IJCRR - 13(19), October, 2021
Pages: 173-177
Date of Publication: 11-Oct-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Antimicrobial Synergism between Bacteriophage UBU-SA1 and Oxacillin against Staphylococcus aureus
Author: Rattanachaikunsopon Pongsak, Phumkhachorn Parichat
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Bacteriophages have been proven to be effective in controlling bacteria and potential as alternatives to antibiotics. Recently, combination treatments using both bacteriophages and antibiotics have been reported to substantially improve antimicrobial activity when compared with their treatments. Objectives: To isolate a lytic bacteriophage specific to Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 and determine antimicrobial activity against S. aureus ATCC 25923 of the isolated bacteriophage and oxacillin when used individually and in co-treatment. Methods: A lytic bacteriophage was isolated from a hospital wastewater sample by enrichment technique. Its host range was examined using the spot test method. The effect of oxacillin on the lytic activity of the bacteriophage was determined. Lastly, the minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of the bacteriophage and oxacillin against S. aureus ATCC 25923 when used individually and in co-treatment were determined using the spot test method. The fractional inhibitory concentration index (FICI) was used to analyze the co-treatment. Results: A bacteriophage, designated bacteriophage UBU-SA1, was isolated. It was found to be highly specific to S. aureus ATCC 25923. Its lytic activity was not inhibited by oxacillin. MICs of bacteriophage UBU-SA1 and oxacillin against S. aureus ATCC 25923, when used alone, were 105 PFU/mL and 50 µg/mL, respectively. Co-treatment of bacteriophage UBU-SA1 and oxacillin substantially reduced the MICs of both agents required to inhibit the bacterial host when compared with their treatments. The FICI indicated a synergistic effect between bacteriophage UBU-SA1 and oxacillin against S. aureus ATCC 25923. Conclusion: Bacteriophage UBU-SA1, by itself or in combination with antibiotics, may be useful as a therapeutic agent in controlling S. aureus
Keywords: Bacteriophage, Beta-lactam, Drug resistance, Oxacillin, Synergism, Staphylococcus aureus
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive, nonmotile, catalase-positive and facultatively anaerobic coccus. Characteristics that differentiate S. aureus from the other species of Staphylococcus are coagulase-positive (from all other Staphylococcus species), novobiocin sensitive (from S. saprophyticus) and mannitol fermentation positive (S. epidermidis). S. aureus is a significant human pathogen causing a wide range of diseases ranging from superficial cutaneous infections to life-threatening systemic diseases. Various human systems can be infected by S. aureus such as the respiratory system, gastrointestinal system, circulatory system, urinary system and reproductive system. S. aureus causes diseases by either production of toxin or direct invasion and destruction of tissues depending on the strains involved and infection sites.1 In general, S. aureus infections are treated by drugs in the beta-lactam class such as penicillin, ampicillin, cephalosporins or oxacillin.2 However, many drug-resistant strains of S. aureus have recently emerged thereby reducing drug efficacy. Most of them are multidrug-resistant strains such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) strains that known so far are resistant to nearly all beta-lactam antibiotics.3 Therefore, the emergence and spread of multidrug-resistant S. aureus have posed a serious challenge to traditional antibiotic therapy.
