IJCRR - 13(19), October, 2021
Pages: 17-22
Date of Publication: 11-Oct-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Comparative Efficacy and Tolerability of Luliconazole versus Terbinafin in Pediatric Patients-A Randomized Trial
Author: Harinkhere Sanjay Kumar, Arya Raj Kumar, Garg Anubhav, Ranjan K. P., Kothari Saroj
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aim/Objective: Luliconazole is a newer imidazole antifungal drug effective against a variety of fungal infections, especially dermatophytosis, which is one of the most common superficial fungal infections, caused by dermatophytes. The present study is designed to compare the efficacy and tolerability of topical antifungal drug luliconazole with terbinafine used for the treatment of a variety of fungal infections, especially dermatophytosis. Materials and Method: In this perspective, the observational and open level study randomly selected patients (those fulfilling the inclusion criteria) are categorized according to diagnosis and had been advised to apply topically the respective drug during the study period. Results: In the present study we found that the luliconazole was more efficacious and tolerable than terbinafine at a short term therapy. Conclusion: Luliconazole was better efficacious and tolerable than terbinafine in relieving signs and symptoms of dermatophytosis, especially pruritus and desquamation.
Keywords: Dermatophytosis, Efficacy, Pruritus, Tolerable, Dermatophytes, Desquamation
Full Text:
Introduction:
Fungal infections are a major health problem all over the world and an important cause of morbidity and may be categorized as superficial or invasive. Superficial fungal infections are primarily caused by dermatophytes, Candida spp, and Malassezia species affects 20%–25% of the world’s population and are associated with interference with daily activities, poor quality of life, and health care expenditure.1Invasive fungal infections are usually appearing in the presence of one or more predisposing factors, especially in immune-compromised patients. Systemic fungal infections are an important cause of hospitalization and may even cause mortality.
Dermatophytes are aerobic fungi and physiologically can digest keratin for their growth as they replicate in the superficial layers of the epidermis. Consequently, in clinical practice, hairs, nails and skin are mostly affected by dermatophytes infection due to rich keratin content. The continued existence of embedded arthroconidia (fungal element) for years in scales of hair and skin leads to frequent recurrence or relapse. These dermatophytes belong to three genera, i.e., trichophyton, microsporum, and epidermophyton. Although there is no standard definition of chronic dermatophytosis in literature at far patients with a duration of disease more than 6 months to 1 year, with or without recurrence, despite being treated with an adequate course of antifungal drugs are considered as chronic dermatophytosis. Recurrent dermatophytosis is defined as the reoccurrence of infection within few weeks of stopping the treatment.2 The lesion of dermatophytosis is present with an annular or ring-shaped red scaly plaque with central clearing, often associated with severe pruritus. Pruritus often leads to an intense desire to itch; affecting the quality of life of the patients and secondly, intense itching of a lesion increases the chance to develop a secondary bacterial infection. Inappropriate use of topical steroids results in unclear morphology of fungal infections.
The clinical manifestations of dermatophytosis differ according to the site of infection and the patient’s immunologic response. Genetic susceptibility is also identified to affect the predisposition to dermatophytic infections.3 The commonest presentation is Tinea pedis, also known as dermatophytosis of the feet, caused by Trichophyton rubrum. The next most common fungal infections caused by T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, and Epidermophyton floccosum areTinea cruris and Tinea corporis. Onychomycosis i.e. invasion of the nail plate can be due to dermatophytes, candida, or non-dermatophytic moulds.
