IJCRR - 13(19), October, 2021
Pages: 99-104
Date of Publication: 11-Oct-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Assessment of Renalase Levels in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients on Maintenance Hemodialysis
Author: Sudha Rangasamy, Vijayasamundeeswari Chinnathambipalayam Kandaswamy, Bharanidharan Samiappan
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: End-stage renal disease (ESRD) is the last stage of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and those patients are at a higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events. Renalase is a novel protein with monoamine oxidase activity and is secreted by the kidney playing a major role in the regulation of blood pressure. Recent studies have suggested serum renalase levels to be related to adverse renal outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease. Aim: To estimate the levels of serum renalase in ESRD patients on Maintenance Hemodialysis (MHD) and to compare the levels with healthy controls and assess the relationship of serum renalase with other analysed parameters in ESRD patients. Materials and Methods: 60 ESRD patients on MHD and 50 healthy individuals were analysed for serum renalase, fasting blood glucose, urea, creatinine, lipid profile, albumin and haemoglobin levels. Results: The mean level of serum renalase in hemodialysis patients was 68.69\?34.52ng/ml which was significantly higher than the controls (45.70\?22.18ng/ml)(p-value< 0.01). Serum renalase had a significant positive correlation with fasting blood glucose, urea, creatinine, triacylglycerol, dialysis duration and age (r=0.55, r=0.51, r=0.32, r=0.30, r=0.38 and r=0.41 respectively, p�value< 0.05) and was negatively correlated with weight, albumin, haemoglobin and eGFR (r-value = -0.33, -0.35, -0.24 and -0.33 respectively, p-value< 0.05). Conclusion: Serum renalase is significantly elevated in ESRD patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Serum renalase levels had an association with age, weight, fasting blood glucose, urea, creatinine, eGFR, dialysis duration, triacylglycerol, albumin, and haemoglobin.
Keywords: Serum renalase, End-stage renal disease, Maintenance hemodialysis, Chronic kidney disease
Full Text:
Introduction:
Chronic kidney disease is characterized by loss of kidney function gradually which progresses to End-stage renal disease over the years. The burden of CKD is enormous that the number of individuals with all stage chronic kidney disease is almost 700 million in 2017, which is more people than those with diabetes, osteoarthritis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, or depressive disorders. A study on the Global Burden of Disease, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) has stated that almost a third of patients with CKD lived in two countries, China (132·3 million cases) and India (115·1 million cases).1 The estimated age-adjusted incidence rate of ESRD is 229 per million population, whereas more than 100,000 new patients enter renal replacement programs annually in India.2
Chronic kidney disease has a major global impact, increasing morbidity and mortality, as well as a financial burden. CKD is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD). CKD if is attended to and treated at an earlier stage, the morbidity and mortality can be considerably reduced. Cardiovascular disease is the most common complication and a chief cause of death in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) accounting for 45% to 50% of causes of death in ESRD patients. CKD is an independent risk factor for CVD and the majority of patients expire due to CVD than progress to ESRD.3In ESRD patients, mortality due to CVD is 10~30 times higher than in the general population. Studies have demonstrated that pathology, manifestations, and complications of CVD differ in the presence of CKD.4 Various reasons have been implicated in the high incidence of CVD in ESRD patients like ventricular hypertrophy as well as non-traditional risk factors, such as chronic volume overload, malnutrition, inflammation, oxidative stress, and other aspects of the uremic milieu. Recently some studies have shown that plasma dopamine and norepinephrine levels are consistently increased in patients with ESRD.5-8 Numerous biomarkers have been tried in recent years which may contribute to the profound increase in circulating catecholamine levels in ESRD patients.
Renalase is a recently recognized novel FAD-dependent amine oxidase that is secreted into the blood by the kidney. It degrades catecholamines in vitro and lowers blood pressure in vivo by decreasing cardiac contractility and heart rate and preventing a compensatory increase in peripheral vascular tone.9,10 It is also expressed in the myocardium, skeletal muscles, small intestine, peripheral nerves, adrenal cortex and adipose tissue.
