IJCRR - 13(19), October, 2021
Pages: 09-13
Date of Publication: 11-Oct-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Adiponectin to Resistin Ratio concerning Insulin Resistance in Different Phenotypes of PCOS in Indian Population
Author: Chaitali M, Ramesh CG, Raj R, Achal AC
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome is an exceptionally common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. Studies show that there is an intensive relationship between Insulin & gonadal function and adipose tissue. Rotterdam Criteria classifies PCOS into four major phenotypes. Estimation of Adipokines in patients with irregular menstrual cycles may contribute to the early detection of metabolic abnormalities related to PCOS. Objective: The objective of our study was to identify serum Adiponectinto Resistin (A: R) ratio in different phenotypes of PCOS and assess the possible correlation between the A: R ratio and insulin resistance with relation to androgenic fat. Method: In this Cross-Sectionalstudy, we analyzed fasting Insulin and fasting Glucose to calculate HOMA IR, Adiponectin and Resistinfor a total of 144 female subjects of the reproductive age group(18 -40 Yrs). Subjects were classified into 4 groups as per Rotterdam Criteria Complete PCOS(PCO-COM), PCO with Oligo/Anovulation(PCO-O), Anovulation with Hyperandrogenism(O�HA), and PCO with Hyperandrogenism(PCO-HA). Regression analysis was done to find the relation among the study variables. ANOVA was used to analyse the significant variance among the groups. Result: We observed a significant difference for the A: R ratio among the groups with the maximum for PCO-HA (3.15\?0.43) and lowest for O-HA (1.04\?0.22). Significant moderate association observed between A:R ratio&Insulin Resistance (r = - 0.41, p < 0.05) for study population. Conclusion: Adiponectin to Resistin ratio (A: R) is significantly different among the PCOS phenotypes. The lowest values were observed for the O-HA group which is consistent with a higher value of HOMA IR in the same group. Significant Association between A: R Ratio and HOMA IR observed in the study population.
Keywords: PCOS, Insulin Resistance, Adiponectin, Resistin, Adiponectin: Resistin Ratio
Full Text:
Introduction:
The first recorded observation of polycystic ovarian syndrome was described in 1935 by stein & Levinthal .1His Syndrome is an exceptionally common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. Amenorrhea, hirsutism, obesity, and ovaries with a gross polycystic appearance are the common manifestation of the disease. Initially, the diagnosis of PCOS was under controversy primarily because of its heterogeneous manifestations. Even these manifestations appear to change alter during the lifetime of the patient.2 There have been several attempts to make a consensus for the diagnosing criteria of this condition. After the 55 years of the first description of the syndrome in 1990, an initial consensus was obtained in the conference held by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD). Two criteria were found to be at the centre of the disease, 1) clinical and/or biochemical hyperandrogenemia; and 2) oligo- or anovulation, with the exclusion of other known disorders.3Later it is realized that the spectrum of PCOS is much broader than it was initially thought of and another need for the consensus on diagnosing criteria for PCOS was felt. In 2005 Rotterdam, Netherlands the diagnosing criteria were revised and termed as Rotterdam Criteria. The fulfilling of two of the following three features prescribed by the Rotterdam Criteria are considered as the cause of PCOS. Three identified features of Rotterdam criteria is 1) oligo- or anovulation; 2) clinical and/or biochemical hyperandrogenemia, and 3) PCO-Ultra Sound with the exclusion of other etiologies as mentioned in the NICHD criteria. Rotterdam criteria gave 4 identifiable phenotypes of the disease. Several Studies reported that PCOS is characterized by hyperinsulinemic insulin resistance 4 independent of obesity.5 Functional ovarian hyperandrogenism due to dysregulation of androgen secretion results in PCOS.6Studies show that there is an intensive relationship between Insulin & gonadal