IJCRR - 13(19), October, 2021
Pages: 117-124
Date of Publication: 11-Oct-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Vitamin D Status in Covid-19 Patients Admitted to ICU in a Tertiary Care Hospital
Author: Ramashetty R, Manjunathaswamy AH, Viswanath N, Chandrashekarappa SM, Kalvapudi D
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: The pandemic outbreak of COVID 19 has affected people worldwide. Studies have shown that deficiency of vitamin D is associated with increased susceptibility to respiratory infection. Aim: To evaluate vitamin D status and the possible association of vitamin D levels and biomarkers in COVID-19 patients admitted to the intensive care unit. Methodology: A cross-sectional study done confirmed COVID 19 patients were admitted to ICU. Blood count, vitamin D, inflammatory markers and blood gas parameters were measured. Duration of stay and outcome were recorded. Statistical analysis was done using SPSS V.25 Results: Study done on 155 patients with COVID 19 showed 94.2% participants had Vitamin D deficiency (Vitamin D 20 ng/mL and vitamin D 50 years and the females had lower vitamin D levels. The majority of COVID-19 patients in whom mortality was the outcome, had lower levels of Vitamin D.
Keywords: Vitamin D, COVID 19 infection, Inflammatory markers, SARS CoV-2
Full Text:
Introduction:
A novel human coronavirus, first detected in a cluster of unexplained pneumonia cases in Wuhan, China has caused a global outbreak and has become a major public health problem worldwide. 1 The World Health Organization officially named this new coronavirus disease as COVID-19 and the virus causing it as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). 2 SARS CoV-2 affected patients present from mild symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection to severe respiratory failure. Clinical data obtained from COVID-19 patients have reported high concentrations of cytokines admitted to the ICU, which indicates the presence of cytokine storm in severe COVID-19 patients. Many COVID-19 patients have died due to complications such as ARDS, pneumonia, acute kidney failure, acute heart failure etc, which is likely attributable to uncontrolled acute inflammation and cytokine storm. 3,4
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble steroid derivative and a prohormone, which plays an important role in bone health by maintaining calcium and phosphate homeostasis. However, research in the last two decades has discovered novel actions of vitamin D on the cardiovascular system, nervous system, respiratory system and immune response. 5,6 Recent experimental pieces of evidence have shown that deficiency of vitamin D is associated with increased susceptibility to infection and autoimmune disorders. 7 Evidence from observational studies shows an association between vitamin D deficiency, chronic airway diseases and respiratory infections indicating the possible role of vitamin D in reducing the risk of respiratory tract infections. 8 In a review and meta-analysis of 25 randomised controlled studies, Martineau et al. have mentioned that vitamin D helps in protection against acute respiratory tract infection. 9 In vitro and in vivo studies have also shown that vitamin D plays an active role in the modulation of innate and adaptive immune responses. 10
Observational studies have shown that COVID-19 positive patients have a higher incidence of low vitamin D levels than COVID-19 negative patients. It is also seen that there is a high prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency in a cohort of patients with moderate-to-severe acute respiratory syndrome due to COVID-19. Growing circumstantial evidence and recent studies have linked the severity and mortality of COVID-19 to the vitamin D status of the patients. A cross-sectional analysis across Europe showed that COVID-19 mortality was significantly associated with vitamin D status in different populations. 11 Another Indonesian retrospective cohort study of 780 Covid-19 patients indicated that the majority of death cases had low vitamin D levels and that vitamin D status was strongly associated with Covid-19 mortality. 12 Recently, some articles also have suggested the possible involvement of vitamin D in reducing the risk of respiratory tract infections, especially from influenza, rhinovirus and previous coronaviruses by enhancing immune response. 13
Observational studies have frequently reported that higher levels of vitamin D were associated with low levels of inflammatory markers including CRP, IL-6 and TNFα in healthy populations and in those with proinflammatory conditions, such as diabetes, arteriosclerosis and inflammatory conditions. 14 Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with increased risk of viral respiratory tract infections and an increase in inflammatory cytokines. Thus, this study aimed to evaluate the possible association of vitamin D levels and various biomarkers in moderate to severe COVID-19 patients admitted to the intensive care unit.
