IJCRR - 13(17), September, 2021
Pages: 31-36
Date of Publication: 12-Sep-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Evaluation of Oxidative Stress Parameters and Lipid Profile in Diabetic Nephropathy Patients
Author: Yadav Bhuneshwar, Kurpad Nagaraj Shashidhar, Anjanappa Raveesha, Chandrappa Muninarayana
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Oxidative stress is responsible for endothelial dysfunction and one of the important factors contributing to pathogenesis of DN. Aim of the study was to evaluate extended diabetic profile and oxidative stress parameters in type 2 diabetes with and without nephropathy. Methods: Hospital based cross-sectional analytical study includes 150 study subjects in the age group of 35-70 years were grouped into three groups; Group I- Healthy Controls; Group II- Clinically proven type 2 diabetes mellitus and Group III- Type 2 diabetes mellitus with nephropathy. Anthropometric and biochemical parameters were analysed by standard methods. Results: Among the oxidative stress parameters Vitamin C, Nitric Oxide and Glutathione peroxidase showed a significant decline in Group III when compared with group I and II with a p-value < 0.001. The mean value of malondialdehyde in group I, II and III was 2.47\?1.02, 4.96\?1.95 and 7.12\?1.7 respectively showing a significant (p< 0.001) increase in group III and group II when compared with the control group. Conclusion: Lipid abnormality is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus with and without nephropathy with increased TG level and a reduced level of HDL-C. Increase in oxidant and low antioxidants level in diabetic and diabetic nephropathy patients were observed. Thus, measurement of oxidative stress and antioxidant system with lipid status may help in evaluating diabetes and aid inpredicting and prevention of long term diabetic complications.
Keywords: Diabetic Nephropathy, Oxidative Stress, Malondialdehyde, Lipid Profile, Glutathione peroxidase, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION:
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disorder resulting from either from deficiency of insulin or resistance to its action causing increased blood glucose levels (Hyperglycaemia) which leads to several systemic complications.1 The classical symptoms of diabetes include polydypsia, polyuria, polyphagia and weight loss. As the disease progress, patients are at high risk for the development of complications, such as retinopathy leading to blindness, nephropathy ending with renal failure, neuropathy resulting in nerve damage and atherosclerosis.2 Prevalence of diabetes is increasing day on day worldwide. International Diabetes Federation (IDF) in year 2013, estimated that around 382 million people had diabetes. The prevalence of diabetes is increasing exponentially and by 2030 it is estimated that the chance of diabetes may be almost doubled.3
Diabetic Nephropathy (DN)is a clinical syndrome characterized by albuminuria (>300 mg/day or >200 mcg/min) confirmed at least on two occasions 3-6 months apart with permanent and irreversible decrease in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and arterial hypertension. It is a progressive kidney disease caused by glomerular as well as tubular structural and functional alteration which is induced by glucose homeostasis disturbance accounting to 30-40% of diabetic patients and is one of the major causes of end stage renal disease (ESRD).4,5
Hyperglycaemia being a crucial factor in the development of diabetic nephropathy induces hemodynamic and metabolic factors which are thought to be the main mediators of renal injury. Increased glucose concentration enhances oxidant production and impairs antioxidant defence by multiple interacting pathways including increased production of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), enhance reactive oxygen species generation and activation of protein kinase (PKC), polyol and renin-angiotensin system (RAS).6
Persistent hyperglycaemic state activates aldose reductase activity and the polyol pathway, which decreases NADPH/NADP+ ratio.7 Further intracellular glucose activates PKC through de novo synthesis of diacylglycerol (DAG)8 and has been associated with processes increasing mesangial expansion, thickening basement membrane, endothelial dysfunction, smooth muscle cell contraction and activation of cytokines and transforming growth factor β (TGF-β).9 PKC induces oxidative stress by activating mitochondrial NADPH oxidase and been recognized as contribution of oxidant production as NADPH oxidase stimulate ROS generation and contributing to the development and progression of DN.6
Dyslipidaemias which is characterized by high plasma triglyceride concentration, low HDL cholesterol concentration and increased concentration of small dense LDL cholesterol particle is being one of the major risk factor for vascular disease in DM. These changes in lipid concentration are attributed to increase free fatty acids flux secondary to insulin resistance in DM.10 Altered lipid profile is common in patient with kidney disease. Dyslipidaemias in DM may cause kidney damage and contributing to a progressive decline in kidney function leading to development and progression of DN.11Thus, this study aimed to evaluate oxidative stress parameter in type 2 diabetes with and without nephropathy compared with clinically healthy controls. Extended diabetic profile and oxidative stress parameters are compared between three groups.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
This Hospital-based cross-sectional analytical study was conducted in R L Jalappa Hospital and Research Centre attached to Sri DevarajUrs Medical College, constituent of Sri DevarajUrs Academy of Higher Education and Research, Tamaka, Kolar, Karnataka India. Study was approved by the Institutional Ethical Committee (SDUMC/KLR/IEC/17/2019-20) and informed consent was obtained from all study subjects participating in this study.