Recent data have shown abnormalities in the renalase pathway which are evident in animal models of chronic kidney disease and hypertension. Plasma levels of renalase were said to be markedly reduced in patients with chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease.11 Several recent observational studies have associated renalase gene polymorphisms with various diseases like essential hypertension, coronary artery disease, stroke and Type 1 diabetes.12 Since renalase is involved in the catabolism of catecholamines, it was said that it may be used therapeutically in conditions accompanied by increased sympathetic activity. The latest study has suggested that renalase protected against the progression of Diabetic Nephropathy and might be a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy.13 However, Ebru Gok Oguz et al have shown that renalase levels are elevated in hemodialysis patients than in the healthy controls.14 Few other studies have stated that the renalase gene can be potentially involved in blood pressure regulation in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and the ischemic and arrhythmogenic myocardial changes of T2DM with or without HTN.15 Dziedzic et al have recognized a significantly longer survival time in hemodialyzed patients with high renalase activity compared with patients with low activity of the enzyme.16 The identification of renalase is an important step in developing a more detailed understanding of cardiovascular physiology and might be helpful for physicians in providing timely care for patients with kidney disease. The relationship of renalase with different human diseases have raised it as a substance with potential pathophysiological pertinence and those results might have vast ramifications in diagnosis as well as therapy. Based on this background, a study was conducted to estimate the levels of Renalase in End-stage Renal disease patients on maintenance hemodialysis.
Materials and Methods:
This study was a cross-sectional observational study conducted over 6 months in a Tertiary care hospital. Institutional ethical clearance was obtained before the study and informed consent was obtained from all the study subjects. The study subjects were stratified into two groups consisting of 60 subjects as Group I, end-stage renal disease patients undergoing MHD and 50 subjects as Group II, apparently healthy controls, who were age and gender-matched. The inclusion criteria were age more than 18 years and patients on regular hemodialysis (3 times weekly) for more than one year. Patients with acute infections were excluded. Group II included healthy individuals over 18 years, not under any medication. For all the subjects, a questionnaire was filled containing the details of age, sex, smoking, alcohol intake, symptoms and aetiology of ESRD, history of medication and duration of hemodialysis. Anthropometric measurements including height, weight, and measurements of systolic and diastolic blood pressure were recorded for all the subjects. Body mass index was calculated and noted.
Fasting blood samples were collected for all the study subjects immediately before the HD procedure and transferred to appropriate containers. Samples for renalase were centrifuged and stored at -200C until analysis. All the samples were analysed for glucose, urea, creatinine, albumin, haemoglobin and lipid profile using a fully automated analyser, Erba EM200. LDL-C was calculated by the Friedwald formula. eGFR was calculated using the MDRD formula.
Serum renalase levels were measured by the ELISA method (Wuhan, China). Renalase levels are presented as ng/ml. The sensitivity of the renalase assay was <0.469ng/ml and the intra and inter-assay coefficients were <8% and <10% respectively.
Statistical analysis: All the statistical work was performed by the SPSS software. The results are presented as Mean ± Standard deviation. To estimate the differences between cases and controls, the Student’s t-test was applied. Pearson’s correlation analysis was used to test the association of renalase with other analysed parameters in Group I subjects. A p-value of less than 0.05 was set as significant.
