IJCRR - 13(20), October, 2021
Pages: 04-11
Date of Publication: 24-Oct-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Role of Greyscale Ultrasound, Colour Doppler and Ultrasound Elastography in the Evaluation of Axillary Lymph Nodes in Primary Breast Cancer - A Prospective Study
Author: PS Priya, K Prakashini, KT Jyothi
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Breast cancer metastasizes, most commonly to lymph nodes of the axilla. Axillary lymph node metastasis has been one of the most important prognostic parameters in patients with breast malignancies. Differentiation between malignant and benign axillary lymph nodes is extremely important at an early stage because a delay in diagnosis leads to disease upstaging thus turning a curable lesion incurable. Hence early detection helps in improving outcomes and survival. Our study was intended to arrive at an accurate, early pre-operative diagnosis of lymph node metastasis by evaluating axillary lymph nodes in biopsy-proven primary breast carcinoma through non-invasive methods such as greyscale ultrasound, Colour Doppler and strain wave elastography and correlate it with histopathology. Aims: To evaluate axillary lymph nodes in primary breast cancer patients on greyscale ultrasound, Colour Doppler, strain wave elastography and correlate it with histopathology. To compare sensitivity, specificity, negative and positive predictive values of greyscale ultrasound with combined greyscale ultrasound and elastography findings. Materials and Methods: Seventy histopathologies proved primary breast carcinoma patients were included. Lymph nodes were assessed for size, shape, presence/absence of hilum, long /short axis ratio (L/S ratio), cortical thickness, cortical thickness/fatty hilum thickness ratio (C/F ratio) on greyscale ultrasound, for vascularity on Colour Doppler followed by elastography. A provisional diagnosis was made and compared with histopathology of the lymph node. Results: Our study showed that round shape, irregular nodular margins, eccentric/compressed or absent hilum, increased cortical thickness; decreased L/S ratio and increased C/F ratio were the morphological characteristics favouring malignancy. Vascular flow pattern type, resistivity index, pulsatility index and peak systolic velocity/end-diastolic velocity ratio helped in differentiating benign from malignant lymph nodes. The mean strain ratio was significantly higher in the malignant lymph node. Conclusions: Ultrasound evaluation (greyscale, colour Doppler and strain elastography) should be incorporated in the initial evaluation of suspected breast carcinoma patients as it is a cheap, radiation-free, easily accessible, reasonably accurate means of staging.
Keywords: Axillary lymph nodes, Primary breast cancer, Grayscale ultrasound, Colour Doppler, Elastography, Prospective study
Full Text:
Introduction:
Breast carcinoma is one of the most common types of tumours affecting women worldwide with its incidence on an increasing trend. Most breast cancers are spread by local invasion, intraductal growth and into the lymphatic system in a stepwise and predictable fashion before the occurrence of distant hematogenous metastasis.
Breast cancer metastasizes, most commonly to lymph nodes of the axilla. Axillary lymph node metastasis has been one of the most important prognostic parameters in patients with breast malignancies. Differentiation between malignant and benign axillary lymph nodes is extremely important at an early stage because a delay in diagnosis leads to disease upstaging thus turning a curable lesion incurable. Hence early detection helps in improving outcomes and survival.1 Sentinel lymph node (SLN) is the earliest lymph node to receive lymphatic drainage from primary breast carcinoma and is highly predictive of the remaining axillary lymph node status.2 Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) has not found wide acceptance in developing countries because of the requirement of nuclear medicine facility, frozen section facilities, intraoperative waiting time for reports, increased post-procedure complications in the form of lymphedema, pain, limitation of shoulder movement and weakness of the arm and a 5-10% false-negative rate and cost.3 It is therefore advantageous to evaluate the efficacy of non-invasive procedures such as ultrasonography, Colour Doppler and strain wave elastography in differentiating malignant from benign lymph nodes in proven primary breast carcinoma. Early diagnosis and treatment can reduce mortality and increase survival and improve quality of life. Our study was intended to arrive at an accurate, early pre-operative diagnosis of lymph node metastasis by evaluating axillary lymph nodes in biopsy-proven primary breast carcinoma through non-invasive methods such as greyscale ultrasound, Colour Doppler and strain wave elastography and correlate it with histopathology.