Methodology:
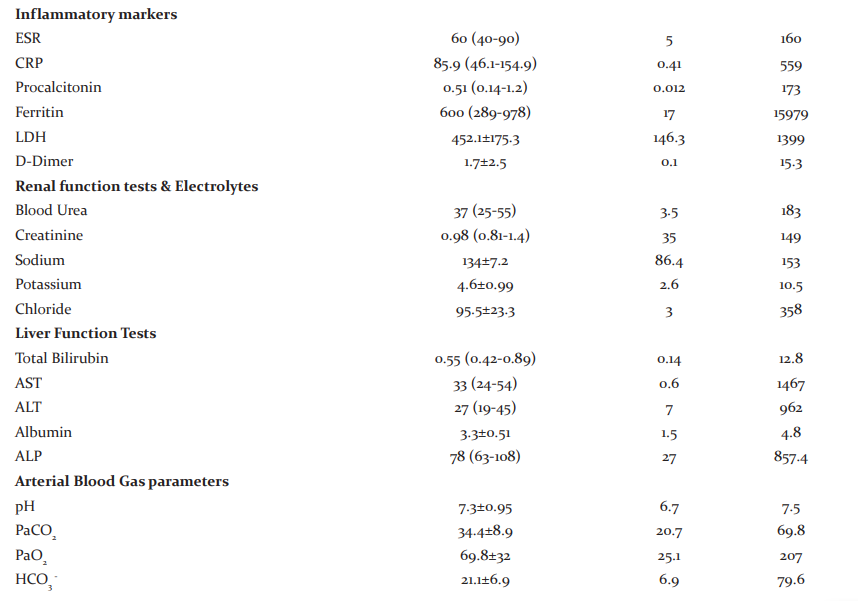
This is a cross-sectional study. Ethical clearance was obtained from the institutional ethical committee, JSS Medical College, Mysuru (LetterNo. JSSMC/IEC/1909/01NCT/2020-21). 155 RT-PCR confirmed COVID-19 patients aged 18 – 60 yrs, admitted to ICU of JSS Hospital, Mysuru, Karnataka, India and willing to participate in the study were recruited. Informed consent was obtained from the study participants. No specific exclusion criteria were considered, except patients not willing to give consent for the study. Information regarding socio-demographic variables, medical history and comorbidities of the patients were collected using a pre-tested and validated questionnaire. Vital signs like Pulse rate, Blood pressure, Respiratory rate and SPO2 were recorded from the patients. SOFA score at admission was calculated.
Laboratory findings like blood count, HbA1C, Vitamin D, Procalcitonin, C-reactive protein, Ferritin, D-dimer, LDH, Renal function tests, liver function tests and blood gas analysis parameters were obtained from the case records. Respiratory parameters such as the fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) was obtained and PaO2/FiO2 ratio was calculated.
Statistical Analysis:
Data were entered in Microsoft Excel and analyzed using SPSS V. 25 (Licensed to the institution). Descriptive statistics were used to calculate Mean, Median, Standard Deviation, Inter Quartile Range, Proportion etc., and continuous variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) or median and interquartile range. Based on the distribution, parametric (independent t-test and ANOVA) tests or non-parametric (Mann-Whitney U Test, Kruskal Wallis) tests were used to compare the variables for differences in the Vitamin D levels and Chi-square analysis was used to find the association of categorical variables with Vitamin D levels.
