IJCRR - 13(18), September, 2021
Pages: 21-26
Date of Publication: 26-Sep-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Pattern Intensity Index, Dankmeijer's Index and Furuhata's Index of Palmar Dermatoglyphics in Patients with Bronchial Asthma
Author: Deepa T K, Sampson Ursula, Sreedharan Ranjith
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Asthma is a chronic airway inflammation, characterised by variable airway obstruction and reduced lung function and leading to wheezing and shortness of breath. Both asthma and dermatoglyphics are influenced by genetic factors. Objective: This study was done to find out the Pattern intensity index, Dankmeijer's index and Furuhata's index of palmar dermatoglyphics in patients with bronchial asthma. Methodology: Palm prints were obtained from both hands of 250 clinically diagnosed bronchial asthma patients who attended the OPDs of Respiratory medicine and Pediatrics of M E S Medical College, Perinthalmanna. Age and sex-matched controls were selected from the staff and students at the same college, without any respiratory or chronic diseases. The study included the dermatoglyphic parameters like a-b ridge count, distance, breadth, pattern intensity index, Dankmeijer's index and Furu Hata's index. Result: The Pattern intensity index and Furuhata's index was more in bronchial asthma patients and male patients showed higher value than females. Dankmeijer's index was less in bronchial asthma patients than controls, female cases showed higher value than male cases. Conclusion: Decrease in the mean value of a-b count, distance, breadth and an increase in the value of Pattern intensity and Furuhata's index can be used as a tool for early identification of at-risk individuals with or without a family history of bronchial asthma.
Keywords: a-b count, Bronchial asthma, Dankmeijer’s index, Dermatoglyphics, Furuhata’s index, Pattern intensity index
Full Text:
Introduction
Dermatoglyphics is the study of configurations of epidermal ridges on the fingers, palms, soles and toes. The word dermatoglyphics is a Greek word, 'derma' means skin and 'glyphic' means carvings, which was coined by Cummins and Midlo in 1926.1The fingerprint, once formed, is very resistant to later prenatal or postnatal influences, thus making it an ideal feature for genetic studies and also for the identification of individuals. Ethnic and racial groups manifest highly significant variations in the occurrence of dermatoglyphic configurations. These include pattern frequencies on the palm, finger ridge counts, and differences between frequencies of patterns on the right and left fingers.
Asthma is a complex, chronic inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs and its clinical control rate is at present lower than that recommended in the GINA guide, making this a serious public health issue.2It has been evaluated that more than 300 million people across the globe suffer from this disorder.3Recently, the morbidity and mortality rates of asthma have been constantly rising worldwide, and 1–18% of the populations of different countries are known to have asthma .4,5The increasing prevalence of asthma is related with genetic changes and gene-environment interactions.6 It has a complex pathogenesis and is dependent on immunological, genetic and environmental factors, and recent studies indicate a hereditary basis.
The dermatoglyphic study has now been established as a useful diagnostic tool in medicine and provides important insights into the inheritance and embryologic development of many clinical disorders. As dermatoglyphic patterns and bronchial asthma are determined genetically, both may have a link that could help identify individuals with bronchial asthma.
Dermal ridges are formed between the 10th to 16th weeks of fetal development and, once formed remains permanent and never changes throughout the life, unless the skin is damaged to a depth of 1mm.7Its development coincides with the regression of embryonic volar pads on fingers. The type and size of patterns are mostly determined by the size and timing of subsidence of these pads.8 Palmar dermatoglyphics has been studied in various diseases and alterations in normal patterns have been noted which is genetically determined. The importance of dermatoglyphics is to identify those people with a genetic predisposition to the development of certain diseases like bronchial asthma. The present study was conducted to elucidate Pattern intensity index, Dankmeijer’s index and Furuhata’s index of palmar dermatoglyphics in bronchial asthma patients.
Materials and Methods
A case-control study was performed in the Department of Anatomy, MES Medical College, Perinthalmanna, Kerala. The study population includes 500 subjects. Among them, 250 were clinically diagnosed bronchial asthma patients, who attended the OPD’s of Pediatric and Respiratory medicine department, M E S Medical College. Age and sex-matched 250 controls were selected from the students, staff and their children of the same institution. Ethical clearance was obtained from the Institutional Ethical Committee of MES Medical College for conducting the study. The details of the study were explained to the participants, and informed consent was taken from them and, parents in the case of children. The demographic data were collected from the medical records and a questionnaire was given to the participants.