Bacteriophages are viruses capable of infecting specific bacteria. Lytic bacteriophages can bind to the outer surface of their bacterial hosts and injects their genetic materials into the host cells. Inside the hosts, more lytic bacteriophages are produced and then burst out of the host cells resulting in bacterial death. The released bacteriophages can in turn attack new bacteria. The killing cycle can continue until all bacteria are eliminated from the ecosystem.4 Based on their ability to kill bacteria, lytic bacteriophages have recently drawn researchers’ attention to use them as alternatives to antibiotics to control bacterial infections. The approach is called bacteriophage therapy. Several lytic bacteriophages have been shown to inhibit S. aureus such as bacteriophages vB_SauS_SA2,5SAJK-IND,6P68, 3A and ROSA.7 El Haddad et al.8 reported the use of a bacteriophage cocktail containing 3 different bacteriophages including phi812, 44AHJD and phi2 to inhibit S. aureus. Treatment of S. aureus mastitis in cows by bacteriophage therapy is an example of the potential of bacteriophages as alternatives to antibiotics.9 Therapeutic bacteriophages have some advantages over antibiotics in that they have been reported to be more effective but cause fewer side effects than antibiotics.10
Recently, the combination of lytic bacteriophages and antibiotics to control bacterial infections has been introduced. This approach has been proven to interfere with bacterial evolution to both bacteriophages and antibiotics; hence, increasing the effectiveness of bacterial infection treatment. Moreover, required concentrations of both agents to kill certain bacteria can be reduced thereby causing minimal side effects. Uses of lytic bacteriophages in combination with antibiotics can inhibit several pathogenic bacteria such as Shigella dysenteriae11Pseudomonas aeruginosa12and Klebsiella pneumoniae.13 Therefore, it is of interest to study bacteriophage-antibiotic combinations to control S. aureus. In this study, a bacteriophage specific to S. aureus was isolated from a hospital wastewater sample. Its host range against various bacteria was examined. The inhibitory ability against S. aureus was also determined when it was used individually and in combination with oxacillin, a common beta-lactam antibiotic used to control S. aureus infection.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacteriophage detection
A wastewater sample collected from Sappasitthiprasong Hospital, Ubon Ratchathani Province, Thailand was used as a source of a bacteriophage specific to S. aureus ATCC 25923. Bacteriophage enrichment using S. aureus ATCC 25923 as a host and preparation of bacteriophage containing cell-free filtrate (CFF) was performed according to the methods previously described.14
The detection of bacteriophage in the prepared CFF was performed by using the spot test method. A log phase culture of S. aureus ATCC 25923 was spread with a sterile swab on a BHI agar plate. Ten μL of the prepared CFF was spotted onto the bacterial lawn. The plate was incubated at 37°C for 24 h before observing the presence of a clear zone. A clear zone at the spot area, representing the lysis of host cells, indicated the activity of bacteriophage.
Plaque assay
The prepared CFF giving a positive result from the bacteriophage detection The prepared CFF giving a positive result from the bacteriophage detection was subjected to plaque assay as mentioned earlier14 to confirm the presence of a bacteriophage and to determine bacteriophage titer.
Bacteriophage host range
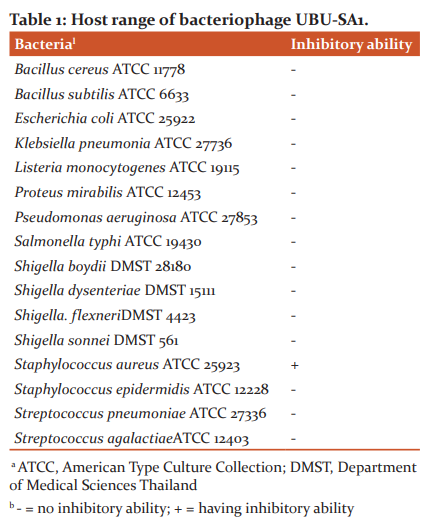
The spot test method (as described above) was used to determine the bacteriophage host range by using bacterial strains listed in Table 1 as tested hosts.
Effect of oxacillin on bacteriophage
To test if oxacillin has an inhibitory effect on bacteriophage, oxacillin was added to the CFF containing 108 PFU/mL of bacteriophage to obtain the concentrations ranging from 200 - 12.5 µg/mL. After incubation at 37°C for 24 h, the lytic activity of the bacteriophage was examined by plaque assay as mentioned above.
Minimal inhibitory concentrations of bacteriophage and oxacillin when used individually
To determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of bacteriophage against S. aureus ATCC 25923, a ten-fold dilution of CFF was performed to obtain the bacteriophage concentrations ranging from 108 to 10 PFU/mL. Each bacteriophage concentration was examined for its ability to inhibit S. aureus ATCC 25923 by the spot test as mentioned above.
To determine the MIC of oxacillin against S. aureus ATCC 25923, a two-fold dilution of the antibiotic was performed to obtain the concentrations ranging from 200 - 12.5 µg/mL. Each oxacillin concentration was examined for its ability to inhibit S. aureus ATCC 25923 by the spot test as mentioned above.