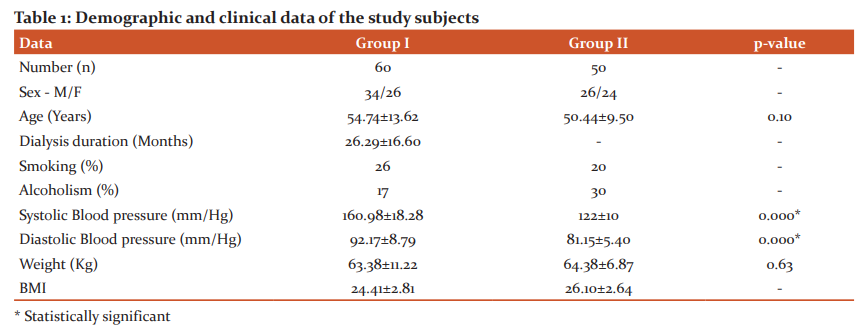
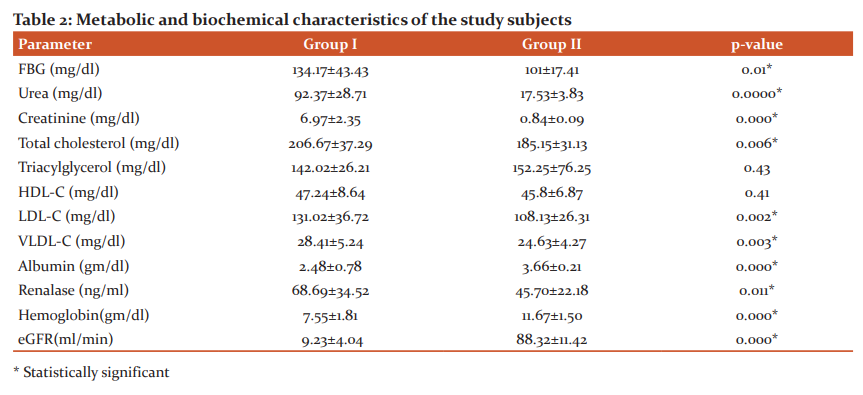
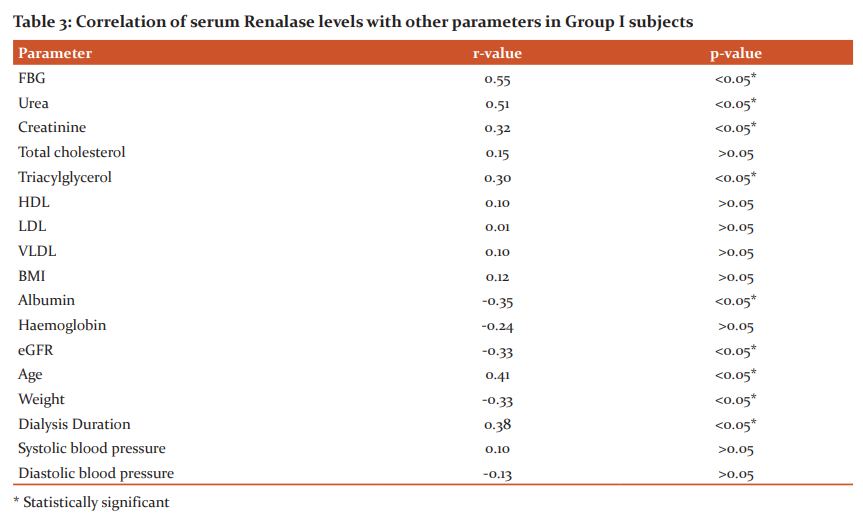
Results: This cross-sectional study on 110 subjects included 60 MHD patients and 50 healthy individuals. The demographic and clinical data of the study subjects are given in Table 1. Table 2 shows the metabolic and biochemical characteristics of the study subjects. The correlation of serum renalase levels with other parameters in Group I subjects are depicted in Table 3. Out of 60 patients included in Group I, 57% were male and 43% were female. Among Group II subjects, 52% were male and 48% were female. The two groups did not differ in terms of age and gender.
The present study showed that serum renalase level in ESRD patients was higher than in healthy controls (68.69±34.52 vs. 45.70± 22.18ng/ml), and also there were significant differences in serum FBG, BP, urea, creatinine, LDL, VLDL, Albumin, Hemoglobin and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) between ESRD patients and healthy controls as presented in Table 2.