Results:
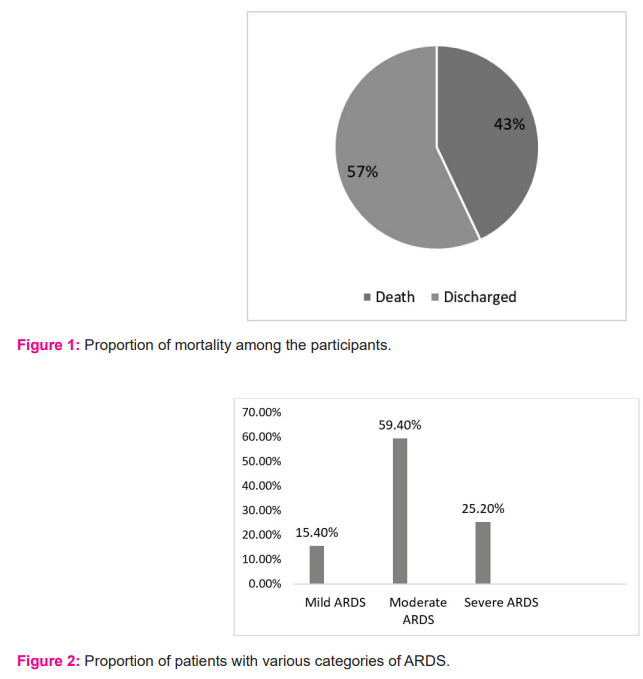
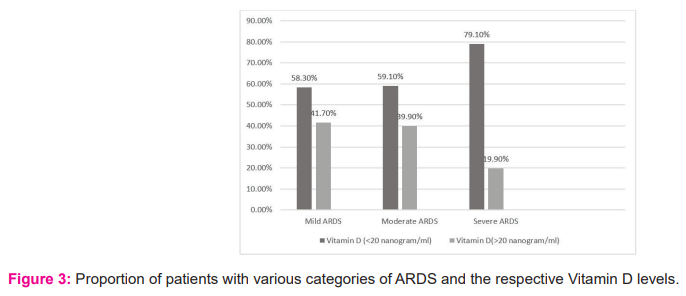
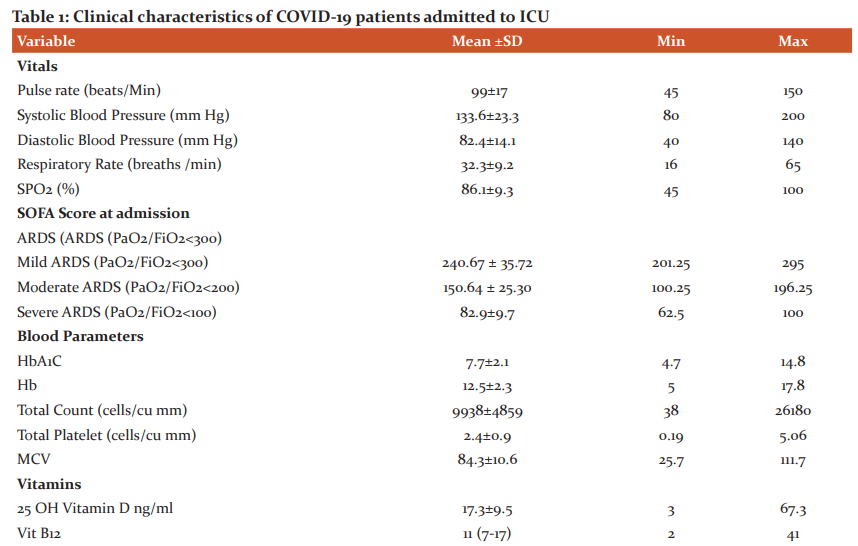
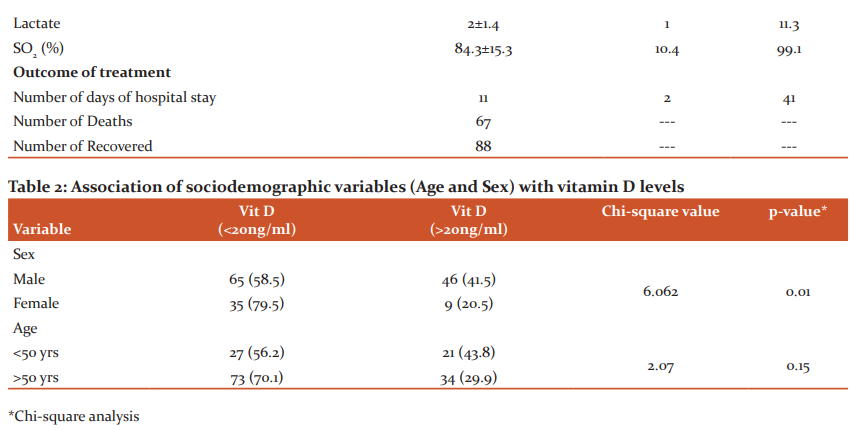
The study included a total of 155 (111 male and 46 female) COVID-19 patients admitted to ICU. The mean age group of the study participants was 55.7±11.8 with a minimum age of 16 yrs. and a maximum of 69 yrs. 71.6% were males and 28.4% were females. 78% of the individuals had one or the other co-morbidities. 54.1% were diabetics, 54% were hypertensives, 13% had a history of ischemic heart disease and 23% had other co-morbidities like asthma, chronic kidney disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, epilepsy, anaemia, pancreatitis, hypothyroidism and hepatitis B. The median SOFA score at admission was 3 (2-4). 43% of the patients expired and the remaining 57% were discharged (Fig 1). 90.32% of patients had ARDS as assessed by PaO2/FiO2 ratio lower than 300 mmHg (Fig 2) and a major proportion of patients with severe ARDS had Vitamin D levels of < 20 ng/ml. The median number of days of stay in the hospital