MICs of bacteriophage and oxacillin when used in co-treatment
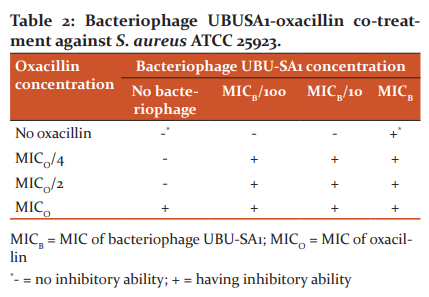
To study the inactivation of S. aureus ATCC 25923 by bacteriophage-oxacillin combination, the bacteriophage and oxacillin, 5 µL each, were mixed to obtain final concentrations as shown in Table 2. Three different concentration levels, MIC and 2 sub MIC, of both antimicrobial agents, were included in this experiment. For bacteriophage, 3 concentration levels including MIC, MIC/10 and MIC/100 were used whereas for oxacillin, 3 concentration levels including MIC, MIC/2 and MIC/4 were used. Each bacteriophage-oxacillin combination was examined for its ability to inhibit S. aureus ATCC 25923 by the spot test as mentioned above.
The inhibitory effect of the bacteriophage-oxacillin combination was analyzed by calculating the fractional inhibitory concentration index (FICI) as follows:
FICI = (MICB+O/MICB) + (MICB+O/MICO)
where
MICB+O = MIC of bacteriophage when the bacteriophage-oxacillin combination was used
MICB+O = MIC of oxacillin when the bacteriophage-oxacillin combination was used
MICB = MIC of bacteriophage alone
MICO = MIC of oxacillin alone
The FICI was interpreted as follows: (1) a synergistic effect when FICI ≤ 0.5; (2) an additive effect when 0.5 < FICI ≤ 1, (3) an indifferent effect when 1 < FICI ≤ 4, (4) an antagonistic effect when FICI >4.
RESULTS
Bacteriophage detection
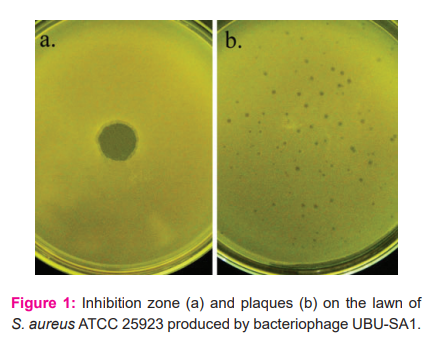
The CFF prepared from the hospital wastewater was found to contain a bacteriophage specific to S. aureus ATCC 25923 because it produced a clear inhibition zone on the lawn of the bacterial host (Figure 1a). When the CFF was subjected to plaque assay by using S. aureus ATCC 25923 as a host, it produced clear plaques of 0.1- 0.2 mm in diameter, indicating the presence of a lytic bacteriophage in the filtrate (Figure 1b). The bacteriophage was designated bacteriophage UBU-SA1.
Bacteriophage host range
The host range of bacteriophage UBU-SA1 was determined by spot test using various tested bacterial strains. The results, summarized in Table 1, showed that the bacteriophage had a highly specific host range. It was able to infect only S. aureus ATCC 25923. The other tested strains were insensitive to this bacteriophage.
Effect of oxacillin on bacteriophage
To use bacteriophage UBU-SA1 in combination with oxacillin, it is very important to examine if the antibiotic has an inhibitory effect on the bacteriophage. After incubating bacteriophage UBU-SA1 (108 PFU/mL) with different concentrations of oxacillin ranging from 200 - 12.5 µg/mL for 24 h, it was found that the bacteriophage titers were not different from the initial titer for every oxacillin concentration. These findings suggest that oxacillin has no detrimental effect on bacteriophage UBU-SA1 and it is safe to use both of them simultaneously to inhibit S. aureus ATCC 25923.
MICs of bacteriophage and oxacillin when used individually
MICs of bacteriophages and antibiotics are not fixed. They are varied depending on sensitive bacterial strains. It is important to determine MICs of bacteriophages and antibiotics whenever different sensitive strains were tested. Therefore, in this study, MICs of bacteriophage UBU-SA1 and oxacillin against S. aureus ATCC 25923 had to be determined since they have not been reported anywhere.
By using the spot test, it was found that concentrations of bacteriophage UBU-SA1 producing a clear inhibition zone against S. aureus ATCC 25923 were 105 PFU/mL and above. From these results, the MIC of bacteriophage UBU-SA1 against S. aureus ATCC 25923 was 105 PFU/mL.
By using the spot test, it was found that concentrations of oxacillin producing a clear inhibition zone against S. aureus ATCC 25923 were 50 µg/mL and above. From these results, the MIC of oxacillin against S. aureus ATCC 25923 was 50 µg/mL.