Discussion: Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a multifactorial disease and there is an increased risk of CAD in hemodialyzed patients which is not fully explained by traditional cardiovascular risk predictors. So, there occurs a need for the evaluation of novel risk markers to improve CAD risk stratification in ESRD patients. Renalase is a novel protein that is secreted by the kidney, circulates in the blood, metabolizes catecholamines and decreases cardiac contractility and systemic blood pressure in vivo.9 It is a protein made up of 342 amino acids with a molecular weight of 37.8kDa. The present study investigated the levels of renalase in hemodialyzed patients and the relationship of serum renalase with other blood parameters.
The key finding of this study was that serum renalase in ESRD patients was significantly higher than in the controls (Table 2). This finding is under many other recent studies such as Baek SH et al, Malyszko J et al. etc.14,17,18,31 Serum renalase levels are higher in peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients too.19 Edyta Zbroch et al. have also shown elevated renalase levels in PD patients but lower than the HD patients.20 In contrast, He B et al have confirmed that plasma renalase level was decreased in CAD patients than healthy subjects and was correlated with CAD, the changes of which may reflect the degree of coronary artery stenosis.21 However, the mean levels of renalase in hemodialysis patients widely vary with different studies which might be due to the different methods used in the studies. In the present study, the ELISA method was used for the estimation of renalase levels since it’s the most widely used method and also a practical method.
The higher renalase levels in hemodialysis patients may be due to much higher SNS activity, lower renal clearance, higher production or slower degradation in these patients. Edyta Zbroch et al. have estimated in vivo together – catecholamines (DA and NE) and renalase concentrations and they have evaluated the strong correlation between renalase and residual diuresis.20 Gu et al. have proposed that the kidney might synthesize and secrete more renalase to compensate for the increased catecholamines levels in the early phase of acute myocardial infarction in animal model.22
Serum renalase had a significant positive correlation with fasting blood glucose, urea, creatinine, triacylglycerol and age. Serum renalase levels increased as their kidney function deteriorated in HD patients. This finding is similar to EG Oguz et al.19, Baek SH et al.17 Gluba-Brzozka et al. found a higher renalase concentration in patients with early stages of CKD than in the control group and supported the previous findings on the relation between renalase and kidney function.23 In a recent study of Oguz et al., it was also found that renalase was significantly higher in hemodialyzed patients in comparison with the control group.
Serum renalase had a significant negative correlation with eGFR. Stojanovic D. et al. demonstrated that plasma renalase is strongly and inversely correlated with glomerular filtration rate and is an independent predictor for decreased eGFR, as well as after multivariate modelling in stable renal transplant recipients. They have found that renalase strongly and inversely correlated with kidney function, positively with creatinine and lipid disturbances. Due to that renalase levels are likely determined mostly by renal function.24 Similar results have been given by Wang F et al.25 and Przybylowski P et al.26
Blood pressure was significantly higher in Group I subjects when compared to Group II. There was no significant correlation between renalase levels and neither systolic nor diastolic pressure in hemodialysis patients. Edyta Zbroch et al. and Przybylowski P et al. have found no correlation between serum renalase concentration and blood pressure in Hemodialysis patients20 and heart transplant recipients26 respectively, whereas Marta Lemiesz et al. has concluded that serum renalase correlates with blood pressure elevation in prospective cohort analysis of adolescents with primary hypertension.27 Weight and BMI did not significantly differ in both groups.
Fasting blood glucose was significantly elevated in Group I patients than in Group II subjects. 60% of group I subjects were diabetic. FBG had a significant positive correlation with serum renalase levels. Review articles have established that diabetic nephropathy is the most common cause or in combination with hypertensive nephropathy are the most common causes of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) in developed and developing countries.28
There were significant differences in the levels of total cholesterol, LDL-C, VLDL-C, albumin, and haemoglobin between group I and II subjects. Serum renalase had a negative correlation with albumin and haemoglobin, among which only albumin was statistically significant. Serum albumin level is frequently used as a nutritional status indicator and malnutrition is a common problem in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) undergoing hemodialysis which increases morbidity and mortality rate in them. A study by Junlin Zhang et al. found that the lower serum level of albumin was associated with the reduced kidney function and poor renal prognosis in patients with T2DM and DN.29
Serum renalase had a significant positive correlation with age and a significant negative correlation with weight. Zbroch E et al. have found that patients aged 65 years and more had higher renalase and there was a significant correlation between age and renalase.30 They have stated that elevated renalase level in older hypertensive patients is related rather to kidney function and cardiovascular diseases than to age itself.