function. In animal models, it was researched that insulin signalling through theca cell insulin receptor results in hyperandrogenic anovulation .7 Excess Insulin up-regulates LH binding sites and enhance steroidogenesis in response to LH.8,6 Obesity plays a major leading to this endocrinological disorder via insulin resistance, while gonadotropin production is suppressed due to production of testosterone from circulating androstenedione .5 Bioavailability of testosterone also increase due to obesity-induced decrease in Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) production.9 The expanded fat mass in obesity does not only act as the store for enormous energy but also act as an endocrine organ with a massive supply of adipokines/cytokines.10 Leptin, Adiponectin and Resistin have widely studied adipokines about PCOS.11Adiponectin has an insulin-sensitizing role and thereby alters glucose metabolism, exhibits anti-inflammatory and antiatherogenic properties.12 On the Other hand Resistinhas Insulin antagonising function. The favourable effect of adiponectin on whole-body metabolism is accepted and it is seen that circulating adiponectin shows an inverse correlation with adiposity.12Metabolic and cardiovascular diseases state normally shows hyper adiponectinemia. Low levels of adiponectin pave the way for insulin resistance and myocardial infraction therefore it may be considered as one of the causative elements of these disorders.13Cysteine rich protein Resistinis secreted primarily by white adipocytes as 94 amino acid polypeptide and circulating levels raised by obesity either genetic or diet-induced.14 PCOS shows disturbed adipokine secretion along with aberrant morphology of adipose tissue which has been linked with insulin resistance.15 PCOS exhibit significantly lower Adiponectin levels compared to weight-matched obese control. 16 Objective of the study is to observe the variation of the ratio of Adiponectin to Resistin in different phenotypes of PCOS with relation to insulin resistance.
Materials & Method
The study was conducted in the Department of Biochemistry, Mayo Institute of Medical Sciences, Barabanki, India. 144 female subjects diagnosed with PCOS aged between 18 – 40 years were chosen from the OPD of Obstetrics and Gynecology department of Mayo Institute of Medical Sciences, Barabanki India. These subjects were already diagnosed with PCOS as per Rotterdam criteria for that they underwent clinical examination, Sonography, Biochemical and Hormonal Assays. Subjects were categorized into four different phenotypes of PCOS, A) PCOS complete fulfilling all three criteria (PCO-COM), B) PCO on ultrasound with oligo or anovulation (PCO-O), C) anovulation with hyperandrogenism (O-HA) and D) PCO with hyperandrogenism (PCO-HA). Subjects less than 18 yrs and more than 40 yrs of age, with late-onset congenital adrenal hyperplasia, thyroid disease, hyperprolactinemia, androgen-secreting tumours were excluded from the study. Subjects using medication (including Oral Contraceptives), a hormonal intrauterine device and pregnant or lactating subjects were excluded from the studies. The study was approved by the institutional ethical committee and written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
waist and hip circumference were recorded for all the subjects to calculate Waist Hip ratio (WHR). An overnight fasting blood sample was collected for the estimation of biochemical parameters. Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay method was used for estimation of serum Insulin, Adiponectin and Resistin levels. Human Insulin ELISA Kit, Diameter, Italy, Adiponectin Elisa kit, Demeditec, Germany, Human Resistin Elisa kit, Sincere Biotech China were used for the study. Homeostasis Model Assessment (HOMA) was calculated for the estimate of Insulin Resistance.
Statistical Analysis:
Data were analyzed using Microsoft Excel 365 Statistical plugin software & statistical package provided by www.stats.blue. Results are expressed as Mean, Standard Deviation. ANOVA with Post hoc Tukey pairwise multiple comparison test and regression analysis were performed with data obtained. Results were considered statistically significant whenever p< 0.05.
