IJCRR - 13(19), October, 2021
Pages: 80-84
Date of Publication: 11-Oct-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Enrichment of Remote Homology Detection using Cascading Maximum Entropy Markov Model
Author: Manikandan P, Ramyachitra D, Muthu C, Sajithra N
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: In computational biology, the remote homology detection of the protein sequence is one of the ultimate problems that aims to discover the protein sequences from the database of known protein structures that are evolutionarily associated with a known query protein. Protein homology detection plays a major role in predicting the structures and functions of the protein. Sequence and structure-based comparison allow to detection of the remote homologous. Aim: Several existing computational techniques have been developed to predict remote homology detection in protein sequences. Due to low similarities in protein sequence, the performance of the existing systems is still low. To overcome the drawbacks of the existing systems, this research work proposed a Cascading Maximum Entropy Markov Model (C-MEMM) for remote homology detection. Methodology: The C-MEMM algorithm improved freedom in selecting features to signify the annotations for sequence tagging methods rather than Hidden Markov Model (HMMs). In sequence tagging circumstances, it is valuable to practice domain knowledge to project special-purpose features. The proposed C- MEMM algorithm allows the user to specify lots of correlated, but informative features. Results: Three different organisms such as Xenopus laevis, Bacillus stearothermophilus and Escherichia coli were used for testing the execution of the C- MEMM algorithm with the existing methods. The effectiveness of the proposed C-MEMM algorithm is tested with Coverage and Precision values. Experimental results show that the proposed method effectively improved prediction performance. Conclusion: From the experimental results, it is inferred that the proposed C-MEMM algorithm gives better results than the existing algorithms based on the performance metrics such as coverage rate and precision values for all the organisms.
Keywords: Protein remote homology detection, Cascading Maximum Entropy Markov Model (C-MEMM), Position-Specific Iterated BLAST (PSI-BLAST), Cascade-HMM (C-HMM), Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP), Xenopus Laevis, Bacillus Stearothermophilus, Escherichia Coli
Full Text:
Introduction
Genome sequence projects provide a huge number of protein sequence data in several databases. The volume of inconsistency among the sum of known protein sequence and the sum of experimentally determined protein structures has been rapidly improved due to the experimental obstacles in analyzing the protein structures and functions. To overcome the limitations, a huge number of computational tools and methodologies have been developed to analyze the protein structure and functions employing the sequence information offered in open-source repositories. If two proteins share evolutionary origins and having more similarities are termed as homolog proteins. Earlier methods in protein homology detection can be clustered into three categories such as pairwise, discriminative and generative methods. Dynamic programming is used in pairwise methods to perform sequence similarity for homology detection.1 Dynamic programming method consumes more computation times for relatively long protein sequences. To accelerate the alignment, a heuristic method named Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST)2 is used to find a near-optimal alignment within a rational period. The general hypothesis is that two proteins sequence identity is above 30% over their entire lengths is termed as homolog.3 The disadvantage of pairwise sequence alignment is biological erroneousness of assessment concerning only one identified protein homolog.
Several iterative techniques such as PSI-BLAST, SAM-T98have been developed to overcome the drawbacks of pairwise methods.4,5 However, the generative methods also produce so much false-positive results. Hence, the recent studies on remote homology detection used discriminative methods to make separation among homolog and non-homolog proteins. Remote homology detection of protein sequence plays a crucial role in the field of computational biology because remote homologous proteins contributing similar functions and structures that can be helpful in the protein studies of 3D structure and function.6 The remaining section of this manuscript is developed as follows: Section 2 designates the background study of existing methods for solving the problem of remote homology detection. The methodology of the proposed C-MEMM algorithm is explained in Section 3. The experimental outcomes of the proposed and the existing algorithms for the Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP) database is emphasized in Section 4. Lastly, Section 5 spotlights the conclusion and future enhancement.
