IJCRR - 13(17), September, 2021
Pages: 167-178
Date of Publication: 12-Sep-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Protective Effect of Citrus reticulata and Citrus Sinensis against Diabetes Associated Alzheimer's Disease: Identification of a Better Model
Author: Navya RY, Madhuri D, Chandrasekhar KB
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Stress became a global challenge that leads various chronic diseases especially neuro-degeneration diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. Polyphenolic compounds were reported to possess protective effects against the cellular stress and can be used in the management of stress associated chronic diseases. Objectives: Our current work is aimed to design a better model to induce Alzheimer's disease through Diabetes and to screen the protective effect of Citrus reticulata and Citrus sinensis against diabetes-associated Alzheimer's disease. Methods: A comparative study was carried out on Streptozotocin - Nicotinamide induced Diabetes and High fat diet-induced Diabetes. Various biochemical, behavioural and histological parameters are considered to evaluate the best model for the diabetes-induced Alzheimer's disease along with the protective effect of selected Citrus reticulata (Tangerine oil) and Citrus sinensis (Orange oil) against diabetes-associated memory deficits. Results: Results showed that the high-fat diet model succeeded to create diabetes-associated memory impairment compared to Streptozotocin - Nicotinamide model. Detailed investigation of all the selected parameters of Tangerine and Orange oil groups by comparing with a standard group showed statistically significant (p>0.0001) improvement in the Alzheimer's disease. Conclusion: To conclude, all the biochemical, behavioural and histological data declared that the high-fat diet model is the best model for studying diabetes-associated memory deficits in animals. It is also apparent that the oil of Citrus sinensis is more potent than Citrus reticulata to give protection against oxidative stress and subsequent improvement of memory and other physiological parameters. The antioxidant property of the oils may be responsible for the reported activity.
Keywords: Diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, Animal model, Citrus sinensis, Citrus reticulata
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is one of the most prevailing causes of death in the elderly population. Reports have suggested that by 2050, more than 11 crores of the world population would be suffering from AD. 1 One of the most common risk factors for AD is Diabetes Mellitus. Studies have also forecasted that by 2050, more than 33 crores population of the world would suffer from Diabetes. Among them, more than 7 crores population will be in India. Since AD and Diabetes are interlinked, the present study was carried out to find out a mono therapeutic approach for both AD and Diabetes. 2 Antioxidants provide ameliorating effect against degenerative disorders. Since natural antioxidants are comparatively safer than synthetic ones, we employed extracts from the peels of citrus fruits as they are rich in antioxidants and also one of the widely consumed fruits. 3 The flavonoids of citrus fruits especially polymethoxyflavones have wide therapeutic activity and are abundantly found in Citrus sinensis (sweet orange) and Citrus reticulata (mandarin oranges). 4,5 The present study was also designed to develop a better model to induce Alzheimer’s disease through Diabetes. A comparative study was therefore carried out on Streptozotocin - Nicotinamide induced Diabetes and high fat diet-induced Diabetes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Collection and Preparation of extracts
The volatile oils of Citrus reticulata (Tangerine oil) and Citrus sinensis (Orange oil) were directly procured from katyani exports, New Delhi. An o/w emulsion of Tangerine and Orange oil was prepared by bottle method, using Tween 80 as emulsifier at 1:3 ratios. Later to the organic phase, water was added little by little with vigorous shaking until a final concentration of 250mg/ml was obtained.
Animals
6 weeks old male Wistar rats weighing 50-80 g and adult male Wistar rats weighing 160 – 200g were procured from the Central Animal House facility of CES college of Pharmacy. The animals were housed in polyacrylic cages [38´23´10cm] with not more than 4 animals per cage under the temperature of 25 ± 2 °C and relative humidity 45–55% and maintained on a 12:12 h light: dark cycle and had free access to food and water. Approval No.: IAEC/ CESCOP/ 2017-15.
Induction of Diabetes associated Alzheimer’s disease by STZ – Nicotinamide model
The fasting blood glucose levels were determined before the start of the experiment. Diabetes was induced in overnight fasted rats by a single i.p injection of 45mg/kg of Streptozotocin (STZ). Two hours before STZ injection, 100mg/kg of Nicotinamide was administered orally. Hyperglycaemia was confirmed by elevated glucose levels in plasma after 48 hours by using the Glucose oxidase (GOD)-peroxidase (POD) method. 6
Induction of Diabetes associated Alzheimer’s disease by High Fat Diet model
Initially, a 35% fat diet was given for 2 months. Since it was not enough for raising lipids and glucose levels, the high-fat diet was continued for another 2 months with 45% fat. After continuing the diet for 16 weeks, diabetes and hyperlipidemia induction was confirmed by estimation of Serum glucose and lipid levels. 7
Grouping of animals
Animals were divided randomly into seven groups (Table 1), each group containing 12 animals that were equally distributed for both models. Doses were selected based on previous studies.
Bodyweight: The body weight of animals was determined once every 7 days to analyze the effect of STZ, HFD and citrus extracts.
