IJCRR - 13(17), September, 2021
Pages: 126-130
Date of Publication: 12-Sep-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Study of Relation between Serum Albumin and Glycosylated Hemoglobin Levels in Patients of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Author: Stuti PU, Shilpa CP
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Diabetes mellitus (DM) can affect people throughout the world, Even though diabetes has been known for a long time, only in the last few decades discoveries have provided measures to minimize morbidity and mortality. Objective: Study of relation between serum albumin and glycosylated haemoglobin levels in patients of type 2 Diabetes mellitus. Method: The present study can be stated as a Hospital-based cross-sectional, observational study design. The study was carried out in the patients admitted in the ward who are diagnosed cases of type 2 DM, in Krishna hospital and Medical Research Centre, Karad. Result: It was observed that along with type 2 DM, hypertension was the most common comorbidity, present in 35.64% of the patients. The second most common comorbidity found was obesity, present in 25.74% of the patients. Conclusion: It was observed that patients who had higher levels of glycosylated haemoglobin had relatively lower levels of serum albumin and patients who had lower levels of glycosylated haemoglobin had normal or near-normal serum albumin levels.
Keywords: Serum Albumin, Glycosylated Hemoglobin, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Hypertension, Obesity
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Diabetes mellitus (DM) can affect people throughout the world, Even though diabetes has been known for a long time, only in the last few decades discoveries have provided measures to minimize morbidity and mortality. Diabetic ketoacidosis, which is a major fatal complication of diabetes, its occurrence has decreased due to the discovery of insulin. However, Diabetes is characterized by metabolic abnormalities along with long-term microvascular and macrovascular complications. The prevalence of diabetes in developing countries is on the rise. It not only multiplies the risk of coronary artery disease but also increases the incidence of Cerebrovascular accidents. End-stage renal disease and also non-traumatic limb amputations.1 Chronic complication of diabetes is often present at the time of diagnosis of Diabetes mellitus. Presently data are scarce when it comes to the occurrence of complications relating to chronic. This case should be specific to diabetic patients at the time of diagnosis.2By educating the high-risk persons about diabetes-related complications, they can be encouraged for seeking medical consultation earlier. Diabetes-associated complications can be prevented only up to a certain point. Also, once the complications are set in, treating hyperglycemia alone itself is not sufficient and even if we treat aggressively, these complications will go on progress further. This emphasizes more aggressive screening for both microvascular as well as macrovascular complications at the time of diagnosis.3 In type 2 diabetes mellitus HbA1c testing is used to measure diabetic glycemic control Diabetic control is categorized as Poor control – HbA1c level >9%, Moderate control – HbA1c level between 7 to 9% Good or desired levels HbA1c level - <7%, However, many factors are known to affect HbA1c values for example – Hemoglobin variants like Hbs, Hbc, Various drugs, anaemia, uremia, and one of them being albumin level. The serum albumin levels are not routinely monitored in all diabetic patients. Albumin levels are routinely monitored only in diabetic nephropathy. Hence identification, critical evaluation and follow-up of serum albumin, as well as HbA1c in type 2 DM, is important.
The present study aimed at analyzing the relation between albumin and HbA1c in Type 2 diabetes patients and its correlation with the severity of the disease. So that timely preventive disability as similar studies was lacking in this particular geographical area. Also, this information will help healthcare professionals to approach management more aggressively to prevent these complications from occurring. Most of the studies in India have been done in cities where people are more educated and aware of the disease. Very little data is available about diabetes and its complication from a rural area in India. A high prevalence of such complications, if documented, will help convince the physicians of the importance of screening for all type 2 diabetics at regularly and to appropriate implement treatment without delay. In the study conducted by Shalbha Tiwari et al.4 929 patients were screened, out of which 319 patients were excluded. A significant negative correlation between HbA1c and albumin concentration (r= -0.284; p< 0.001) was observed in the study.5 The results suggested that the HbA1c and albumin association existed only at non-hyperglycemic fasting blood glucose levels, but not at hyperglycemic ranges, this leads to speculation whether this means that higher glucose levels were able to glycate both haemoglobin and albumin. Whether this increase in HbA1c attributable to lower albumin might still link to diabetic complications is an issue that deserves further study.