Historically, the term medical mycology, specifically related to human fungal diseases, began with the discovery of the fungal aetiology of favus. According to Seeliger.4 However, Robert Remak recognized that the etiologic agent of favus was infectious. He cultured it on apple slices, and authentically described it as Achorionschoenleinii, in honour of his mentor and his initial discovery.5 Etothrix invasion of the beard and scalp by Microsporum, which is referring to the small spores around the hair shaft; audouinii, and endothrix hair invasion by Herpes (trichophyton) tonsurans.5 In addition to his observations on dermatophytes, he also explained the clinical and microscopic appearance of thrush in children5 Sabouraud’s treatment of tinea capitis by a single-dose, single-point roentgenology epilation achieved cures in 3 months in contrast to the current therapy of manual epilation and topical application of medications.6
Systemic or topical antifungal drugs are used as treatment strategies to deal with fungal infections. Antifungal drugs interfere with the biosynthesis of ergosterol which is an integral component of the fungal cell membrane and cell wall, thus causing inhibition of fungal growth and replication. Though, their action on different enzymes in the same pathway probably results in different properties and degrees of efficacy. Allylamines are squalene epoxidase inhibitors; act early in the ergosterol biosynthesis pathway with resulting accumulation of squalene compound that is toxic to the fungal cell membrane thus responsible for the fungicidal activity of allylamines. They have very good efficacy against Trichophyton spp. however only fungistatic action against C. albicans and M. furfur. Amorolfine is a morpholine antifungal compound, has strong activity against Trichophyton spp., C. albicans, and M. furfurthat acts by inhibiting both C14 reductase and C7–C8 isomerase activity.7 The azole antifungal drugs act by inhibiting 14α-lanosterol demethylase and have strong activity against C. Albicans and Trichophyton spp. As a consequence, lanosterol accumulation has a less toxic effect than squalene, so imidazoles have a fungistatic action.8 The efficacy of topical drugs in the treatment of superficial mycoses depends not only on the type of lesion and mechanism of action of the drug, but also on the viscosity, hydrophobicity, and acidity of the formulation as well and its distribution and retention in the stratum corneum. Regardless of the type of formulation, penetration of topical agents in hyperkeratotic lesions is often doubtful.9
Materials and Methods: The present prospective, observational and open-label study was conducted in the department of pharmacology in association with departments of microbiology and skin & VD, Gajra Raja Medical College and associated J.A. Group of Hospitals, Gwalior from a period of March 2018 to May 2019 after getting clearance from institutional ethical clearance letter No. Bio/MC/Ethical/555 dated 10/04/2018. A total of 100 clinically diagnosed dermatophytosis patients with the age ranges from 1 to 12 years, who fulfilling the inclusion criteria were randomly selected for the study after taking written informed consent.
The inclusion criteria consist (1) Patients had an age between 1-12 years, (2) Both male and female were included, (3) those are positive by mycological (10% KOH mount) examination, (4) those patients who apply the medication for the recommended duration of therapy.
The exclusion criteria consist (1) Patients below the age of 1 year and above the age of 12 years, (2) those patients who were taking immunosuppressant or corticosteroid therapy either orally or topically, (3) those patients who were receiving oral/topical other antifungal drugs, (4) patients having known history of hypersensitivity with terbinafine and luliconazole, (5) chronically ill patients, and (6) patients who were failed to follow-up for two consecutive visits.
Clinically diagnosed Selected patients were grouped in Group A and Group B and treated with 1% luliconazole cream and terbinafine cream respectively and were instructed to apply for respective medicine over the affected part twice daily for 2 weeks. Clinical assessment was based on pruritus, erythema and desquamation on the affected lesion and graded accordingly. The mycological assessment was based on KOH and culture mounting of the specimen. Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) is a method, was used to assess the severity of pruritus.11
VAS grading:
-
0 – No Pruritus
-
1-3 – Mild Pruritus
-
4-7 – Moderate Pruritus
-
8-10 – Severe Pruritus
Specimens were collected from the margins of the lesion by skin scraping and scales following all the aseptic precautions and then transported aseptically in the department of microbiology within 1-2 hours of collection, for mycological examination to confirm the infection.
In the microbiology department, a 10% KOH mount slide of the specimen was made to see fungal hyphae under low (10X) and high power (40X) consecutively followed by culture on SDA with or without antibiotic media at 37oc for 48 hours incubation. After 48 hours, morphological identification of fungal isolates was done by Gram’s stain, LPCB (Lacto -phenol cotton blue) mount and slide culture. At the end of the study mycological examination was performed to ascertain the mycological cure. Patients were asked for any adverse reaction and effectiveness (relief from symptoms) of the drug during each visit.
