IJCRR - 13(19), October, 2021
Pages: 85-89
Date of Publication: 11-Oct-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Nomophobic Rate of Higher Secondary Level Students - A Pilot Study
Author: Elias Jijish, Mirunalini M
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: In the context of the lockdown due to Covid-19, usage of mobile phones has increased among adolescents. Usage of mobile phones for educational purposes as well as for entertainment makes them more addicted to mobile phones and electronic gadgets. In this scenario, Nomophobia, which is fear towards the situation when there is no phone, has increased among the adolescent. Aim: This research study aimed to prepare a nomophobic rating scale (NPRS) for adolescents and to implement it for students at the Higher secondary levels to check their nomophobic rate. Methods: In this study, investigators developed and standardized a Nomophobic rating scale to identify the addiction rate of Higher Secondary school students to mobile phones. Nomophobic Rating Scale was applied to 92 Higher Secondary Level students in Kerala and the collected data analyzed for evaluation. Results: The study shows that most of the students are prevalent to nomophobia. But the nomophobic rate does not depend on their locality, gender, course stream, but depend on the management of the school. Conclusion: This study points out certain serious concerns regarding the necessity of proper monitoring among adolescents about their usage of mobile phones. It also highlights the necessity of timely interventions on the part of teachers, parents and professionals which will invariably enhance the physical, social and emotional development of the students at the higher secondary level.
Keywords: Nomophobia, Nomophobic rate, Mobile phone, Higher secondary level, Students, Nomophobic rating scale
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The pandemic situation increased the usage of technology as well as mobile phones in the nook and cranny of life. It had a huge impact on the teaching and learning process too. In the context of COVID-19 teaching-learning strategies had changed a lot and a predominant role goes to the usage of mobile phones and social media among students as well as teachers. Even before the widespread of COVID -19, adolescent students had a high affinity towards modern gadgets like smartphones to play online games and use various social media applications. This affinity towards smartphones coined a new term among psychologists, which is known as nomophobia.
The term NOMOPHOBIA or NO Mobile Phone PhoBIA is used to describe a specific psychological condition when people have a fear of being detached from their mobile phone connectivity.1 Nowadays nomophobia has become a psycho-social condition because the socialization process is carried out through social media and most people have access to social media through their smartphones.
The usage of mobile phones and other electronic gadgets were not much motivated by the parents of higher secondary school students who are in their adolescent stage of development. Some studies regarding the usage of mobile phones and social media were conducted by researchers in the eastern countries but they haven’t concentrated on adolescent students much.2 In the Indian situation, there were very few studies conducted by researchers in the field of nomophobia. Lack of usage of mobile phones among the students was the main reason for that. But the pandemic situation increased the usage of mobile phones among the students and the continuous usage lead to a kind of addiction towards mobile phones. This makes the study more relevant and the needs of the current era and this makes the suitability to fill the research gap.
Mobile phones and similar electronic gadgets became part and parcel of everyone’s life, especially among adolescents and youngsters. Internet facilities are available at every village at a very cheap and affordable cost. Every smartphone is connected to the internet through 4G or higher band connectivity. Speed of data transfer and communication increased at a very high rate. Most of the people are active on any of the social media platforms. All these things made people show more affinity towards smartphones.
Usage of mobile phones for educational purposes as well as for entertainment makes them more addicted to mobile phones and electronic gadgets.3,4 In this scenario, Nomophobia, has increased among adolescent. Sufficient studies on this field, especially in India were very few. So the study has its importance in the current situation.
