IJCRR - 13(19), October, 2021
Pages: 39-48
Date of Publication: 11-Oct-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Validated Approach of High-performance Liquid Chromatography Method for Degradation Study of Saxagliptin and Metformin HCl
Author: Abhilasha Mittal, Manoj Charde, Imran A Sheikh
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The study focus on its degradation pattern well know antidiabetic drugs are Saxagliptin and Metformin HCl Aim: The research study aims to validate the high-performance liquid chromatography method for the degradation study of Saxagliptin and Metformin HCl. Method: In support of the determination and to study its degradation pattern in various pharmaceutical dosage forms a novel and simple reverse phase liquid chromatographic method has been established. Saxagliptin and Metformin HCl are well known to use in Type 2 Diabetes. The planned work was performed on Younglin (S.K) isocratic System UV Detector C18 column (150 mm × 4.6 mm). A mixture of Potassium Acetonitrile: Pot. Phosphate Buffer (ph 3.2) in the ratio of 25:75 was used as mobile phase in this method and the method was validated as per ICH guidelines along with flow rate 1.0 ml/min (UV detection at 212 nm) Result: By exposing the drug the Saxagliptin and Metformin HCl to acidic, alkaline, H2 O2 and Neutral degradations forced degradation studies were performed. This method (RP-HPLC) is suitable for kinetic studies as well as the assay of pharmaceutical dosage forms and was found to be robust and specific. Conclusion: In any pharmacopoeia, Saxagliptin is not an official drug. While MET was determined by United States Pharmacopeia (USP), and British Pharmacopoeia (BP) both suggest a non-aqueous titration method using anhydrous formic acid as a solvent and 0.1 M perchloric acid as titrant for the assay of MET. An endpoint is determined potentiometrically.
Keywords: Saxagliptin, Metformin HCl, RP-HPLC, validation, stability-indicating, pharmacopoeia., USP The study focus on its degradation pattern well know antidiabetic drugs are Saxagliptin and Metformin HCl
Full Text:
Introduction
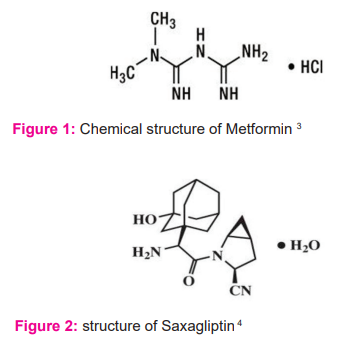
The Metformin hydrochloride- biguanide in patients with type 2 diabetes improves glucose tolerance and is a highly recommended drug, especially when compared to other antihyperglycemic drugs. Its chemical name is N, N -Dimethyl imidodicarbonimi dicyandiamide. The recommended dose is 500 mg orally twice daily or 500 to 2000 mg once daily. Lactic acidosis is a rare, but serious, problem that can occur due to the accumulation of metformin. Hemodialysis is recommended to correct the acidosis and to remove accumulated Metformin.1
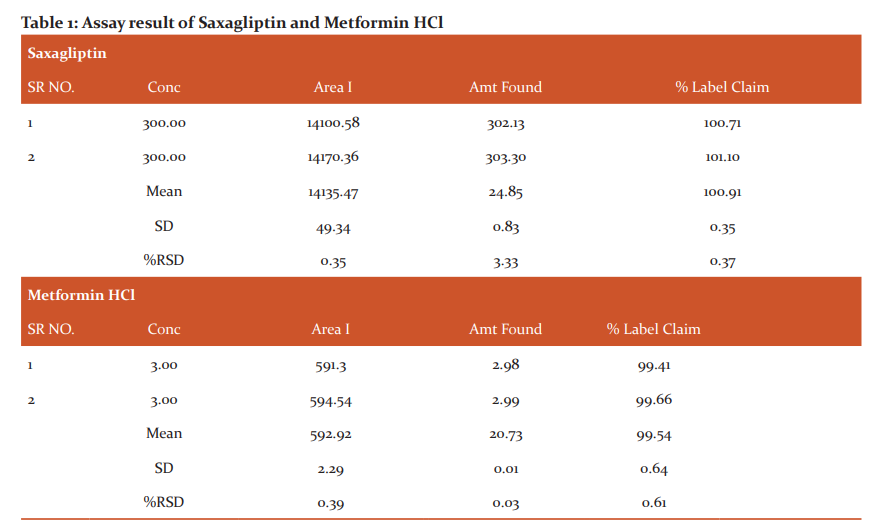
Saxagliptin competes with a DPP4 inhibitor that reduces the activity of incretin hormones, thereby increasing its concentration in the blood and reducing glucose uptake and glucose-based preparation in patients with type 2 diabetes. The recommended dose is 2.5mg or 5mg orally once daily.2
2. Material and Methods
Materials:
2.1 Chemicals and reagents Saxagliptin and Metformin HCl were provided from Merck Laboratories ltd. HPLC grade Potassium Acetonitrile, Pot. Phosphate Buffer was procured from Merck Ltd. Millipore Mili Q plus purification system was used to prepare highly pure water.
