IJCRR - 13(18), September, 2021
Pages: 72-78
Date of Publication: 26-Sep-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic on Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHA) in Karnataka: A Empirical Analysis
Author: Devarajappa S, Khalida Khanum A, Nagaraja S
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHA) programme has been acknowledged and the service utilization has been expanded among Indian Communities since its commencement in 2005 under National Rural Health Mission (NRHM). ASHA workers have been recognized as a viable connection between the community and the health framework regardless of the financial status of community members. Objectives: The present paper discusses the impact of Covid-19 on ASHA workers special on their social and economic status and also examined the challenges faced by ASHA Workers during this pandemic period. Methodology: The researcher has studied 250 ASHA workers randomly from various districts in Karnataka and collected information regarding work difficulties during the Covid-19 pandemic lockdown and its impacts on socio-economic status. For analysis, statistical tools like mean percentage and ANOVA has been employed. Results: It is found in this study that, on average 165 of the respondents faced difficulties frequently during this pandemic and which is also proved in the ANOVA test (i.e., F, 6.39, 3.25> sign) and 80 to 90 per cent of ASHA s opine that Covid-19 has a lot of impact on social and economic status. Conclusion: The present study discusses the economic impacts of the Covid-19 pandemic, majority of respondents felt financial difficulty during the pandemic situation, and said that this situation had also impacted their savings, regular expenditure and jobs of their family members. From this study, it is suggested the Government take some steps to improve the conditions of the ASHA Workers by the means of enhancing their socio-economic status.
Keywords: ASHA workers, National Rural Health Mission, Covid-19 Pandemic, Lockdown, Socio-Economic Status.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
ASHA workers are serving as the first line of defence during the covid-19 pandemic in Karnataka, where around 42000 odd ASHA workers are working in Karnataka. They have successfully mapped 15.9 million households by screening vulnerable persons for covid-19, despite their measly pay and no safety gear. True to the names they have served and spread hopes during this time according to Nalini R.1 In 2005, the National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) had introduced the Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHA), female cadres of India’s community health workers program. The main goal of the ASHA programme is to promote uptake of skilled birth attendance in collaboration with facility-based auxiliary nurse midwives (ANMs) and Anganwadi workers. Each ASHA worker is meant to cover 1000 population and receives the performance and service-based compensation for facilitating immunizations, referral and escort services for institutional deliveries. Other common tasks of ASHA workers in promoting institutional delivery under the national scheme Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY), providing informal counselling, support and following up, advocating for local health needs etc. by Supril et.al.2
The ASHA programme guidelines envisage three different roles for ASHAs. First, ASHAs function as “Link Workers” a bridge between the rural and vulnerable population within the health service centres. Second, ASHAs are to function as a “Service Extension Worker”; whereby they are trained and provided with a kit, that includes commodities such as condoms, oral Chloroquine. Third, they are conceptualized as “Health Activists” in the community to create awareness on health and social detriments and mobilize the community towards local health planning and increased utilization and accountability of the existing health services.