was found to be 11 (7-17), with a minimum of 2 days and a maximum of 41 days. Other clinical characteristics of patients admitted to the Intensive Care Unit has been represented in Table 1.
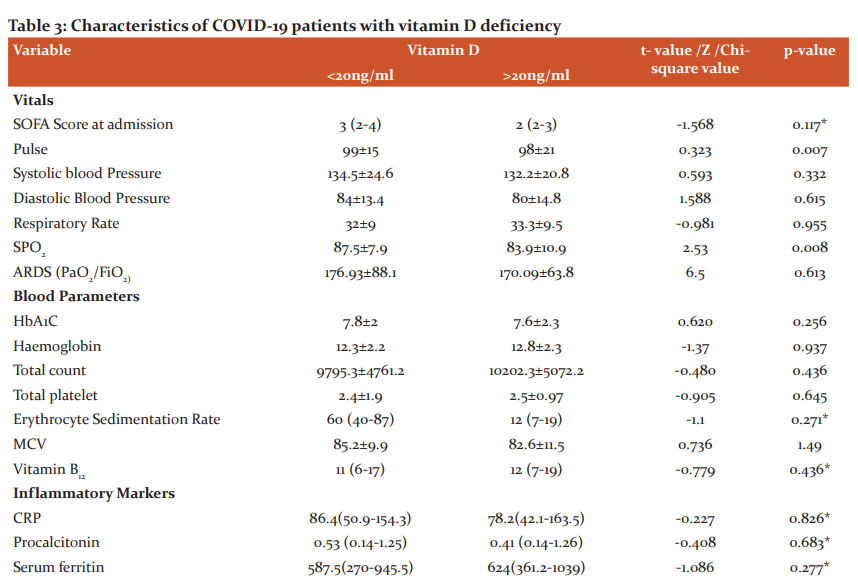
Concerning Vitamin D, while we initially started the study to compare the profile of covid-19 patients getting admitted to ICU with normal and lower levels of Vitamin D, at the end of the study, when the data was analysed, it was seen that majority i.e 94.2% of the study participants had Vitamin D deficiency and only 5.8% had normal Vitamin D >30 ng/ml. Out of those who had lower serum levels of Vitamin D, 68.4% had Vitamin D levels <20ng/ml. There was a significant statistical association seen between sex and Vitamin D levels. (Table 2)
The mean Vitamin D level of the patients with COVID-19 was 17.3±9.5 ng/ml. The mean Vitamin D level of the male patients with COVID-19 was 19.31±10.15 ng/ml and of the female patients was 14.46±6.72 ng/ml. Depending on the age in patients ≤ 50 yrs the mean Vitamin D level was 19.59±8.40 and in patients >50 yrs was 17.19±9.95.