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
A cross-sectional study among undergraduate students who were using mobile phones for more than one year found that phone dependence among undergraduate students was common and there was no difference between the male and female students. Shankar, V., Singh, K., & Jangir, M.K.(2018) found 40.93 percentages of addiction and the study also showed that females were more addicted to mobile phones than males.5 A study on the perception among College Students by Gnanadhas J, Venkatachalam J, Menon V and Olickal J in Puducherry about nomophobia found that a sizeable minority of the students showed signs of severe nomophobia, distinct patterns of usage, and misperceptions regarding health and their usage pattern .6
The study conducted among undergraduate medical students from India in 2019 by Myakal & Vedpathak concluded that 71.4 % of them were prevalent to nomophobia. The study also concluded that male students are more addicted to mobile phones.7 Another study suggested a high prevalence of smartphone addiction among medical students, particularly in male medical students.8 A study by Ahmed, Pokhrel, Roy & Samuel among students pursuing physiotherapy course has been established that there is a relation between nomophobia rate and academic performance.9 In a study conducted by Muralidhar et al. in Kerala, a great prevalence of nomophobia was found among medical college students. According to the study, the rate of nomophobia was not found to be associated with their sex admission type, place of birth, and place of their stay.10 The results of the study by Yasan & Yildirim showed that undergraduate students had an average nomophobia level and they used their mobile phones for several educational purposes.11 The students’ level of nomophobia was significantly related to educational activities done by mobile phones. A study by Gonçalves et al., 2020 analyzed the propensity of young adults (18–24 years old) towards nomophobia and lifestyle.12 Aguilera-Manrique et al., 2018 studied nursing students' clinical practicum and found that there was a connection between nomophobia and the distraction caused by smartphone use. They concluded from the study that nursing students with high levels of nomophobia often use their smartphones during clinical practicum, while they also agree that regulations limiting smartphone usage while working should be implemented.13 Cerda-Flores et al. carried out a transverse-analytical study among 200 nursing university students. The instrument “Are you a nomophobic?” was applied. The frequencies obtained from men and women showed high heterogeneity.14 The study of Prasad et al (2017) discovered about 39.5% of students agreed that they score low marks in professional exams if they spend more time on the phone.15Most of the study concluded that academic achievement of students affected negatively by nomophobia and such studies on adolescent higher secondary school students were not done effectively, especially in India.
NEED AND SIGNIFICANCE OF THE STUDY
A review of related literature shows that several studies have been conducted in the field of nomophobia by several researchers at different levels, especially among undergraduate and medical students. But mobile phone usage of secondary or higher secondary school students was not investigated in detail by any of the studies, especially from India.16 The main reason behind the negligence of that age group is that they didn’t possess a mobile phone. But when the pandemic situation necessitated an academic ambience where the mobile phone was indispensable, most parents were forced to purchase it for their wards. The study is conducted at the time when one year is over after the first COVID -19 case was reported in the world and so seems significant for the current context.
The usage of smartphones became a part of each student at a higher secondary level because the teaching-learning process moved from the traditional ways to online mode by using plenty of online platforms. Teachers who are well versed with technology and the internet shifted to google classrooms, google meets and zoom meets while others depended on what's app and youtube channels. Whatever be the mode of teaching and platform used by the teacher, students are forced to use their smartphones for learning purposes. But while using smartphone for learning purposes, there is a chance of deviation from the academic usage of the phones to something else. The other purposes including the usage of phones for using social media platforms for communication and watching entertainment videos and songs. Thus the investigators believe that a study on nomophobia rate of higher secondary school students would be the need of the present.
RESEARCH OBJECTIVES
The general objective of this research was to study the nomophobic rate among Higher Secondary school students.
The specific objectives were;
-
To develop and standardize a nomophobic rating scale.
-
To determine the Nomophobic rate of Higher secondary school students.
-
To establish the relation between demographic factors and nomophobic rate.
METHODS
Research design
A descriptive research design was followed by the investigators for the current study. This pilot study was conducted in one government and one aided higher secondary school in the Palakkad district of Kerala. The participants of this study consisted of students who were enrolled in the second year of higher secondary courses.
Instrument of the study
A nomophobic rating scale developed and standardized by the investigators was used for the present study. The nomophobic rating scale for Higher Secondary Level Students was a Likert type 5 point scale developed through three stages. In the pre-try-out stage, investigators formulated 46 statements from the ideas gained from the review of related literature and the statements were validated by experts in the field. After that, it was tried out to selected a sample and finalized to 26 items with 6 negatively polar statements.