A total of 150 study subjects in the age group of 35-70 years of males and females were included. These study subjects were grouped into: Group I- Healthy Controls; Group II- Clinically proven T2DM; Group III- Type 2 DM with nephropathy. Patients with active urinary tract infection, renal disease other than diabetic nephropathy, chronic liver or heart diseases, cancer, gestational diabetes mellitus, Acute kidney injury Type 1 DM along with patient on dialysis were excluded from the study.
Clinical details such as anthropometric measurement of all the study subjects enrolled in the study were obtained from the hospital medical records. A minimum of 8 hours of fasting blood sample was collected and divided into parts with specified sample requirements per the investigations into serum (plain tubes), whole blood and plasma (EDTA&NaF tubes) for parameters as mentioned in measurement methods.2 hours post- prandial blood sample was also collected for Post-prandial blood sugar estimation.
Fasting and post-prandial blood glucose, urea, Creatinine, Uric acid, total cholesterol, triglyceride and HDL-cholesterol were analyzed using Vitros 5.1 FS dry chemistry auto analyzer from Ortho Clinical Diagnosis (OCD) United States, based on the principle of Reflectance Photometry. HbA1C was determined by HPLC method. Malondialdehyde (MDA) by Thiobarbituric acid reactive substance (TBARS) method, Vitamin C by 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine method, Nitric oxide by Modified Griess method were measured spectrophotometrically using Perkin Elmer UV/VIS spectrophotometer. Glutathione peroxidase was determined by using ELISA kit from 2018 Geno Technology Inc., USA. LDL-C was calculated using Friedwald Equation as well as VLDL and Non-HDL-C was also calculated.
Statistical analysis was performed using IBM-SPSS statistical package 20. An Independent sample t-test was used to compare the means of different parameters. The difference between the three groups was assessed using analysis of variance (ANOVA). Pearson correlation coefficient was used to demonstrate a correlation between oxidative stress parameter & lipid profile. p-value<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS:
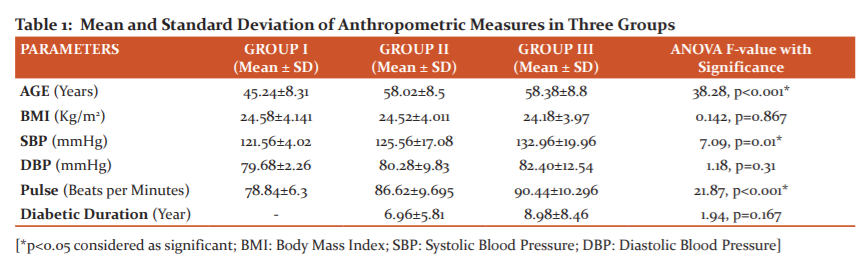
A total 150 participants out of whom 58 were female and 92 males within an age group of 35-70 years were included in the present study. Mean and standard deviation of anthropometric and physical variables of 150 subjects were shown in Table 1. The mean value of age, systolic blood pressure (SBP) and pulse rate were significantly higher in group II and III compared to group I with a p-value of < 0.001. There was no significant difference observed in duration of diabetic in group II and group III.
