IJCRR - 13(19), October, 2021
Pages: 33-38
Date of Publication: 11-Oct-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A Study to Compare the Effect of Electromyography Biofeedback Versus Mime Therapy on Clinical and Electrophysiological Parameters in Subjects with Bell's Palsy - A Comparative Interventional Study
Author: Bhagat P., Kakkad A.
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Bell's palsy is the weakness of muscles supplied by the 7th cranial nerve i.e., the facial nerve. It is a lower motor neuron type of disease of the facial nerve. Objectives: To compare the effects of Electromyography Biofeedback (EMG BFB) and Mime Therapy on electrophysiological parameters in subjects with Bell's palsy. Method: A group of 31 subjects were selected for the study and randomly divided into two groups: Group A and Group B. There were 16 subjects in Group A and 15 subjects in Group B. Group A received EMG BFB (for Frontalis, Nasalis & Mentalis muscle), and group B received Mime Therapy. Pre and post measurements are taken by using the Electromyography (EMG) test (Amplitude of Frontalis, Nasalis & Mentalis muscles), Nerve Conduction Test (Latency & Amplitude of the facial nerve)and, Sunny brook facial grading score. Results: Wilcoxon signed-rank test was done to see the difference within the group and the Mann-Whitney U test was used to see the difference between the groups. The p-value was set at p< 0.05. The result of Intragroup groups showed a significant difference between pre-and post-score for all outcome measures. The result of Intergroup showed no significant difference between Group A and Group B. Conclusion: Conventional physiotherapy with an EMG BFB and Mime therapy has a positive effect on electrophysiological parameters in subjects with Bell's palsy. However, both treatments EMG BFB and Mime therapy are equally effective in subjects with Bell's palsy
Keywords: Bell’s Palsy, Facial Muscle Weakness, Nerve Conduction Studies, Electromyography biofeedback, Mime therapy, Sunnybrook facial grading score.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Bell’s palsy is an acute, apparently isolated, lower motor neuron facial palsy for which no cause can be found.1 It is a lower motor neuron type of paralysis or weakness of the 7th cranial nerve i.e., facial nerve demonstrated by unilateral peripheral facial muscle paralysis or weakness. It may affect the forehead, face, and neck muscles. Facial palsy may depend on local axonal damage. Within a few days after the infliction of the primary injury, the distal parts of the affected axons degenerate. Significant initial damage normally leaves the sequel with incomplete facial function. Due to immobility, skeletal muscles atrophy very quickly. A reduction in fibre size and diameter appears to be the most striking morphologic finding, together with a simultaneous increase in intramuscular connective tissue and a reduction in capillary density. Facial muscles differ from other skeletal muscles and do not react in the same way during periods without movement. These muscles are relatively slow to degenerate, have small motor units, and are mostly without muscle spindles. Restoration occurs slowly (months), through the growth of new neurons from the area of the injury, or distally through the growth of branches from remaining axons.2Bell’s palsy accounts for half peripheral facial nerve paralysis with an incidence at about 1 in 60 persons. It is more common in people with diabetes. Idiopathic facial paralysis occurs in every decade of life, with a mean age of between 40 and 44 years. It was less common before the age of 15 and after the age of 60 years. The incidence in men and women was similar. Between 6% and 9% of patients had a previous history of facial paralysis. Facial paresis alone occurred in 31%, while the remainder had total unilateral paralysis.3
The Surface Electromyography(SEMG) Biofeedback provides the information necessary for the correction of the movement and supports the process of rehabilitation3.SEMG biofeedback may be used as an adjunct to the retraining exercises in each of the treatment-based categories. Learning facial movements is difficult without feedback. The use of SEMG biofeedback is to provide a visual or auditory representation of facial function at the time of the rehabilitation session.4
Mime therapy is a performance art to improve the symmetry of facial muscle functions and increases the voluntary strength of muscle to help subjects regain functions of their facial muscles. Mime therapy includes stretching exercises, massage, specific facial expression exercises like vowels & consonants, relaxation techniques & active-assisted range of motion exercises.2 The brain reduces abnormal patterns of movement and restores appropriate patterns of facial muscle activity for intended facial actions.5
The primary outcome measure chosen was Sunnybrook facial grading system with 13 items and Electrophysiologically, Electromyography (EMG) test and Nerve conduction test were the objective investigations of facial muscles function most useful in determining the prognosis of a Facial Nerve Lesion.