Data collection and data analysis
After the standardization of tools, a pilot study was conducted among 92 higher secondary school students. For the pilot study, the NPRS shared with Higher Secondary School students who were indifferent streams of study through WhatsApp groups of their respective schools and 92 responses were collected through Google form. The collected responses were exported as a google sheet and transformed into scores as per the scoring key. Students to test and one-way ANOVA was used to compare the means of nomophobic rate concerning each independent variable, namely, gender, stream, of course, management of school and locality of the student.
Significance of difference between the mean values of nomophobic rate concerning the gender, locality of students and management of the school was analyzed using t-test while Significance of difference between the mean values of nomophobic rate concerning a stream, of course, analyzed using one-way ANOVA test. The mean value of nomophobic rate of HSS students was 79.23 and have positive skewness.
The ethical clearance number for this study was No. 16872/Ph D K7/ Education/part Time January 2018 dated 28.12.2017.
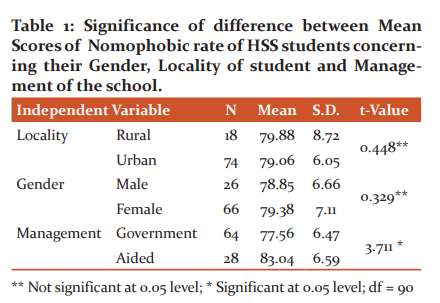
From table 1, it is clear that the male and female students, as well as students from rural and urban areas, do not have any significant difference concerning their nomophobic rate. But nomophobic rate is significantly different among government and aided school students.
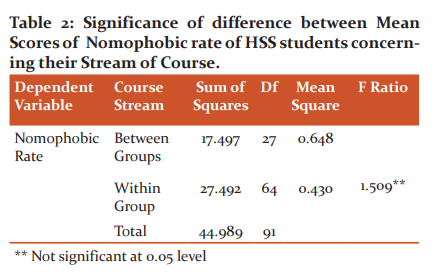
One way ANOVA test depicted in table 2 shows that there is no significant difference between science, commerce and humanities students concerning their nomophobic rate.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The NPRS was constructed and standardized according to the standard techniques for the standardization of a Likert-type scale with a five-point rating scale. It contains 24 items among 7 of them are negatively polar and the rest were positively polar. The maximum score which can be obtained by a sample is 120 and the minimum score is 24. If the sample is 100% neutral to the statement, the score will be 72. If a sample gains a score below 72, then it means that the sample is moderately or less nomophobic while a score that is higher than 72 shows that the sample is more addicted to the gadgets. As the score reaches 120, the sample needs adequate attention and may be requested for an intervention from a professional for retrieval from the symptoms.
The data collected and analyzed shows a mean value of 79.23 for nomophobic rate. This mean value tells that most of the students are prevalent to nomophobia. Male and female students as well as students from rural and urban areas do not have any significant difference concerning their nomophobic rate. But nomophobic rate is significantly different among government and aided school students. So the nomophobic rate does not depend on their locality, gender, course stream but depends on the management of the school.
Conclusion
Technology is a boon when it is used productively. In the age of digital natives, the creative usage of mobile phones can never be ruled out. During the contemporary scenario when the entire world faces an unprecedented standstill, mobile phones play a pivotal role in carrying out academic activities by teachers and students throughout the globe. Even after the threat of this pandemic vanishes, the academic community will undoubtedly move forward in tune with the technological advancements in the years to come. Still, this study points out certain serious concerns regarding the necessity of proper monitoring among adolescents concerning their usage of mobile phones. It also highlights the necessity of timely interventions on the part of teachers, parents and professionals which will invariably enhance the physical, social and emotional development of the students at the higher secondary level.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors would like to thank the authorities of the Department of Educational Technology Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli and various school authorities who helped during data collection.