Materials and Methods:
This prospective observational, hospital-based time-bound study was conducted in a tertiary care university teaching hospital from December 2017 to August 2019 over 2 years. Recruiting the subjects and data collection started after obtaining Institutional ethics committee (IEC:866/2017) and Clinical trials registry [India CTRI/2018/09/021650] approval. We enrolled a total of 70 female subjects between 34-80 years of age having histopathology proven primary breast carcinoma with axillary lymph nodes on imaging having a short axis diameter >5mm in the study. Patients with bilateral breast cancer, those who had undergone breast surgery, those scheduled for radiotherapy, neoadjuvant chemotherapy and those with prior axillary interventions were excluded.
Greyscale ultrasound, Colour Doppler and strain wave elastography of the axillary lymph nodes were done with a multi-frequency linear array transducer (8-13 MHz; AplioXG Toshiba medical systems corp. Japan). Ultrasound of the ipsilateral axilla of primary breast carcinoma was performed with the patient in supine position with external rotation and 90-degree abduction of the shoulder. This was to position the axillary vessels to have a nearly straight course and all parts of the axilla could be thoroughly examined. A variable amount of compression was applied with the transducer to thin the axillary area, further improving penetration and image quality.4
We assessed the morphology of visualized lymph nodes. If all the lymph nodes appeared normal, the most representative lymph node in the lower part of the axilla was chosen for further analysis.
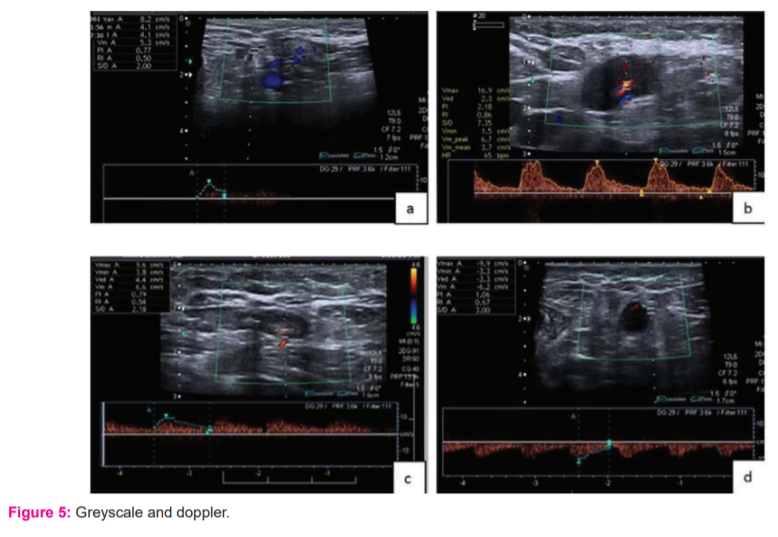
Greyscale ultrasound: Lymph nodes were measured in longitudinal (long axis) and transverse (short axis) dimensions and documented using the Solbiati index (long/short axis ratio). The hilum and cortical thickness were also measured ( Figure 1). Finally, the following grayscale ultrasound qualitative criteria were described: oval or round appearance, present /absent fatty hilum, sharpness of margins and focal thickening of the cortex, long axis/short axis ratio (L/S), cortical/fatty hilum thickness ratio(C/F).