All the data of total patients taking luliconazole and terbinafine including age group, sex, clinical feature, diagnosis, cure and adverse reactions to the respective drug was collected and tabulated. Data are summarized and compared statistically by frequency distribution and percentage proportion. Chi-square test and students t-test was applied to know the significant (p-value) ratio of difference statistically by using software IBM SPSS.
Results:
Out of total enrolled 100 patients, 79 patients with the age ranging from 1-12 years and fulfilled the inclusion criteria were included for the study statistically significant p-value:0.009616 as shown in Figure no.1, while rest 21 patients were fails to do regular follow up and were excluded from the study.

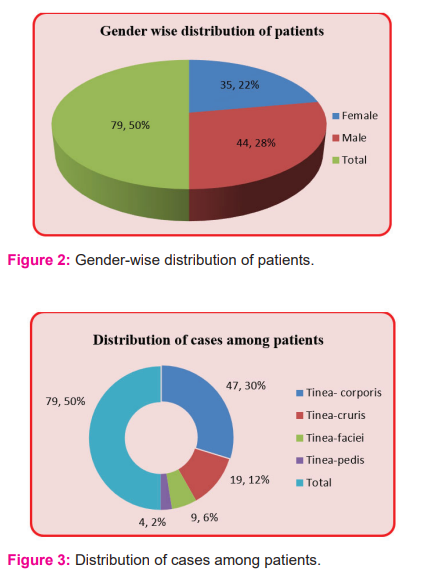
In the present study, among the selected patients male patients contributes (n=44, 55.7%) and female (n=35, 44.3%) with male: female ratio was 5:4,statistically insignificant p-value:0.254286 as shown in Figure no.2.
In the present study, cases were categorized according to diagnosis which shows that infection by Tinea corporis (59.5%) was commonest among the other species of tinea while only n=4 (5.1%) patients were showed infection by Tinea pedis. Data were summarized in Table no.1 / Figure 3 statistically significant p-value: 0.000001.
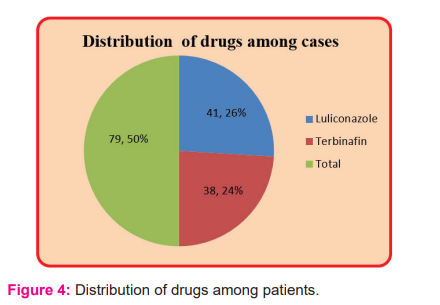
In the present study patients treated with luliconazole antifungal cream (group A) were n=41/79,51.9%; while those treated with terbinafine were n=38,48.1% as shown in Fig 4.
In the present study, we found that pruritus and desquamation were significantly reduced in patients treated with luliconazole (n=40/41) than terbinafine (n=27/38 and n=22/38 respectively) p=0.04 and p=0.005. Erythema was almost completely disappeared by luliconazole (n=41/41) than terbinafine (n=25/38) p=0.02. Data are summarized in table no 1.

In the present study, we found that only n=5 /79, 6.33% of patients were reported with adverse drug reactions, which is more in terbinafine n=3/79 than luliconazole group n=2/79. Data is summarized in Figure no.5 statistically significant p-value: 0.000001.

Discussion:
Dermatophytosis is one of the earliest known fungal infections of humans and affects the world population.12 Although dermatophytosis does not cause mortality, it does cause morbidity especially in tropical countries like India due to its hot and humid climate.13 No race in the world is entirely free from dermatophytosis,14 as the degree of immunosuppression and the numbers of immunosuppressed patients are increasing at a speed; the management of dermatophytosis would be a big challenge in the years to come. It affects the quality of life of a patient due to the associated inflammatory symptoms mainly pruritus. Recurrence of tinea infections is common due to inadequate treatment or re-infections, especially of the intertriginous areas. In the present analysis based on data of 79 evaluable patients, both the study drugs showed a significant reduction in signs and symptoms (pruritus, erythema, and desquamation) of tinea infections as compared to baseline. At the end of the ‘Treatment Phase’ greater proportion of patients in luliconazole group had absence of pruritus (98%) and erythema (100%) as compared to terbinafin.