Background Study
Genome sequence projects generate a huge amount of sequence information and it needs to be annotated. Most of the homology detection methods use the scoring metric to predict the similarity among a query protein with the database sequences. The Smith-Waterman score is frequently used for comparing two protein sequences. In Bioinformatics, the structural and functional annotation of an unknown protein is a crucial task. The annotation of a new protein sequence is based on the similarity among the query protein with the structures and function of the known protein.
If such protein relationship cannot be identified using direct sequence-based approaches, it can be termed as remote homologues and the discovery of remote homologue relationship is a difficult task in computational biology. In several cases, the functional annotation for the new proteins can be done using the protein structures. But the information of protein structures is inadequate and the structure database is also very deliberate.7 Hence, there is a need to find distant homologues by abusing protein sequence information. Several techniques have been developed to identify the homologue sequences grounded on profile Hidden Markov Models (HMM) and Position-Specific Scoring Matrices (PSSM). The probabilistic model-based profile Hidden Markov Models are further complex in detecting the remote homologue proteins. 4,8,9 HHblits and HH search are used to find the remote homologues by the HMM-HMM comparison.10,11 The Cascading PSI-BLAST method cover more distant relationships, but the major drawback of this method is computational time, which increases the size and complexity of the databases.12,13
Pcons delivers improved automated tools for the prediction of protein structure and analysis of this structure using consensus.14 The difficult target protein sequence is robotically submitted to open-source servers of fold recognition to find distant structural homologies. Inside the kernel formulation background, the consensus method is used to merge heterogeneous data by semidefinite, second-order cone, semi-infinite linear programming and Bayesian framework.15 These kernel learning methods are not scalable and guide to very complex frameworks. The Motifs pattern of protein sequence represents highly conserved regions of proteins. The motif content of two protein sequences is used to express a similarity among them. On completion of motifs, significant hints to a protein function can habitually be exposed even if it is not universally similar to any known protein in sequence databases. In consequence, the motif method suits well in remote homology detection and emphasis conserved segments of sequence having more similarity in the vaguely related protein sequence.16 An enhancement in protein remote homology detection is accomplished by emerging techniques grounded on the profile-sequence comparison.17 The profile is typically constructed from the query protein sequence or directly from an input multiple sequence alignment.
SAM - T04 approach used Neural Networks (NNs) to evaluate the alignment and map the similarities among pairs of proteins.18 The main improvements made by the human intervention were from adding constraints to build beta-sheets and from splitting multi-domain proteins into separate domains. Support Vector Machines (SVM) are mainly used to resolve the problem of binary classification. The support vector machine technique builds one-versus-rest classification models. These models are assessed with esteem to how well each binary classifier can identify the proteins that fit its own modelled class.19 Long Short - Term Memory (LSTM) is a moderately quicker approach than using alignments and SVM based models. The LSTM is a recurrent NN method that can be used for remote homology detection by determining the discriminating patterns.20 However, this technique does not attain comparable performance. The Cascade-Hidden Markov Model (C-HMM) involves cascading of HMM to identify the true distant homologues at various levels.14 The execution time of cascade searches are higher than the other existing methods. Even though several methods have been developed for predicting the remote homologues proteins, but they do not promise to provide better results. Hence, the C-MEMM algorithm has been developed in this research work to overcome the drawbacks of the existing methods.
Methodology
In this research, the existing algorithms, namely PSI-BLAST, C-HMM and the proposed C-MEMM algorithms are compared to predict the remote homology detection. From the results, it is inferred that the C-MEMM method provides improved results than the existing algorithms.
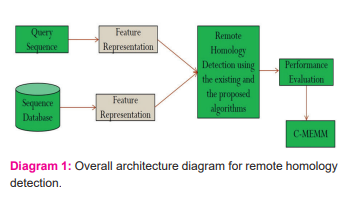
Drawing stronger links will be equally valuable for both areas of research is the key motive of Cascading Maximum Entropy Markov Models (C-MEMM) model. Markov models are used for both prediction and estimation, where the states of sequence produce a consistent sequence of annotations. In the maximum entropy method, the annotations are self-determining is also known as logistic regression. Hence, the Maximum Entropy Markov Model can be obtained from logistic regression through an assumption of Markovian between target variables.