MICs of bacteriophage and oxacillin when used in co-treatment
When bacteriophage UBU-SA1 or oxacillin with concentrations less than MIC values (sub MIC values) were used together to inhibit S. aureus ATCC 25923, each of them could not inhibit the bacterial host. However, when they were used in combination, they were able to inhibit S. aureus ATCC 25923 and the lowest concentrations of bacteriophages UBU-SA1 and oxacillin that could inhibit the host were 103 PFU/mL (MICB/100) and 12.5 µg/mL (MICO/4), respectively (Table 2). To analyze the effect of bacteriophage and oxacillin combination against S. aureus ATCC 25923, FICI was calculated to be 0.26. This FICI value indicates a synergistic effect between bacteriophage UBU-SA1 and oxacillin against S. aureus ATCC 25923.
DISCUSSION
In general, bacteriophages are often found in places where their hosts are present. Therefore, theoretically, the best way to isolate bacteriophages is to isolate them from the same samples where their hosts exist. For example, bacteriophage PAh4 specific to a fish pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila UR1was isolated from pond water where its specific host was found.15 However, in this study, bacteriophage UBU-SA1 and its specific host are isolated from different sources. This is not an unusual case because several bacteriophages were isolated from places outside from where their specific hosts exist. These findings emphasize that bacteriophages are widespread in environments. Examples of bacteriophages isolated from sources different from places where their hosts were found include bacteriophage ST1 (specific to Salmonella Typhimurium)16 and bacteriophage Kpn5 (specific to Klebsiella pneumoniae).17 Both bacteriophages were isolated from sewage influents whereas their specific hosts were derived from clinical samples.
The narrow host range of bacteriophage UBU-SA1 should be advantageous, in principle, as a therapeutic bacteriophage resulting in less harm to normal flora than commonly used antibiotics. However, bacteriophages with a narrow host range may cause limitations in their therapeutic use. This problem can be overcome by using cocktails of several bacteriophages18 or combinations of bacteriophages and antibiotics.19
To our knowledge, no beta-lactam antibiotics have been reported to have inhibitory activity against bacteriophages. For oxacillin, its bactericidal activity results from the inhibition of cell wall synthesis and is mediated through oxacillin binding to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). By binding to specific PBPs located inside the bacterial cell wall, oxacillin inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cell lysis is then mediated by bacterial cell wall autolytic enzymes such as autolysins. Oxacillin may interfere with an autolysin inhibitor.20 Unlike bacteria, bacteriophages have no cell wall thereby escaping from the bactericidal activity of oxacillin.
Several cases of synergistic effects between bacteriophages and antibiotics against bacterial hosts have been reported. Bacteriophage EPA1 when combined with gentamicin showed profound improvement in killing effect against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1.21 Antimicrobial synergy between bacteriophage T4 and cefotaxime was also observed against Escherichia coli ATCC 11303.22However, antagonistic effect between bacteriophages and antibiotics against bacterial hosts has been observed. This can be in part explained by interference of antibiotics with aspects of bacterial physiology that can be crucial to bacteriophage antibacterial activities such as by interfering with bacterial ribosome functioning.23
CONCLUSION
Bacteriophage UBU-SA1 was isolated from a hospital wastewater sample. It was highly specific to S. aureus ATCC 25923. The combined treatment using bacteriophage UBU-SA1 and oxacillin profoundly improved antimicrobial activity against S. aureus ATCC 25923 when compared with their treatments. With further investigation, the bacteriophage, by itself or in combination with antibiotics, may be useful as a therapeutic agent in controlling S. aureus.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors also wish to express gratitude to the management of the Faculty of Science, Ubon Ratchathani University, Thailand for the support throughout the manuscript preparation process. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals, and books from which the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Source of funding: None
Authors’ Contribution: Phumkhachorn P: Conceived idea, conducted research, collected and analysed data and wrote manuscript; Rattanachaikunsopon P: Helped in data collection, analysis and article write-up.
References:
-
Oliveira D, Borges A, Simoes M. Staphylococcus aureus toxins and their molecular activity in infectious diseases. Toxins2018;10(6):252.
-
Bartash R, Nori P. Beta-lactam combination therapy for the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus species bacteremia: A summary and appraisal of the evidence. Int J Infect Dis2017;63:7-12.
