IJCRR - 13(17), September, 2021
Pages: 04-09
Date of Publication: 12-Sep-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Effect of Carbon Dioxide Fractional Laser on the Levels of Regulated Upon Activation Normal T-Cell Expressed and Secretedserum Chemokines and Vitiligo Clinical Scoring in Stable Non-Segmental Vitiligo: A Case-Control Study
Author: Shokeir HA, Soliman MM, Emam HM, Abdel Latif Y, Abou Zeid OO
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Vitiligo is an acquired disorder that is recurrent with certain chemokines that were found to play a significant role in its complex pathology. Objective: This study aimed to evaluate carbon dioxide (CO2 )fractional laser efficacy on serum RANTES (regulated upon activation, normal T-cell expressed and secreted) and clinical scoring in vitiligo patients. Case Report: Sixty participants, selected from Kasr Al-Ainy teaching hospital dermatology outpatient clinic, Cairo University from August 2017 till March 2019 were assigned into a control group (A), including 30 age and gender-matched healthy volunteers and a study group (B) including 30 adult stable non-segmental vitiligo patients. All participants in group (A) were exposed to daily sunlight for 3 months, while patients in group (B) received 3 CO2 fractional laser monthly sessions with a wavelength of 10600nm along with sunlight exposure starting on the 5th day after every session for 3 months. Assessment of serum RANTES in all participants was done before and after interventions in both groups and vitiligo area severity index (VASI) score was taken before and after the intervention in all patients of the group (B). Discussion of Results: There was a significant difference (p < .001) in the serum RANTES levels when comparing pre to post-study results in the patients 'group, while there was no significant difference (p = .72) in serum RANTES levels when comparing pre to post-study results in the control group. For the VASI score, there was a significant difference (p < .001) in scores when comparing pre to post-study results in the patients 'group. Conclusion: Adding fractional CO2 laser to sun exposure surpasses sun exposure alone in improving stable non-segmental vitiligo patients' outcomes.
Keywords: Vitiligo, RANTES, CO2 Laser, sunlight, Laser Ablation, Patient-Relevant Outcome
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Vitiligo is known as the most prevalent multi- dimensional depigmenting disorder that represents a global incidence of 0.8% reaching up to 8%, specially recorded in African females.1,2Being a visible skin condition, vitiligo could be a source of great psychological distress as it limits social interactions, resulting in affected quality of life and increased liability for more serious psychiatric disorders. However, it does not reflect a life-threatening case causing the case to be underestimated.3
Vitiligo has a complex aetiology where a variety of underlying genetic, autoimmune, autotoxicity, neural and environmental theories lead eventually to melanocytes’ destruction causing vitiligo in inherently susceptible persons.4
The hallmark of the pathogenesis is the oxidative stress produced that affects defected melanocytes causing them to release reactive oxygen species and chemokines especially, chemokine ligand 5 (CCL5) or regulated upon activation, normal T-cell expressed and secreted (RANTES), leading to a vast imbalance between pro-oxidants and antioxidants, which compromises cell functioning.1,5
As vitiligo is a multifaceted disorder, its management remains a challenge with the available options being inconclusive. The first treatment line, aside from topical ointments and oral medication, is phototherapy, a relatively effective but with a high rate of patient’s dissatisfaction.6
That fact raises the need for more efficient alternatives as laser therapy. Carbon dioxide (CO2) lasers are commonly known to be effective in managing some cutaneous lesions, mild scars, and photoaging.7 Treatment using fractional CO2involves dividing the single beam of laser into multiple microbeams, producing microscopic ablative zones encircled by normal intact skin, thus it gives the same benefits as a full ablative treatment but with fewer side effects. Skin normally contains an elevated percentage of water, making CO2 laser perfect for accurate and safe ablation in the dermatology field, as its energy is highly absorbed in water.8 Fractional CO2 laser has demonstrated better efficiency in treating vitiligo, especially stable non- segmental form when combining with conventional treatments than when using the latter alone.9