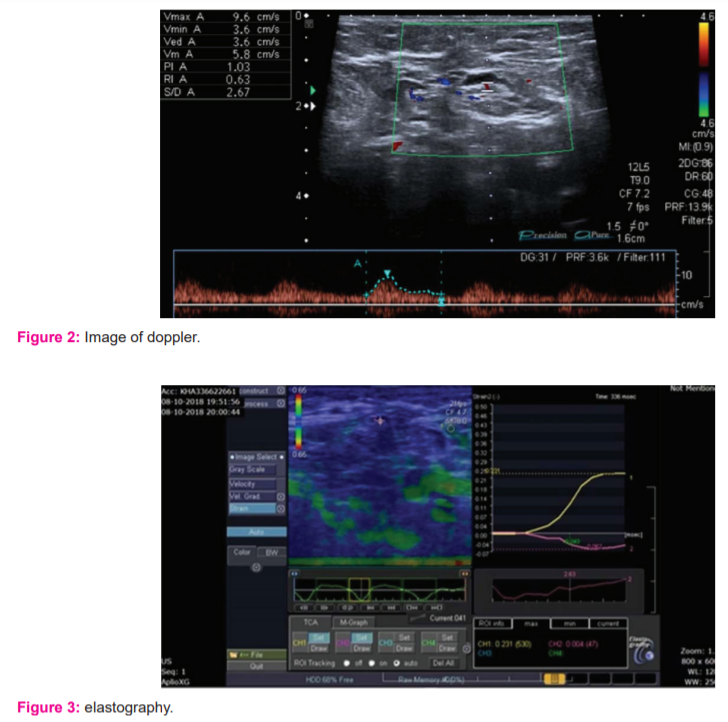
Colour Doppler ultrasonography: Sample volume was adjusted according to the vessel size in the lymph node, with the angle of insonation kept at 60 degrees or less. Spectral waveforms were recorded of the different vessels visualised in each lymph node whenever possible and the highest value was considered. The lymph nodes were initially assessed for distribution of vascularity as hilar, central perihilar, peripheral non-hilar and mixed vascular patterns. Quantitative analysis in the form of pulsed Doppler spectral analysis waveform pattern was generated where resistivity index (RI), pulsatility index (PI) and systolic/diastolic (S/D) ratio were measured where highest value was recorded (Figure 2).
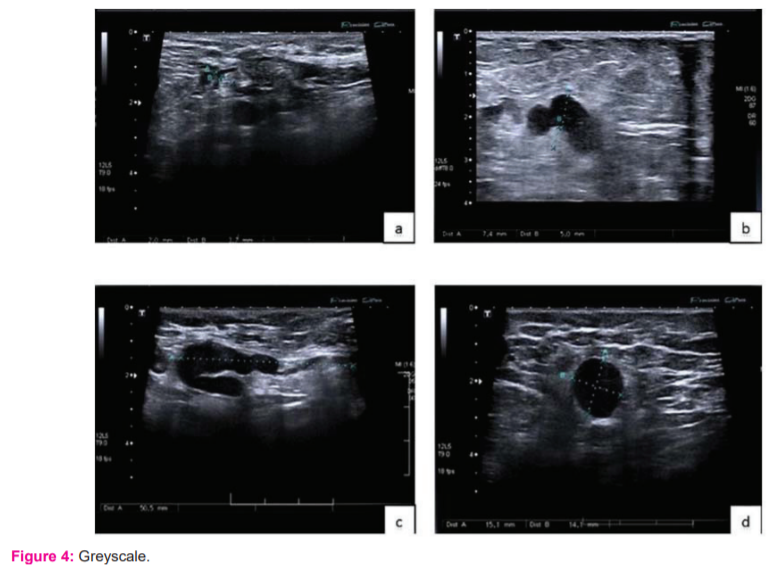
Strain wave elastography (SWE): Keeping the probe perpendicular to the skin over the lymph node, repetitive manual compression and decompression (around 5-6) were applied using minimal pressure. Elastogram obtained with a well-formed wave touching the baseline was selected. One ROI was placed in the axillary fat with the highest strain value, at a depth similar to that of the lymph node being evaluated. The second ROI was placed in the lymph node cortex. The software program embedded in the ultrasound machine automatically calculated the strain ratio for the lymph node.5 We recorded 3 strain wave ratios for each lymph node and considered the mean of the ratios (Figure 3).