In general, the Maximum Entropy Markov Models (MEMM) algorithm is measured by forwarding pass in separation. In HMMs, the backward pass is no longer candid. MEMM algorithm is very efficient, but they grieve from the problem of label bias, where a feeble probability reduces the probability of inactivity across time. To overcome the problem label bias, the linear chain Conditional Random Fields (CRFs) are used. Classifier Chain (CC) is a Cascading MEMM and it can be observed as a T order MEMM. Several existing multi-label methods already split the sequence into subsets.
An associated method is developed in this research work which furthermore links the blocks together, this data is not separated. Most of the existing multi-label techniques are previously transformed the datasets earlier working on them. The same flow of C-HMM is used in C-MEMM, only the Hidden Markov Model (HMM) is replaced with MEMM. All the modules Cluster-MEMM, Cascade MEMM and Custom MEMM are used to classify remote homologues proteins from the sequence databases. The key inspiration of developing the C-MEMM method is to authorize effective detection of remote homology compared to any accessible sequence database, regardless of its dimensions.
C-MEMM algorithm includes cascading of MEMMs by numerous generations to identify true distant remote homologues at various levels such as superfamily and fold. Every true hit of the first group is measured as query sequences to instigate the second group of C-MEMM. Cluster-HMM Module clusters the collected homologues (hits) while penetrating against such enormous databases. Custom-MEMM filter hits gained from the first group are clustered at a specific sequence identity cut-off by Cd-hit. This technique further diminishes the search time without remarkable loss in sequence information in contrast with the two existing modules.
Results and Discussion
In this research work, the proposed algorithm is tested with the well-known benchmark dataset named SCOP 1.53 for analyzing the performance of the algorithm based on its effectiveness. The proposed C-MEMM algorithm has been assessed by comparing with two existing techniques, namely PSI-BLAST and C-HMM.
Dataset Description
The SCOP 1.53 database has been used as a standard database for remote homology detection. The datasets are retrieved in FASTA format from the ASTRAL compendium for sequence and structure analysis. The SCOP 1.53 database comprises 4352 protein sequences gathered into seventy-four families and fifty-four superfamilies. The dataset was further reduced into 1294 protein sequences which is gathered into forty-six families, one hundred fifty-five superfamilies and two hundred sixty-five folds. The protein domains inside the family are taken as test instances and protein domains inside and outside the superfamily are taken as training positive instances. This produces fifty-four families with ten training and five test positive instances. The negative instances of the protein family are selected via the exterior of the positive sequences fold and were stochastically divided into training tests and test sets in a similar ratio as the positive example.
Performance Measures
The execution of PSI-BLAST, C-HMM and C-MEMM algorithm is assessed by the performance metrics such as coverage and precision values. The coverage is termed as the true positives acknowledged by the method of sequence search via the total amount of true associations extant in the database at various levels namely family, superfamily and fold (Eq.1).
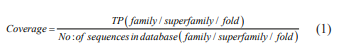
The false-positive can be term as, “any hit that did not belong to the same fold as query sequence”. Precision scores are used to detect the fraction of hits that are related to the sequence search (Eq.2).
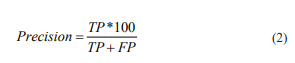
where TP and FP stand for the number of True Positives and False Positives which are recognized through sequence searches.
Experimental Results
The Scop 1.53 database is used for testing the performance of the proposed C-MEMM algorithm with the existing algorithms namely PSI-BLAST and C-HMM. The comparison of performance measures such as coverage and precision for the existing and the proposed algorithms are shown in Table 1.