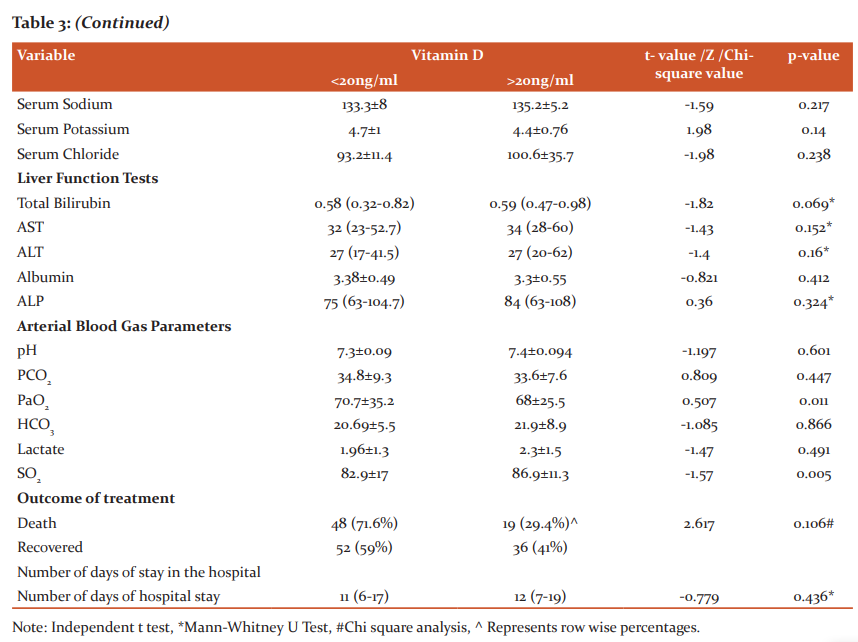
We divided patients into two groups by serum vitamin D level in patients: vitamin D > 20 ng/mL and vitamin D <20 ng/ml. It was seen that there was a statistically significant difference between the Pulse rate (p=0.007), SPO2 (p=0.008), PaO2 (p=0.011), and SO2 (p=0.005) among the groups. None of the other parameters showed any such significant difference. Concerning the Outcome of variables, though there was no significant association found between the outcomes between the groups, it was seen that the majority i.e nearly 72% in whom mortality was the outcome, had lower levels of Vitamin D. (Table 3)
Discussion:
Vitamin D is one of the major hormones involved in calcium and phosphorus metabolism. Studies have shown that low serum vitamin D levels are associated with chronic diseases such as autoimmune diseases, diabetes mellitus, chronic renal failure, depression, cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, and cancer. The impact of vitamin D on COVID-19 infection, hospitalization, and mortality rate has gained importance in the scientific community.