The results of all three imaging modalities were correlated with histopathology. Since the histopathology report states only the largest lymph node size and number of lymph nodes with tumour deposits only, the size of the lymph node according to ultrasound correlating with the histopathological size was selected for further statistical analysis. Hence, our study included 70 cases with 70 lymph nodes for assessment.
Data were entered into Microsoft excel 2013 and analysed by using software version of SPSS 22(IBM SPSS Statistics, Somers NY, USA). Categorical data were presented in the form of frequencies and proportions. The Chi-square test was used as a test of significance for qualitative data. Continuous data were presented as mean and standard deviation. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were obtained for cortical thickness, long axis/short axis ratio, cortical thickness/fatty hilum thickness ratio, resistivity index, pulsatility index, S/D ratio and mean strain ratio. The cut-off values were derived for each variable which helped in differentiating benign from metastatic lymph nodes. The sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values of greyscale ultrasound were compared with combined greyscale ultrasound and strain elastography findings.
RESULTS
Among the 70 subjects enrolled in our study, the highest proportions of cases were from the age group range of 50-59 years with a mean age of 51.47 ± 11.205 years. A family history of breast carcinoma was found only in 7 subjects out of 70 patients. A total of 65 subjects were multiparous and the remaining 5 were nulliparous. Our subjects had right-sided neoplasm in 37 (53.6%) and the remaining 32 (46.4%) had it in left. In the study, maximum breast carcinomas (47.1%) were found in the upper outer quadrant and lower outer, lower inner quadrant and upper inner quadrants had 15.7%, 14.3% and 12.9% respectively.
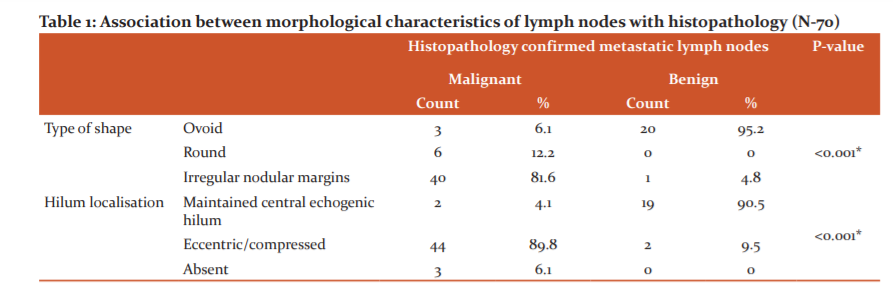
Out of 70 lymph nodes from the 70 subjects, 47 lymph nodes showed metastasis and the remaining 23 were benign. Our study showed that lymph nodes that were positive for metastasis on histopathology had round shapes and irregular nodular margins (81.6%) and eccentric or compressed hila (89.8%). Among the benign lesions, the majority of subjects had ovoid shape (95.2%) and maintained central echogenic hila (90.5%). (Table 1)( Figure 4)
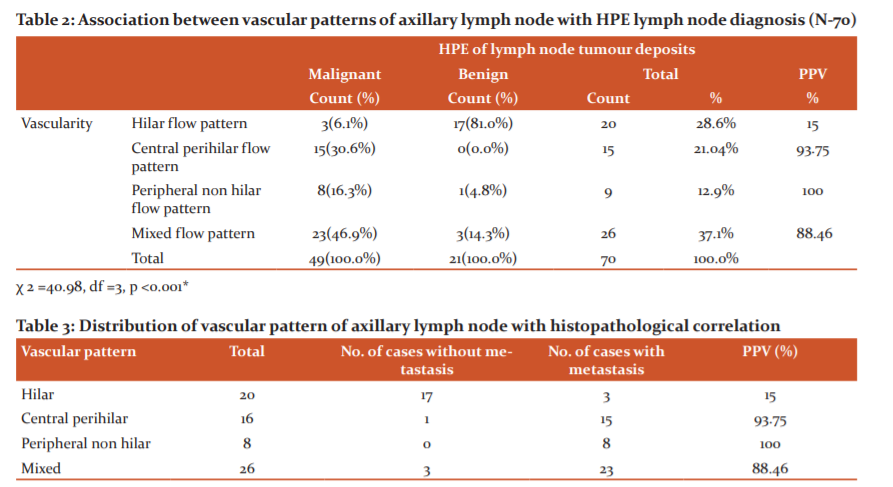