It is well known that HbA1c may falsely overestimate prediabetes in Indians, and this had been attributed to iron deficiency anaemia and other factors.6, 7 In the study conducted by Sarojini C et al on 50 subjects, 8 the subjects were divided into two groups. This study concluded that serum albumin negatively correlates with HbA1c concentrations, so average glucose levels from the HbA1c concentration, which may efficiently inform patients their glycemic control needs to be further investigated.9
OBJECTIVE
Study of relation between serum albumin and glycosylated hemoglobin levels in patients of type 2 Diabetes mellitus.
METHOD
The present study can be stated as a Hospital-based cross-sectional, observational study design. The study was carried out in the patients admitted inward who are diagnosed cases of type 2 DM, in Krishna hospital and Medical Research Centre, Karad. The study was conducted over 18 months (1st Dec 2018 to 31st May 2020). This study was approved by Institutional Ethics and Protocol committee. ( protocol number 0253/2018-2019). A total of 101 patients were enrolled in the present study. The sample size is calculated by using Pearson’s correlation coefficient from a previous study conducted by S. Tiwari et al, where a significant negative correlation between HbA1c and serum albumin was observed with r= -0.284
Sample size = N = [(Zα+Zβ)/C]2 + 3
The standard normal deviate for α = Zα = 1.960 The standard normal deviate for β = Zβ = 0.842 C = 0.5 * ln[(1+r)/(1-r)] = 0.292
So,
Total sample size = N = [(Zα+Zβ)/C]2 + 3 = 95
Inclusion Criteria:
-
Males and females aged more than 18 years who are known cases of type 2 DM
Exclusion Criteria:
1. Patients diagnosed with Type 1 Diabetes mellitus.
2. Patients with severe anaemia.
3. Renal impairment (with serum creatinine > 2mg/dl)
4. Pregnancy.
5. Chronic liver disease. (Total bilirubin > 3mg/dl)
6. Hypertriglyceridemia.
7. Iron or vitamin B12 deficiency.
Demographic information such as age, gender, past medical history, personal history and general examination findings such as weight, height, BMI were recorded with the help of standard, pre-validated semi-structured case record proforma. All enrolled patients underwent the following investigations-
-
Haemoglobin by fully automated 3 part cell analyzer
-
Total leukocyte count by fully automated 3 part cell analyzer
-
Platelet count by fully automated 3 part cell analyser
-
Urine routine and microscopy examination.
-
Blood urea by Urease-GLDH method
-
Serum creatinine by Modified JAFFE’S method
-
Random blood sugar by Hexokinase-mediated reaction
-
Fasting blood sugar by Hexokinase-mediated reaction
-
Postprandial blood sugar by Hexokinase-mediated reaction
-
Liver function tests by calorimetry
-
Serum albumin by bromocresol green assay
-
HbA1c by immune turbidimetry method.