Results:
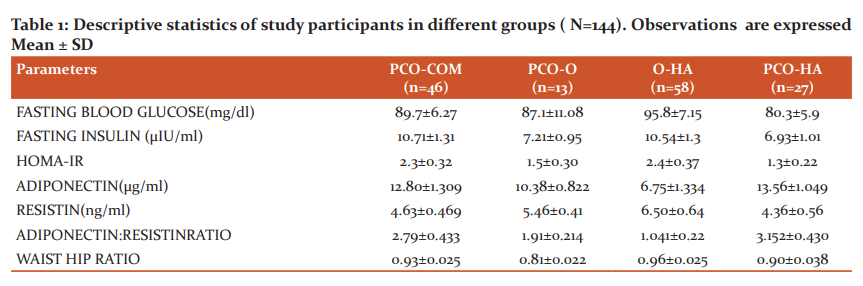
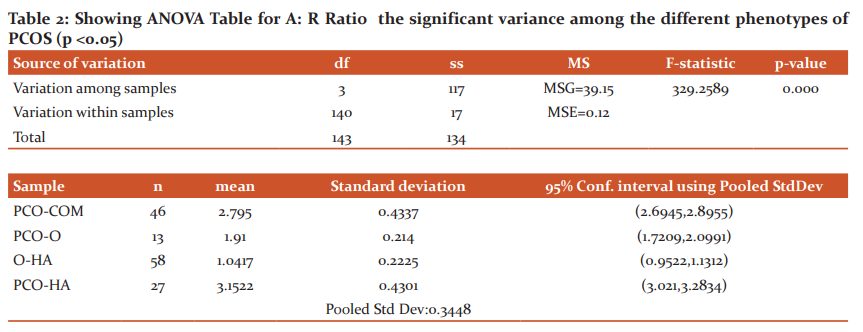
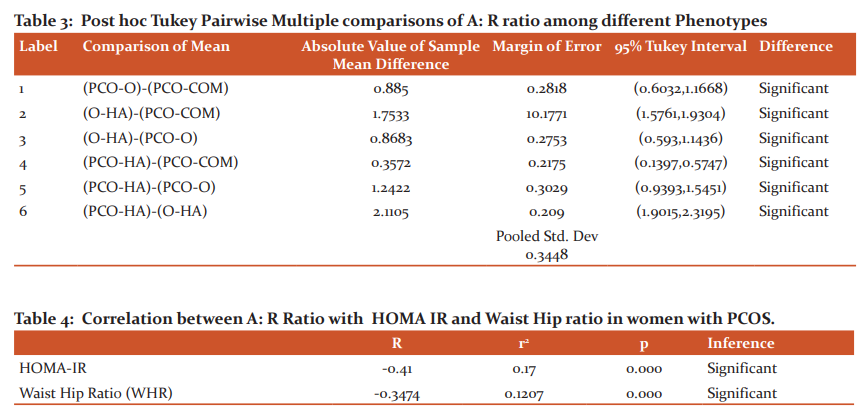
Baseline observations of the subject population (Table 1) showed WHR was greatest among the group O-HA and lowest for the group PCO-O. HOMA-IR variation was observed among groups and a maximum value was obtained of 2.4in the A-HA group and a minimum of 1.3 for the PCO-HA group. A: R ratio was found to be highest among the PCO-HA group and lowest for O-HA. ANOVA results for A: R RATIO for the groups shows that the variance is significant (F = 329.258, F>0, p = 0) (Table 2). Post hoc Tukey pairwise multiple comparison tests (Table 3)shows the difference between the groups is significant. A: R ratio values decreases as PCO-HA>PCO-COM>PCO O> O-HA among the groups. Linear regression analysis shows that there is a significant moderate negative association between HOMA IR and A: R Ratio ( r= -0.41, p= 0.000). Significant moderate association also observed between WHR&A:R ratio (r = - 0.34, p = 0.000). Between HOMA IR &WHR, the former shows a stronger association with A: R Ratio (Table 4).