The vascular flow patterns in the malignant nodes were found to be central perihilar, peripheral non-hilar and mixed flow patterns, the majority being mixed-flow patterns (46.9%) and among those with benign lesions on histopathology, the majority had hilar flow patterns (81%). There was a significant association between vascular flow pattern and HPE lymph node diagnosis (p <0.001). (Table 2, Table 3) (Figure 5)
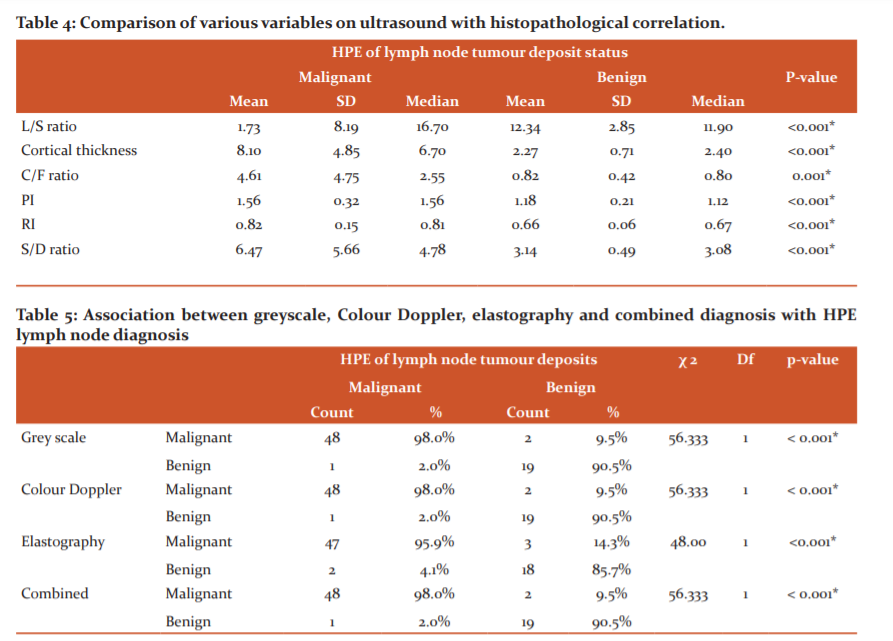
We also observed that the cut off value of >3mm or more for cortical thickness yielded a sensitivity of 87.76% and a specificity of 95.24% with a p-value of <0.001. The L/S ratio of ≤1.89 was the cut off value favouring metastatic lymph node status with a sensitivity of 71.43% and a specificity of 47.62% with a p-value of 0.324. C/F ratio cut off value for malignancy was ≥1.08 with a sensitivity of 93.88% and a specificity of 85.71% with a p-value of 0.001 showed a statistically significant difference. Resistivity index >0.69 was the best cut off value favouring malignant lymph nodes yielding a sensitivity of 89.8% and a specificity of 80.95% (AUROC 0.853 and p-value of <0.0001). PI of >1.25 was the best cut off value favouring malignant lymph nodes with a sensitivity of 89.8% and a specificity of 76.19% (AUROC 0.853 and p-value of <0.0001). S/D ratio of >3.97 was the best cut off value yielding a sensitivity of 75.51% and a specificity of 95.24 % (AUC 0.904 and p-value of <0.0001) favouring malignant lymph node. Mean strain ratio of >3.83 was the cut off value with a sensitivity of 91.84% and a specificity of 80.95 % (AUC 0.872) and a p-value of <0.0001 favouring malignant lymph node status. Our study showed significant differences in mean cortical thickness, C/F ratio, vascular flow pattern, PI, RI, S/D ratio and mean strain ratio between malignant and benign lymph nodes. Mean of cortical thickness, C/F ratio, PI, RI and S/D ratio was significantly higher in malignant lymph nodes when compared to benign lymph nodes and mean strain ratio was also significantly higher in malignant lymph nodes in comparison to benign lymph nodes. (Table 4)
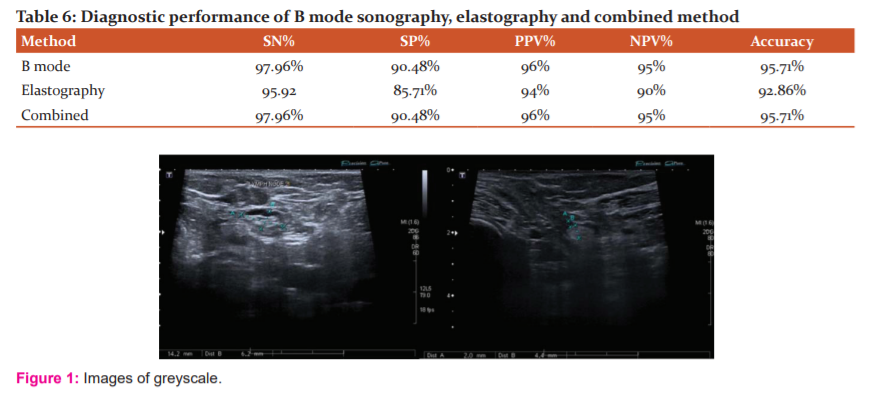