All CBC parameters were performed in an automated 3 part analyzer by Nihon Kohden (Model number MEK 6420P)
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
The statistical analysis was performed using the statistical package for social science (SPSS) 21(trial version) for windows. The data was recorded in the study Performa sheet and was entered into the statistical software for further evaluation. The data was arranged in the form of tables and groups for frequency analysis. Data were expressed as mean values ± standard deviations (SD), the percentage for continuous variables. Frequency and proportions were reported for categorical variables. A Chi-square test was used and The ‘P’ value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
The majority of the study subjects in the study belonged to the age group of 56 to 65 years (33.66%) 74(73.27%) patients were male and 27(26.73%) patients were female, with a male to female ratio of 1:0.36The duration of type 2 DM was observed to be between 11 to 15 years in 33.66% of the patients and 6 to 10 years in 32.67% patients. It was observed that along with type 2 DM, hypertension was the most common comorbidity, present in 35.64% of the patients. The second most common comorbidity found was obesity, present in 25.74% of the patients. The mean fasting blood sugar level was found to be 140mg/dl, with a minimum value of 90mg/dl and a maximum value of 256mg/dl. The mean postprandial blood sugar level was found to be 202 mg/dl, with a minimum value of 100mg/dl and a maximum value of 299 mg/dl. The mean glycosylated haemoglobin was found to be 8.1%. It was observed that 47.5% of the patients had glycosylated haemoglobin levels between 7 to 9%. 30.7% of the patients had glycosylated haemoglobin levels less than 7% and 21.8% patients had levels more than 9%. In the study the glycosylated haemoglobin levels were compared with the age of the patient using Pearson’s correlation method, It was observed that there is weak negative correlation ( r- valve is 0.165 and ‘P’-value is 0.099)The mean serum albumin level was found to be 3.12 gm/dl 53.5% subjects had serum albumin levels below 3gm/dl, while 22.8% subjects had levels between 3 to 3.5, and 23.8% subjects had albumin levels more than 3.5gm/dl. In the study, the serum albumin levels were compared with the age of the patient using Pearson’s correlation method, and a weak positive correlation was observed (r value is 0.026 and P-value is 0.798)In the study the mean albumin levels and HbA1c groups were compared, it was observed that the group in which HbA1c was less than 7 had mean albumin concentration 3.89 ± 0.86, the group of patients which had HbA1c between 7 to 9 had mean albumin concentration 2.97± 0.51, and the group of patients who had HbA1c more than 9 had mean albumin concentration 2.48 ± 0.67.The present study aimed at seeing the relation between serum albumin and HbA1c levels in patients of type 2 Diabetes mellitus. A negative correlation was observed among both the parameters (r-value is -0.12)
DISCUSSION
Comorbidities
In the present study, the subjects were assessed according to the presence of comorbidities. It was observed that hypertension was the most common comorbidity present in 36 (35.64%) study subjects while, 26 (25.74%) study subjects were overweight, 15 study subjects (14.85%) had IHD and 12 (11.88%) study subjects had CVA and COPD each. Sarojini C et al, in the study conducted on 50 subjects included study subjects with BMI more than 26 and waist circumference more than 102 centimeters.9In the study by Shalbha Tiwari et al, the most common comorbidity seen in the study subjects of Diabetes mellitus was hypertension, seen in 30% subjects, which is similar to the present study.10
Haemoglobin levels
In the present study, the study subjects were assessed according to their mean haemoglobin levels. The mean haemoglobin level observed was 12.661 ± 1.4345 g/dl.
Blood sugar levels
Fasting and post-meal blood sugar levels were done for all the study subjects. It was observed that the mean fasting blood sugar level was 140.633 ± 23.93, and the mean Postprandial blood sugar level was 202.19 ± 28.74 mg/dl. In the study by Sarojini c et al, the mean fasting blood sugar level observed was 125.68 ± 23.97 mg/dl and the mean Postprandial blood sugar level was 189.78 ± 23.45 mg/dl.[9]In the study by Shalbha Tiwari et al, the mean fasting blood sugar level observed was 117.86 ± 49.83 and the mean postprandial blood sugar level was 169.49 ± 85 mg/dl The findings were similar to the present study.10
HbA1c levels
In the study, the study subjects were categorized according to their HbA1C levels. It was observed that the mean HbA1c level was 8.175±1.7053. It was observed that 48 (47.5%) study subjects had HbA1c levels between 7 to 9, whereas 31(30.7%) study subjects had a value less than 7, and 22(21.8%) subjects had values more than 9. In the present study, the HbA1c levels were compared with the age of the subjects. A weak negative correlation among both the parameters (r-value is -0.165 and p-value is 0.099).In the study by Sarojini C et al, 60% of study subjects had HbA1c more than 7% which is similar to the present study 40% of patients had HbA1c less than 7% which is similar to the present study.[9]In the study by Santiago Rodriguez et al, it was observed that 44.6% of study subjects had HbA1c less than 7%, 18.6% of study subjects had HbA1c between 7 to 9% and 36.8% of patients had HbA1c more than 9% which is similar to the present study.11
Serum Albumin levels
In the present study serum albumin levels were assessed for the study subjects. It was observed that the mean albumin level was 3.122± 0.83. 54(53.5%) subjects had serum albumin levels below 3 mg/dl, while 23(22.8%) subjects had levels between 3 to 3.5, and 24(23.8%) subjects had albumin levels more than 3.5. In the present study serum albumin levels were compared with the age of the subjects. A weak positive correlation among both the parameters(r-value is 0.026 and p-value is 0.798). In the study by Shalbha Tiwari et al. 33% of study subjects had serum albumin levels of more than 4mg/dl, which is more than the present study. 33% of study subjects had serum albumin levels less than 3.5mg/dl which is less than the present study.10 In the study by Sarojini C et al, 40% of study subjects had serum albumin levels less than 3.5mg/dl which is similar to the present study.
