IJCRR - 13(17), September, 2021
Pages: 26-30
Date of Publication: 12-Sep-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Low-level Laser Therapy Versus Pelvic Exercise on Female Pelvic Girdle Pain
Author: Shehata Saad, Sabbour Adley, Morsy Mona, Hegazy Samya, El Noury Amr
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Girdle pain represents one of the important health issues affecting pregnant women. The exact cause and the prognostic factors of girdle pain are not known. An individualized Exercises program is recommended during and after pregnancy to promote pain outcomes. Lower-level laser therapy is expected to promote girdle pain prognosis. Aim: Comparing the effects of low-level laser therapy versus pelvic exercises therapy in female pelvic girdle pain in reducing pain and improving function. Methodology: Experimental study design, Comparative study type, sixty females were selected and divided into 2 groups, Exercises group(A) consisted of 30 females and Laser group(B)consisted of 30 females, assessed with pain, serum cortisol level, Faber test and posterior pelvic pain provocation test. Results: Statistical analysis was done by using paired' test which showed significant improvement in both groups. Therefore, there is a significant difference between Group-A and Group-B, showing that LLLT group(B) is more effective than group(A) on pain, cortisol level and PPPPT, pelvic girdle pain women's (p < 0.05). Conclusion: Low-level laser therapy has shown significant results in the reduction of pain, stress and improving function in subjects with pelvic girdle pain.
Keywords: Pregnancy, Pelvic girdle pain, Low-level laser therapy, Pelvic Exercise, Cortisol level
Full Text:
Introduction
the pain of the pelvic affects one out of every five pregnant women, causes physical impairment, and is a leading cause of maternity leave. 1,2 consequently, it should be considered a significant women's health problem. After delivery, the rate of recovery has been reported to be better. 3 Pelvic girdle pain (PGP), on the other hand, may develop into a condition of chronic pain and disability in some women, with serious personal and social consequences.4 The diagnosis is a subjective health complaint since it is founded on the woman's subjective perception rather than empirical results. However, (PGP)usually appears in the beginning half of pregnancy and disappears immediately after delivery,3 suggesting that reproductive factors are likely to play a role. 5,6,7,8 Despite that the causes of pelvic girdle may differ from the causes of other pain conditions, however, the factors that affect the recovery process can be the same. The number of pain sites and the severity of the pain have been considered as important factors in the progression from acute to subacute pain to chronic pain and disability. 8 In cases of (PGP), these factors are also related to a poor prognosis. Little is known about prognostic factors (PGP), except for pain intensity during pregnancy, and most studies suffer from methodological flaws such as insufficient research samples and/or improper design. Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) is a bio stimulatory physical modality that aids in tissue regeneration and pain relief by inducing collagen formation and enhancing tissue tensile strength, proving LLLT's effectiveness in tissue repair and pain management. This study aims comparing the effects of pelvic exercises and low-level laser therapy (LLLT) in the treatment of PGP on pain and pelvic flower structure. 9 exercise programs for after delivery pelvic pain stabilization, enhanced functional capacity, and pain reduction. Segmental muscles are strengthened, the neutral spine is stabilized, and the prime movers are reinforced in the stabilizing series. Stabilization exercises aim to concentrate training on specific muscles that are necessary for stability, to reflect the full spectrum of possible difficulty levels, and to increase moment to the muscles that stabilize the lumbar spine. Stabilization of timber. Lumbar stabilization exercises mainly act through transverses abdominis and multifidus, which mainly stabilize the spine. 10,11,12
Subjects, Materials and methods
Study design: It is Experimental design and Comparative study type. It was carried out between March 2019 and May 2020.it followed the Guideline of the Declaration of Helsinki on the conduct of human research.
Participants: Sixty women with pelvic girdle pain were included in this study and randomly assigned into two equal groups. These works were piloted in the physical therapy sector of Imbaba general Hospital, Cairo University.