Inclusion criteria
-
Clinically diagnosed case of bronchial asthma.
-
Both male and female patients in the age group 6 – 60 years.
-
Subjects were residents of North Kerala.
Exclusion criteria
-
Subjects with a known case of chromosomal abnormalities.
-
Subjects who failed to deliver legible fingerprint patterns of one or both hands.
-
Subjects whose finger ridges were obscured by scars, deformities, birth defects and diseases on one or both hands.
-
Any other systemic diseases
Methodology
The palm print from both hands of case and control was done using the Ink and paper method adopted from Cummin and Midlo.9The subjects were asked to wash their hands with soap and water. A small paste of the link was spread as a thin film on a glass sheet using a roller. With a relaxed arm, they were required to place their palm on the inking sheet so that the entire palm was evenly covered with ink. Then the right palm was placed from the wrist to the tip of the fingers on the printing sheet, with minimum pressure applied on the dorsum of the hand. The same procedure was repeated for the left palm using another finger and a palm printing sheet. The print for each fingertip was taken on the same paper for the second time. The subjects were asked to keep their thumb with the ulnar edge downward and rolled toward the body. Other digits were placed with the radial edge downward and rolled away from the body. The fingerprints were taken onto the respective pre-labeled squares, one for each of the ten fingers. The palmprint obtained were subjected to detailed dermatoglyphic analysis with the help of a magnifying hand lens. The fingertip patterns were then classified into whorls, loops, and arches, according to the number of triradiiasper Galton’sbasic pattern.10 The dermatoglyphic parameters like a-b count, distance, breadth, Pattern intensity index (PII), Dankmeijer’s index (DI) and Furuhata’s index (FI) were calculated.
Ridge Counts: - They were counted between two digital triradii. a, b, c and d are alphabets described to the triradial point located at the base of the index, middle, ring and little finger respectively. The ridge counts most frequently obtained is between triradii a and b, and is referred to as the a-b ridge count.11The a-b distance is measured in millimetres between the triradius and the b triradius. Ridge breadth is the distance from the centre of one ridge furrow to the centre of the next furrow, along a line at the right angle to the ridges. The ridge breadth is obtained by the following calculation.12,13
DL + DR / (CL + CR + 2)
where
DL = left a-b distance in millimeter
DR = right a-b distance in millimetre
CL = left a-b count
CR = right a-b count
plus 2, as the two triradii are not counted.
Pattern Intensity Index (PII): - It is calculated by counting the triradii present in a given area. The value of pattern intensity is stated either as the number of triradii per individual or the average number of triradii per finger.14
The PII is calculated after Cummins and Midlo as follows.9
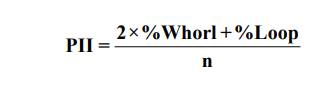
Dermatoglyphics can be used as a useful adjunct to aid in preliminary medical diagnosis. The present study shows an increased PII, FI and a decreased DI, a-b count and distance in bronchial asthma patients compared with controls. In the dermatoglyphic pattern, any deviation from the regular pattern will be strongly indicative of a particular anomaly. Although no dermatoglyphic patterns can be studied alone in making a diagnosis, several patterns, when combined, can be used to establish an uncertain diagnosis or point to a disorder that could be identified only later. We can conclude that increase in the number of whorls and a decrease in the number of arches in bronchial asthma patients can be used as a tool for the early identification of at-risk individuals with or without a family history of bronchial asthma.Where ‘n’ is the number of fingers.
Dankmeijer’s Index (DI): - It is an index expressing the total frequency of arches divided by the total frequency of whorls x 100 as follows.15
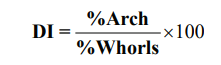
Furuhata’sIndex (FI): - It is calculated by dividing the total frequency of whorl with loops x 100 as follows.1
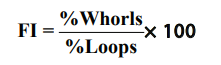
Result
The dermatoglyphic parameters of 250 bronchial asthma patients and 250 healthy controls were studied, compared, and analyzed statistically.