REVIEW OF LITERATURE:
Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs) are community health workers under the national rural health mission of the government of India. They have been contributing and devoting the majority of their time in Covid-19 work as warriors. It is affecting them a lot both socially and economically and they have also faced a lot of health issues not only in India all over the world. The study of Bandyopadhyay S et. al. infection and mortality of health workers worldwide from Covid-19 reveals that 1, 52,888 health workers are infected and 1413 deaths were reported. Infection was mainly in women but deaths mainly in men with 71.6% and 70.8% respectively.4 Niyati and Mandela SN have studied the impact of the pandemic on ASHAs in India. The study is based on the available secondary data, which highlights the various problems faced by the ASHA worker during this pandemic.4 Kingsley JP et. al. in their study of the changing aspects of motherhood in face of the covid-19 pandemic in low and middle-income countries have found that multi-sectorial investments providing high-quality care and available to all segments of the population are needed and pandemic preparedness programme must include action plan resilient material health service.5 Azeez EP et. al. examined the impact of covid-19 on migrant women workers in India. The study reveals that the dismal state of women migrant workers and their families and argues that urgent policy intervention is required to address the impoverishment. Dutta & Fischer studied local governance of covid-19 and social security in rural areas of a developing country. They have examined the elected rural government in coordinating state response in Rajasthan, Kerala and Odisha.6 Bawza V et. al. experienced the covid-19 pandemic in rural Odisha and examined the various challenges faced by the rural people in India. Gumber and Nebhinani examined the impact of covid-19 pandemic child and adolescent mental health and identified that they have been struggling with fear, anxiety and uncertainty, depression and constant worries about their future and they have to face the psychological and emotional brunt of this pandemic. Jelly P et. al. in their study impact of the covid-19 pandemic on the psychological status of pregnant women. The survey result reveals that around 73.6% of pregnant women have a minimal psychological impact and a minimal level of anxiety.7,8 Vora KS et. al. examined the impact of covid-19 women and children and the need for a gendered approach in the vaccine. Taking into account gender-based biological differences; the inclusion of pregnant women is of vital importance for the development of the covid-19 vaccine.9
It is observed from the above literature is that most of the researchers have concentrated the impact of covid-19 on women concerning their health issues. No studies have researched the impact of covid-19 on the socio-economic status of the ASHA workers in India. Therefore the present study gets most important to study the impact of covid-19 on the socio-economic status of ASHA workers.
THE RESEARCH PROBLEM
As of 20th May 2021, Karnataka recorded 23 lakhs Covid-19 cases of which 17.8 Lakhs cases recovered and 23, 854 deaths. During this period, ASHA workers workloads became fourfold and they have been facing many problems socially and economically. In July 2020 all ASHA workers boycotted their work and had indefinite strikes to fulfil their demands.
-
At present, ASHA workers receive a fixed salary of Rs. 4000 Pm from the state government of Karnataka and the central government gives incentive-based pay which depends on 30 plus components but now they are demanding a fixed salary of Rs. 12,000 pm.
-
Every day, they leave home at 9.30 AM after wearing the mask and done by around 2 PM, until that, they don’t drink water even in the scorching heat. On average they cover 25 houses a day, most of the time on the field no washrooms are available ( Reported The Hindu Paper April-2020, Tanu Kulkarni).
-
In Karnataka, two attacks on ASHA workers happened in Bengaluru and Belagavi District in April 2020 while doing service of Covid-19. Therefore the children and husbands of ASHA workers worry a lot about their safety.
-
Many of the ASHA workers infected Covid-19 and the state have lost two ASHA workers in Kalburgi and Yadgeri districts.
Many more problems have been faced by ASHA workers socially and economically. Against this backdrop, there is a need to study the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on the socio-economic status of ASHA workers in Karnataka. 10
OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
The present study “impact of Covid-19 pandemic on the socio-economic status of ASHA workers” sets forth the following objectives;
-
To study the challenges faced by the ASHA workers during the Covid-19 period.
-
To analyse the effects of the Covid-19 pandemic on the socio-economic status of ASHA workers.
RESEARCH HYPOTHESIS
Based on the Objective of the study the following research hypothesis is formulated:
H0: There is no significant impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on the socio-economic status of ASHA workers.
H1: There is a significant impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on the socio-economic status of ASHA workers
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Karnataka is a state in the southwestern region of India. It is the largest state in the south of India having a 6.41 crore population. In this state, more than 42000 ASHA workers are working. Randomly 250 ASHA workers have been taken in select districts of Karnataka for the study from both rural and urban areas. This qualitative study will consist of both primary and secondary data. The qualitative data will be collected through structured interview schedules concerning their socio-economic status and the required secondary data will be collected through Government reports and health Department reports, articles, magazines etc. The Likert scale has been adopted for measuring the opinion of the respondents. Statistical tools like Percentage and mean have been employed for the analysis of the data. And two-way ANOVA was used for testing of hypothesis.