Among 49 lymph nodes with histopathology confirmed malignancy, 48 (98%) were diagnosed on a grey scale where 1 case (2%) was false-negative and among 21 with benign lesions, 19 (90.5%) were benign in greyscale and 2 (9.5%) were false positive. There was a significant association between greyscale and histopathology diagnosis. The one false-negative case found on greyscale when subjected to elastography however was diagnosed correctly as benign and the 2 false positives found on elastography were correctly classified as benign on greyscale ultrasound. Colour Doppler and combined greyscale ultrasound and strain elastography had similar observations to the greyscale. Among 49 subjects with malignant lymph node status on histopathology, 47(95.9%) were diagnosed on elastography and 2 (4.1%) were false negatives and among 21 subjects with benign lymph node status on histopathology, 18 (85.7%) were non-metastatic on elastography and 3 (14.3%) were false positives. There was a significant association between elastography and histopathological diagnosis. (Table 5)
Discussion
The status of the axillary lymph node is one of the most relevant prognostic factors in breast carcinoma and its pre-operative evaluation is important for subsequent treatment. Several studies show the importance of ultrasound combined with fine-needle aspiration in the pre-operative assessment of lymph nodes for the presence of metastasis as mammography and physical examination has limited value. Therefore, ultrasound evaluation should be incorporated into the initial evaluation of suspected breast carcinoma patients; especially as it is a cost-effective, radiation-free, easily accessible, reasonably accurate means of staging. Ultrasound reveals excellent morphological details of lymph nodes which are reproducible. Major sonographic criteria for metastatic lymph nodes have focused on the shape of the node and its echogenicity, but focal cortical morphologic changes may be more important because of a centrifugal pattern of metastatic deposition. Metastasis initially involves the subcapsular and cortical sinuses through the afferent lymphatic channels giving the characteristic eccentrically enlarged cortex. Eccentric cortical thickening displaces completely the hilum of lymph nodes to one edge which occurs rarely in inflammatory conditions. In the more severely abnormal lymph node, the hilar echoes can become completely non-identifiable and obliterated.
Lymph nodes with a short axis diameter of <9.5mm were considered non-metastatic and those with >9.5 mm had the sensitivity of 65.3% and a specificity of 100% of being metastatic however size alone cannot be used as criteria, as metastatic nodes may be small and reactive or inflammatory nodes quite large.