Discussion
Obesity is often measured by BMI despite the fact it may not necessarily be the most accurate measure of adiposity.17BMI do not describe the proportion of lean versus adipose tissues related to morbidity and mortality in clinical scenario.18 WHO guidelines also admit that Waist Hip ratio is a better predictor than BMI for assessment of abdominal adiposity.19Obesity is the leading determinant factor for cardiovascular complications among women with PCOS.20 In our study we observed that O-HA group having the maximum WHR thus visceral fat. our observation also depicts that insulin resistance is also found to be maximum in O-HA phenotypes and supports the theory that insulin resistance is a consequence of obesity among PCOS patients.21 Obesity and Adiponectin has an inverse relationship and seems to have a significant role in the pathophysiology of PCOS.22 Level of Serum Adiponectin in PCOS is controversial. Serum Adiponectin values were found to be lower than the control15whereasevidence are there to suggest that it didn’t differ among PCOS and healthy controls.23 Between Obese and non-obese PCOS patients Adiponectin levels were found to be lower in the former group.24 Resistin on the other hand performs its function as a paracrine and endocrine molecule. Resistin is believed to have an inhibitory effect on insulin signalling.25 Serum Resistin level in PCOS is also controversial and data with varied conclusions are available.10 Here authors are willing to suggest that it may be because the levels of Adiponectin and Resistin are not studied among the different phenotypes (Rotterdam Criteria) but most of the studies included PCOS as a whole without considering the phenotypes. Our study shows the Serum Adiponectin and Resistin level varies among the 4 phenotypes of Rotterdam criteria. Adiponectin /Leptin ratio and Adiponectin/Resistin Ratio was found to be significantly lower in women with PCOS when compared to normal control.26 The ratio is significant for both obese and non-obese PCOS pools. Adiponectin/Resistin ratio negatively correlated with HOMA IR.26 Our study reiterates the findings. Study also observed that the ratio of Adiponectin /Resistin ratio significantly differs among the study of the phenotype. A: R ratio was found to be significantly associated with Insulin resistance and WHR.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we would intend to suggest Adiponectin /Resistin as a sensitive parameter for different phenotypes of PCOS. Our study lacks in the estimation of actual fat content and used WHR as a proxy for adiposity. A large sample size with diverse backgrounds is required to understand the actual mechanism behind the pathophysiology of different manifestations of PCOS.
Acknowledgement:
The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the management of Mayo Institute of Medical Sciences and Nims University for providing the infrastructure for this research. The authors also acknowledge the help from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Source of Funding:
Self-financed research project
Conflict of Interest:
The study has no conflict of interest
Authors’ Contribution:
All the authors contributed to this article significantly
Author 1: Designing, data collection, data analysis, article writing
Author 2: Designing, data verification, article editing
Author 3: Data collection, article writing
Ethical Clearance Letter No.:
The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee vide approval letter no. MIMS/Ex/2019/199 dated 19/11/19
References:
- Shroff R, Syrop CH, Davis W, Van Voorhis BJ, Dokras A. Risk of metabolic complications in the new PCOS phenotypes based on the Rotterdam criteria. Fertil Steril. 2007;88(5):1389–1395.
- Ehrmann DA. Polycystic ovary syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(12):1223–1236.
- Zawadzki JA, A. D. Diagnostic criteria for polycystic ovary syndrome: towards a rational approach. Dunaif A, Givens JR, Haseltine FP, Merriam GR, editors. Boston: Blackwell Scientific; 1992. 377–384 p.
- Nestler JE. Role of hyperinsulinemia in the pathogenesis of the polycystic ovary syndrome, and its clinical implications. Semin Reprod Endocrinol. 1997;15(2):111–122.
- Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Dunaif A. Insulin resistance and the polycystic ovary syndrome revisited: an update on mechanisms and implications. Endocr Rev. 2012;33(6):981–1030.
- Rosenfield RL, Ehrmann DA. The pathogenesis of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): The hypothesis of PCOS as functional ovarian hyperandrogenism revisited. Endocr Rev. 2016;37(5):467–520.
- Wu S, Divall S, Nwaopara A, Radovick S, Wondisford F, Ko C, et al. Obesity-induced infertility and hyperandrogenism are corrected by deletion of the insulin receptor in the ovarian theca cell. Diabetes. 2014;63(4):1270–1282.
- Endoh A, Kristiansen SB, Casson PR, Buster JE, Hornsby PJ. The zona reticularis is the site of biosynthesis of dehydroepiandrosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate in the adult human adrenal cortex resulting from its low expression of 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases. J ClinEndocrinolMetab. 1996;81(10):3558–3565.