Commercial Formulation: Saxagliptin and Metformin HCl tablets were available in the market. The tablets were checked and stored properly.
2.2 HPLC instrumentation and conditions
Chromatographic conditions
Subsequent chromatographic conditions were established by trial and error and maintained consistently throughout the study
Chromatographic conditions for proposed method
HPLC: Younglin (S.K) isocratic System UV Detector
Software:Autochro -3000
Column:4.6 x 150 mm
Stationary phase:C18 (Primesil)
Particle size packinV: 5 mm
Mobile Phase: Acetonitrile: Pot.Phosphate Buffer(ph 3.2 with opa):25: 75
Detection Wavelenth: 212 nm
Flow rate:1.0 ml/min
Temperature: Ambient
Sample size: 20 ml
2.2.1 Standard Sample Preparation
Preparation of the Metformin & Saxagliptin Standard & Sample Solution:
Standard Solution Preparation: The drug’s standard stock solution was prepared by weighing accurately and transferred 10 mg Metformin and 10mg Saxagliptin working standard into a 10ml & 100ml clean dry volumetric flask respectively. To dissolve it completely about 7ml & 70ml of diluent were added and sonicated and with the same solvent, the volume was made up to the mark. Further pipette out 2ml of Metformin and Saxagliptin into a 10ml volumetric flask and diluted up to the mark with diluents from the above prepared Stock Solution.
Sample Solution Preparation: The Sample Stock Solution was prepared by weighing accurately and transferred 936.9 mg of Metformin and Saxagliptin Tablet powder into a 100ml clean dry volumetric flask. 70ml of the diluents was added and sonicated to dissolve it completely and the volume was made up to the mark with the same solvent.
Further from the above-prepared Stock
-
Std. Metformin Hcl 1000 mg and 10 mg Saxagliptin in 100 ml NAOH= 10,000 µgm/ml Metformin Hcl and 100µgm/ml Saxagliptin stock-001
-
Take 0.1 ml stock and make 10 ml with mobile phase =
1 µg/m/ml Saxagliptin & 100 µgm/ml Metformin Hcl
-
Take 0.2 ml stock and make 10 ml with mobile phase =
2 µg/ml Saxagliptin & Metformin Hcl 200 µgm/ml
-
Take 0.3 ml stock and make 10 ml with mobile phase =
3µm/ml Saxagliptin & Metformin Hcl 300 µgm/ml
-
Take 0.4 ml stock and make 40 ml with mobile phase =
4 µg/ml Saxagliptin & Metformin Hcl 400 µgm/ml
-
Take 0.5 ml stock and make 50 ml with mobile phase =
5 µgm/ml Saxagliptin & Metformin Hcl 500 µg/ml
Tab solution Preparation
20 tablets were taken and were triturated to powder weighing Powder wt. =12.00 gms, having average Powder Weight = 1.200 gms. / Tablet Eq.Wt for 1000 mg= 1000 x1200 / 500 = 2400 mg. 2400 mgs was taken in 100 ml NAOH i.e = 10000 µgm/ml Metformin Hcl and 100 µgm/ml Saxagliptin STOCK –I (Sonicate 30 min then fitter with 0.45 µm) was taken as Tablet Stock solution
Tablet Assay
Take 0.3 ml from tab stock and makeup 10 ml with MP 3+ 300 µgm/ml for assay
2.3 Forced degradation studies 5, 6
To prove the stability-indicating property of the method the forced degradation studies were performed on Metformin HCl and Saxagliptin. The stress conditions employed for degradation study of Metformin Hcl and Saxagliptin include light exposure, water hydrolysis and oxidation (3 % H2O2), acid hydrolysis (1 N HCl), base hydrolysis (1N NaOH), heat (105°C), Peak purity of the principal peak in the chromatogram of stressed samples of Saxagliptin and Metformin Hcl tablets was checked using PDA detector.