The present study was conducted to evaluate the vitamin D status in the confirmed COVID-19 patients admitted to ICU in a tertiary care hospital and to analyze the possible influence of vitamin D status on the severity of the COVID-19. Our study showed that the majority i.e 94.2% of the study participants had Vitamin D deficiency and only 5.8% had normal Vitamin D >30 ng/ml. Out of those who had lower serum levels of Vitamin D, 68.4% had Vitamin D levels < 20ng/ml. Study participants > 50 years and the females had lower vitamin D levels and there was significant statistical association only between sex and Vitamin D levels. Similar to our study, J L Hernandez et al, also have shown that hospitalized COVID-19 patients had lower 25OHD levels and a higher prevalence of vitamin D deficiency when compared to the population-controlled group. But, in their study Serum 25OHD values were lower in men than in women. 15 A Study by A Jain et al. on the Indian population also compared Vitamin D levels between asymptomatic COVID-19 patients and severely ill patients requiring ICU admission and reported that Vitamin D levels were markedly low in severe COVID-19 patients. 16 Serum 25(OH)D concentrations tend to decrease with age and thus low serum 25OHD levels are frequently found in elderly individuals which may be important for COVID-19 because more severity and case-fatality rates are seen in elderly people. 17 Also, low 25OHD levels are seen in those individuals with comorbidities, such as hypertension, diabetes, or cardiovascular diseases, which have also been reported as poor prognostic factors for COVID-19. 18
When assessed for the association between Vitamin D deficiency and clinical parameters, it was seen that there was a statistically significant difference between the Pulse rate (p=0.007), SPO2 (p=0.008), PaO2 (p=0.011), and SO2 (p=0.005) among the groups. Inflammatory markers like CRP, ferritin, LDH did not show any such significant difference. Concerning the Outcome of variables, though there was no significant association found between the groups, it was seen that majority i.e nearly 72% in whom mortality was the outcome, had lower levels of Vitamin D. Some retrospective studies have demonstrated a correlation between vitamin D status and COVID-19 severity and mortality, while other studies did not find the correlation when confounding variables are adjusted. Maghbooli Z et al reported that Vitamin D sufficiency was associated with a statistically significant lower risk of hypoxia, defined by an arterial blood oxygen saturation level below 90%. The study also showed that in vitamin D sufficient patient’s serum CRP and blood lymphocyte percentage were significantly lower and higher respectively and there were no significant differences in hospitalization duration between patients with and without vitamin D sufficiency. 19 An Indonesian retrospective cohort study by Raharusun P et al has reported that vitamin D status is strongly associated with COVID-19 mortality outcome of cases after controlling for age, sex, and comorbidities. 12 In a report, Alipio M observes a significant association between vitamin D status and clinical outcomes (p<0.001) and suggested that serum 25(OH) D level was low in critical cases when compared to mild cases indicating increased odds of having a mild clinical outcome rather than a critical outcome by approximately 19.61 times. 20
Recent experimental evidence has shown that deficiency in vitamin D is associated with increased susceptibility to infection and autoimmune disorders. Vitamin D can modulate both innate and adaptive immune responses which are distinct but interacting. Vitamin D increases the production of the anti-inflammatory cytokine and inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. 21 Several studies have shown the association between Vitamin D and renin-angiotensin system (RAS) with increased plasma renin activity, higher Angiotensin II concentrations and higher RAS activity in vitamin D deficiency status. 22 But in our study, we did not find any association between lower Vit D levels and inflammatory markers.
Strength and Limitation of the study: The strength of this study was its objective to understand the association of Vitamin D in the severity of the illness and hence would contribute to the understanding of this novel virus and its management with Vitamin D. The limitation would be, a) the smaller sample size and the inability of the study to reflect the course of the disease through follow up due to constraints in time and funding. b) No control or comparison group, only ICU admitted patients were participants. c) there were only a few patients with normal vitamin D levels to do the comparison between normal Vitamin D levels and Vitamin D deficiency.
Conclusion: In our study, we found that majority of the COVID-19 patients admitted to ICU had Vitamin D deficiency. Patients > 50 years and the females had lower vitamin D levels with significant statistical association seen only between sex and Vitamin D levels. We did not find any such significant difference in Inflammatory markers like CRP, ferritin, LDH between the groups. It was seen that the majority of COVID-19 patients in whom mortality was the outcome, had lower levels of Vitamin D but there was no significant association found between the groups for the outcome variables.
Acknowledgement: Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed
Conflict of interest: No conflict of interest to declare
Funding: No funding was received
Author contribution:
-
Dr. Rajalakshmi R: Conception and design, acquisition, analysis, interpretation of data and drafting the manuscript
-
Dr Akshay H M: Design, acquisition of data, interpretation of data and revising the manuscript critically for important intellectual content
-
Dr Nagashree V: Design, analysis and interpretation of data and drafting of the manuscript
-
Dr Smitha M C: Design, analysis and interpretation of data and drafting of the manuscript
-
Dr Devaki K: Acquisition of data and analysis.