- Anderson A, Solorzano C, McCartney C. Childhood obesity and its impact on the development of adolescent PCOS. Semin Reprod Med. 2014;32(03):202–213.
- Chen X, Jia X, Qiao J, Guan Y, Kang J. Adipokines in reproductive function: a link between obesity and polycystic ovary syndrome. J Mol Endocrinol. 2013;50(2): R21-37.
- Rasouli N, Kern PA. Adipocytokines and the metabolic complications of obesity. J ClinEndocrinolMetab. 2008;93(11 Suppl 1):S64-S73.
- Ziemke F, Mantzoros CS. Adiponectin in insulin resistance: lessons from translational research. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;91(1):258S-261S.
- Deng Y, Scherer PE. Adipokines as novel biomarkers and regulators of the metabolic syndrome: Adipokines as novel biomarkers and regulators of the metabolic syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1212(1): E1–E19.
- Farshchian F, RamezaniTehrani F, Amirrasouli H, Rahimi Pour H, Hedayati M, Kazerouni F, et al. Visfatin and resistin serum levels in normal-weight and obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2014;12(3):e15503.
- Mannerås-Holm L, Leonhardt H, Kullberg J, Jennische E, Odén A, Holm G, et al. Adipose tissue has aberrant morphology and function in PCOS: enlarged adipocytes and low serum adiponectin, but not circulating sex steroids, are strongly associated with insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96(2): E304-E311.
- Glintborg D, Andersen M, Hagen C, Frystyk J, Hulstrøm V, Flyvbjerg A, et al. Evaluation of metabolic risk markers in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Adiponectin, ghrelin, leptin and body composition in hirsute PCOS patients and controls. Eur J Endocrinol. 2006;155(2):337–345.
- Mukherjee D, Ojha C. Obesity paradox in contemporary cardiology practice. JACC CardiovascInterv. 2017;10(13):1293–1294.
- Prado CMM, Heymsfield SB. Lean tissue imaging: a new era for nutritional assessment and intervention: A New Era for nutritional assessment and intervention. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2014;38(8):940–953.
- Nishida C, Ko GT, Kumanyika S. Body fat distribution and noncommunicable diseases in populations: an overview of 2008 WHO Expert Consultation on Waist Circumference and Waist-Hip Ratio. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2010;64(1):2–5.
- Shen S-H, Shen S-Y, Liou T-H, Hsu M-I, Chang Y-CI, Cheng C-Y, et al. Obesity and inflammatory biomarkers in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2015;192:66–71.
- Dunaif A, Segal KR, Futterweit W, Dobrjansky A. Profound peripheral insulin resistance, independent of obesity, in polycystic ovary syndrome. Diabetes. 1989;38(9):1165–1174.
- Escobar-Morreale HF, Villuendas G, Botella-Carretero JI, Alvarez-Blasco F, Sanchón R, Luque-Ramírez M, et al. Adiponectin and resistin in PCOS: a clinical, biochemical and molecular genetic study. Hum Reprod. 2006;21(9):2257–2265.
- Lecke SB, Mattei F, Morsch DM, Spritzer PM. Abdominal subcutaneous fat gene expression and circulating levels of leptin and adiponectin in polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril. 2011;95(6):2044–2049.
- Pajvani UB, Hawkins M, Combs TP, Rajala MW, Doebber T, Berger JP, et al. Complex distribution, not the absolute amount of adiponectin, correlates with thiazolidinedione-mediated improvement in insulin sensitivity. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(13):12152–12162.
- Shen YH, Zhang L, Gan Y, Wang X, Wang J, LeMaire SA, et al. Up-regulation of PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten) mediates p38 MAPK stress signal-induced inhibition of insulin signalling. A cross-talk between stress signalling and insulin signalling in resistin-treated human endothelial cells: A cross-talk between stress signalling and insulin signalling in resistin-treated human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(12):7727–7736.
- Sarray S, Madan S, Saleh LR, Mahmoud N, Almawi WY. Validity of adiponectin-to-leptin and adiponectin-to-resistin ratios as predictors of polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril. 2015;104(2):460–466.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License