Biochemical parameters: Serum was collected and used to estimate Glucose (Glucose oxidase aminophenazone or GOD- PAP method), Cholesterol (cholesterol oxidase/peroxidase aminophenazone or CHOD-PAP method), Triglycerides (GPO-TOPS method), and HDL (Precipitation method) as per kit. Samples were analysed using Semi-auto Analyzer (MISPA EXCEL, Chemistry Analyzer). Mathematically VLDL and LDL were calculated using the formula: VLDL = Triglycerides ÷ 5 and LDL = (cholesterol – (HDL+VLDL)).
Behavioural studies
Morris Water Maze: In this experiment, the time required to locate the hidden platform i.e. escape latency was measured. On the 5th day, the hidden platform was removed and the rat was placed randomly from one of the three quadrants and the percentage of time spent in the target quadrant was measured as an index of memory retention. The test was performed every week from induction of hyperglycemia till drug treatment for 28 days. 8
Elevated Plus Maze: In this experiment, the total number of entries into open arms and the total time spent in open arms were recorded manually for 5 minutes. Entry into an arm was considered when all the four paws were placed inside. The training was given for four consecutive days and the test was done on the 5th day of every week from induction of hyperglycemia till drug treatment for 28 days. 9
Brain homogenate was prepared according to the standard protocols and used to estimate acetylcholinesterase, lipid peroxidation, reduced glutathione, catalase and superoxide dismutase levels. 10
In vivo antioxidant studies
Lipid Peroxidation: The malondialdehyde content, a measure of lipid peroxidation, was assayed by Willls method with little modifications. The absorbance of the sample mixture was quantitatively measured at 532nm and it is expressed as the number of moles of malondialdehyde per mg protein using an extinction coefficient of 1.56×105 /M cm. 11
Estimation of reduced glutathione: Reduced glutathione was assayed by the method of Jollow et al. The yellow colour developed was read immediately at 412 nm and the reduced GSH levels were expressed as nmol/mg protein. 12
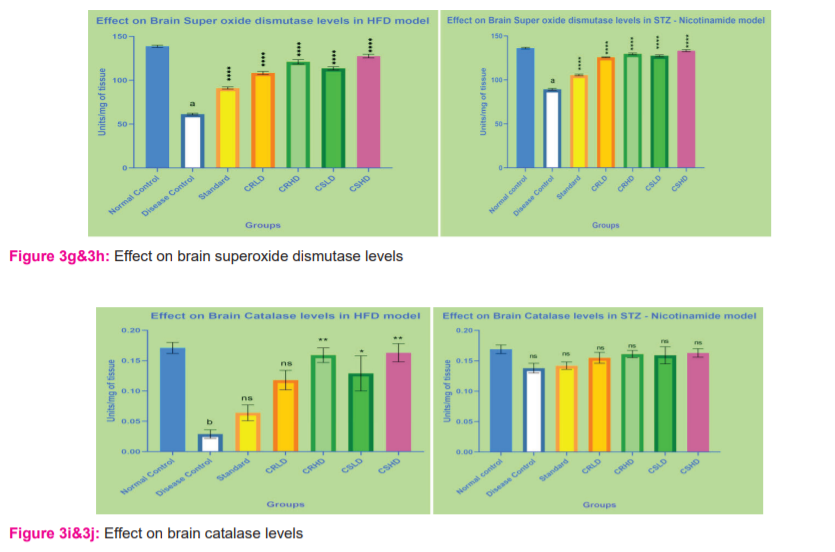
Estimation of superoxide dismutase: Cytosolic superoxide dismutase activity was assayed by the method of Kono. The auto-oxidation of hydroxylamine was observed by measuring the change in optical density at 560 nm for 2 min at 30/60 s intervals. Superoxide dismutase activity was expressed as units/mg of protein. 13
Estimation of Catalase: Catalase activity was assayed by the method of Claiborne (1985). Changes in absorbance were recorded at 240 nm. Catalase activity was expressed as units/mg of protein. 14
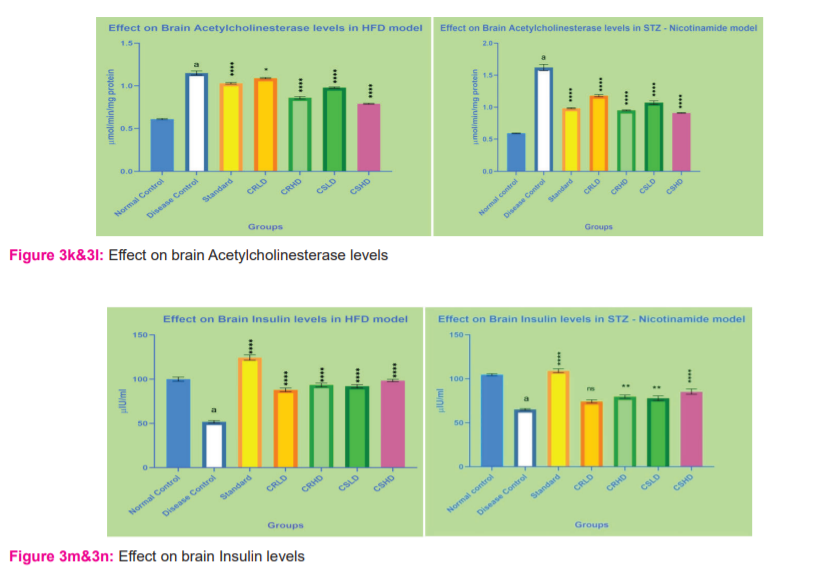
Estimation of Acetylcholinesterase levels in the brain: Cholinergic dysfunction was assessed by quantitative measurement of acetylcholinesterase levels in the brain were performed according to the method of Ellman et al. (1961). The change in absorbance was measured at 412 nm for 2 min. Results were calculated using the molar extinction coefficient of the chromophore (1.36×104 M−1 cm−1) and expressed as µmol/min/mg protein. 15
Estimation of insulin levels in the brain: This experiment was done according to the protocol described by Tamas Csont. The optical density was measured at 450 nm within 30 minutes and the values were expressed as µIU/ml. 16