Bell’s palsy is very common at a young age & as it affects the cosmetic part of an individual, it becomes the responsibility of the physiotherapist to provide his/her best effort for recovery in subjects. Nowadays many recent advances are available for treatments of Bell’s palsy e.g., mime therapy, EMG BFB, Taping, etc. along with conventional treatment like electrical stimulation, facial exercises, etc. The systematic review showed the usefulness of these modalities,6 but no single form of treatment seemed to be superior. In the era of evidence-based practice, individually mime therapy & EMG biofeedback both are proven effective but one out of these two treatments, which one is more effective is not currently available in any literature.
Therefore, the purpose of the present study was to compare the effectiveness of EMG BFB&Mime therapy on clinical &electrophysiological parameters in Bell’s palsy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study Design: Comparative Interventional Study
Sampling technique: Purposive Sampling
Study Settings & SourceofData: Various Physiotherapy OPDs in Surat.
Allocation: Subjects were allocated to Group A and Group B by Simple Random Sampling (chit method)
Sample Size: 31
Group A: 16, Group B: 15
Inclusion criteria:
-
Unilateral Bell’s palsy,
-
Acute onset 1-3 weeks,
-
Age group 16-75 years
Exclusion criteria:
-
Central facial palsy7,
-
Facial palsy recurrence7,
-
Subject along with surgery for ear & facial nerve palsy.
Ethical clearance was taken from Institutional Ethical Committee. The reason for the study was explained and written informed consent and demographic details were obtained from all the subjects.
Description of the groups:
Group A: Electromyography Biofeedback + Conventional therapy
Group B: Mime therapy + Conventional therapy
All the subjects were treated with the session of Conventional therapy for 30 minutes, 6 days per week, and additional treatment of EMG BFB or Mime therapy was given for 30 minutes, 6 days per week.2The procedure was continued for 5 weeks for both groups.
Description of the Intervention:
Interrupted Direct Current (I.D.C.) was used with a pulse duration of 100msfor the muscles of the face (Frontalis, Orbicularis oculi, Buccinators, Nasalis, Orbicularis oris, Mentalis. Ninety contractions were given to each muscle in three sessions. Stimulus intensity was adjusted according to the subject’s tolerance at the level which produced a visible muscle contraction without discomfort. Electrical stimulation was given by using Tapsi computerized muscle stimulator, Model no. 535 and serial no.750213.
A ground electrode was placed on the chin or base of the neck. The reference electrode was placed on a 3cm distal from the recording electrode. Active electrode placement accordingly to activate the muscle (Frontalis-1 cm above the eyebrow, Nasalis- posterior end of the lower margin of ala, and Mentalis-1 cm lateral to middle of chin midway between chin lower border & the lip.) Subjects were asked to perform the actions of those muscles. EMG BFB therapy was initiated as soon as the first action potential in the affected muscle was recorded. EMG BFB was given by the Bio Stream MEDICAID machine. Serial No. Bo 71713 with sweep speed of 10 ms/division & Gain or sensitivity of 200uV.
It includes:
-
Stretching exercises to relieve muscles involved in synkinesis.
-
Massage for face and neck daily for 10-15 minutes.
-
Facial expression exercises: 5 repetitions.
-
Relaxation technique, which is combined significant asymmetry of facial posture at rest (as for movement control category) with muscle twitching and facial spasm.
Outcome measures:
Data of all subjects were taken on before the 1st session, at the end of the 15th session, and end of the 30th session. Data were evaluated by the Sunnybrook scale, Electromyograph test, and Nerve conduction test.