2.4 Method Ruggedness 7
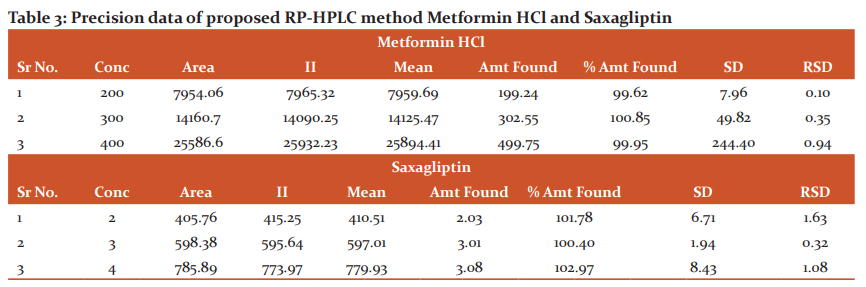
Ruggedness was tested by analyzing six samples from the corresponding combination of one group by a different analyst using a different column, format and date. % RSD for% assay of ruggedness found was 0.10% for Saxagliptin and 0.32% for Metformin Hcl and Overall% RSD found was 0.14% for Saxagliptin and 0.29% for Metformin Hcl as based in Table no. 3
Linearity 8, 11
With the emergence of the analysis method, the mixture of the standard solution of Saxagliptin and Metformin Hcl at concentration concentrations of 0.5123 μg / ml to 11.2299 μg / ml of Saxagliptin and 159.6713 μg / ml to 3500.0690 μg / ml according to the analysis method according to Metformin in the HPLC system. The coefficient (r) of Saxagliptin and Metformin Hcl using the regression equation and 1 / (concentration2) of the equilibrium weight were calculated. The correlation coefficient (r) found was 0.99942 for Saxagliptin and 0.99990 for Metformin HCl.
Method Precision 13, 15
From a homogenous mixture of a single batch six samples were prepared as per the test procedure of methodology and analyzed on HPLC system to evaluate the method of precision for the analytical method. The % RSD of six samples found was 0.16% and 0.15% for % assay of Saxagliptin and Metformin Hcl as tabulated in Table no.2
Accuracy 9, 12
For the determination of the accuracy of the method, a recovery study was carried out by analyzing the samples at three different concentrations at 50, 100 and 150%. The percentage of recoveries at three concentrations was calculated.
Robustness 10, 14
A robustness study of the method was carried because of the insignificant variations of the technique, such as changes in the composition of the mobile column temperature, altering flow rate, and mobile phase.
Results:
Tablet assay: The assay results for Saxagliptin and Metformin HCl were found within the specifications. The developed method was validated as per ICH guidelines. Results are shown in Table 1.
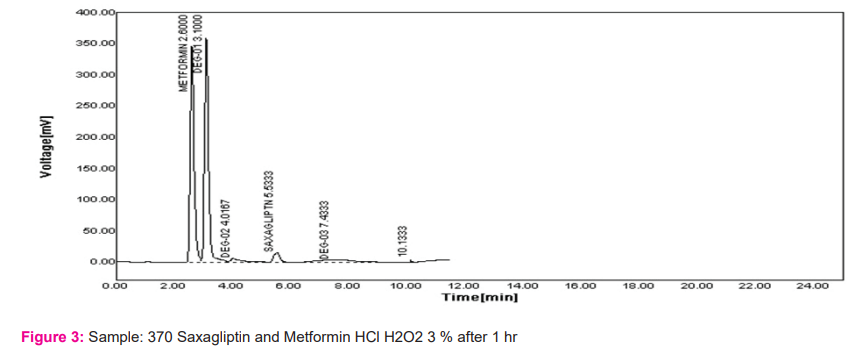
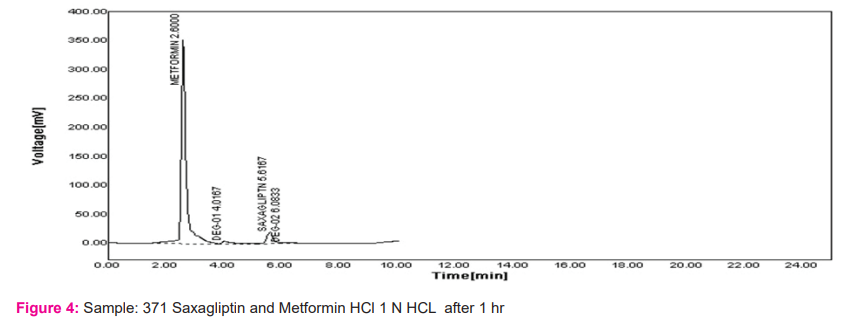
Forced Degradation Study: In these results of the study the report on the stability-indicating assay of combination Saxagliptin and Metformin HCl by HPLC in presence of degradation products. For analysis of combination, in this method, the isocratic elution method was selected. The reason behind it is, it gave better peak width and baseline separation, which is suitable for routine analysis of combination. In the study as per ICH guidelines, the developed method was validated.