RESULT AND DISCUSSION:
In this section, the researcher has examined the demographic profile of the respondents and perception of ASHA workers towards covid-19 works and the impact of covid-19 on the social and economic status of the ASHA workers.
Demographic analysis of the respondents:
In the demographic analysis, the researcher has examined the religion, family pattern, age, education and marital status of the respondents which have been presented in Table-1.
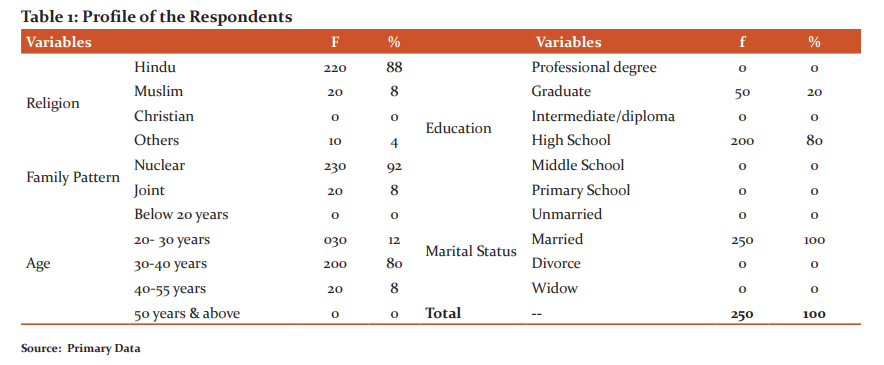
Primary data was collected from 250 ASHA workers working in various villages of the Tumkur District. The study found that 220 (88%) of the respondents belongs to the Hindu religion, 20 (8%) belongs to Islam and 10 respondents belong to others. With regards to the family pattern of the respondents, the majority 230 (92%) of them belongs to nuclear families while 20 (8%) living in joint families. The data were collected concerning the age of the respondents in which the majority 200 (80%) of the respondents belongs to the age group of 30-40 years, 30 (12%) belongs to the age group of 20-30 years and 20(8%) belongs to 40-55 years of age. Concerning the education level of the respondents, the study found that the majority 200 (80%) of the respondents are having educational qualifications of high school while 50 (20%) are graduates. The study also collected information related to the marital status of the respondents and the study found that all respondents that are 250 (100%) were married.
Perception of ASHA workers towards covid-19 work
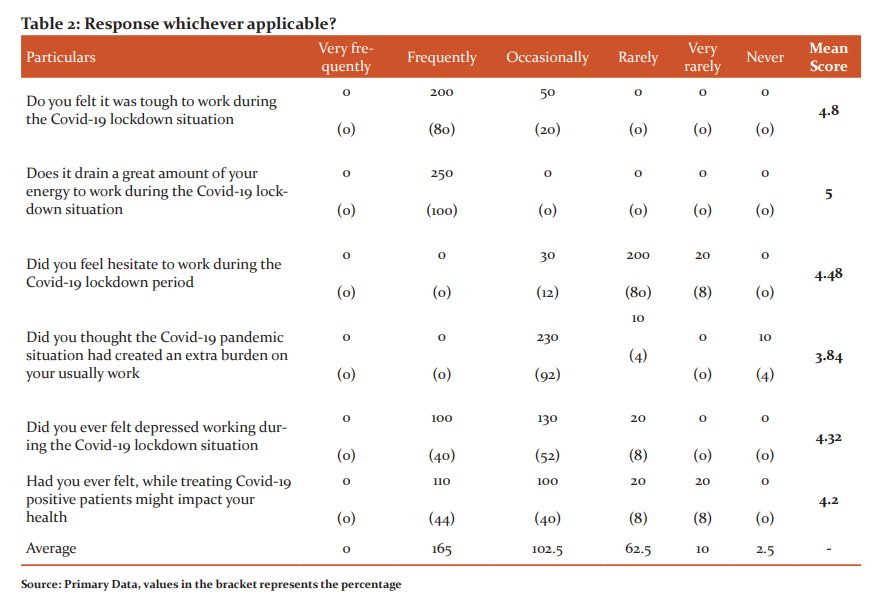
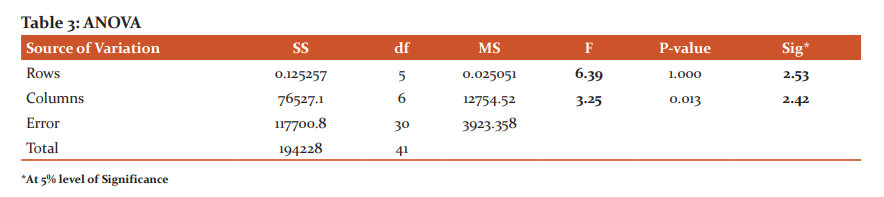
ASHA workers are facing a lot of problems while doing covid-19 work. They are working as warriors in the country. Their perception was collected and presented in Table-2; which represents the data about the respondents’ working conditions during the Covid-19 lockdown. The study found that 200 (80%) of the respondents frequently felt it was tough to work during the Covid-19 lockdown situation. 