use of either TCAs or SSRIs group of antidepressants resulted in the activation of the HPA axis, while few others have reported no change in cortisol indicators.20, 21
LIMITATIONS: The major limitation of this study was that we did not investigate the association on some more cortisol parameters such as AUC, Cmax and Tmax. Further studies are needed on the patients with major depression and comparing them with healthy controls to assess the in-depth association of HPA axis overactivity and the effects of different groups of antidepressants on such parameters.
CONCLUSION:
Major depression has been shown to be associated with dysregulated HPA axis as manifested by altered cortisol parameters. Salivary cortisol may be used as diagnostic marker for non-invasive assessment of patients with MDD. It can help in the monitoring and follow up of antidepressant therapy.
Acknowledgement:
The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/ editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
DECLARATIONS
Source of Funding: None
Conflict of interest: None declared
Ethical approval: The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee.
Author’s contribution:
-
Kavita, Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacology, Government Medical College, Ambikapur, Chhattisgarh, India. (Chief investigator)
-
Ravi Kant Tiwari, Associate Professor, Department of Pharmacology, Government Medical College, Ambikapur, Chhattisgarh, India. (Co-investigator) and corresponding author.
-
Usha Joshi, Professor, Department of Pharmacology, Pt. J. N. M. Medical College, Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India. (Co-investigator)
-
Manoj Kumar Sahu, Associate Professor, Department of Psychiatry, Pt. J. N. M. Medical College, Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India. (Co-investigator)
References:
-
Carpenter T, Grecian S, Reynolds R. Sex differences in early life programming of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in humans suggest increased vulnerability in females. Psychoneuroendocrinology.2015;61:32.
-
Levinson DF. The genetics of depression: a review. Biol Psychiatry.2006;60(2):84-92.
-
Otte C, Gold SM, Penninx BW, Pariante CM, Etkin A, Fava M, et al. Major depressive disorder. Nature Reviews Disease Primers. 2016 Sep 15;2:16065.
-
Joyce PR, Mulder RT, Luty SE, Sullivan PF, Mackenzie JM, Abbott RM, et al. Patterns and predictors of remission, response and recovery in major depression treated with fluoxetine or nortriptyline. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2002;36(3):384-391.
-
McKay MS, Zakzanis KK. The impact of treatment on HPA axis activity in unipolar major depression. J Psychiatric Res. 2009 Feb;44(3):183-192.
-
Dienes KA, Hazel NA, Hammen CL. Cortisol secretion in depressed, and at-risk adults. Psychoneuroendocrinology.2013;38(6):927-940.
-
Keller MB. Past, present, and future directions for defining optimal treatment outcome in depression: Remission and beyond. JAMA.2003; 289(23): 3152-3160.
-
Khan QU, Khan HA, Tauseef A, Hafeez F, Qamar M, Fatima SA, et al. Salivary cortisol levels in severely depressed patients and healthy individuals. Int J Med Sci Public Health .2019;8(5):21-25.
-
Herbert J, Ban M, Brown GW, Harris TO, Ogilvie A, Uher R, et al. Interaction between the BDNF gene Val/66/Met polymorphism and morning cortisol levels as a predictor of depression in adult women. Brit J Psychiatry. 2012;201(4);313-19.
-
Yonekura T, Takeda K, Shetty V, Yamaguchi M. Relationship between salivary cortisol and depression in adolescent survivors of a major natural disaster. J Physiol Sci.2014;64(4):261-67.
-
Howland RH, Wilson MG, Kornstein SG, Clayton AH, Trivedi MH, Wohlreich MM, et al. Factors predicting reduced antidepressant response: experience with the SNRI duloxetine in patients with major depression. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2008;20(4):209-218.
-
Bhagwagar Z, Hafizi S, Cowen PJ. Increased salivary cortisol after waking in depression. Psychopharmac.2005;182(1):54-57.
-
Dedovic K, Ngiam J. The cortisol awakening response and major depression: examining the evidence. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015;11:1181-9.
-
Adam EK, Quinn ME, Tavernier R, McQuillan MT, Dahlke KA, Gilbert KE. Diurnal cortisol slopes and mental and physical health outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocr.2017;83:25-41.
-
Fischer S, Macare C, Cleare AJ. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis functioning as a predictor of antidepressant response-meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017: 83:200-211.
-
Adam EK, Kumari M. Assessing salivary cortisol in large-scale, epidemiological research. Psychoneuroendocr.2009;34(10):1423-1436.
-
Hinkelmann K, Moritz S, Botzenhardt J, Muhtz C, Wiedemann K, Kellner M, et al. Changes in cortisol secretion during antidepressive treatment and cognitive improvement in patients with major depression: a longitudinal study. Psychoneuroendocr.2012;37(5):685-692.
-
Knorr U, Vinberg M, Gether U, Winkel P, Gluud C, Wetterslev J, et al. The effect of escitalopram versus placebo on perceived stress and salivary cortisol in healthy first-degree relatives of patients with depression—a randomised trial. Psych Res.2012; 200(2-3):354-360.
-
Juruena MF, Cleare AJ, Papadopoulos AS, Poon L, Lightman S, Pariante CM. The prednisolone suppression test in depression: dose-response and changes with antidepressant treatment. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2010; 35(10):1486–1491.
-
Wilhelm I, Born J, Kudielka BM, Schlotz M, Wust S.Is the cortisol awakening rise a response to awakening?Psychoneuroendocrinology 2007; 32(4):358–366.
-
Penninx BW, Nolen WA, Lamers F, Zitman FG, Smit JH, Spinhoven P, et al. Two-year course of depressive and anxiety disorders: results from the Netherlands Study of Depression and Anxiety (NESDA). J Affect Disord. 2011 Sep;133(1-2):76-85.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License