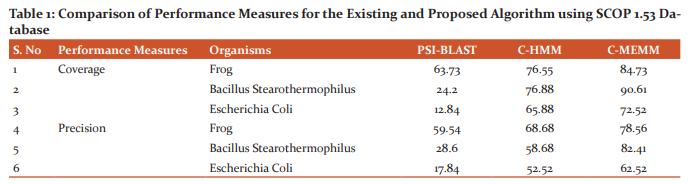
Fig.1 shows the comparison of Coverage for the proposed and the existing algorithm such as PSI-BLAST and C-HMM. From Fig.1, it is inferred that the C-MEMM algorithm performs better than the other existing techniques in terms of Coverage values. Fig.2 shows the comparison of precision values for the proposed C-MEMM algorithm with the other existing algorithms. From Fig,2, it is inferred that the proposed C-MEMM algorithm provides better results compared to existing PSI-BLAST, C-HMM approaches. For the coverage values in Fig.1, it is inferred that the proposed C-MEMM algorithm performs 24.78 % better than the PSI-BLAST algorithm and 9.65% better than the C-HMM algorithm for the Frog organism.
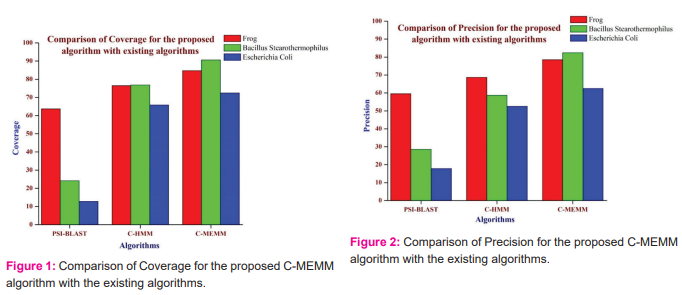
For the Bacillus stearothermophilus organism, it is inferred that the proposed C-MEMM algorithm performs 73.29% better than the PSI-BLAST algorithm and 15.15% better than the C-HMM algorithm. For the Escherichia Coli organism, it is inferred that the proposed C-MEMM algorithm performs 82.29 % better than the PSI-BLAST algorithm and 9.16% better than the C-HMM algorithm. For the precision values in Fig.2, it is inferred that the proposed C-MEMM algorithm performs 31.94 % better than the PSI-BLAST algorithm and 12.58% better than the C-HMM algorithm for the Frog organism. For the Bacillus stearothermophilus organism, it is inferred that the proposed C-MEMM algorithm performs 65.29% better than the PSI-BLAST algorithm and 28.79% better than the C-HMM algorithm. For the Escherichia Coli organism, it is inferred that the proposed C-MEMM algorithm performs 71.47% better than the PSI-BLAST algorithm and 51.99% better than the C-HMM algorithm.
5. Conclusion and Future Enhancement
Remote homology detection is one of the crucial tasks for detecting homology in low sequence similarity cases. The discriminative method has classified the proteins using the sequences that must be transformed into fixed-length feature vectors. In this research work, the C-MEMM model was successfully implemented to detect protein remote homologies. When the C-MEMM method was applied to the feature data set, the sequence returned a prediction score of every instance. The effectiveness of the proposed approach is tested with Coverage and Precision values. Experimental results show that the proposed method effectively improved prediction performance. In future, this research work can be enhanced to discover novel features of protein sequences and applying other language processing methods for the detection of protein remote homology.
Acknowledgement
The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Source of Funding: NIL
Author’s Contribution
Dr Manikandan P: Manuscript Preparation
Dr Ramyachitra D: Manuscript Editing
Dr Muthu C: Manuscript Reviewing
Ms Sajithra N: Literature Review
References:
-
Smith TF, Waterman MS. Identification of common molecular subsequences. J. Mol. Biol.. 1981 Mar 25;147(1):195-7. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90087-5. PMID: 7265238.
-
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol.. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403-10. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. PMID: 2231712.
-
Pearson WR. An introduction to sequence similarity ("homology") searching. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics. 2013; Chapter 3: Unit3.1. doi:10.1002/0471250953.bi0301s42.