Inclusion Criteria:
Participants' age is at least ≥20 years old. Group, (A): composed of 30 patients, treated with low-level laser therapy only. Group(B) include 30 women's, treated with pelvic exercises only, for twelve sessions over four week's period; three sessions per week. The ethical committee clearance and informed consent of the subjects were taken. patients have all rights to withdraw from the study at any time without any responsibility.
Study methods Instrumentation
Laser machine stricture: Laser medium: Semiconductor - Gallium Aluminum- Arsenide (Ga Al As), Model & manufacture: Sundom Laser-(Taiwan) RG - 300IB, Wavelength: 810 nm, Output power: 500mw±20mw, Mode: Continuous Wave (CW), Spot diameter: ≤ 10mm.
Assessment procedures: complete medical history will be checked including age, weight, and height and body mass index (BMI). All patients will be assessed before and after the treatment program.
Outcome Measure:
Pain: Visual analogue scale (VAS) is assessing pain that is a 10 mm calibrated line with zero representing no pain and10 representing worst pain. [Time Surround: Baseline to six weeks after treatment].13
Serum cortisol level: is a hormone excreted by the adrenal gland. It is the major corticosteroid. It accounts for around 95% of all glucocorticoid production in the body.14 It is released during stress. Cortisol levels are higher during pain relative to non-pain. A blood sample will be taken to determine plasma cortisol levels since there is a positive correlation between pain severity and cortisol level.5 1ml blood samples from cubital vein two times. One sample baseline and at 4 weeks after treatment.15
Posterior pelvic pain provocation test (PPPPT): This test is used to differentiate between pelvic girdle pain and LBP (especially in postpartum women). It assesses the presence of sacroiliac dysfunction. One measure will be done at baseline and 4 weeks after.16
FABER Test: Flexion, Abduction and External Rotation. These three movements combined result in a clinical pain provocation test to find pathologies at the hip, lumbar and sacroiliac region. Time Frame: Baseline to 4 weeks after treatment.17
Intervention
Treatment procedures: sixteen women's randomly classified into two groups.
A) Laser machine stricture: Laser medium: Semiconductor - Gallium Aluminum- Arsenide (Ga Al As), Model & manufacture: Sundom Laser-(Taiwan) RG - 300IB, Wavelength: 810 nm, Output power: 500mw±20mw, Mode: Continuous Wave (CW), Spot diameter: ≤ 10mm. Procedures: A) the laser therapy is applied to the sacral region by laser probe at the top, and the anterior pelvis. During all therapy sessions, the physiotherapist wears protective glasses, and the treatment area is locked, with limited access and no reflective surfaces. The standard probe moved 1cm/second from a starting point to an end-point repeatedly during the treatment period at sacral points, bilaterally. Energy density 288 J/cm2 Fluency of irradiation of 36 J/cm2 per point, exposure of 120 seconds per point, eight points of irradiation on the pelvic area 4 point sacral region and 4 points on the pubic area the typical probe held perpendicular to the body surface and pressed to the skin.11,18
B) Pelvic exercises: The stress was on bridging the transverse abdominal muscles, posterior pelvic rocking exercise, bilateral hip abduction and adduction exercise, hip shrugging, and bilateral knee elevation. The participants were asked to lie on their sides, kneel, sit, and stand. The participants were encouraged to use their transversely focused abdominal muscles regularly during their everyday activities. They performed two sets of exercises about 10-15 times each (initially 10 times in the six sessions after that15 times, for the other twelve sessions).Respite for 30-second to one minute between each exercise. Home program session achieved for 10 minutes twice a day. Each session lasted 45 minutes.19
Statistical analysis
The scores of VAS, PPPPT, and Faber test and cortisol levels in each group before and after the treatment were compared with paired-sample t-test. The change between the two groups measured before and after physiotherapy was analyzed. A statistical significance was known as p-value <0.05
Ethical approval: The study has been approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the National Institute of laser enhanced science, University of Cairo.
Informed consent: Informed consent has been obtained from all study participants.
Results: None of the 60 female patients was excluded or dropped out of the study during or after the study period. Patient demographic data including age as well as weight, height and body mass index (BMI), were collected, which are summarized in Table(1).