Conflict of interest and source of Funding
Nil
Author Contributions
Elias, Jijish designed and formulated research goals and objectives as a whole. After discussion with Mirunalini, M both determined the right method and designed the study model. Elias, Jijish prepared the tool and validated it with the help of Mirunalini. Data for the pilot study was collected by Elias, Jijish and analyzed under the supervision of Mirunalini, M. Both critically revised the manuscript and all authors had approved the final version
References:
-
King AL, Valença AM, Nardi AE. Nomophobia: the mobile phone in panic disorder with agoraphobia: reducing phobias or worsening of dependence?. Cogn Behav Neurol. 2010;23(1):52-4.
-
Beranuy M, Oberst U, Carbonell X, Chamarro A. Problematic Internet and mobile phone use and clinical symptoms in college students: the role of emotional intelligence. Comput Hum Behav. 2009;25(5):1182–1187.
-
Daei A, Ashrafi-Rizi H, Soleymani MR. Nomophobia and Health Hazards: Smartphone Use and Addiction Among University Students. Int J Prev Med.2019:10(1):202.
-
Thapa K, Lama S, Pokharel R, Sigdel R, Rimal SP. Mobile Phone Dependence among Undergraduate Students of a Medical College of Eastern Nepal: A Descriptive Cross-sectional Study. J Nepal Med Assoc.2020:58(224):234-239
-
Shankar V, Singh K, Jangir M. NOMOPHOBIA: Detection and Analysis of Smartphone Addiction in Indian Perspective.Int J Appl Eng Res. 2018 [cited 7 January 2021];13(14):11593-11599. Available from: https://www.ripublication.com/ijaer18/ijaerv13n14_36.pdf
-
Gnanadhas J, Venkatachalam J, Menon V, Olickal J. Nomophobia: A Mixed-Methods Study on Prevalence, Associated Factors, and Perception among College Students in Puducherry, India. Indian J Psychol Med . 2019;41:541-548.
-
Myakal VV, Vedpathak VL. Nomophobia - mobile phone dependence, a study among students of a rural medical college. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2019;6(5):2034–2040.
-
Lei LY-C, Ismail MA-A, Mohammad JA-M, Yusoff MS. The relationship of smartphone addiction with psychological distress and neuroticism among university medical students. BMC Psych. 2020;8(1).
-
Ahmed S, Pokhrel N, Roy S, Samuel AJ. Impact of nomophobia: A non-drug addiction among students of physiotherapy course using an online cross-sectional survey. Ind J Psych. 2019;61(1):77-80.
-
Madhusudan M, Sudarshan BP, Sanjay TV, Gopi A, Fernandes SDA. Nomophobia and determinants among the students of a medical college in Kerala. Int J Med Sci Public Heal. 2017;6(6):1046-1049.
-
. Yasan KN, Yildirim S. Nomophobia omophobia among undergraduate students and its link to mobile learning. 10th International Conference on Education and New Learning Technologies Project: Nomophobia. 2018. p.3018-3025.
-
Gonçalves S, Dias P, Correia A-P. Nomophobia and lifestyle: Smartphone use and its relationship to psychopathologies. Computers in Human Behavior Reports. 2020;2:100025.
-
Aguilera-Manrique G, Márquez-Hernández VV, Alcaraz-Córdoba T, Granados-Gámez G, Gutiérrez-Puertas V, Gutiérrez-Puertas L. The relationship between nomophobia and the distraction associated with smartphone use among nursing students in their clinical practicum. PLOS ONE. 2018;13(8).
-
Cerda-Flores R, Martinez-Hernandez R, Tamez-Rodríguez V, Treviño-Sordia V, Hernandez-Saldaña M. Nomophobia in Mexican Nursing Students. Revista Medicina de Torreón. 2018;10(1):44–7.
-
Prasad M, Patthi B, Singla A, Gupta R, Saha S, Kumar JK, et al. Nomophobia: A Cross-sectional Study to Assess Mobile Phone Usage Among Dental Students. J. Clin. Diagnostic Res. 2017;11(2): ZC34–ZC39.
-
Kanmani A, Bhavani U, Maragatham R . NOMOPHOBIA – An Insight into its Psychological Aspects in India, Int. J. Indian Psychol.2017:4(2):5-15.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License