250 (100%) respondents opine that it was frequently drained a great amount of their energy to work during the Covid-19 lockdown situation. The majority of 200 (80%) of the respondents rarely felt hesitant to work during the Covid-19 lockdown pandemic period. 230 (92%) of the respondents occasionally thought the Covid-19 pandemic situation had created an extra burden in their usual work. 130 (52%) of the respondents occasionally felt depressed working during lockdown situations. 110 (44%) of the ASHA workers frequently felt while treating covid-19 positive patients might be impacted on their health, while 100 (40%) occasionally and 20 (8%) of the respondents rarely felt for same. From this discussion, it is clear that the covid-19 lockdown caused abnormal working situations for many ASHA workers. In table 3, Two-way ANOVA is calculated, which indicates that both between column and rows H0 is rejected. Therefore ASHA workers do have a negative perception towards covid-19 work.
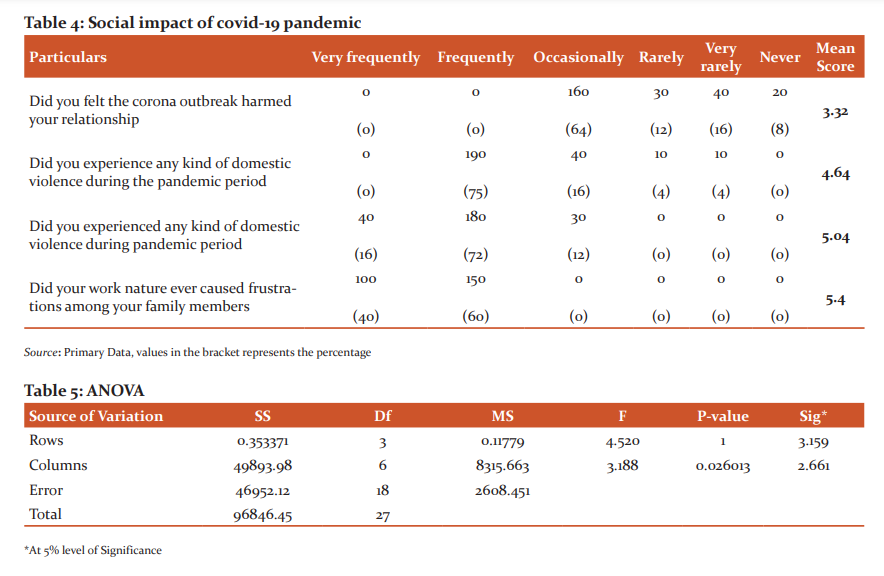
Impact of Covid-19 on Social Status of ASHA workers:
Table No 4 discusses the social impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on ASHA workers. The study found that the majority 160 (64%) of the respondents occasionally felt the corona outbreak harmed their relationships, while 40 (16%) and 20 (8%) very rarely and never felt the same respectively. The study also focuses on the issue of domestic violence experienced by ASHA workers, in this regard 190 (76%) of the respondents frequently experienced an issue of domestic violence during the pandemic period, 40 (16%) of them rarely experienced such problems. The question had been asked regarding the adverse effect of the covid-19 pandemic on the upbringing of children of their family, the study found that 180 (72%) frequently, 40 (16%) very frequently and 30 (12%) occasionally felt covid-19 pandemic harmed the upbringing of their children. 150 (60%) of the respondents opine that their work nature frequently caused frustrations among the family members. The calculated F (Table 5) test both between the column and rows F > Critical value @ 5% level of significance, hence H0 is rejected, hence it can be concluded that covid-19 does have any impact on the social status of ASHA workers.