Histopathology
Neurodegeneration: 30-μm thickness sections taken from cortex and hippocampus, were deparaffinized and hydrated to water. Later stained for 3-5 minutes in Hematoxylin, Eosin (HE stain) and processed using water, 95% alcohol and xylene followed by microscopic examination under 45x. 17
Amyloid-beta plaques deposition: This procedure is done according to Yamaguchi. The ThS-stained brain sections were mounted on slides and then cover-slipped. All histochemical samples were photographed with a Zeiss laser scanning microscopes 700 (Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, German), and results were analyzed using Image J software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA).18
Screening of β-secretase in Alzheimer’s disease: A multi-well microtiter-plate based colourimetric assay for the screening of BACE1 inhibitors was followed as per Mancini et al. Extracts prepared were used in this assay to screen for beta-secretase inhibitors. Standardization of bioassay was carried out to adjust various components to get optimum results and reading. Absorbance values measured at 410 nm were corrected via the corresponding blank sample. 19
Establishment of HeLa cell culture: The HeLa cell line was purchased from National Centre for Cell Science (NCCS) Pune, Maharashtra, India. The processed and suspended cells were observed under an inverted microscope and stored in a CO2 incubator with the cap of the flask slightly uncapped for CO2 to reach the cells. 20
Statistical Analysis
The results were expressed as Mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was calculated using Two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons and statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. P > 0.05 was considered non significant (ns). The analysis was carried out using Graph Pad Prism software of version 8.4.3. Values are represented as **** - p<0.0001, *** - p<0.001, ** - p<0.01, *- p<0.05 in comparison with disease control and represented as a P < 0.0001 b P < 0.001, c P < 0.01, d P < 0.05 in comparison with normal control.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Effect of High Fat Diet (HFD), Streptozotocin (STZ), Citrus reticulata and Citrus sinensis on the animals
Bodyweight
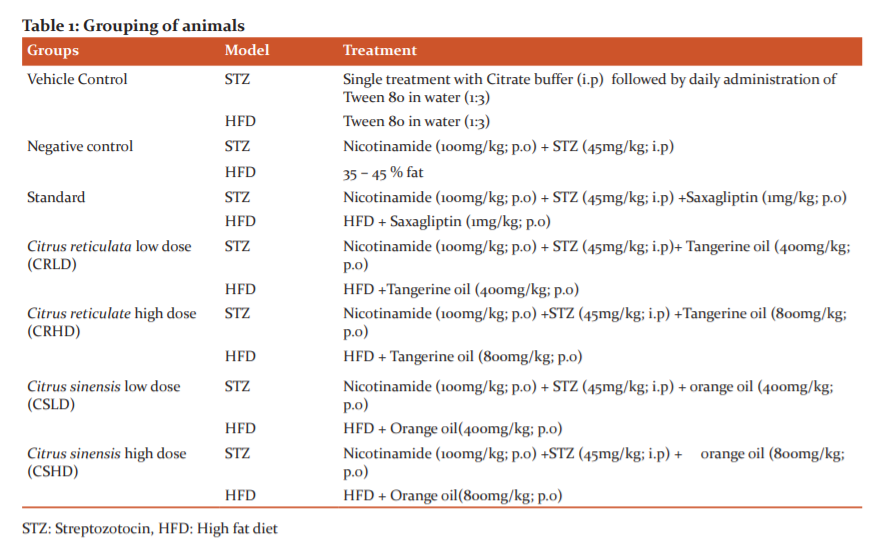
Animals treated with HFD, showed a significant increase (p>0.0001), while those treated with STZ - Nicotinamide, showed a significant decrease (p>0.0001) in body weight of disease control when compared to that of normal control. By the end of the treatment, all the standard and treatment groups of HFD showed significant reduction (p>0.0001) and those of STZ showed significant increase (p>0.0001) when compared to disease control (Figure 1a&1b).
Serum glucose levels
When the animals were treated with HFD and STZ - Nicotinamide, there was a significant increase (p>0.0001) in the serum glucose levels of disease control when compared to that of normal control. By the end of the treatment, all the standard and treatment groups showed significant reduction (p>0.0001) in the serum glucose levels compared to disease control. Serum glucose levels were found to be slightly high in STZ – Nicotinamide model when compared to that of the HFD model (Figure 1c&1d).