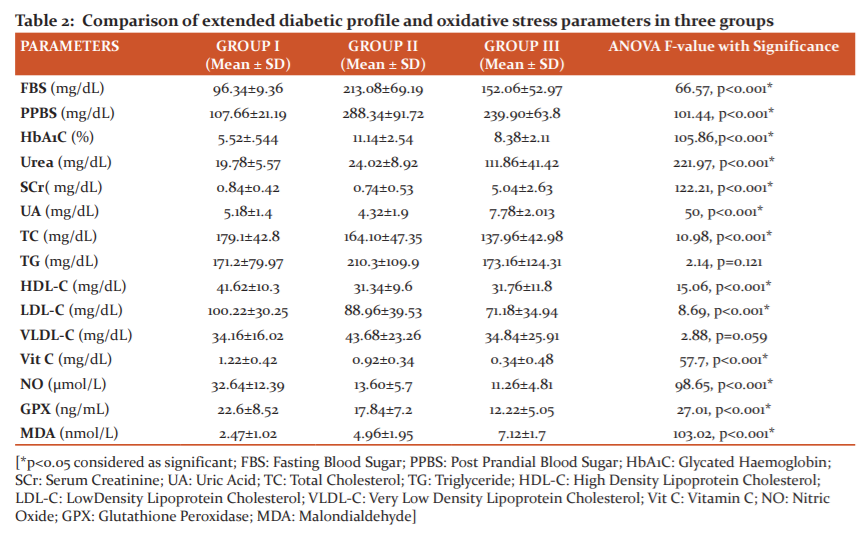
Table 2 shows the comparison of mean and standard deviation of all the biochemical parameters between the three groups. Fasting blood sugar, postprandial blood sugar, HbA1C, urea, serum creatinine, uric acid and triglyceride level were significantly higher in group II and III when compared with the control group I study subjects. The level of total cholesterol and HDL-C were significantly lowered in diabetes and diabetic nephropathy cases when compared with the control study subjects. Vitamin C, Nitric Oxide and Glutathione peroxidase levels showed a significant reduction in Group III compared to group I and II. The mean value of malondialdehyde in group I, II and III was 2.47±1.02, 4.96±1.95 and 7.12±1.7 respectively showing a significant (p<0.001) increase in group III and group II when compared with the control group.
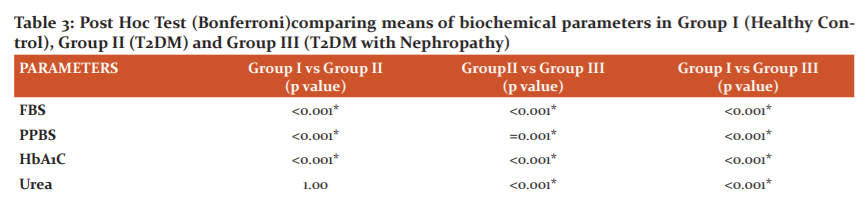
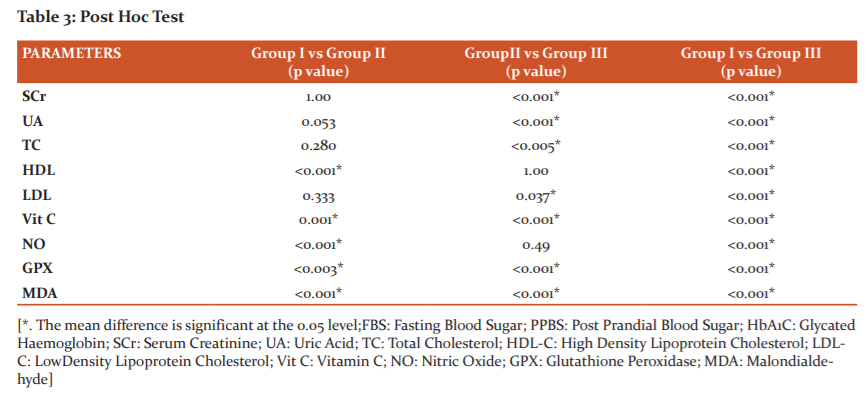
Post Hoc analysis using Bonferroni criteria was performed to assess significant between the biochemical parameters among the groups and showed in Table 3. FBS, PPBS, HbA1C, HDL-C, Vitamin C, nitric oxide, glutathione peroxidase and malondialdehyde were significant (p<0.001, p<0.005) between Group I and Group II. Group II vs Group III showed a significant difference (p<0.001, p<0.005) with respect to all biochemical parameters except TG, HDL-C, VLDL-C and Nitric oxide. On comparison between group I vs III, except TG and VLDL-C all other parameters were highly significant (p<0.001).