In our study we found that luliconazole is more efficacious and safe compare to terbinafin in relieving the symptoms of dermatophytosis. A similar review study carried out by Khanna D et al.10 and Gupta A et al.15, both demonstrated that luliconazole is more efficacious than terbinafin which support the result of our study. In contrast to our study; a separate study carried out by Ghannoum MA et al.16 demonstrated that terbinafine is more efficacious than luliconazole.
In the present study, we found that the overall symptoms cure rate (composite score) of luliconazole was 99.6% while terbinafine had89.73% composite score. Similarly reported by H.R.Jerajani et al.17 that means total composite score (pruritus, erythema, vesicle and desquamation) of luliconazole was 92.9% than it was terbinafine 91.2%.
In the present study, we found that only a few patients (n=5/79, 6.33%) were reported adverse events during the treatment, out of which n= 2/41, 4.87% of patients were reported adverse reactions from luliconazole while n=3/38, 7.9% from terbinafine. These adverse reactions were very mild i.e. itching, burning and hyperpigmentation and did not require discontinuation of the drugs.
A similar study from the other state of India was carried out by VC Laxmi et al.18 in their study they reported four patients in the terbinafine group showed mild contact dermatitis versus none in the luliconazole. Similarly, Jones et al.19 and Watanabe et al.20 reported fewer side effects of 1% application of luliconazole than terbinafine. No application site reactions or systemic events were reported in the other trials.17-23 In contrast to our study, a separate study is carried out by Chandana T et al.24and demonstrates that luliconazole has more adverse effects (20.0%) than terbinafine (16.6%).
Conclusion: Adequate treatment of fungal skin lesions with most of the currently used antifungal drugs requires prolonged treatment for complete clearance of the fungal elements which frequently results in noncompliance of the patients; once the clinical features begin to subside. It is possible that a small number of dermatophytes may remain below the detection limit and can survive to some extent in these partially treated lesions and/or surrounding tissues. As a result, the high relapse rate in patients who were previously considered cured is one of the biggest challenges in the treatment of fungal infection.
To tackle this, it is desirable for an ideal antifungal drug should have broad-spectrum fungicidal activity at a minimum concentration along with a high mycologic and clinical cure rate with a low incidence of adverse drug reactions even after short-term use.
The present study reveals that luliconazole is a safe and effective drug for the treatment of dermatophytosis even in paediatric patients with mild adverse reactions at short term therapy.
Acknowledgement: Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Source of Funding: Nil
Conflict of Interest: Nil
Authors’ Contribution: Dr. Harinkhere Sanjay Kumar (Postgraduate Student)– Principal Investigator
Dr. Arya Raj Kumar (Professor) - Co-Investigator/ Supervisor / Guide
Dr. GargAnubhav (Professor)- Co-Investigator/ Co-Supervisor / Co-Guide
Dr. Ranjan K. P. (Associate Professor)-Co-Investigator/ Co-Supervisor / Co-Guide
Dr. Kothari Saroj- Professor and Head
References:
-
Havlickova B, Czaika VA, Friedrich M. Epidemiological trends in skin mycoses worldwide. Mycoses 2008; 51: 2–15
-
Zayas N, Tosti A, Rebell G, Morelli R, Bardazzi F, Bailey H, et al. Autosomal dominant pattern of distal subungual onychomycosis caused by Trichophyton rubrum. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996 Feb;34(2 Pt 1):302-4
-
Seeliger, H. P. R. The discovery of Achorionschoenleinii: facts and ‘‘stories.’’ Mykosen 1985; 28:161–182
-
Weitzman I, Summerbell RC. The dermatophytes. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1995 Apr;8(2):240-59.
-
Borelli C, Korting HC, Bödeker R-H, Neumeister C. Safety and Efficacy of Sertaconazole Nitrate Cream 2% in the Treatment of Tinea Pedis Interdigitalis: A Subgroup Analysis. Cutis; 2010. 85:107-111.