Conclusion: Elevated levels of renalase have been found in ESRD patients which is related to kidney function. Measurement of renalase might have a greater implication in decreasing the morbidity and mortality of ESRD patients. The limitation of our study is its cross-sectional design and smaller sample size.
Acknowledgement: We are indebted to all the patients and volunteers who participated in this study. The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references to this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/ editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Ethical clearance: Taken from the Institutional Ethics committee before the start of the study. (VMKVMC/IEC/17/71)
Source of funding: Self
Conflict of interest: Nil
References:
-
Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017 GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Lancet 2020; 395: 709–33.
-
Singh AK, Farag YM, Mittal BV, Subramanian KK, Reddy SR, Acharya VN, et al. Epidemiology and risk factors of chronic kidney disease in India – Results from the SEEK (Screening and Early Evaluation of Kidney Disease) study. BMC Nephrol 2013; 14:114.
-
Subbiah AK, Chhabra YK, Mahajan S. Cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease: a neglected subgroup. Heart Asia. 2016;8(2):56-61.
-
Herzog CA, Asinger RW, Berger AK, Charytan DM, Diez J, Hart RGet al. Cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease. A clinical update from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int 2011;80:572–86.
-
Joles, J.A., Koomans, H.A. Causes and consequences of increased sympathetic activity in renal disease. Hypertension. 2004;43:699–706.
-
Zoccali, C, Mallamaci F, Tripepi G, Parlongo S, Cutrupi S, Benedetto FA, et al. CREED investigators. Norepinephrine and concentric hypertrophy in patients with end-stage renal disease. Hypertension. 2002;40(1):41–46.
-
Zoccali, C., Mallamaci F, Parlongo S, Cutrupi S, Benedetto FA, Tripepi G, et al. Plasma norepinephrine predicts survival and incident cardiovascular events in patients with end-stage renal disease. Circulation. 2002;105:1354–1359.
-
Hausberg, M, Kosch M, Harmelink P, Barenbrock M, Hohage H, Kisters K, et al. Sympathetic nerve activity in end-stage renal disease. Circulation.2002;106:1974–1979.
-
Xu J, Li G, Wang P, Velazquez H, Yao X, Li Y, Wu Y, et al. Renalase is a novel, soluble monoamine oxidase that regulates cardiac function and blood pressure. J Clin Invest. 2005 May;115(5):1275-80.
-
Gary V.Desir, Ling Wang, Aldo J.Peixoto.Human renalase: a review of its biology, function, and implications for hypertension. Journal of the American Society of Hypertension.2012;6(6):417-426.
-
Xu J, Desir GV. Renalase, a new renal hormone: its role in health and disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2007 Jul;16(4):373-8.
-
Gary V. Desir, Aldo J. Peixoto. Renalase in hypertension and kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant.2014; 29: 22–28.
-
Yin J, Liu X, Zhao T, Liang R, Wu R, Zhang F et al. A protective role of renalase in diabetic nephropathy. Clin Sci(Lond).2020; 134(1):75-85.
-
Oguz EG, Gursoy GK, Yayar O, Yildirim T, Cimen T, Bulut C, et al. Increased serum renalase in hemodialysis patients: is it related to left ventricular hypertrophy? Ren Fail. 2016 Sep;38(8):1180-6.
-
Refaie W, Elewa A. Renalase gene polymorphisms in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with and without hypertension. Egypt J Intern Med 2013;25:149-53.