The important part of the process of drug product development is the stability testing forms. How the drug quality substance varies with time under influence of various environmental factors such as light, humidity, temperature, and enables recommendations of retest periods, shelf life to be established, storage conditions is stability testing intends to provide evidence. Results are shown in Figures 3-6.
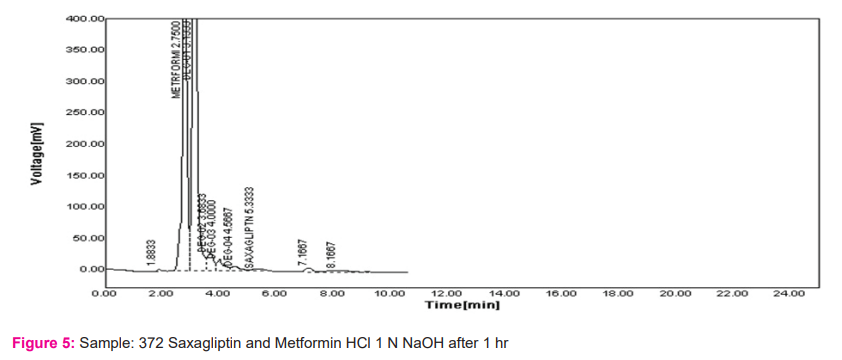
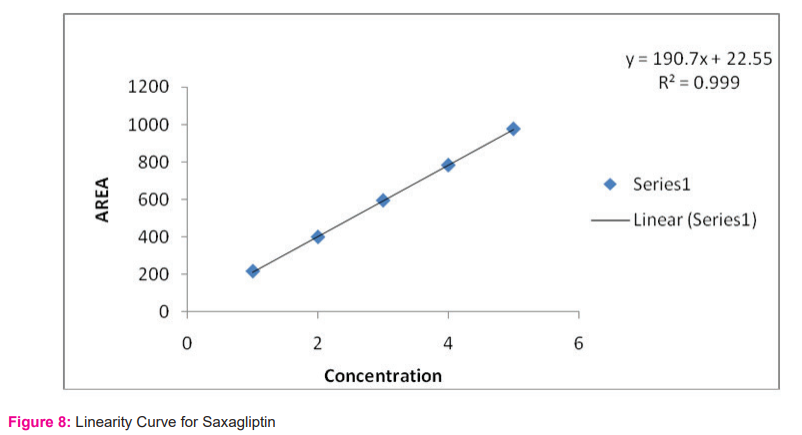
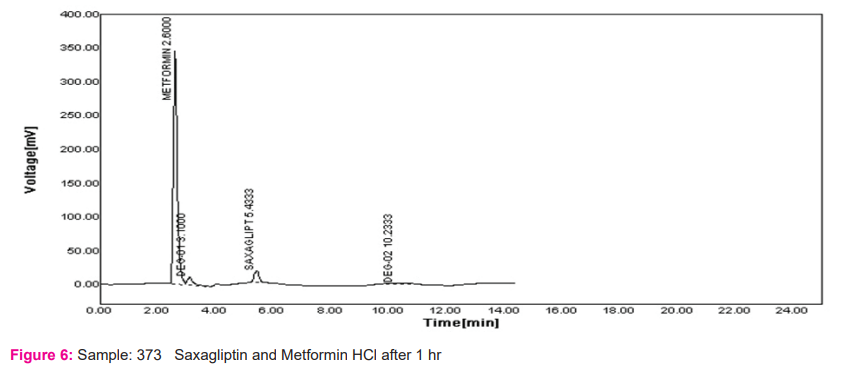 Linearity: The calibration curve showed good linearity in the range of 100-500 mg/ml for Metformin HCl and 1-5 mg/ml For Saxagliptin. In the results, a typical calibration curve has the regression equation of y = 59.68x – 3931 and R² = 0.999 for Metformin HCl and y = 190.7x + 22.55 and R² = 0.999 for Saxagliptin. Results are shown in table no. 2 and figure 7 and 8.