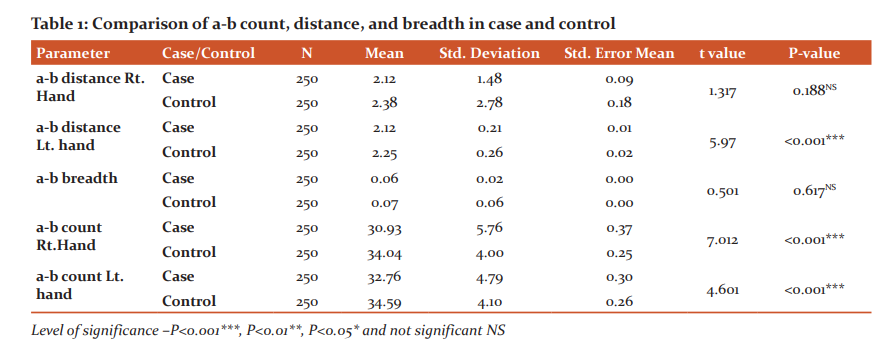
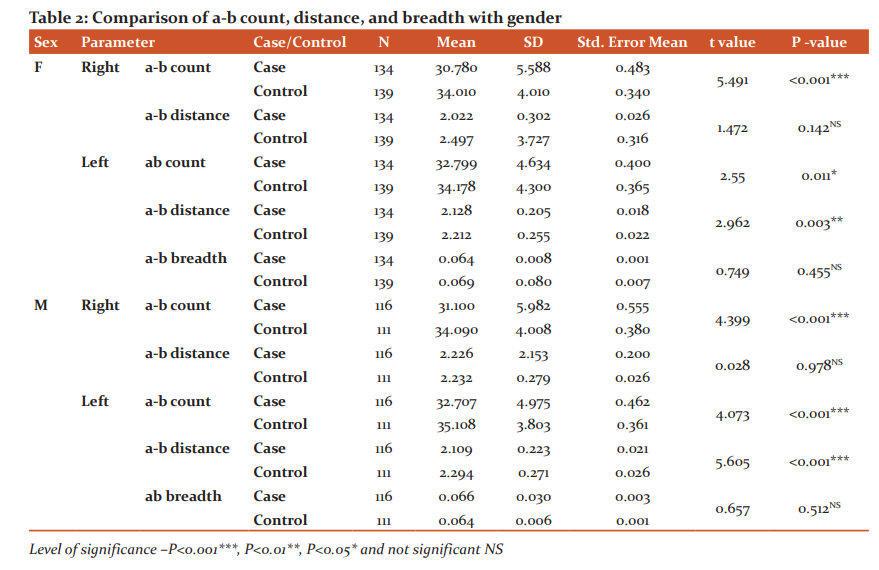
Table 1 shows the comparison of a-b count, a-b distance and a-b breadth in case and controls. It was seen that the mean value of a-b count of the right hand (30.93±5.76) and left hand (32.76±4.79) hand were less in bronchial asthma patients compared with controls (34.04±4.00, 34.59±4.10) and shows highly significant p-value (P≤0.001) on both sides. The mean value of a-b distance was less in the case on both hands (right 2.12±1.48, left 2.12±0.21) than the controls (right 2.38±2.78, left 2.25±0.26) but the value is significant only on the left side (P≤0.001). The a-b breadth in the case was statistically insignificant (P=0.617) when compared with the controls.
Table 2 shows the comparison of a-b count, a-b distance and a-b breadth with gender. In both sexes, a significant reduction was observed in the mean values of a-b count on both palms (Right, P≤001; Left P=0.011) and a-b distance on the left palm (P=0.003).The mean value of a-b breadth among the groups in both genders were found to be statistically insignificant (Female, P=0.455; Male, P=0.512).
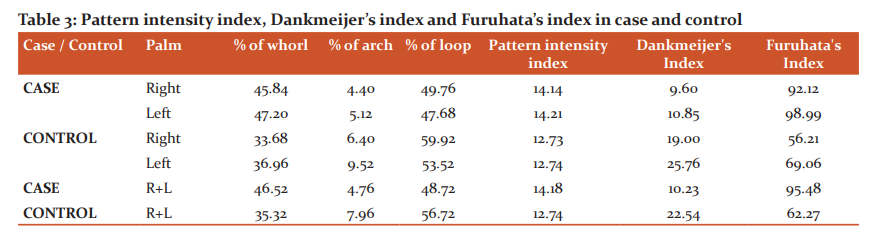
Table 3 shows the frequency percentage of fingertip patterns in both hands combined in case (46.52% of whorls, 4.76% of archers and 48.72% of loops) and controls (35.32% of whorls, 7.96% of archers and 56.72% of loops). The Pattern intensity index (14.18) and Furuhata’s index (95.48) were higher in bronchial asthma patients than controls (12.74, 62.27). But the Dankmeijer’s index was less in bronchial asthma cases (10.23) than in controls (22.54).