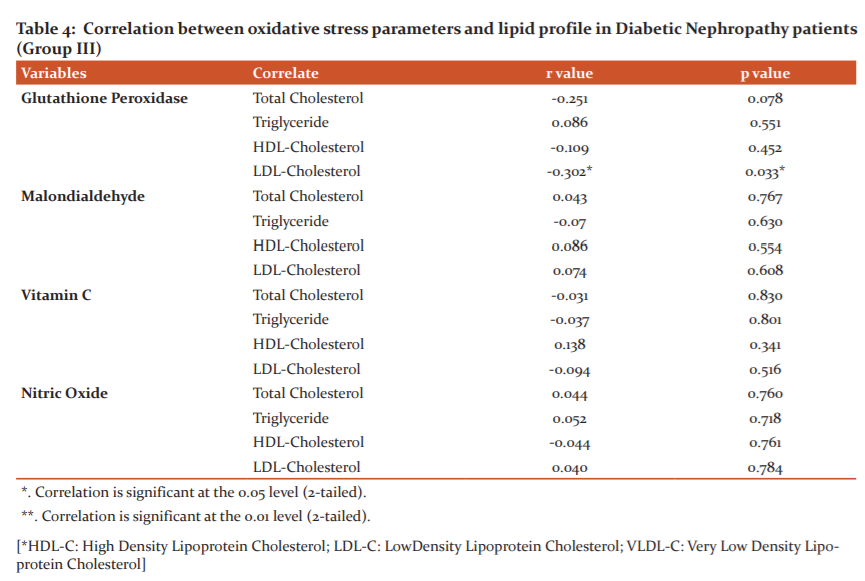
Pearson’s correlation coefficient of oxidative stress parameters with lipid profile parameters in DN patients (Group III)were presented in Table 4. Among these parameters only glutathione peroxidase showed a significance with a weak negative correlation with LDL-C (r= -0.302, p=0.033*).
DISCUSSION:
The incidence and prevalence of diabetes mellitus have grown significantly throughout the world, due primarily to the increase in type 2 diabetes. This increase in the number of people developing diabetes had a major impact on the development of diabetic kidney disease. Diabetic nephropathy is one of the major chronic microvascular complications in diabetes mellitus & a leading cause of end-stage renal disease, accounting for nearly half of all incident cases of ESRD in the developed world.12,13In India, DN accounts for about 46% of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in elderly people and is associated with increased cardiovascular mortality and morbidity. A dramatic increase in prevalence of diabetic nephropathy has been seen in Indian diabetic patients, which has become the single most common cause of end-stage kidney disease.5 The anthropometric measurement showed a significant different in age and systolic blood pressure when compared the control group with T2DM and T2DM with nephropathy patients. In our study, the duration of diabetes was not significantly different in group II and group III.