-
Turner NA, Sharma-Kuinkel BK, Maskarinec SA, Eichenberger EM, Shah PP, Carugati M, et al.Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an overview of basic and clinical research. Nat Rev Microbiol2019;17(4):203-18.
-
Phumkhachorn P, Rattanachaikunsopon P. Bacteriophages: Biology and applications. J Sci Technol UBU 2019;21(3):1-13.
-
Wang J, Zhao F, Sun H, Wang Q, Zhang C, Liu W, et al. Isolation and characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage vB_SauS_SA2. AIMS Microbiol 2019;5(3):285-307.
-
Ganaie MY, Qureshi S, Kashoo Z, Wani SA, Hussain MI, Kumar R, et al. Isolation and characterization of two lytic bacteriophages against Staphylococcus aureus from India: newer therapeutic agents against Bovine mastitis. Vet Res Commun2018;42(4):289-95.
-
Kwan T, Liu J, DuBow M, Gros P, Pelletier J. The complete genomes and proteomes of 27 Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA2005;102(14):5174-9.
-
El Haddad L, Roy JP, Khalil GE, St-Gelais D, Champagne CP, Labrie S, et al. Efficacy of two Staphylococcus aureus phage cocktails in cheese production. Int J Food Microbiol2016;217:7-13.
-
Hamza A, Perveen S, Abbas Z, Rehman SU. The lytic SA phage demonstrate bactericidal activity against mastitis causing Staphylococcus areus. Open Life Sci 2016;11(1):39-45.
-
Rattanachaikunsopon P, Phumkhachorn P: Bacteriophages: Discovery and therapeutic uses in humans and animals. Int J Cur Res Rev2010;2(11):3-8.
-
Pornnikom P, Phumkhachorn P, Rattanachaikunsopon P. Synergistic effect of bacteriophage and ampicillin against Shigella dysenteriae. Bio Bulletin 2019;5(1):5-9.
-
Nouraldin AAM, Baddour MM, Harfoush RAHH, Essa SAM. Bacteriophage- antibiotic synergism to control planktonic and biofilm producing clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Alexandria J Med 2016;52(2):99-105.
-
Verma V, Harjai K, Chhibber S. Structural changes induced by a lytic bacteriophage make ciprofloxacin effective against older biofilm of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biofouling 2010;26(6):729- 37.
-
Rattanaborvorn W, Phumkhachorn P, Rattanachaikunsopon P.Potential of bacteriophages in controlling drug resistant Shigella sonnei. Asian J Microbiol Biotechnol Environ Sci2017;19(3):526-30.
-
Phumkhachorn P, Rattanachaikunsopon P. Use of bacteriophage to control experimental Aeromonas hydrophila infection in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Pak J Biol Sci2020;23(12):1659-65.
-
Somnate T, Phumkhachorn P, Rattanachaikunsopon P. Potential of virulent bacteriophage as a biocontrol agent against Salmonella Typhimurium in beverages. J Pure Appl Microbiol 2014;8(2):1131-9.
-
Kumari S, Harjai K, Chhibber S. Isolation and characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae specific bacteriophages from sewage samples. Folia Microbiol2010; 55(3): 221-227.
-
Chan BK, Abedon ST, Loc-Carrillo C. Phage cocktails and the future of phage therapy. Future Microbiol2013;8(6):769-83.
-
Wolska KI, Grzes K, Kurek A. Synergy between novel antimicrobials and conventional antibiotics or bacteriocins. Pol J Microbiol2012;61(2):95-104.
-
Bush K, Bradford PA. β-Lactams and β-Lactamase Inhibitors: An Overview. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6(8):a025247.
-
Akturk E, Oliveira H, Santos SB, Costa S, Kuyumcu S, Melo LDR, et al. Synergistic action of phage and antibiotics: Parameters to enhance the killing efficacy against mono and dual-species biofilms. Antibiotics (Basel). 2019;8(3):103.
-
Ryan EM, Alkawareek MY, Donnelly RF, Gilmore BF. Synergistic phage-antibiotic combinations for the control of Escherichia coli biofilms in vitro. FEMS Immunol MedMicrobiol2012;65(2):395-8.
-
Abedon ST. Phage-antibiotic combination treatments: Antagonistic impacts of antibiotics on the pharmacodynamics of phage therapy? Antibiotics (Basel)2019;8(4):182.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License