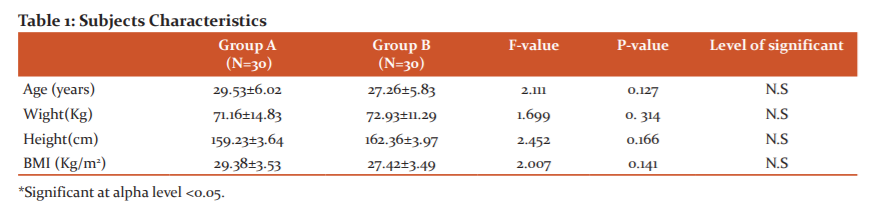
Therefore, there is a significant difference between Group-A and Group-B, showing that low-level laser therapy (LLLT) is more effective than pelvic exercises on pelvic girdle pain (p<0.05).
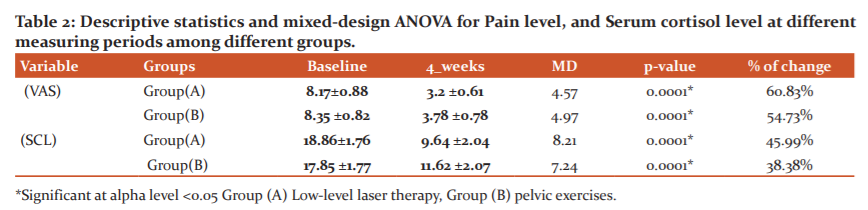
In a group comparison, in the pretreatment test, no significant differences were observed between pain and cortisol levels. In the comparison of groups in post-treatment test. Significant differences were noted between the two groups. Therefore, the pain value (p = 0.001*) and the serum cortisol level (p = 0.001*) for both Groups but group (A) improved significantly compared to the other group (B). As shown in this table-(2), there are statistical differences in the two groups studied in this regard.
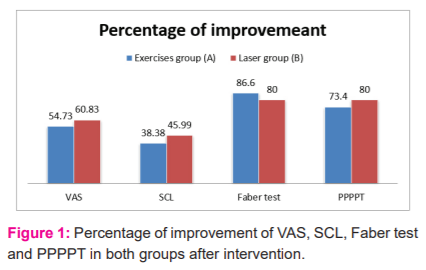
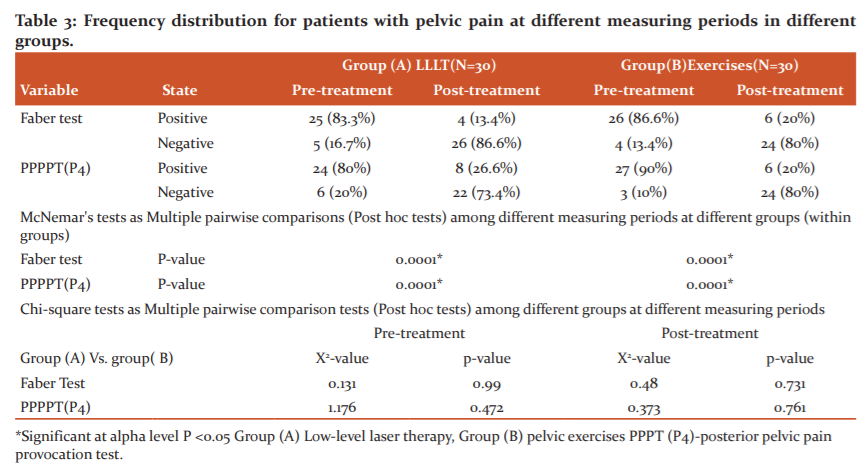
The percentage of Faber test readings of pelvic pain for Group (A) increased by 86.6%, the value for Group (B) increased by 80%. The Chi-square tests (Post hoc tests) revealed that there was no significant difference in the Faber Test between (groups A versus B) (X2= 0.131, p-value =0.99). The mean of posterior pelvic pain provocation test readings of pelvic pain for Group (A) increased by 73.4%, the value for Group (B) increased by 80%, The Chi-square tests (Post hoc tests) revealed that there was no significant difference in the posterior pelvic pain provocation test between (group A versus B) (X2= 1.176, p-value =0.472). within groupsMcNemar's tests" revealed that there was a significant difference of the Faber test and posterior pelvic pain provocation test in these two groups with (p=0.0001*). This significant improvement in favour to post-test in compared to pretest, as see in the table (3).