Our study showed a significant increase in FBS, PPBS and HbA1c when compared control group with type 2 diabetes mellitus and T2DM with nephropathy group respectively similar to the study conducted by Patel and Kaila in the year 2019.14Comparison between T2DM and T2DM with nephropathy studied groups regarding parameters of glycaemic control showed a significant difference with decreased level in nephropathy group and is contra indicatory to the result of study conducted by Mohamed ShawkyElsayed et al.15
Patients with diabetic nephropathy showed a significant increase in blood urea and serum creatinine level when compared with control group subjects and type 2 diabetic subjects in the present study indicating decline kidney function with progression of nephropathy. A significant elevated uric acid level in group III was found when compared with group I and II. A similar result was observed in study conducted by Kentaro et al., showing elevated uric acid level as consequence of renal function decline16 as renal excretion is the primary mode of its clearance.17
Among lipid profile parameters TG showed a significant increase in T2DM patients when compared with control study subjects indicating that increased blood sugar might have contributed to the elevated triglycerides. A significant reduction in HDL-C was observed in T2DM and T2DM with nephropathy subject. This results correlate with study conducted by Srinidhi Rai et al.in the year 2017.18Altered lipid profile in T2DM is due to insulin resistance and defective insulin action on lipoprotein metabolism. It will also increase triglyceride synthesis and promote quick breakdown of HDL-C.19To our surprise, we observed that total cholesterol and LDL-C was significantly lowered in T2DM and Nephropathy patients when compared with the control study subjects and it may be because of certain factors such as lifestyle modification, strict diet control, statins, awareness of the sequelae. DN which is considered as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease and altered lipid levels will increase the risk.18
Our study showed, the level of nitric oxide was significantly reduced in diabetic nephropathy when compared with control group. However, there was no much difference in nitric oxide level in T2DM and T2DM with nephropathy cases. Oxidative stress being the main cause of endothelial dysfunction and releasing inflammatory markers such as cytokines from the damaged renal tissues. Thus altered endothelial causes excess expression and plasma level of vasoconstrictors such as angiotensin II and endothelin-1 with increased expression of adhesion molecules and enhanced adhesion of platelets and monocytes to vascular endothelium releasing nitric oxide leading to reduced nitric oxide responsiveness causing renal injury.20It may also reflect increased NO degradation promoted by oxidative stress in renal cortex during kidney dysfunction.
Hyperglycaemia is known to enhance free radical generation and facilitate lipid peroxidation. MDA which is marker of lipid peroxidation, the levels were significantly elevated in both T2DM and T2DM with nephropathy patients when compared with control study subjects.
The level was almost 3 times higher in nephropathy cases when compared with the control group. Vitamin C act as antioxidant and plays a major role in protecting against oxidative stress damage. The levels of vitamin C were gradually decreased in group II and III, when compared with control study subjects and results, are consistent with study done by Munilakshmi et al.21 We observed in our study the serum level of glutathione peroxidase was decreased in diabetes and diabetic nephropathy patients and similar results were observed in previous study conducted by Zagrodzki et al. and EL-Far MA et al.22,23 The decreased level of glutathione peroxidase may be due to increased level of lipid peroxidation or decreased in functional renal mass24 as the plasma form of glutathione peroxidase is synthesized in the kidney.23
CONCLUSION:
Diabetic nephropathy is one of the chronic complications of type 2 diabetes and finally progresses to end stage renal disease which requires dialysis therapy. Oxidative stress is one of the important factors contributing to pathogenesis of DN. The present study showed that the lipid abnormality is associated with T2DM and T2DM with nephropathy with increased TG level and reduced level of HDL-C. We also observed increased oxidant (MDA) and a low antioxidants (Vitamin C & Glutathione peroxidase) level in diabetic and diabetic nephropathy patients.
Thus, the measurement of oxidative stress along with antioxidant system and lipid status seems to be more helpful while evaluating diabetic complications and assessment of oxidative stress in diabetic patients may be more important for prediction and prevention of long term diabetic complications.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT:
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
SOURCE OF FUNDING: Nil
CONFLICT OF INTEREST:
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTION:
Bhuneshwar Y contributed in the formulation of study, biochemical analysis, data collection and is the principal investigator. Planning and correction of the write up was done by K.N. Shashidhar and is the corresponding author. Evaluation and Review of literature and clinical case finding was done by Raveesha A.Muninarayana C helped with statistical analysis and manuscript editing.
References:
-
Sacks D B.Teitz Textbook of clinical chemistry and molecular diagnostics. In: Carl A. Burtis, Edward R. Ashwood, David E. Bruns, editors. Diabetes mellitus. 5th ed. Elsevier publisher; 2014. p. 1415-56.