-
Dziedzic M, Powrózek T, Or?owska E, Koch W, Kukula-Koch W, Gawel K, et al. Relationship between microRNA-146a expression and plasma renalase levels in hemodialyzed patients. 2017;PLoS ONE 12(6): e0179218.
-
Baek SH, Cha RH, Kang SW, Park CW, Cha DR, Kim SG, et al. Circulating renalase predicts all-cause mortality and renal outcomes in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease. Korean J Intern Med.2019;34(4):858-866.
-
Malyszko J, Zbroch E, Malyszko JS, Koc-Zorawska E, Mysliwiec M. Renalase, a novel regulator of blood pressure, is predicted by kidney function in renal transplant recipients. Transplant Proc. 2011;43(8):3004–3007.
-
Gok Oguz E, Akoglu H, Ulusal Okyay G, Karaveli Gursoy G, Yildirim T, Merhametsiz O, et al. Increased serum renalase in peritoneal dialysis patients: Is it related to cardiovascular disease risk? Nefrologia. 2017;37(2):189-194.
-
Zbrush E, Koc-Zorawska E, Malyszko J, Malyszko J, Mysliwiec M. Circulating levels of renalase, norepinephrine, and dopamine in dialysis patients. Ren Fail 2013;35:673–679.
-
He B, Hao J, Sheng W, Xiang Y, Zhang J, Zhu H, et al. Correlation between plasma renalase level and coronary artery disease. Pak J Med Sci. 2014;30(5):863-967.
-
Gu R, Lu W, Xie J, Bai J, Xu B. Renalase deficiency in heart failure model of rats- a potential mechanism underlying circulating norepinephrine accumulation. Plos One.2011;6:e14633.
-
Gluba-Brzozka A, Michalska-Kasiczak M, Franczyk-Skora B, Nocun M, Banach M, Rysz J. Markers of increased cardiovascular risk in patients with chronic kidney disease. Lipids Health Dis 2014;13:135.
-
Stojanovic D, Cvetkovic T, Stojanovic M, Stefanovic N, Velickovic-Radovanovic R, Zivkovic N. Renalase Assessment About Kidney Function, Lipid Disturbances, and Endothelial Dysfunction Parameters in Stable Renal Transplant Recipients. Progress in Transplantation. 2017;27(2):125-130.
-
Wang F, Li J, Xing T, Xie Y, Wang N. Serum renalase is related to catecholamine levels and renal function. Clin Exp Nephrol 2015;19:92–98.
-
Przybylowski P, Malyszko J, Kozlowska S, Malyszko J, Koc-Zorawska E, Mysliwiec M. Serum renalase depends on kidney function but not on blood pressure in heart transplant recipients. Transplant Proc 2011;43:3888–3891.
-
Lemiesz M, Tenderenda-Banasiuk E, Sosnowska D, Taranta-Janusz K, Wasilewska A. Serum Renalase Levels in Adolescents with Primary Hypertension. Pediatr Cardiol. 2018 Aug;39(6):1258-1264.
-
Ghaderian SB, Hayati F, Shayanpour S, Beladi Mousavi SS. Diabetes and end-stage renal disease; a review article on new concepts. J Renal Inj Prev. 2015; 4(2): 28-33.
-
Zhang J, Zhang R, Wang Y, Li H, Han Q, Wu Y, et al. The Level of Serum Albumin Is Associated with Renal Prognosis in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy. J Diabetes Res.2019: Article ID 7825804, 9 pages.
-
Zbroch E, Musialowska D, Koc-Zorawska E, Malyszko J. Age influence on renalase and catecholamines concentration in hypertensive patients, including maintained dialysis. Clin Interv Aging 2016:11 1545–1550.
-
Dziedzic M, Or?owska E, Petkowicz B, Bednarek-Skublewska A, Solski J, Gozdziewska M. Levels of renalase and advanced oxidation protein products with regard to catecholamines in haemodialysed patients. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2017;24(3):453-458.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License