Discussion
The effectiveness of low-level laser therapy (LLLT) and pelvic exercises therapy in women with pelvic girdle pain is compared in this review. Women between the ages of 20 and 40, of the female gender, and suffering from pelvic girdle pain were chosen for the research, which included only 60 women. Pelvic exercises were given to 30 women in Group A. In Group B, 30 Only low-level laser therapy was used to treat the patients. (LLLT). When the results of the pre-test and post-test of the current study were compared, it was discovered that There was a statistically significant distinction between the two groups. (p=0.05) in pain severity and improved function in both groups, but Group-B improved more than Group-A. (A). The effects of LLLT are non-thermal and photochemical, with no cell disruption, and the light stimulates In healing tissue, the body's mechanisms are at work. Phototherapy relieves pain and swelling by reducing inflammation. According to a review report that looked at all of the therapies for pelvic girdle pain, it was discovered that multiple treatments are more effective than single-agent treatments. In the pelvic stabilization exercises research, the most successful introduced therapeutic approach is that which is under the guidance of a relevant expert. However, the studies also suggest that simply stabilizing the pelvis is enough. Exercising does not seem to have enough clinical benefits. This is sufficient to illustrate the need to incorporate the given therapeutic method with other methods. 20,21 LLLT is one of the suggested methods. Previous research has shown the utility of using LLLT., While some of them have reported that low-level laser therapy reduces pain severity and patient impairment, just the treatment's short-term benefits have been proven.22Although we discovered in our research that low-level laser therapy combined with pelvic stabilization exercises can minimize pain intensity and patient impairment in the long run. Nonetheless, the importance of pelvic stabilization exercises is not reduced as a result of this observation. We believe that laser therapy is effective as a supplementary treatment to pelvic stabilization exercises in the treatment of patients group) and that this laser therapy is effective as a supplementary cure of pelvic stabilization exercises. At the end of four weeks, the mean value of Pain (VAS) and serum cortisol level (SCL) in group A treated with LLLT was 3.2 and 18.85, respectively, and group B treated with pelvic exercises was 3.78 and 19.73. As a result, in group-A women treated with LLLT, recovery is quicker, pain-free, and efficient. As a result, these statistical results may indicate the fact that LLLT is statistically more effective than pelvic exercises.
Conclusion
The results of this study show that four weeks of low-level laser therapy (LLLT) treatment only reduced pain and improved function. through reduction of muscle tension and reduces inflammation of women with pelvic girdle pain better than exercises.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors acknowledge the immense help received from responsible authorities in the involved settings and the participants in the study.
Conflicts of Interest: NIL
Source of Funding: NIL
References:
1. Vleeming A, Albert HB, Ostgaard HC, Sturesson B, Stuge B. European guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pelvic girdle pain. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(6):794-819.
2. Robinson HS, Mengshoel AM, Veierød MB, Vøllestad N. Pelvic girdle pain: potential risk factors in pregnancy concerning disability and pain intensity three months postpartum. Manual therapy. 2010;15(6):522-8.
3. Albert HB, Godskesen M, Westergaard JG. Incidence of four syndromes of pregnancy-related pelvic joint pain. Spine. 2002;27(24):2831-4.
4. Larsen E, Wilken-Jensen C, Hansen A, Jensen D, Johansen S, Minck H, et al. Symptom-giving pelvic girdle relaxation in pregnancy, I: prevalence and risk factors. J Acta obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica. 1999;78(2):105-10.