Linearity: The calibration curve showed good linearity in the range of 100-500 mg/ml for Metformin HCl and 1-5 mg/ml For Saxagliptin. In the results, a typical calibration curve has the regression equation of y = 59.68x – 3931 and R² = 0.999 for Metformin HCl and y = 190.7x + 22.55 and R² = 0.999 for Saxagliptin. Results are shown in table no. 2 and figure 7 and 8.

Precision: The results of system precision for Metformin HCl and Saxagliptin method precision are found within the prescribed limit of ICH guidelines. Results are shown in table 3.
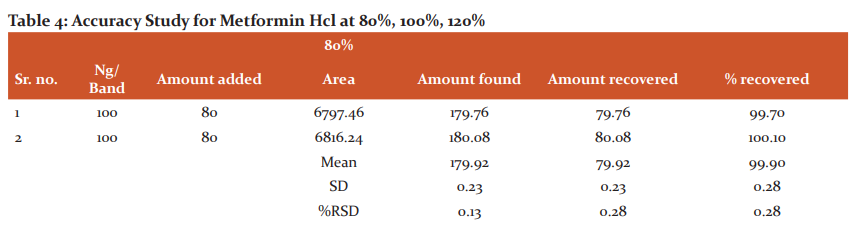
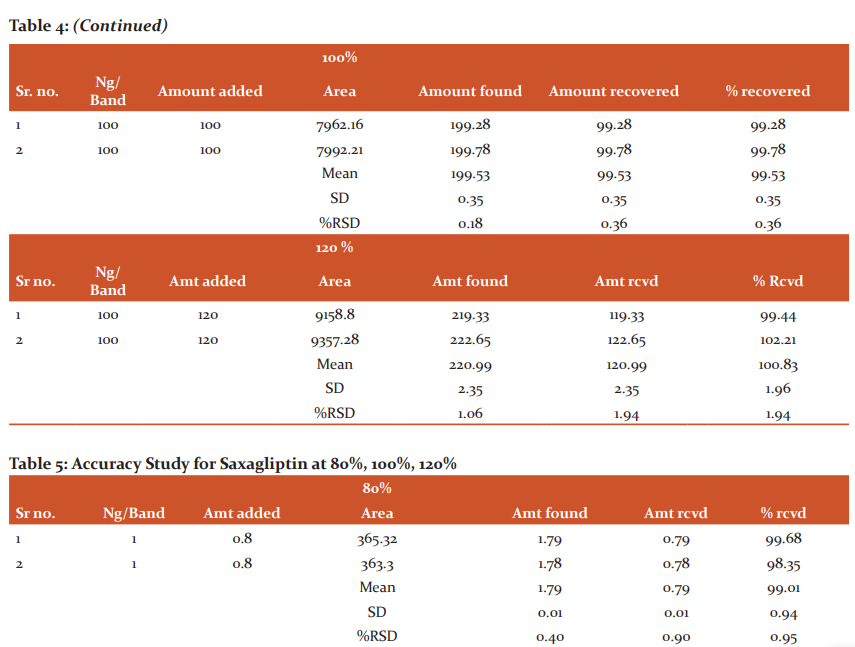
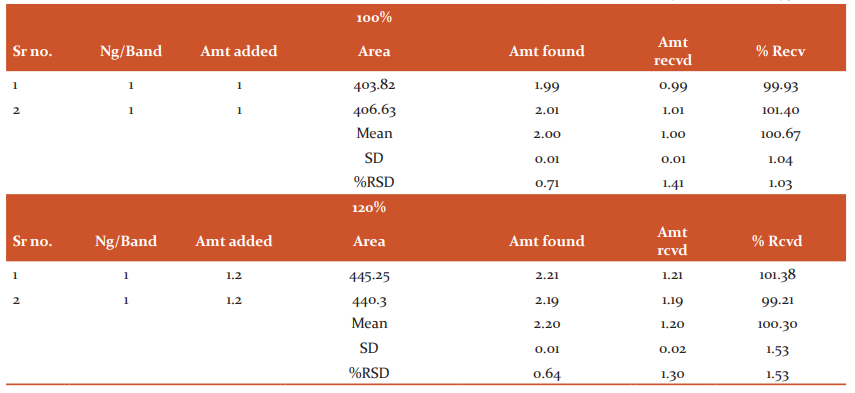
 Accuracy: For the accuracy study from all the samples, i.e. n=3 for 80 %, n=3 for 100 % and n=3 for 120 %. The results indicated that the mean of recovery for Saxagliptin was 100.08 %, and % RSD was 0.86, similarly, the mean of recovery for Metformin Hcl was 99.99 %, and % RSD was 1.17. As both % RSD values are less than 2 % hence, the reported % recovery by the developed method of the known added amount of analyte in the sample was within the confidence intervals. The results are shown in Tables No 4 and 5.