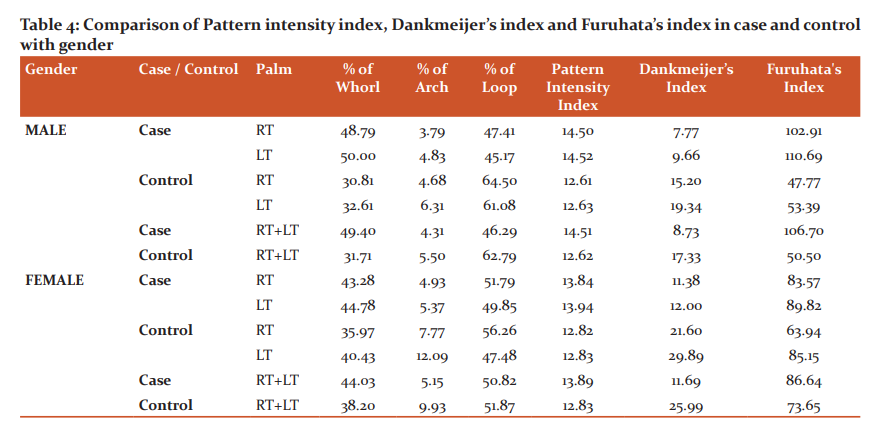
Table 4 shows the various indices compared with gender. Male cases (14.51) showed a higher value for Pattern intensity index and Furuhata’s index (106.70) than female cases (PII 13.89, FI 86.64). The Dankmeijer’s index is more in the female cases (11.69) than the male cases (8.73).
Discussion
Dermatoglyphics is presently being investigated to demonstrate not unique individual differences but also to give insight into group differences. Therefore, it appears that dermatoglyphics are a part of the picture that can bring some understanding to how persons are developmentally different. It turned the attention of medical researchers when it was found that many patients with chromosomal aberrations had unusual ridge formation. By the advancement of human genetics, dermal pattern indices, together with clinical features, are being employed for the diagnosis of many inherited diseases.
In the present study, the a-b count, distance and breadth is less in bronchial asthma patients than in controls. Sreenivasuluet al.16 and Amrut et al.17 found that the a-b count was more in bronchial asthma patients and their first-degree relatives. Melloret al.18 found that the digital-palmar dermatoglyphics in schizophrenics exhibited significantly higher levels of fluctuating asymmetry in palmar a-b count than controls. Shirahatti et al.19 found that the a-b count difference between diabetes mellitus cases and the controls in both right and left hand was statistically not significant. In the present study, when we compare with gender, in both sexes a significant reduction was observed in the mean values of a-b count on both palms and a-b distance on the left palm. Since no previous study was available on a-b distance and a-b breadth in respect to gender in bronchial asthma, the present results could not be compared.
The Pattern intensity index and Furuhata’s index is more in bronchial asthma patients and male patients show higher value than female cases. Dankmeijer’s index is less in bronchial asthma patients than controls, female cases showed higher value than males. Bansal et al.20conducted a study in Jat-Sikh Males and found that there is not much difference in the values of various indices calculated for patients suffering from bronchial asthma. The increased value of PII and FI in the present study envisaged a higher prevalence of whorls in bronchial asthma patients.
In both gender, PII and FI were more in cases as compared to controls whereas DI was less in cases. This shows an increased frequency percentage in the number of whorls in both hands combined and a decrease in the number of arches in male patients. Several studies were conducted among the various groups for the PII, DI and FI. Ibewuikeet al.21 found that the PII of right and left hands was higher in uterine leiomyoma patients as compared to the controls. Wijerathne et al.claimed that the PII, DI and FI are found higher in males compared to females in the Sinhalese when compared with other populations. Shirahatti et al.19 found that the DI was significantly more in both male and female diabetes mellitus cases compared with controls, FI significantly more in cases of both sexes and Pattern intensity index significantly more in female cases and controls as compared to males.