Lipid Profile
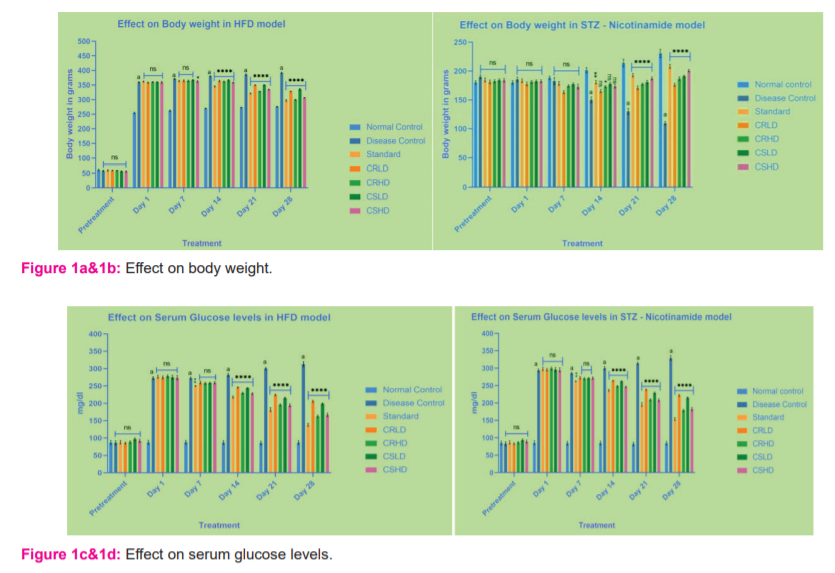
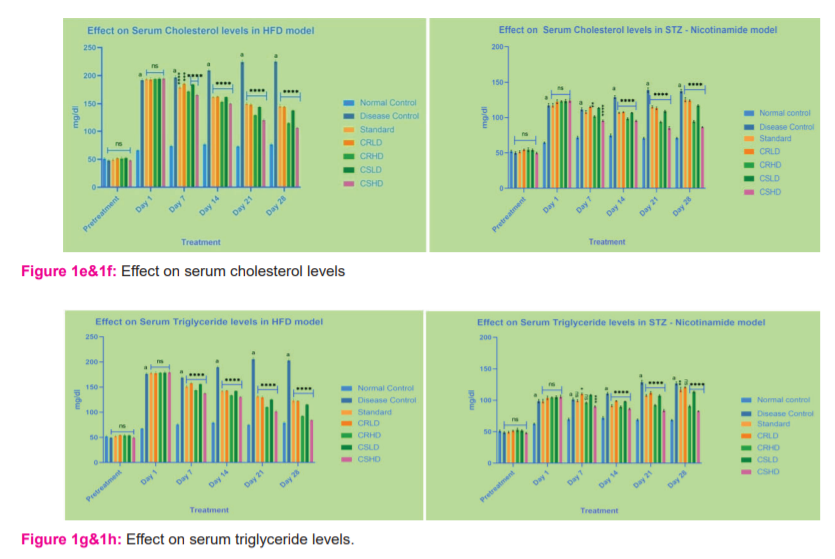
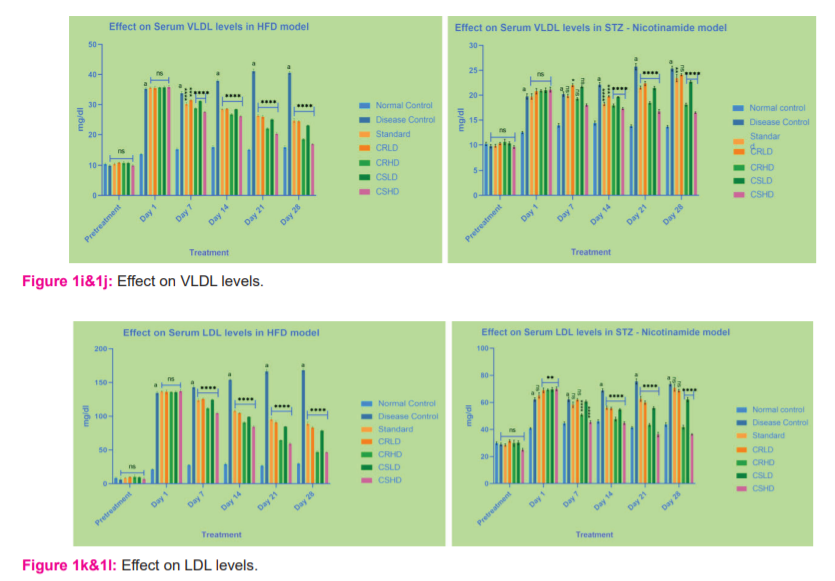
Animals treated with HFD and STZ - Nicotinamide, showed a significant increase (p>0.0001) in the serum cholesterol, Triglyceride, VLDL and LDL levels of disease control when compared to that of normal control. By the end of the treatment, all the standard and treatment groups of HFD showed significant reduction (p>0.0001) in the serum cholesterol, Triglyceride, VLDL and LDL levels compared to disease control.