Accuracy: For the accuracy study from all the samples, i.e. n=3 for 80 %, n=3 for 100 % and n=3 for 120 %. The results indicated that the mean of recovery for Saxagliptin was 100.08 %, and % RSD was 0.86, similarly, the mean of recovery for Metformin Hcl was 99.99 %, and % RSD was 1.17. As both % RSD values are less than 2 % hence, the reported % recovery by the developed method of the known added amount of analyte in the sample was within the confidence intervals. The results are shown in Tables No 4 and 5.
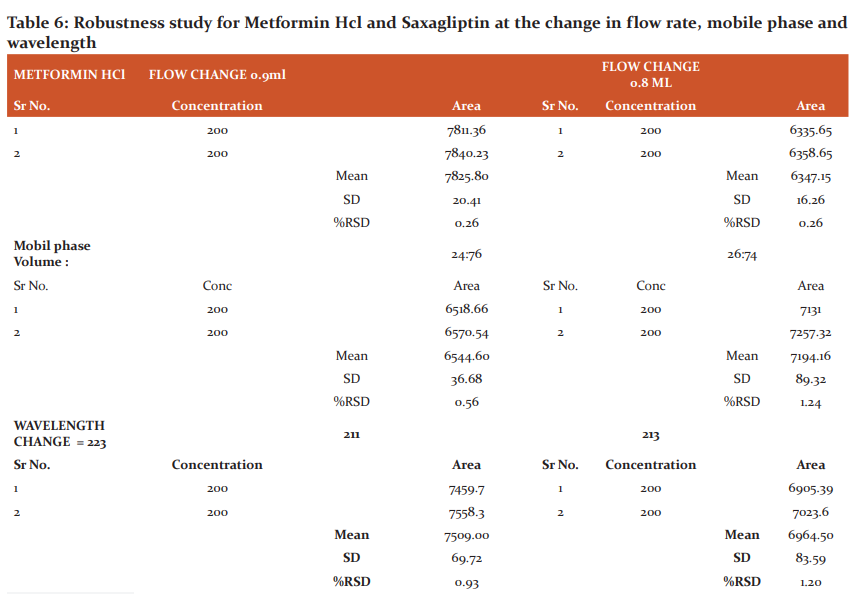
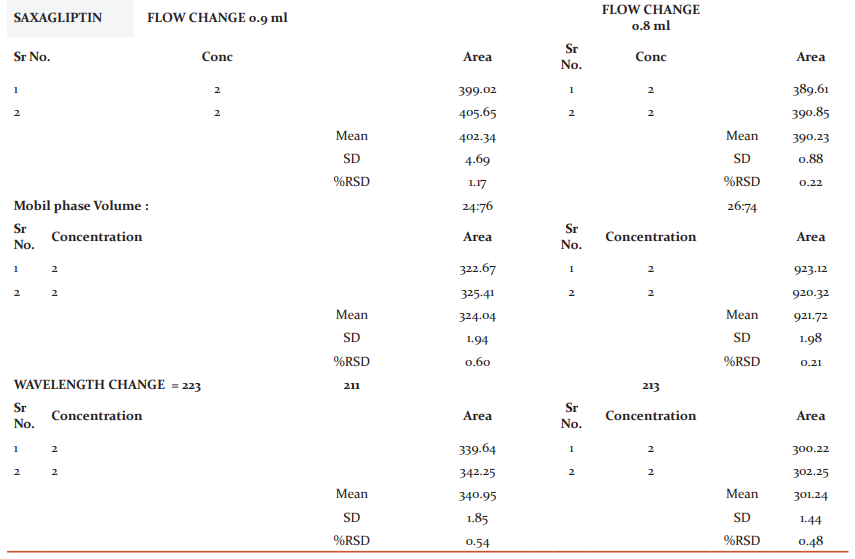
 Robustness: Chromatographic small changes influence the conditions such as organic content in pH of buffer in the mobile phase (0.2%), the wavelength of detection (5%), mobile phase (2%), and change in flow rate (10%), various previous research supported to determine the robustness of the method are also in favour of the developed RP-HPLC. The results are shown in table number 6.