Impact of Covid-19 on Economic Status of ASHA workers:
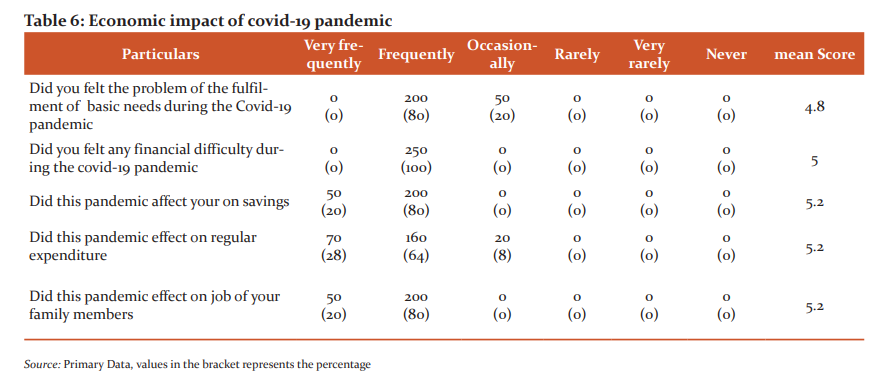
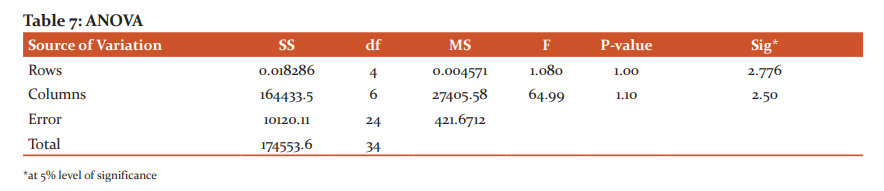
Table No 6 represents economic impact of the covid-19 pandemic on ASHA workers, the majority 200 (80%) of the respondents frequently felt problem of the fulfilment of basic needs during the covid-19 pandemic. It is evident from the above study that all respondents 250 (100%) frequently felt some sort of financial difficulty during the Covid-19 pandemic. Information was also collected regarding the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on the savings of the respondents, as per this, results showed that 200 (80%) of the respondents opine that the Covid-19 pandemic has frequently affected their savings. With regards to the pandemic effect on regular expenditure, the study found that 160 (64%) of the respondents are frequently affected during the pandemic lockdown. Finally, questions had been asked regarding the pandemic effect on the jobs of their family members. The study found that 200 (80%) of the respondents’ family members were lost their jobs or mode of income that they were dependent on like business and they have unquestionable relies on the salary of ASHA workers. From table 7, it is clear that the F value between rows and between columns is p>0.05. Hence H0 should not be rejected, therefore it can be concluded that covid-19 does not have an impact on the economic status of ASHA workers.