Whereas, in the STZ model, only the groups treated with CRHD, CSLD, CSHD showed significant reduction (p>0.0001) in the serum triglyceride, VLDL and LDL levels compared to disease control (Figures 1e -.1l)
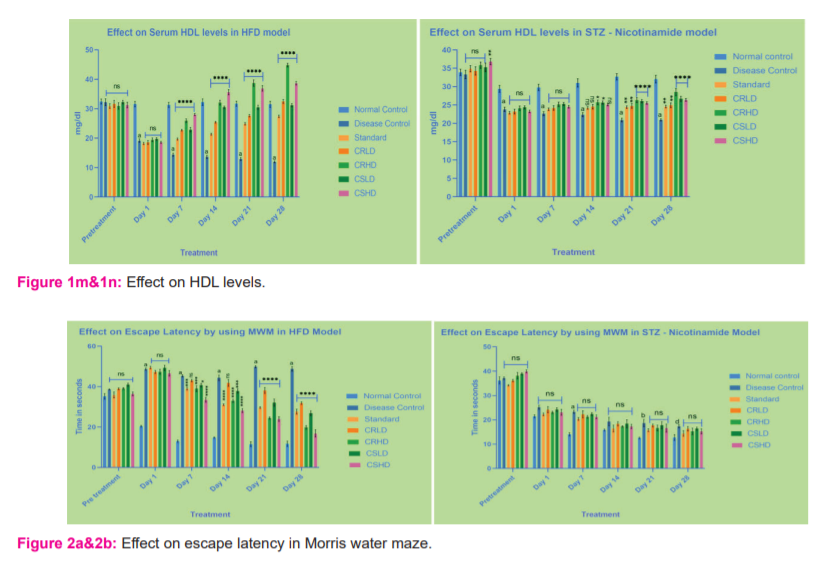
Animals treated with HFD and STZ - Nicotinamide, showed a significant decrease (p>0.0001) in serum HDL levels of disease control when compared to that of normal control. By the end of the treatment, all the standard and treatment groups of HFD showed a significant increase (p>0.0001) compared to disease control. Whereas, in the STZ model, only the groups treated with CRHD, CSLD, CSHD showed a more significant increase (p>0.0001) followed by a slight increase when treated with standard and CRLD (p>0.01) when compared to disease control (Figure 1m&1n).
Effect on Behavioural Parameters:
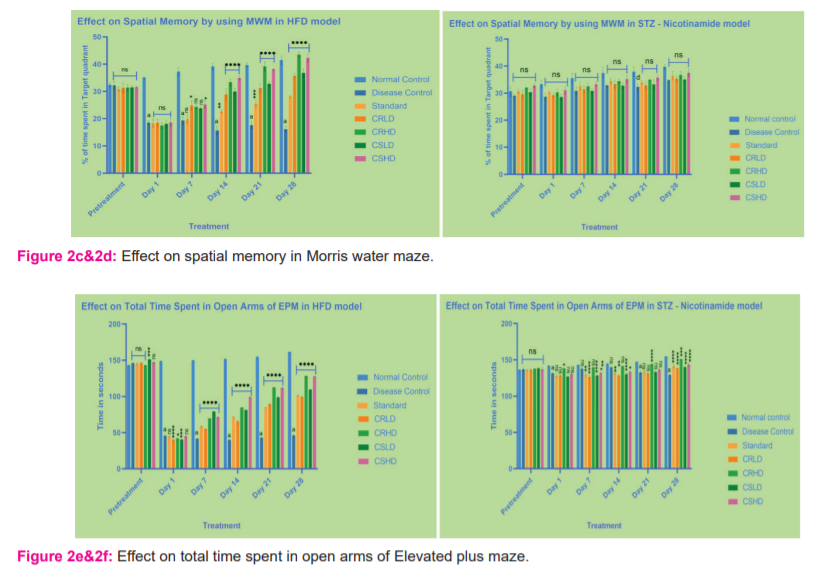
Morris water maze: In the HFD model, the escape latency (s) of the control group decreased significantly over the trial days. Extract (low and high doses) treated groups showed significantly (p>0.0001) decreased escape latencies (s) after 7 days of treatment except for CRLD, which became significant after 21 days of treatment. There was a significant difference between the low and high doses after 21 days of treatment. Citrus sinensis showed comparatively better escape latency than the Citrus reticulata at given doses (Figure 2a&2b). Similarly, In the HFD model, the time spent in the target quadrant for the control group increased significantly (p>0.0001) over the trial days. All the test groups exhibited improved spatial memory after 14 days of treatment. Citrus reticulata showed comparatively better improvement in spatial memory than the Citrus sinensis at given doses. Surprisingly, there is no significant improvement in the STZ model (Figure 2c&2d).