Robustness: Chromatographic small changes influence the conditions such as organic content in pH of buffer in the mobile phase (0.2%), the wavelength of detection (5%), mobile phase (2%), and change in flow rate (10%), various previous research supported to determine the robustness of the method are also in favour of the developed RP-HPLC. The results are shown in table number 6.
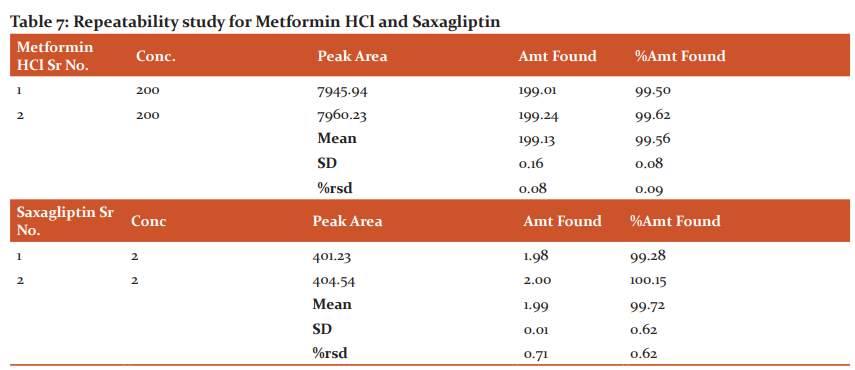
Repeatability: Here, the average area, standard deviation and % RSD were calculated for two drugs and obtained as 0.5% and 0.5% respectively for Dapagliflozin and Saxagliptin (Table 16, 17).
The combination Saxagliptin and Metformin HCl in presence of degradation products by HPLC is the report on the stability-indicating assay. For analysis of combination in this method, the isocratic elution method was selected. The reason, it gave better peak width, baseline separation, which is suitable for routine analysis of combination. As per ICH guidelines, the developed method was validated. The important part of the process of drug product development is stability testing.
The important part of the process of drug product development is the stability testing forms. How the drug quality substance varies with time under influence of various environmental factors such as light, humidity, temperature, and enables recommendations of retest periods, shelf life to be established, storage conditions is stability testing intends to provide evidence. The results are shown in table number 7.
Conclusion: The procured pure drug of Saxagliptin and Metformin HCl were found to melt in the range of 149-169°C respectively. The drug was found to be freely soluble in Acetonitrile, potassium buffer, Sparingly soluble in water, alcohol. UV absorption of 10µg/ml of Saxagliptin and Metformin HCl methanol was generated and absorbance was taken in the range of 200-400 nm. λmax of saxagliptin and Metformin HCl in acetonitrile was 214nm and 234 nm respectively. It has been observed that using the mobile phase of acetonitrile + pH buffer gave adequate retention time with good peak shape. Assay for % Label claim for %RSD Calculated. The analysis process was repeated five times with tablet formulations. Tablet Assay for % Label claim for % RSD Calculated. To validate the accuracy of the established method the recovery studies were done. To analysed tablet solution, a definite concentration of standard drug (80%,100%, and 120%), to ascertain the resolution and reproducibility of the proposed chromatographic system for estimation of Saxagliptin and Metformin HCl system suitability parameters were studied. Hereby analyzing various replicates standards of Saxagliptin and Metformin HCl, the method was established. To record any intra-day & inter-day variation in the result that concluded respectively all the solution was analyzed thrice. The Robustness of a method is its capability to remain unpretentious by small thoughtful changes in parameters. Small but careful variations in the optimized method parameters were done to assess the robustness of the proposed method. The effect of changes in mobile phase composition and tailing factor of drug peak, wavelength, flow rate, and retention time was studied. The mobile phase composition was changed in proportion to flow rate was varied and wavelength change of optimized chromatographic condition. %RSD for peak area for Metformin HCl was calculated which should be less than 2%. the result was revealed in the analytical method that was determined. %RSD for peak area for Saxagliptin was calculated which should be less than 2%. the result was revealed in the analytical method that was determined. Liquid chromatography is a technique of physical separation in which the components of a liquid mixture are distributed between two immiscible phases; this has provided us with information regarding the degradation part of the drug under study.