CONCLUSION
ASHA Workers playing an important role in realizing the objectives of the National Rural Health Mission (NRHM). Their role is remarkable during the situations like Covid-19 pandemic. As found in the present study, out of 250 ASHA Workers selected, 200 of them frequently felt it was tough to work during Covid-19 lockdown situation still they performed their duties properly, which is proved through the present study that 200 respondents rarely felt hesitate to work during this situation and 230 of them occasionally thought that pandemic situation had created an extra burden on their usual work. But concerning the social impacts of the Covid-19 pandemic, some of the respondents felt negative impacts on their relationships, experienced domestic violence and felt negativity about the upbringing of the children of their families. The present study also discusses the economic impacts of the Covid-19 pandemic, 200 respondents frequently felt the problem of the fulfilment of basic needs during the Covid-19 pandemic, all most all respondents felt financial difficulty during the pandemic situation and said that this situation had also impacted their savings, regular expenditure and jobs of their family members. From this study, it is suggested the Government take some steps to improve the conditions of the ASHA Workers by the means of enhancing their socio-economic status other initiatives.
Acknowledgement: We acknowledged gratefully all 250 ASHA workers who have responded promptly to our research questions and we are also grateful to the authors, editors and publishers of all the articles cited in this manuscript.
Source of Funding: The research has been done with the own funds of the authors.
Conflict of Interest: There is no conflict of interest in this study. The study is confined to examine the impact of Covid-19 on ASHA Workers.
Authors Contribution: The study examined the challenges faced by ASHA Workers during this Covid-19 period and its impact on their socio-economic status, the results of this research is suggested to the Government to take appropriate action.
References:
1. Articles by Nalini Ravichandran | The Wire: The Wire News India, Latest News, News from India, Politics, External Affairs, Science, Economics, Gender and Culture [Internet]. [cited 2021 Jul 9]. Available from: https://m.thewire.in/byline/nalini-ravichandran
2. Community health workers in rural India: analysing the opportunities and challenges Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs) face in realizing their multiple roles | Human Resources for Health | Full Text [Internet]. [cited 2021 Jul 9]. Available from: https://human-resources-health.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12960-015-0094-3
3. Bandyopadhyay S, Baticulon RE, Kadhum M, Alser M, Ojuka DK, Badereddin Y, et al. Infection and mortality of healthcare workers worldwide from COVID-19: a systematic review. BMJ Global Health. 2020 Dec 1;5(12):e003097.
4. RAS | Impact of the Pandemic on Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHA) in India [Internet]. [cited 2021 Jul 9]. Available from: http://www.ras.org.in/impact_of_the_pandemic_on_accredited_social_health_activists_%28asha%29_in_india
5. Kingsley JP, Vijay PK, Kumaresan J, Sathiakumar N. The Changing Aspects of Motherhood in Face of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Matern Child Health J. 2021 Jan;25(1):15–21.
6. P AAE, Negi DP, Rani A, P SKA. The impact of COVID-19 on migrant women workers in India. Eurasian Geography and Economics. 2021 Jan 2;62(1):93–112.
7. Experience of the COVID-19 pandemic in rural Odisha, India: knowledge, preventative actions, and impacts on daily life | medRxiv [Internet]. [cited 2021 Jul 9]. Available from: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.11.20.20235630v1
8. Gumber A, Bulsari S. COVID-19 Impact on Indian Economy and Health: The Emergence of Corona-Economics. :6.
9. (PDF) Impact of COVID-19 on women and children health and the need for a gendered approach for vaccine development [Internet]. [cited 2021 Jul 9]. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343017053_Impact_of_COVID-19. _on_women_and_children_health_and_the_need_for_a_gendered_approach_for_vaccine_development
10. Kulkarni T. ASHA workers in Karnataka spend hours tracing COVID-19 contacts daily. The Hindu [Internet]. 2020 Apr 24 [cited 2021 Jul 9]; Available from: https://www.thehindu.com/news/cities/bangalore/they-go-where-others-fear-to-tread/article31428115.ece
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License