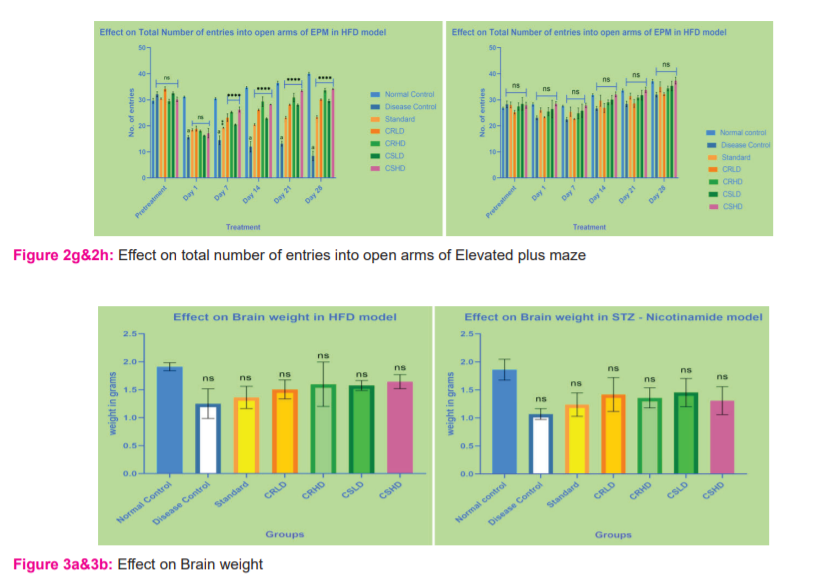
Elevated plus-maze: In the HFD model, the number of entries and time spent in the open arms for the control group increased significantly over the trial days. Extract (low and high doses) treated groups showed significant (p>0.0001) increased performance after 7 days of treatment. There was a significant difference between the low and high doses even after 7 days of treatment. Citrus sinensis showed comparatively better performance than the Citrus reticulata at given doses. But, there is no significant improvement in the STZ model (Figure 2e – 2h).
Effect on Brain weight
After the completion of the last day of treatment, animals were euthanized and the brain was isolated. The isolated brain was rinsed with ice-cold normal saline to remove the blood and other connective tissues. Wet weight was measured. In both HFD and STZ – Nicotinamide models, when compared to normal control, all other groups showed a slight reduction in the brain weight was not significant (Figure 3a&3b).
Effect on in vivo antioxidant activity
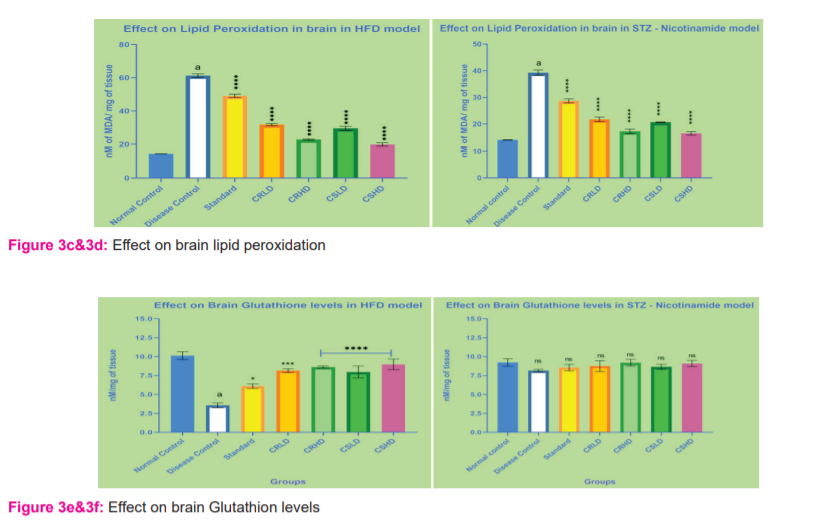
Animals treated with HFD and STZ – Nicotinamide, showed a significant decrease (p>0.0001) in endogenous CAT, GSH and SOD levels and an increase (p>0.0001) in lipid peroxidation when compared to normal control. After treatment for 28 days with standard, CRLD, CRHD, CSLD and CSHD, lipid peroxidation was significantly decreased (p>0.0001) when compared to disease control in both the models. In HFD and STZ – Nicotinamide model, when compared to disease control, all groups showed a significant increase (p>0.0001) in SOD levels. In STZ – Nicotinamide model, there was no significant increase in brain Catalase and GSH levels when compared to disease control. Whereas in HFD, only groups treated with CRHD and CSHD showed a slight significant increase (p>0.01) in Catalase levels when compared to disease control, followed by CSLD (p>0.05). Groups treated with CRHD, CSLD, CSHD showed a significant increase (p>0.0001) in brain GSH levels, followed by CRLD (p>0.001) and standard group (p>0.05) when compared to disease control of the HFD model (Figure 3c-3j).
Effect on Brain Acetylcholinesterase levels
Animals treated with HFD and STZ – Nicotinamide, showed a significant increase (p>0.0001) in acetylcholinesterase levels when compared to normal control. After treatment for 28 days with standard, CRHD, CSLD and CSHD, acetylcholinesterase levels were significantly decreased (p>0.0001) when compared to disease control in both the models. In the case of groups treated with CRLD, the STZ – Nicotinamide model showed a significant decrease (p>0.0001) but the HFD model showed less significance (p>0.05) when compared to disease control (Figure 3k&3l).