-
Amplitude (mV) of Motor Unit Action Potential (MUAP) of facial muscles by Electromyography test:
The amplitude of Motor Unit Action Potential (MUAP) was measured from peak to peak of phase. The ground electrode is on the chin or base of the neck. The reference electrode was placed at 3 cm distal to the recording electrode. Recording active electrode was placed accordingly to activate the muscle (Frontalis-1 cm above the eyebrow, Nasalis- posterior end of the lower margin of ala and mentalis-1 cm lateral to middle of chin midway between chin lower border & the lip). Subjects were asked to perform the actions of those muscles.9
-
The latency (ms) and amplitude of Compound Motor Action Potential (CMAP) of the facial nerve:
The latency (ms) of the facial nerve is measured from stimulus artefact to the 1st deflection from the baseline. The normal latency (ms) is below 4.1ms. Amplitude is measured from peak to peak of the negative phase with all the subjects in supine lying. Recording surface electrodes are placed on Nasalis for evaluation of facial nerve. The reference electrode was placed on the bridge of the nose. A ground electrode was placed on the chin or base of the neck. The nerve is stimulated just below the earlobe either anterior or posterior to it.9
-
Sunny-brook facial grading system score:
Subjects were assessed with Sunny-brook facial grading system score.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
The whole statistical analysis was done by using the SPSS 20.0 version for Microsoft windows. All statistical analysis was calculated using an alpha level of 0.05. The normality of the data was checked by the Shapiro-Wilk test. Means and standard deviations were calculated as a measure of central tendency and measure of dispersion respectively.
RESULTS
In the present study, 31 subjects with the age group of 16 to 75 years were taken and randomized into 2 groups. Group A (EMG BFB &Conventional treatment) and Group B (Mime therapy &Conventional treatment). Subjects were evaluated before the 1st session and at end of the 30th session.
See Table 1 for baseline characteristics of the subject of both groups. Patients in both groups were found with no significant difference in their baseline characteristics.
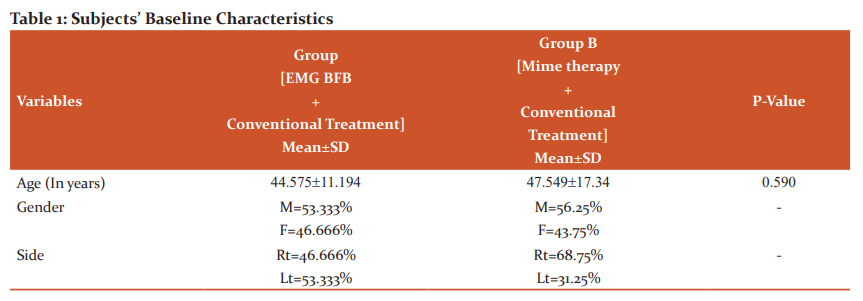
The effects of treatment in Group A on the EMG test, Nerve conduction test and Sunny brook facial grading score were evaluated using Wilcoxon signed-rank test as shown in Table 2. A significant difference was found in all outcome measures except amplitude (mV) in the nerve conduction test suggestive of the effectiveness of SFBFB with conventional treatment.
The effects of treatment in Group B on the EMG test, Nerve conduction test and Sunny brook facial grading score were evaluated using Wilcoxon signed-rank test as shown in Table 3. A significant difference was found in all outcome measures except amplitude (mV) in the nerve conduction test suggestive of the effectiveness of Mime therapy with conventional treatment.

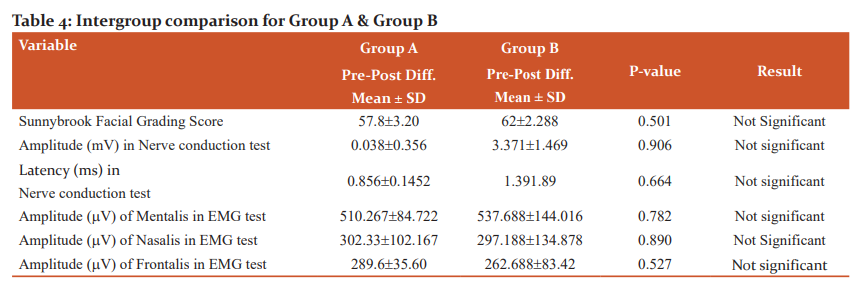
The effects over time of the interventions on Sunnybrook facial grading score, EMG test, and Nerve conduction test were evaluated using Mann Whitney U test for intergroup analysis and no significant difference was found when compared intergroup improvements as explained in Table 4.
DISCUSSION
The study was conducted to compare the effect of EMG BFB and Mime Therapy on patients with acute Bell’s palsy. All the patients had received conventional physiotherapy treatment along with EMG BFB in Group A and Mime therapy in Group B. The duration of electromyography biofeedback is 20 minutes and conventional treatment was 30 minutes. Treatment was given 6 days for 5 weeks. For the comparison of pre and post effects of both the groups' Electromyography test, Nerve conduction test, and Sunnybrook facial grading score.