5. Kristiansson P, Svärdsudd K, von Schoultz B. Serum relaxin, symphyseal pain, and back pain during pregnancy. Am J of obstet and gynecol. 1996;175(5):1342-7.
6. Bjelland EK, Stuge B, Vangen S, Stray-Pedersen B, Eberhard-Gran M. Mode of delivery and persistence of pelvic girdle syndrome 6 months postpartum. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013;208(4):298 e1-7.
7. Bjelland E, Stuge B, Engdahl B, Eberhard?Gran M. The effect of emotional distress on persistent pelvic girdle pain after delivery: a longitudinal population study. BJOG: An Inter J of Obstet & Gynae. 2013;120(1):32-40.
8. Yuko U, Toshiyuki Y, Kimiyo H, Kazuhisa M, Hirokazu U, Mari H, et al. Factors related with low back pain and pelvic pain at the early stage of pregnancy in Japanese women. Inter Jof Nurs and Mid. 2017;9(1):1-9.
9. Vallone F, Benedicenti S, Sorrenti E, Schiavetti I, Angiero F. Effect of diode laser in the treatment of patients with nonspecific chronic low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. Photomed Laser Surg. 2014;32(9):490-4.
10. Stuge B. Evidence of stabilizing exercises for low back- and pelvic girdle pain - a critical review. Braz J Phys Ther. 2019;23(2):181-6.
11. Mr. Prashant B. Mukkannavar DBRD. “Effectiveness of specific stabilization exercises for pelvic girdle pain following caesarean section delivery: a randomized controlled trial”. The KLE Academy of Higher Education and Research, Belgaum KLE Deemed University; November - 2013.
12. Simões LCF, Teixeira-Salmela LF, Wanderley ELS, Barros RRd, Laurentino GEC, Lemos A. Cross-cultural adaptation of "Pelvic Girdle Questionnaire" (PGQ) to Brazil.J Acta Fisiátrica. 2016;23(4).
13. Crichton N. Visual analogue scale (VAS). J Clin Nurs. 2001;10(5):706-6.
14. Tennant F. The physiologic effects of pain on the endocrine system. J Pain Ther. 2013;2(2):75-86.
15. Suliman S, Ericksen T, Labuschgne P, de Wit R, Stein DJ, Seedat S. Comparison of pain, cortisol levels, and psychological distress in women undergoing surgical termination of pregnancy under local anaesthesia versus intravenous sedation. J BMC Psychiatry. 2007;7:24.
16. Thabet AA, Hanfy HM, Ali TAR. Effect of low-level laser therapy and pelvic rocking exercise in the relief of primary dysmenorrhoea. Bull Fac Phys Ther. 2008;13(1).
17. Hilde G, Gutke A, Slade SC, Stuge B. Physical therapy interventions for pelvic girdle pain (PGP) after pregnancy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Rev. 2016.
18. Monticone M, Barbarino A, Testi C, Arzano S, Moschi A, Negrini S. Symptomatic efficacy of stabilizing treatment versus laser therapy for sub-acute low back pain with positive tests for sacroiliac dysfunction: a randomised clinical controlled trial with 1 year follow-up. J Europa Medico Physica. 2004;40(4):263-8.
19. Elden H, Ladfors L, Olsen MF, Ostgaard H-C, Hagberg H. Effects of acupuncture and stabilizing exercises as adjunct to standard treatment in pregnant women with pelvic girdle pain: a randomised single-blind controlled trial. Bri Med J. 2005;330(7494).
20. Gam AN, Thorsen H, Lønnberg F. The effect of low-level laser therapy on musculoskeletal pain: a meta-analysis. Pain. 1993;52(1):63-6.
21. Ferreira D, Zângaro R, Villaverde AB, Cury Y, Frigo L, Picolo G, et al. Analgesic effect of He-Ne (632.8 nm) low-level laser therapy on acute inflammatory pain.J Photo and laser Surg. 2005;23(2):177-81.
22. Yamany AA, Sayed HM. Effect of low-level laser therapy on the neurovascular function of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J of Advan Rese. 2012;3(1):21-8.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License