-
Nishiyama Y, Asagi Y, Hiratani T, Yamaguchi H, Yamada N, Osumi M et al. Morphological changes associated with growth inhibition of Trichophyton mentagrophytes by amorolfine. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1992;17 Supp 1:13–17
-
Nimura K, Niwano Y, Ishizuka S, Fukumoto R. Comparison of in vitro antifungal activities of topical antimycotics launched in 1990s in Japan. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2001;18:173–178.
-
Dias MF, Bernardes-Filho F, Quaresma-Santos MV, Amorim AG, Schechtman RC, Azulay DR et al. Treatment of superficial mycoses: Review. Part II. A Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:937–944.
-
Khanna D, Bharti S. Luliconazole for the treatment of fungal infections: An evidence-based review. Core Evid. 2014 Sep 24;9:113-24
-
Phan NQ, Blome C, Fritz F. Assessment of pruritus intensity: a prospective study on validity and reliability of the visual analogue scale, numerical rating scale and verbal rating scale in 471patients with chronic pruritus. Acta DermVenereol 2012; 92:502–7.
-
Venkatesan G., Ranjit Singh A.J.A., Murugesan A.G., C. Janaki C., Gokul Shankar S.Trichophyton rubrum – the predominant etiological agent in human dermatophytoses in Chennai, India. Afr J Microb Res. 2007,5: 009-012.
-
Emmons, C. W. Dermatophytes: natural groupings based on the form of the spores and accessory organs. Arch. Dermatol. Syphilol. 1934; 30:337–362.
-
Rippon, J. W. The changing epidemiology and emerging patterns of dermatophyte species. Curr. Top. Med. Mycol. 1985; 1:209–234.
-
Gupta A, Daigle D. A critical appraisal of once-daily topical luliconazole for the treatment of superficial fungal infections. Infect Drug Resist. 2016;9:1-6
-
Ghannoum MA, Long L, Kim HG, Cirino AJ, Miller AR, Mallefet P et al. Efficacy of terbinafine compared to lanoconazole and luliconazole in the topical treatment of dermatophytosis in a guinea pig model. Med Mycol. 2010 May;48(3):491-7
-
Jerajani H, Janaki C, Kumar S, Phiske M. Comparative assessment of the efficacy and safety of sertaconazole (2%) cream versus terbinafine cream (1%) versus luliconazole (1%) cream in patients with dermatophytoses: a pilot study. Indian J Dermatol. 2013 Jan;58(1):34-8
-
Lakshmi VC, Bengalorkar GM, Shiva Kumar V. Clinical efficacy of topical terbinafine versus topical luliconazole in treatment of tinea corporis/tinea cruris patients. Br J Pharm Res. 2013;3:1001–1014.
-
Jones TM, Jarratt MT, Mendez-Moguel I. A randomized, multi-center, double-blind, vehicle-controlled study evaluating the efficacy and safety of luliconazole cream 1% once daily for 7 days in patients aged $12 years with tinea cruris. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:32–38.
-
Watanabe S, Takahashi H, Nishikawa T. A comparative clinical study between 2 weeks of luliconazole 1% cream treatment and 4 weeks of bifonazole 1% cream treatment fortinea pedis. Mycoses. 2006;49:236–241.
-
Jarratt M, Jones T, Kempers S. Luliconazole for the treatment of interdigital tinea pedis: a double-blind, vehicle-controlled study. Cutis. 2013;91:203–210.
-
Selvan A, Girisha G, Vijaybhaskar, Suthakaran R. Comparative evaluation of newer topical anti-fungal agents in the treatment of superficial fungal infections (tinea or dermatophytic) Int Res J Pharm. 2013;4:224–228.
-
Jones T, Tavakkol A. Safety and tolerability of luliconazole solution 10 percent in patients with moderate to severe distal subungual onychomycosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:2684–2689.
-
Chandana T, Saritha CH, Shankaraiah P. Comparison of safety and efficacy of laliconazole and other antifungal agents. Int. J. Pharma Sci. Res. Vol 5 No 01 Jan 2014
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License