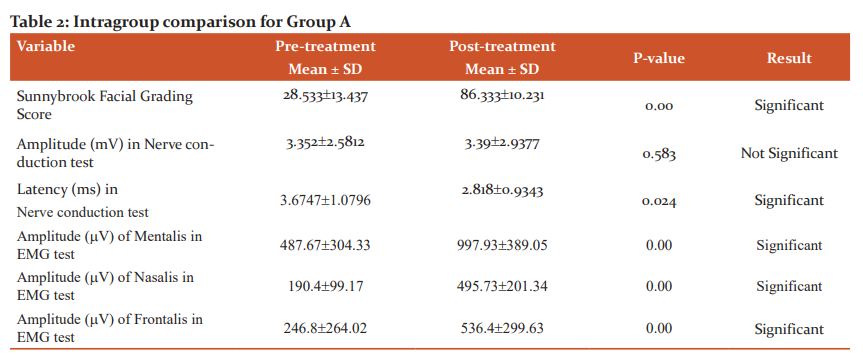
The result of intragroup comparison in Group A (EMG BFB) showed significant improvement in amplitude (mV) of MUAP Frontalis, Nasalis, and Mentalis muscle in EMG test with a significant reduction in latency (ms) of Nerve conduction test and significant improvement in Sunnybrook facial grading score in patients with Bell’s palsy. There is no significant improvement in amplitude (mV) of CMAP in the nerve conduction test.
The result of intragroup comparison in Group B (Mime therapy) shows significant improvement in amplitude (mV) of Frontalis, Nasalis and Mentalis muscle in EMG test with a significant reduction in latency (ms) in Nerve conduction test as well as significant improvement Sunnybrook facial grading score on patients with Bell’s palsy. There is no significant improvement in amplitude (mV) of CMAP in the nerve conduction test.
The result of the intergroup comparison showed there is no significant difference between EMG BFB and Mime therapy on EMG test, Nerve conduction test, and Sunnybrook facial grading score. The study did not demonstrate statistically significant differences among the two different treatment groups.
A systematic review about exercise therapy for Bell’s palsy was published in 2008 with four studies. Meta-analysis was not done because the studies had an opposing combination of characteristics like time of duration of the intervention, treatment type, and outcome measures. The study did not demonstrate clinical or statistical differences among the different treatment groups but improvements were noted in all treatment groups.9
Similar findings were reported in a previous study of Balliet et al. (1992) conducted a study on combined with EMG facial exercises to increase functional facial movements, including eyelid control, through a comprehensive program as neuromuscular retraining with 7 to 8-month program. Balliet referred to his comprehensive program as neuromuscular facial retraining.10 May et al(1972) reported improvement in 12 of 13 Bell’s palsy patients in only 1 or 2 EMG sessions.11In accordance with a study of Cronin and Steenerson (2003) conducted a study on surface electromyography results revealed improvement in facial symmetry.12
Referred to as EMG biofeedback, its purpose is to bring the normally unconscious control of muscles under conscious control. Decreased activity in hyperactive muscles and increased activity in weak muscles as well as improve coordination of muscle groups.EMG is an important part of the program because it provides immediate feedback to the patient, providing an objective means of measuring movements and outcomes. The facial paralysis, and aberrant regeneration presented before treatment in the treatment group and the success made in normalization of movements and function as a result of treatment support the need for this type of intervention.13
In 2008, the Cochrane Library published a systematic review about physical therapy and Bell’s palsy including six studies with patients who had a whole diagnosis of Bell’s palsy and underwent various types of treatment: faradic stimulation, galvanic current, massage, infrared, acupuncture, and drugs. No statistically significant inter-group differences were found.9
Mistry Gopi et al. (2013) conducted a study on the comparison of the role of Mime therapy vs. conventional therapy on Sunnybrook facial grading system in patients with acute Bell’s palsy. The result showed that Mime therapy improved facial symmetry & functions more than conventional therapy & home exercise in people with acute Bell’s palsy. So, this study supported the use of Mime therapy. Massage done in Mime therapy increases production and creates new growth of connective tissue and collagen in facial muscles and restores facial muscle action. The cost of the treatment is low as along with therapy at a physiotherapy centre, a home program is an integral part of the treatment. So, Mime therapy is also a good choice of treatment for people with Bell’s palsy. Thus, Mime therapy can be used in the treatment of people with acute Bell’s palsy to get improvement in facial asymmetry within a shorter period.14
Statistical analysis for both the groups demonstrated that there is no significant difference in EMG BFB and Mime therapy on the EMG test, Nerve conduction test, and Sunnybrook facial grading score outcome measures between the two groups.