-
Kirti S. API Textbook of Medicine. In: YP Munjal, editors. Disease Mellitus: Microvascular Disease: pathogenesis of chronic complications. 10th ed. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publisher; 2015. p. 524-27.
-
International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes atlas. 6th ed. Brussels, Belgium; 2013.
-
International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas 2015, 7th edition; 2017.
-
Sharma RK. API Textbook of Medicine. In: YP Munjal, editors. Diabetes and kidney disease. 10th ed. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publisher; 2015. p. 528-33.
-
Yamagishi S, Imaizumi T. Diabetic vascular complications: pathophysiology, biochemical basis and potential therapeutic strategy. Curr Pharm Des 2005; 11:2279-99.
-
Tesfamariam B. Free radicals in diabetic endothelial cell dysfunction.Free RadicBiol Med1994; 16(3): 383–91.
-
Ishii H, Jirousek MR, Koya D, Takagi C, Xia P, Clermont A,et al. Amelioration of vascular dysfunctions in diabetic rats by an oral PKC ? inhibitor. Science 1996; 272(5262): 728–31.
-
Koya D, King GL. Protein kinase C activation and the development of diabetic complications. Diabetes 1998; 47(6): 859–66.
-
Mooradian AD. Dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol2009; 5(3): 150–59.
-
Nosadini R, Tonolo G. Blood glucose and lipid control as risk factors in the progression of renal damage in type 2 diabetes. J Nephrol 2003; 16(7): 42-7.
-
Tuttle KR, Bakris GL, Bilous RW, Chiang JL, de Boer IH, Goldstein-Fuchs J, et al. Diabetic kidney disease: a report from an ADA Consensus Conference. Diabetes Care 2014;37: 2864-83.
-
Nakai S, Iseki K, Itami N, Ogata S, Kazama JJ, Kimata N, et al. An overview of regular dialysis treatment in Japan (as of 31 December 2010). TherApher Dial 2012;16: 483-521.
-
Patel DN, Kaila K. Characterization of low molecular weight urinary proteins at varying time intervals in type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy patients. DiabetolMetabSyndr 2019; 11(39): 1-11.
-
Elsayed MS, El Badawy A, Ahmed A, Omar R, Mohamed A. Serum cystatin C as an indicator for early detection of diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes MetabSyndr2019;13(1):374-81.
-
Tanaka K, Hara S, Hattori M, Sakai K, Onishi Y, Yoshida Y, et al.Role of elevated serum uric acid levels at the onset of overt nephropathy in the risk for renal function decline in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Investig2014; 6(1): 98–104.
-
Kutzing MK,Firestein BL. Altered Uric Acid Levels and the Disease States. J PharmacolExpTher2007; 324(1):1–7.
-
Rai S, Prajna K, Rai T. Lipid profile in Type 2 diabetes mellitus and in diabetic nephropathy. Int J ClinBiochem Res2017;4(4): 379-82.
-
Trovati M, Cavalot F. Optimization of hypolipidemic and antiplatelet treatment in the diabetic patients with renal disease. J Am SocNephrol 2004;15:12-20.
-
Ishii N, Patel K, Lane PH, Taylor T, Bian K, Murad F, et al. Nitric oxide synthesis and oxidative stress in the renal cortex of rats with diabetes mellitus. J Am SocNephrol2001;12: 1630?39.
-
Munilakshmi U, Shashidhar K N, Muninarayana C, Madhavi R, Lakhsmaiah V. Expediency of markers for early detection of acute kidney injury sequelae to type 2 diabetes mellitus. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 2016; 9(4): 1-5.
-
Elfar MA, Bakr MA, Farahat SE, Afattah EA. Glutathione peroxidase activity in patients with renal disorders. Clin Exp Nephrol 2005; 9: 127-31.
-
Zagrodzki P, Barton H, Walas S. Selenium status indices, laboratory data and selected biochemical parameters in end-stage renal disease patients. Biol Trace Elem Res 2007; 116: 29-41.
-
Ceballos P, Witko SV, Merad BM. Glutathione antioxidant system as a marker of oxidative stress in chronic renal failure. Free RadicBiol Med 1996; 21: 845-53.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License