According to Shobha Tiwari et al. and Santiago Rodriguez et al. higher serum albumin levels may decrease HbA1c levels and that lower serum albumin levels may raise HbA1c levels which were reported earlier in Western studies. In this study also there is a significant negative correlation between HbA1c and serum albumin noted, this may be due to serum albumin was to compete with haemoglobin for glycation and lower HbA1c negatively. As we did not measure glycated albumin levels, we can only speculate that this could be due to higher albumin levels competing with haemoglobin to get excessively glycated. As this study has several limitations, the finding of an association of statistically increasing HbA1c with low albumin tertiles, suggest that albumin could be one more factor that alters HbA1c levels. This further strengthens the current understanding that only HbA1c may not be as reliable in diagnosing diabetes in Indian subjects. It can be believed that such studies in Indian subjects, could lead to new approaches in studying how glucose and proteins might interact with one another, and such studies could have an impact on understanding hyperglycemia and its estimation.
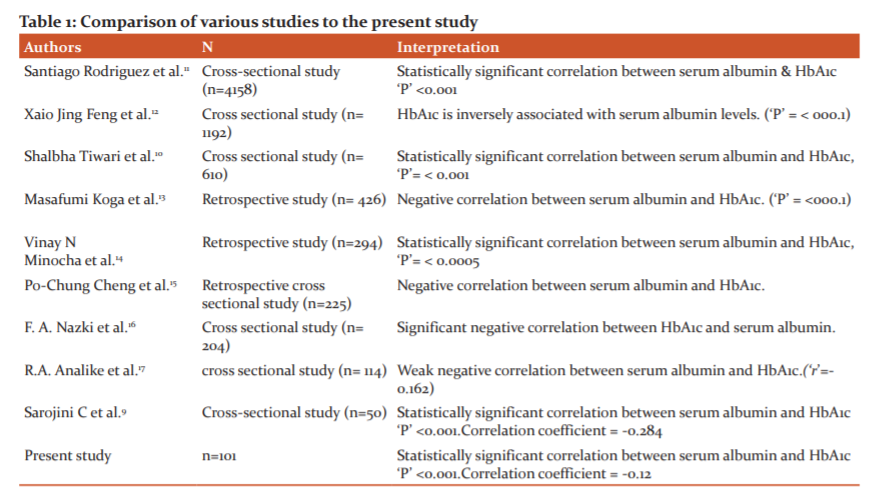
In Table 1, various studies which have similar objectives have been compared.
CONCLUSION
In the present study, the population was largely confined to the 5th and 6th decades with the predominance of the male gender. Hypertension was the most common comorbidity seen along with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Obesity was the second most common comorbidity. In this study a comparison between serum albumin and glycosylated haemoglobin was done, it was observed that patients who had higher levels of glycosylated haemoglobin had relatively lower levels of serum albumin and patients who had lower levels of glycosylated haemoglobin had normal or near-normal serum albumin levels.
Conflict of Interest: There is no conflict of Interest
Source of Funding: No Source of Funding
Authors Contribution: This is a collaborative work among all authors. Dr. Stuti Pradeep Ugile, and Dr. Shilpa C. Patil performed the statistical analysis, wrote the protocol, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Dr. Stuti Pradeep Ugile, and Dr. Shilpa C. Patil managed the literature searches. All authors read and approved the final manuscript
References:
[1] Harrison’s Principle of Internal Medicine, 20th edition, chapter 396 - Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnosis, Classification, and Pathophysiology, by lvin C. Powers; Kevin D. Niswender; Carmella Evans-Molina.