LIMITATIONS:
-
The sample size was small.
-
Subjects were not followed up for a longer period.
-
The therapist was not blinded.
FUTURE RECOMMENDATIONS:
-
The same study can be done with larger sample size.
-
A comparative study including different age groups can be done.
-
The same study can be done with sub-acute & chronic Bell’s palsy patients.
-
A future study can be carried out to know the long-term benefits of the intervention.
-
Different outcome measures can be taken.
-
A Control group can be added.
CONCLUSION
From this study, one can state that conventional physiotherapy with an EMG biofeedback and Mime therapy has a positive effect on electrophysiological parameters in patients with Bell’s palsy. Hence, both interventions are effective for improving facial muscle functions in patients with Bell’s palsy. However, both treatments EMG BFB and Mime therapy are equally effective in patients with Bell’s palsy.
AUTHOR’S CONTRIBUTION:
The first author searched the literature, collected data and wrote the manuscript. The second author reviewed and revised the manuscript as her supervisor.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We would like to thank the Management, Principal, and Staff members of SPB Physiotherapy College, Surat for allowing us for this research.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST:
Nil
SOURCE OF FUNDING:
Nil
References:
-
Golwalla A. Golwalla's Medicine for Students. Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical P; 2017
-
Sharvani Belle Praveen Kumar et al., Efficacy of mime therapy and conventional therapy versus conventional therapy in improving the facial functions of Bell’s palsy.Int J Sci Res Rev. 2018, 7(1), 427–441
-
Balliet R, Shinn JB, Bach-y-Rita P. Facial paralysis rehabilitation: retraining selective muscle control. Int Rehab Medicine. 1982 Jan 1;4(2):67-74.
-
Mistry G., Sheth M., Vyas N.Comparison of the effect of mime therapy versus conventional therapy on the sunny brook facial grading system in subjects with acute Bell’s palsy. Int J Med Res Health Sci. 2014 Jan 1;3(1):133-136.
-
Peitersen E. Bell's palsy: the spontaneous course of 2,500 peripheral facial nerve palsies of different etiologies. Acta Oto-Laryng. 2002 Jan 1;122(7):4-30.
-
Sittel C, Steinert E. Prognostic value of electromyography in acute peripheral facial nerve palsy. Otol Neur. 2001 Jan 1;22(1):100-4.
-
Ordahan B, Karahan A. Role of low-level laser therapy added to facial expression exercises in subjects with idiopathic facial (Bell’s) palsy. Lasers Med Sci. 2017 May 1;32(4):931-6.
-
Hauser S, Josephson S. Harrison's Neurology in Clinical Medicine, 3E. New York: McGraw-Hill Publishing; 2013.
-
Misra D. Clinical Neurophysiology. [Place of publication not identified]: Elsevier India; 2014.
-
Akcan FA, Dundar Y, Uluat A, Korkmaz H, Ozdek A. Clinical prognostic factors in patients with idiopathic peripheral facial nerve paralysis (Bell’s palsy). The European Research Journal. 2017;3(2):170-4.
-
Peitersen E. Bell's palsy: the spontaneous course of 2,500 peripheral facial nerve palsies of different etiologies. Acta Oto-Laryngologica. 2002 Jan 1;122(7):4-30.
-
GW Cronin, RL Steenerson. The effectiveness of neuromuscular facial retraining combined with electromyography in facial paralysis rehabilitation. Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery 128(4):534-538
-
Neely JG, Cherian NG, Dickerson CB, Nedzelski JM. Sunnybrook facial grading system: reliability and criteria for grading. The laryngoscope. 2010 May;120(5):1038-1045.
-
Mistry G, Sheth M, Vyas N. Comparison of the effect of mime therapy versus conventional therapy on the sunnybrook facial grading system in patients with acute bell's palsy. International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences. 2014;3(1):133.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License