Effect on Brain Insulin levels:
Animals treated with the HFD model showed a significant increase (p>0.0001) in insulin levels when compared to normal control. After treatment for 28 days with standard, CRHD, CSLD and CSHD, insulin levels were significantly decreased (p>0.0001) when compared to disease control in the HFD model. In the case of the STZ model, CSHD only showed a significant decrease (p>0.0001) but the HFD model showed less significance (p>0.05) when compared to disease control (Figure 3m&3n).
Histopathology:
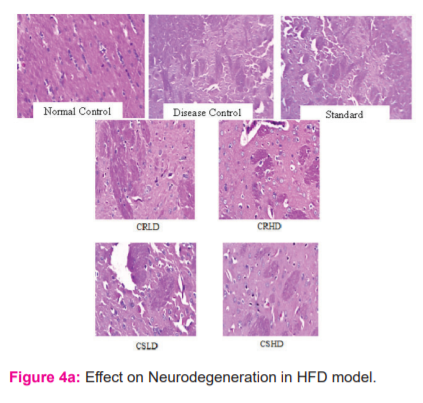
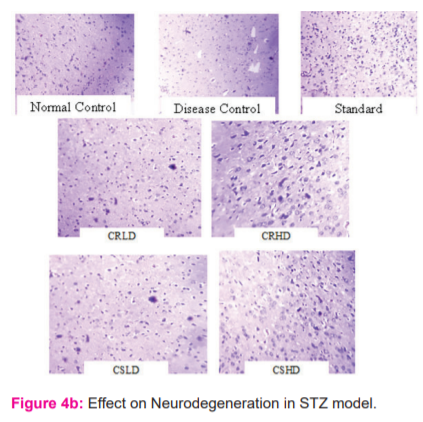
Neurodegeneration in HFD and STZ induced diabetes-associated cognitive decline (DACD):
From the histopathological results, it was evident that HFD has caused predominant neurodegeneration when compared to that of normal control and treatment with citrus extracts has reduced the extent of neurodegeneration when compared to the disease group. On the other hand, STZ – Nicotinamide did not cause any prominent neurodegeneration when compared to normal control. No difference was seen among all the other treated groups of STZ – Nicotinamide model when compared to disease control (Figure 4a&4b).
Amyloid-beta Plaques in HFD induced diabetes-associated cognitive decline (DACD):
By using fluorescent staining, Amyloid-beta plaque deposition in the HFD model was carried out as predominant neurodegeneration was observed. Disease control showed predominant amyloid plaque deposition when compared to normal control. After treatment with standard, CRLD, CRHD, CSLD and CSHD, clearance of amyloid plaques was observed. When compared to all other groups, CSHD showed better clearance of amyloid plaques(Figure 4c).
Effect on beta-secretase activity:
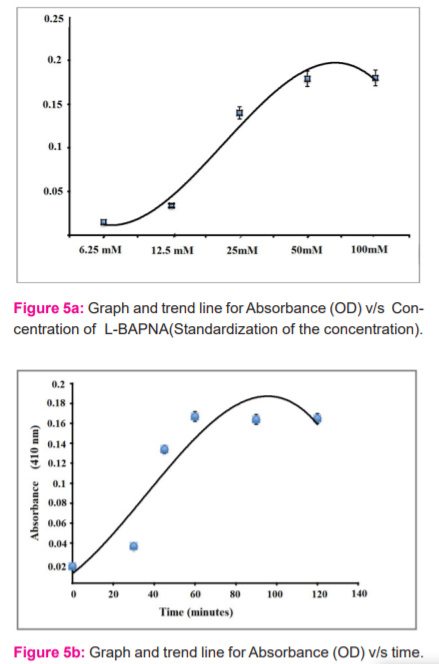
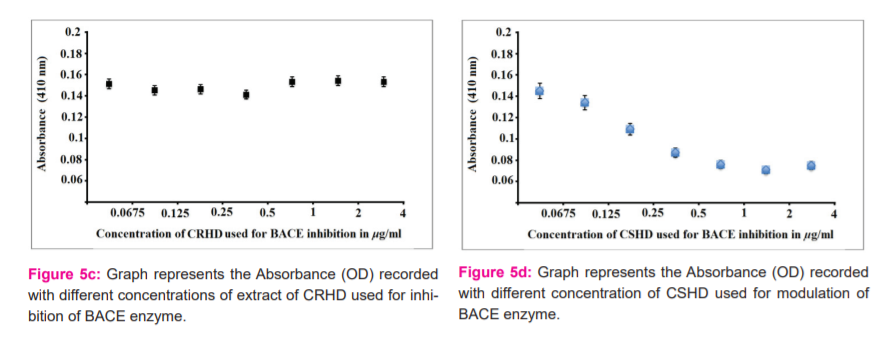
The in-vitro bioassay has been performed with purified BACE enzyme and substrate L-BAPNA for optimization of substrate concentration, time duration of incubation and volume of crude extract. Standard data is represented in Figure 5a&5b. It was found that the best amount of substrate Na-Benzoyl- L -arginine 4-nitroanilide hydrochloride (L-BAPNA) was 50mM, time for incubation was 60 minutes and the best volume was about 2 L of extract that provide inhibition. Figure 5a shows the values of the BACE-L-BAPNA reaction mixture without the administration of any herbal extract. It is representing the standardization of the concentration of substrate. Figure 5b shows the same experimental setup for the standardization of time. This showed the maximum absorbance at 60 minutes and then the saturation in absorbance in respect to time. Figure 5c & 5d shows the experimental setup of BACE and L-BAPNA with the administration of plant extract of test substances.