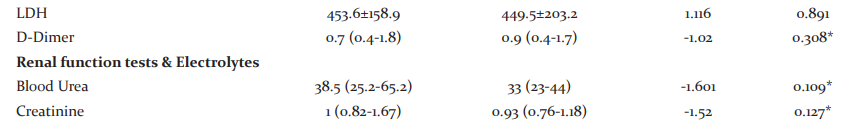
References:
-
Zhu N., Zhang D., Wang W., Li X., Yang B., et al . A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. New Engl. J. Med. 2020;8:727–733.
-
https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technical-guidance/naming-the-coronavirus-disease-(covid-2019)-and-the-virus-that-causes-it
-
Huang C., Wang Y., Li X., Ren L., Zhao J., et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;10223:497–506.
-
Song P, Li W, Xie J, Hou Y, You C. Cytokine storm induced by SARS-CoV-2. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;509:280-287.
-
DeLuca HF. Vitamin D: Historical Overview. Vitam Horm. 2016;100:1-20.
-
Christakos S, Hewison M, Gardner DG, Wagner CL, Sergeev IN, et al. Acad Sci. 2013 May;1287(1):45-58.
-
Adorini L. Intervention in autoimmunity: the potential of vitamin D receptor agonists. Cell Immunol. 2005 Feb;233(2):115-124.
-
Ginde AA, Mansbach JM, Camargo CA Jr. Association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and upper respiratory tract infection in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arch Intern Med. 2009 Feb 23;169(4):384-390.
-
Martineau Adrian R, Jolliffe David A, Hooper Richard L, Greenberg Lauren, Aloia John F, et al. Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data Bri Med J. 2017 Feb; 356:i6583.
-
Wei R, Christakos S. Mechanisms Underlying the Regulation of Innate and Adaptive Immunity by Vitamin D. Nutr. 2015 Sep 24;7(10):8251-8260.
-
Laird E, Rhodes J, Kenny RA. Vitamin D and Inflammation: Potential Implications for Severity of Covid-19. Ir Med J. 2020 May;113(5):81.
-
Raharusun P, Priambada S, Budiarti C, Agung E, Budi C. Patterns of COVID-19 Mortality and Vitamin D: An Indonesian Study. SSRN Elect J. 2020; 19(8): 312-316.. 10.2139/ssrn.3585561.
-
Gunville CF, Mourani PM, Ginde AA. The role of vitamin D in the prevention and treatment of infection. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2013 Aug;12(4):239-245.
-
Azizieh F, Alyahya KO, Raghupathy R. Association between levels of vitamin D and inflammatory markers in healthy women. J Inflamm Res. 2016 Apr 27;9:51-57.
-
Hernández JL, Nan D, Fernandez-Ayala M, García-Unzueta M, Hernández-Hernández MA, et al. Vitamin D Status in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Mar 8;106(3): e1343-e1353
-
.Jain, A., Chaurasia, R., Sengar, N.S. et al. Analysis of vitamin D level among asymptomatic and critically ill COVID-19 patients and its correlation with inflammatory markers. Sci Rep.2020;10: 20191.
-
Mosekilde L. Vitamin D and the elderly. Clin Endocrinol. 2005 Mar;62(3):265-281.
-
Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020 Mar 28;395(10229):1054-1062.
-
Maghbooli Z, Sahraian MA, Ebrahimi M, Pazoki M, Kafan S, et al. Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection. PLoS ONE.2020 Sep;15(9): e0239799.
-
Alipio M. Vitamin D Supplementation Could Possibly Improve Clinical Outcomes of Patients Infected with Coronavirus-2019 (COVID-2019). SSRN Electr J .2020; 8(2): 211-215. 10.2139/ssrn.3571484.
-
Aranow C. Vitamin D and the immune system. J Investig Med. 2011 Aug;59(6):881-886.
-
Kota S, Kota Siva, Jammula S, Meher L, Panda S, et al. Renin-angiotensin system activity in vitamin D deficient, obese individuals with hypertension: An urban Indian study. Indian journal of endocrinology and metabolism. 2011 Oct;15 (4): 395-401.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License