-
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, et al. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Research. 1997 Sep 1;25(17):3389-402. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389. PMID: 9254694.
-
Karplus K, Barrett C, Hughey R. Hidden Markov models for detecting remote protein homologies. Bioinformatics. 1998;14(10):846-56. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/14.10.846. PMID: 9927713.
-
Chen J, Guo M, Wang X, Liu B. A comprehensive review and comparison of different computational methods for protein remote homology detection. Briefings in Bioinformatics. 2018 Mar 1;19(2):231-244. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbw108. PMID: 27881430.
-
Levitt M. Growth of novel protein structural data. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2007 Feb 27;104(9):3183-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611678104. Epub 2007 Feb 20. PMID: 17360626; PMCID: PMC1802002.
-
Eddy SR. Profile hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics. 1998;14(9):755-63. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/14.9.755. PMID: 9918945.
-
Eddy SR. Accelerated Profile HMM Searches. PLOS Computational Biology. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002195. Epub 2011 Oct 20. PMID: 22039361.
-
Remmert M, Biegert A, Hauser A, Söding J. HHblits: lightning-fast iterative protein sequence searching by HMM-HMM alignment. Nature Methods. 2011 Dec 25;9(2):173-5. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1818. PMID: 22198341.
-
Söding J. Protein homology detection by HMM-HMM comparison. Bioinformatics. 2005 Apr 1;21(7):951-60. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti125. Epub 2004 Nov 5. Erratum in: Bioinformatics. 2005 May 1;21(9):2144. PMID: 15531603.
-
Kaushik S, Mutt E, Chellappan A, Sankaran S, Srinivasan N, Sowdhamini R. Improved detection of remote homologues using cascade PSI-BLAST: influence of neighbouring protein families on sequence coverage. PLOS One. 2013;8(2):e56449. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056449. Epub 2013 Feb 20. PMID: 23437136.
-
Sandhya S, Chakrabarti S, Abhinandan KR, Sowdhamini R, Srinivasan N. Assessment of a rigorous transitive profile-based search method to detect remotely similar proteins. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2005 Dec;23(3):283-98. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2005.10507066. PMID: 16218755.
-
Kaushik S, Nair AG, Mutt E, Subramanian HP, Sowdhamini R. Rapid and enhanced remote homology detection by cascading hidden Markov model searches in sequence space. Bioinformatics. 2016 Feb 1;32(3):338-44. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv538. Epub 2015 Oct 10. PMID: 26454276.
-
Damoulas T, Girolami MA. Probabilistic multi-class multi-kernel learning: on protein fold recognition and remote homology detection. Bioinformatics. 2008 May 15;24(10):1264-70. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn112. Epub 2008 Mar 31. PMID: 18378524.
-
Ben-Hur A, Brutlag D. Remote homology detection: a motif based approach. Bioinformatics. 2003;19 Suppl 1:i26-33. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg1002. PMID: 12855434.
-
Melvin I, Weston J, Noble WS, Leslie C. Detecting remote evolutionary relationships among proteins by large-scale semantic embedding. PLOS Computational Biology. 2011 Jan 27;7(1):e1001047. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1001047. PMID: 21298082.
-
Karplus K, Katzman S, Shackleford G, Koeva M, Draper J, Barnes B, et al. SAM-T04: what is new in protein-structure prediction for CASP6. Proteins. 2005;61 Suppl 7:135-42. doi: 10.1002/prot.20730. PMID: 16187355.
-
Rangwala H, Karypis G. Building multiclass classifiers for remote homology detection and fold recognition. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Oct 16;7:455. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-455. PMID: 17042943.
-
Hochreiter S, Heusel M, Obermayer K. Fast model-based protein homology detection without alignment. Bioinformatics. 2007 Jul 15;23(14):1728-36. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm247. Epub 2007 May 8. PMID: 17488755.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License