CONCLUSION
To curb the results, it can be concluded that the HFD model efficiently induced Diabetes associated Cognitive Decline than STZ– Nicotinamide model and can be declared as a best-fit model for screening Diabetes associated Alzheimer’s disease. From the results, it is also evident that an emulsion of the volatile oil obtained from Citrus sinensis showed a better protective effect when compared to Citrus reticulata in the selected In vivo models along with standard groups. Histopathological examination of the brain of the treated animals exposed the physiological and pathological changes during the treatment. Biochemical parameters also supported the protective effect of the plants against the diabetes-induced AD model. The free radical scavenging propensity of the volatile oils of the plant gives protection against oxidative damage and maybe the reason for the restoration of the memory and other physiological and histological parameters.
Acknowledgement
Authors are thankful to CES college of Pharmacy, Kurnool for providing the necessary facilities.
Author Contribution:
Navya Reddy Y performed the work and wrote the manuscript, Madhuri D and Chandrasekhar KB guided the work, prepared and reviewed the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Source of Funding: The authors declare that there are no funding sources to carry out this work.

References:
-
Qiu, Chengxuan. Epidemiology of Alzheimer's disease: occurrence, determinants, and strategies toward intervention. Dialogue Clin Neurosci. 2009;11(2):111-28.
-
Rowley SP, William R. Diabetes 2030: Insights from Yesterday, Today, and Future Trends. Popul Health Manag. 2017;20 (1):6-12.
-
Neeraj M, John P, Sheena S, Joydeep S. Role of free radicals and antioxidants in human health and disease. Int J Curr Res Rev. 2013;05 (19):1-2.
-
Zou Z, Xi W, Hu Y, Nie C, Zhou Z. Antioxidant activity of Citrus fruits. Food Chem. 2016; 196:885–896.
-
Ghulam Mustafa Kamal, Muhammad Yasin Ashraf, Abdullah Ijaz Hussain Andleeb Shahzadi, Muhammad Ismail Chughtai. Antioxidant potential of peel essential oils of three Pakistani citrus species: Citrus reticulata, Citrus sinensis and Citrus paradisii. Pak J Bot. 2013;45 (4):1449-1454.
-
Szkudelski T. Streptozotocin–nicotinamide-induced diabetes in the rat. Characteristics of the experimental model. Expt Biol Med. 2012;237(5):481–490.
-
Wang Z, Fan J, Wang J, Li Y, Xiao L, Duan D, Wang Q. Protective effect of lycopene on high-fat diet-induced cognitive impairment in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2016;Aug 3;627:185-191.
-
Vorhees CV, Williams MT. Morris water maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat Prot. 2006;1(2):848–858.
-
Itoh J, Nabeshima T, Kameyama T. Utility of an elevated plus-maze for the evaluation of memory in mice: effects of nootropics, scopolamine and electroconvulsive shock. Psychopharmacol. 1990;101(1):27–33.
-
Simeonova Rumyana, Vitcheva Vessela, Kondeva-Burdina Magdalena, Popov Georgi, Shkondrov Aleksandar, Manov Vassil, & Krasteva Ilina. Alcesefoliside protects against oxidative brain injury in rats. Rev Brasil de Farmacog. 2019;29(2):221-227.
-
Wills ED. Mechanisms of lipid peroxide formation in animal tissues. Biochem J. 1966;99(3):667-676.
-
Jollow DJ, Mitchell JR, Zampaglione N, Gillete JR. Bromobenzene induced liver necrosis. Protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3, 4-bromobenzene oxide as a hepatotoxic metabolite. Pharmac. 1974;1:151–169.
-
Kono Y. Generation of superoxide radical during autoxidation of hydroxylamine and an assay for superoxide dismutase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978;186:189–195.
-
Claiborne A. Catalase activity. In: Greenwald R.A., editor. Handbook of Methods for Oxygen Radical Research. CRC Press Inc. Boca Raton. 1984; 283–284.
-
Ellman Gl, Courtney KD, Andres VJR, Feather-Stone Rm. A new and rapid colourimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961;7(5):88–95.
-
Csont T. Determination of serum insulin level by ELISA. Practical course: Basic biochemical methods and ischemic heart models. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013; 6(2):3-4.
-
Ikonomovic MD, Buckley CJ, Abrahamson EE. Post-mortem analyses of PiB and flutemetamol in diffuse and cored amyloid-β plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2020;140:463–476.
-
Yamaguchi H, Shen J. Histological Analysis of Neurodegeneration in the Mouse Brain Necrosis. 2013;1004:91–113.
-
Yan R, Vassar R. Targeting the β secretase BACE1 for Alzheimer’s disease therapy. Lancet Neur. 2014;13(3):319–329.
-
Sierant, Malgorzata. Evaluation of BACE1 Silencing in Cellular Models. Int J Alzheimer's Disease. 2009;14:257403.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License