There are well established previous data for cortical thickness and L/S ratio as criteria for characterising malignant lymph nodes. There are hardly any studies on the C/F ratio being one of the criteria to characterise malignant lymph node status, which we had incorporated in our study and found very useful. C/F ratio had a higher sensitivity of 93.88% when compared to cortical thickness alone which had a sensitivity of 87.76%. Cortical thickness and C/F ratio were the variables that we found significant in differentiating benign and malignant lymph nodes.
Irregular or nodular margins represent suspicion for metastasis indicating invasive, extracapsular and extranodal spread, while benign nodes are characterized by sharp margins. In our study, among malignant lesions majority of subjects had irregular nodular margins (81.6%) and among benign lesions, the majority of subjects had ovoid shape (95.2%).
With regards to colour Doppler on the distribution of vascular patterns, most of the studies classified vascular patterns as central, peripheral and mixed flow patterns and few studies have made sub-classification as hilar and central perihilar which we also incorporated in our study. Hilar pattern favours benign lymph node status and central perihilar favours malignant lymph node status. Jyoti Choudhary et al.6 in their study have found that the peripheral non-hilar vascular pattern showed the highest positive predictive value (PPV) of 100% to detect metastasis. We also had similar results in our study. But in their study of 39 metastatic cases, 28 had peripheral non-hilar vascular patterns whereas in our study of 47 malignant lymph nodes we had the majority (23 cases) of mixed vascular patterns. The above study had RI > 0.7, and PI >1.4 and our cut off values of RI >0.69 and PI>1.25 were closer to their values, but in the study done by Sanjeeb Kumar et al. 7 RI of >0.8 and PI >2 were significant values. S/D ratio was not incorporated in any of the previous studies to the best of our knowledge and we have included it in our study. Thus, we found that pulsed Doppler spectral waveform for metastatic lymph nodes tend to have high RI, high PI and sharp systolic peaks.
There are not enough established studies favouring strain elastography as a modality of choice for differentiating benign from malignant lymph nodes, various studies have mostly used Colour elastography and some have used both Colour elastography and strain ratio. We used only the strain ratio in our study. Cut off the value of >3.83 for strain ratio was found to have a sensitivity of 91.84% and specificity of 80.95% for malignant lymph nodes in our study. Young Mi park et al. 9 in their study have concluded that strain elastography did not improve the diagnostic ability of conventional ultrasound in the evaluation of axillary lymph nodes. Wanying Chang et al.9 in their study concluded that elastography was a useful adjuvant tool in addition to greyscale ultrasound for pre-operative assessment of axillary lymph nodes in patients with breast cancer. Our study showed elastography as an adjuvant tool to greyscale ultrasound and Colour Doppler although less sensitive than greyscale. Our study concluded that whenever there is a mismatch between greyscale ultrasound and histopathological correlation elastography can act as an adjuvant tool and vice versa (Table 6). Most of the previous studies have one or two imaging modalities for assessing axillary lymph nodes. Our study is unique in the way, that we have combined three imaging modalities for assessing axillary lymph nodes, which could be done on a single machine in a single sitting and our study also incorporated CF ratio which we found to be very reliable, can be easily incorporated and showed statistically significant results.
However, our study had the following limitations. Our Sample size was only 70 cases and the study may give greater insight with a higher number of cases. Morphological assessment of the cortex is more solidly based on the histology of lymph node metastasis than on the size of the lymph node. Only the assessed lymph nodes in our study were not subjected to FNAC, instead, all the subjects underwent surgical excision of all the axillary lymph nodes. Histopathology report did not clarify the level of lymph node involved most of the time. Due to lack of uniformity in reporting, we had to correlate the largest lymph node size in the histopathology report with the corresponding size in our study. Hence, we had only one lymph node per subject for statistical analysis. As a result, we could not do lymph node to lymph node correlation with histopathology findings in this study.
Conclusion:
Our study showed round shape, irregular nodular margins, eccentric/compressed or absent hilum, increased cortical thickness, L/S ratio ≤1.89 and C/F ratio ≥1.08 are amongst the morphological characteristics favouring malignant lymph nodes on grayscale. Vascular flow pattern type, RI, PI and S/D ratio helps in differentiating benign from malignant lymph nodes on Colour Doppler. The mean strain ratio was significantly higher in malignant lymph nodes.