[2] Sosale A, Prasanna Kumar K, Sadikot S, Nigam A, Zargar A, Singh S et al. Chronic complications in newly diagnosed patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus in India. Ind J Endocrin Metab. 2014;18 (3):355-60.
[3] Kumar M, Rawat R, Verma V, Zafar K, Kumar G. Chronic complications in newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the rural area of western Uttar Pradesh, India. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016;4 (6):2292-2296.
[4] Shalbha Tiwari, Manish Bothale, Imtiaz Hasan, Mahesh J. Kulkarni, Mehmood G. Sayyad, Rita Basu, Ananda Basu, AmbikaGopalakrishnan Unnikrishnan,. Association between serum albumin and glycated haemoglobin in Asian Indian subjects. Ind J Endoc Metab. 2015, Jan-Feb, 19(1) 52-55.
[5] Shalbha Tiwari, Manish Bothale, Imtiaz Hasan, Mahesh J. Kulkarni, Mehmood G. Sayyad, Rita Basu, Ananda Basu, AmbikaGopalakrishnan Unnikrishnan,. Association between serum albumin and glycated haemoglobin in Asian Indian subjects. Ind J Endoc Metab. 2015, Jan-feb, 19(1) 52-55.
[6]Hardikar PS, Joshi SM, Bhat DS, Raut DA, Katre PA, Lubree HG, et al. Spuriously high prevalence of prediabetes diagnosed by HbA1c in young Indians partly explained by haematological factors and iron deficiency anaemia. Diab Care. 2012;35:797-802.
[7] Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Smith Shetty A, Nanditha A. Predictive value of HbA1c for incident diabetes among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance – analysis of the Indian Diabetes Prevention Programmes. Diabet Med. 2012;29:94-98.
[8] Sarojini C. Role of albumin in the estimation of HbA1c in south Indian subjects. Int J Sci Res. 2016; 5(4): 629-634.
[9] Sarojini C. Role of albumin in the estimation of HbA1c in south Indian subjects. Int J Sci Res. 2016;5(4)179-183.
[10] Shalbha Tiwari, Manish Bothale, Imtiaz Hasan, Mahesh J. Kulkarni, Mehmood G. Sayyad, Rita Basu, Ananda Basu, AmbikaGopalakrishnan Unnikrishnan. Association between serum albumin and glycated haemoglobin in Asian Indian subjects. Ind J Endocri Metab. 2015; 19(1): 52-55.
[11]Santiago R, Javier RI, Dolores M. Plasma Albumin Concentration Is a Predictor of HbA1c Among Type 2 Diabetic Patients, Independently of Fasting Plasma Glucose and Fructosamine. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(2):185-191.
[12] Xiao jing Feng, Influence of serum albumin on HbA1c and HbA1cdefined glycemic status: a retrospective study.2015;46(12):571-574.
[13] Masafumi Koga, Jun Murai, Hiroshi Saito, Soji Kasayama, Glycated Albumin and Glycated Hemoglobin Are Influenced Differently by Endogenous Insulin Secretion in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes, American diabetes association, Diabetes Care. 2010 Feb; 33(2): 270-272.
[14] Vinay N Minocha, Kavita Pal and Robert Zaiden, The association of serum albumin and glycated haemoglobin with all-cause mortality in patients with breast cancer, Thirty-Seventh Annual CTRC-AACR San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium. 2014;12: 9-13.
[15] Po-Chung Cheng, Shang-Ren Hsu, and Yun-Chung Cheng, Association between Serum Albumin Concentration and Ketosis Risk in Hospitalized Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, J. Diabetes Res, 2016;23(5): 126-129.
[16]F A Nazki, A Syyeda, S Mohammed, F A Nazki, A Syyeda, S Mohammed. Int J Biochem. 2017; 3(9): 497-501.
[17] Rosemary Adamma Analike, Assessment of glycated haemoglobin, total protein and albumin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus visiting NAUTH, Nnewi, Ind J Pathol Oncol, 20196(4):700-703
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License