Acknowledgement: Authors are thankful to Principal NIMS Institute of Pharmacy Jaipur and RSITC Jalgaon for giving me the opportunity to carry out research work successfully.
Conflict of interest: None
Source of Funding: Research work is self-financed
Author’s contribution: Complete
References:
-
Thangabalan B, Srisowmya P, ManoharBabu S. Method development and validation for simultaneous estimation of saxagliptin and metformin in tablet dosage form by RP-HPLC method. Int J Pharm Res. 2014;3(4):363-9.
-
Aswini R, Eswarudu MM, Babu PS. A novel RP-HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of dapagliflozin and saxagliptin in the bulk and pharmaceutical dosage form.Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2018 Dec 1;9(12):5161-7.
-
Nyola N, Jeyalaban G. Simultaneous Estimation of Saxagliptin Hydrochloride And Metformin Hydrochloride In Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient by RP-HPLC. Ame. J. pharm Res Sci. 2013;4(3):70-7.
-
Chandrika SK, Yoganarasimha RB, Pujitha S, Quantification of Novel Dpp4 Inhibitor-Saxagliptin by Spectrophotometric and Chromatographic Techniques: Brief Review. Int J Curr Res. 2019; 11(05) 3796-3804.
-
Karimulla SK, Vasanth PM, Ramesh T, Ramesh M. Method development and validation of sitagliptin and metformin using reverse phase HPLC method in bulk and tablet dosage form. Der Pharmacia Lettre. 2013;5(5):168-74.
-
Sheikh IA, Chakole RD, Charde MS, Application of Validated HPLC Method for Degradation Study of Sitagliptin and Metformin HCl, Int J Adv Pharm. 2017; 07(02): 21-24.
-
Sudhir A, Bidkar JS. Sunil H, Dama GY. RP- HPLC Method Development and Validation for Simultaneous Estimation for Metformin and Sitagliptin in Bulk and Tablet Formulation, Int J Chemtech Res. 2018; 11(11): 428-435.
-
Shaikh J, Shaikh A, Mohamad A, Pathan A, Ali K. Validation of stability-indicating high performance liquid chromatographic method for simultaneous determination of assay of Linagliptin and Metformin drugs in the pharmaceuticals tablet formulations using bupropion as a common internal standard. J Int Phar Sci. 2018;5 (1): 21-28.
-
Harshalatha P, Chandrasekhar KB, Chandrasekhar MV. A novel RP-HPLC method for simultaneous determination of Ertugliflozin and Sitagliptin in bulk and tablet dosage form. Int J Res Pharm Sci. 2019;9(3):1042-50.
-
Sultana S, Hossain MS, Islam MS, Rouf AS. Quantitation of Sitagliptin in Drug Product by Validated Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatographic Technique. Dhaka University J Pharm. Sci. 2018 Jun 24;17(1):123-129.
-
Gundala A, Prasad VK, Koganti B. Application of quality by design approach in RP-HPLC method development for simultaneous estimation of saxagliptin and dapagliflozin in the tablet dosage form. Brazilian J Pharm Sci. 2019;55.
-
Upadhyay NK, Rathore C, Sapra S, Negi P. Novel RP-HPLC method development and validation for the simultaneous estimation of saxagliptin and glimepiride. Int J App Pharm. 2018;10(3):151-156.
-
Donepudi S, Achanta S. Simultaneous Estimation of Saxagliptin and Dapagliflozin in Human Plasma by Validated High-Performance Liquid Chromatography - Ultraviolet Method. Turk J Pharm Sci. 2019 Jun;16(2):227-233.
-
Vetapalem R, Yejella RP, Atmakuri LR. Development and Validation of a Stability Indicating RP-HPLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Teneligliptin and Metformin. Turk J Pharm Sci. 2020 Apr;17(2):141-147.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License