C/F ratio can improve diagnostic performance when compared to the L/S axis ratio. Among a range of US criteria, cortical thickness >3mm is one of the most reliable criteria for defining suspicious lymph node metastasis.
Greyscale ultrasound is technically sound, proven and established in several previous studies and can form a baseline for morphological analysis of lymph nodes. But it cannot be used as a single-mode and needs to be substantiated with Colour Doppler or elastography or both for additional credibility. Both Colour Doppler and strain elastography cannot be used singly as they are subjective with no standard technical guidelines. In addition, there is a lack of standardization of technique, data capture, data analysis and uniformity which needs to be addressed in the case of elastography. Overall ultrasound evaluation (greyscale, Colour Doppler, strain elastography) should be incorporated in the initial evaluation of suspected breast carcinoma patients as it is non-invasive, affordable, radiation-free, easily accessible, reasonably accurate means of staging.
Declarations
Compliance with ethical standards
Funding: Authors have not received any funding of any sort for the study
Conflict of interest: Authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Conflict of interest: Informed consent was taken from all subjects for their voluntary participation.
Ethical approval: All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were following the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent: Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Acknowledgement:
NIl
Conflict of interest:
NIL
Authors Contribution:
-
PS Priys: Principal investigator
-
K Prakashini: Principal investigator and guide
-
KT Jyothi: Design and statistics.
References:
-
Alvarez S, Anorbe E, Alcorta P, Lopez F, Alonso I, Cortes J. Role of sonography in the diagnosis of axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer: a systematic review (Structured abstract). Am J Roentgenol. 2006;186(5):1342–8.
-
Liu H, Xu G, Yao MH, Pu H, Fang Y, Xiang LH, et al. Association of conventional ultrasound, elastography and clinicopathological factors with axillary lymph node status in invasive ductal breast carcinoma with sizes >10mm. Oncotarget. 2018;9(2):2819–28.
-
Maxwell F, De Margerie Mellon C, Bricout M, Cauderlier E, Chapelier M, Albiter M, et al. Diagnostic strategy for the assessment of axillary lymph node status in breast cancer. Diagn Interv Imaging [Internet]. 2015;96(10):1089–101. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.diii.2015.07.007
-
Okunade K. January-March 2018. An Official Publication of The National Postgraduate Medical College of Nigeria. 2018;(January):19–26.
-
Latif MA, Shady M, Hegazy MAE, Abdo YM. B-mode ultrasound, sono-elastography and diffusion-weighted MRI in the differentiation of enlarged axillary lymph nodes in patients with malignant breast disease. Egypt J Radiol Nucl Med [Internet]. 2016;47(3):1137–49. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrnm.2016.05.018
-
Choudhary J, Agrawal R, Mishra A, Nandwani R. Ultrasound and Color Doppler Evaluation of Axillary Lymph Nodes in Breast Carcinoma with Histopathological Correlation. Int J Sci Study [Internet]. 2017;5(10). Available from: https://www.ijss-sn.com/uploads/2/0/1/5/20153321/ijss_jan_oa13_-_2018.pdf
-
Pradhan SK, Das BB, Sahoo N, Das SK, Panda C. Role of Doppler Usg for Evaluation of Axillary Lymph Node Status in Carcinoma Breast. J Evid Based Med Healthc. 2016;3(33):1576–80.
-
Park YM, Fornage BD, Benveniste AP, Fox PS, Bassett RL, Yang WT. Strain elastography of abnormal axillary nodes in breast cancer patients does not improve diagnostic accuracy compared with conventional ultrasound alone. Am J Roentgenol. 2014;203(6):1371–8.
-
Chang W, Jia W, Shi J, Yuan C, Zhang Y, Chen M. Role of elastography in the axillary examination of patients with breast cancer. J Ultrasound Med. 2018;37(3):699–707
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License