Conclusion
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful to all the individuals who donated their prints for the study. We are incredibly grateful to the Respiratory Medicine and Pediatric department of MES Medical college for allowing us access to individuals used in the study. We also express our deepest gratitude to all authors of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Source of Funding- None
Conflict of Interest - There are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Clearance Letter No. IEC/MES/76/2014
Authors’ Contribution
Author 1- Carried out the experiment.
Author 2 and Author 3- Conceived and designed the study.
References:
-
Cummins H, Midlo C. Palmar and plantar epidermal ridge configurations (dermatoglyphics) in European Americans. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1926 Oct;9(4):471-502.
-
Zhu S, Li P, Suo H, Dong J, Cui L. Association of ADAM33 gene polymorphisms with asthma in Mongolian and Han groups in Inner Mongolia. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018 Dec 1;25(8):1795-99.
-
Miller SM, Ortega VE. Pharmacogenetics and the development of personalized approaches for combination therapy in asthma. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2013 Oct 1;13(5):443-52.
-
Bousquet J, Bousquet PJ, Godard P, Daures JP. The public health implications of asthma. Bull World Health Organ. 2005;83:548-54.
-
Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. Available online: http://ginasthma.org/ (accessed on 3 April 2018)
-
Koppelman GH. Gene by environment interaction in asthma. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2006 Mar 1;6(2):103-11.
-
Adamu LH, Taura MG. Embryogenesis and applications of fingerprints-a review. Int J Health Ass. 2017 Jun 27;1(1):1-8
-
Penrose LS, Loesch D. A study of dermal ridge width in the second (palmar) interdigital area with special reference to aneuploid states. J Ment Defic Res. 1967;11(1), 36–42.
-
Cummins H, Midlo C. Fingerprints, palms and soles: an introduction to dermatoglyphics. 1st ed. New York: Dover Publications; 1961.p. 178-81
-
Galton F. Fingerprints. Macmillan and Company; 1892.
-
Prabhu N, Issrani R, Mathur S, Mishra G, Sinha S. Dermatoglyphics in health and oral diseases-A review. J Res Adv Dent.2014;2(4):1-5 2014; 3:2:20-6
-
Penrose LS. Finger-print pattern and the sex chromosomes. Lancet. 1967 Feb 11;289(7485):298-300.
-
Floris GU. On the breadth of dermal ridges in Sardinians. J Biol Res. 2012;85(1):114-15
-
Basu A, Namboodiri KK. The relationship between total ridge count and pattern intensity index of digital dermatoglyphics. Am J PhysAnthropol. 1971 Mar;34(2):165-73
-
Wijerathne BT, Rathnayake GK, Adikari SC, Amarasinghe S, Abhayarathna PL, Jayasena AS. Sexual dimorphism in digital dermatoglyphic traits among Sinhalese people in Sri Lanka. J Physiol Anthropol. 2013 Dec;32(1):1-9.
-
Sreenivasulu K, Kumar PA, Nagaraju GC, Ravindranath G, Gaikwad MR. A study of palmar dermatoglyphics of bronchial asthma patients and their first-degree relatives in Kurnool district. Indian J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2012 Jan 1;26(1):2-5.
-
Mahajan AA, Gour KK, Thakare AE. The dermatoglyphic patterns in patients of the bronchial asthma-a qualitative study. Int J Biol Med Res. 2011;2(3):806-07.
-
Mellor CS. Dermatoglyphic evidence of fluctuating asymmetry in schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 1992 Apr 1;160(4):467-72.
-
Shirahatti A, Dixit D. A cross-sectional study of palmar dermatoglyphic pattern in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus at a hospital in South India. Indian J Clin Anat Physiol. 2019 Dec 15;6(4):503-8.
-
Bansal IJ, Bector I. A comparative study of the finger dermatoglyphics of normal and asthmatic patients (male jatsikhs). Anthropologie. 1975 Jan 1:213-8.
-
Ibewuike OH, Olotu EJ, Paul JN. Dermatoglyphic Digital Patterns and Pattern Intensity Index in Uterine Leiomyoma. Int J Pharma Res Health Sci. 2019;7(2):2923-7.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License