Nevertheless, there is a scarcity of research regarding the effect of fractional treatment using CO2 laser on serum RANTES levels and clinical vitiligo outcomes. Thus, the present study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of CO2 laser on serum RANTES levels and clinical outcomes in stable non-segmental vitiligo patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
The present study was designed as a non-randomized, comparative study, using a non-probability, consecutive, sampling technique for recruiting participants. The trial was conducted at Kasr Al-Ainy teaching hospital dermatology outpatient clinic, Cairo University, including 60 participants equally assigned into two groups from August 2017 till March 2019. Thirty age and gender-matched healthy volunteers were included as a control group (A), while thirty vitiligo patients have been included in the group (B) when they met the eligibility criteria of having stable non-segmental vitiligo, with stable refractory lesions and no response to conventional treatments. Pregnant, breastfeeding women, individuals with an active infection, or other autoimmune diseases were excluded. A total of 60 participants was determined using Stats Direct statistical software version 2.7.2 for MS (Windows, Stats Direct Ltd., Cheshire, UK), and the effect size was obtained from Yang et al.10
Ethical approval was obtained from the local ethics and research committee of Dermatology, Venereology and Andrology Department, of the National Research Centre. The study ran in concordance with the Declaration of Helsinki principles and other ethical guidelines and written informed consent was taken from every participant before the study enrollment.
All healthy participants in the control group (A) were exposed to sunlight daily for three months, whereas vitiligo patients in the study group (B) received three sessions of CO2 fractional laser therapy (Microxel MX7000, Daeshin Enterprise, , Korea), with a wavelength of 10600nm, the power output of 15 Watts, 1 millisecond as pulse width, 0.5 density and 15 mJ energy/point, at a monthly basis, together with sun exposure to the affected areas starting at the 5th day after each session, with the intact areas protected by sunscreen. Before the laser session, each patient applied topical anaesthetic on the areas to be treated for pain reduction. For ocular safety, laser-protective goggles were required for both the patients and the operator.
For the procedure of data collection and before starting the interventions, demographic characteristics, and serum RANTES level of every participant in both groups, clinical types and/or patterns of vitiligo as well as Vitiligo Area Severity Index (VASI) were attained from every patient in the group (B). Assessment of both RANTES and VASI was repeated after three months for all participants of both groups and the patients’ group, respectively.
Measuring serum RANTES in all participants was done using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) technique based on the manufacturer’s guidelines,11 through a kit supplied by Glory Science Co., Ltd, Del Rio, TX 78840, USA, in the medical Biochemistry department in the National Research Center. To detect serum RANTES level, venous serum samples of 3-5 cc were withdrawn from the anti-cubital fossa of each participant and were left to clot for 30 minutes at room temperature, then the samples were subjected to centrifugation for 10 minutes at 5000 rotation per minute (rpm). The supernatant serum was separated in Eppendorf tubes and stored at -80°c till the tie of analysis. Repeated freeze and thaw cycles were avoided.
To evaluate clinical vitiligo patients’ outcomes, VASI was selected as it is a well-defined performance metric used to detect the level of depigmentation and can be relied on as an indicator of disease incidence and patient management.12 The patient’s body is divided into five distinctive regions, while the face and neck are independently examined. VASI is determined for each body region according to the vitiligo area in the hand units (the palm plus the volar digit surface) and the depigmentation pattern within each hand-unit patch (no pigment=100%, specks of pigment=90%, vitiligo> pigment=75%, vitiligo=pigment=50%, vitiligo< pigment=25%, specks of vitiligo=10%). The whole body VASI score is then calculated using a specific formula.13
Data entry, processing, and statistical analysis were carried out using Microsoft Excel 2007 (Microsoft Corporation, NY, USA) and SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Science; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) version 22 for Microsoft Windows. Quantitative data were described in terms of mean ±standard deviation (±SD), while qualitative data were expressed as frequencies (number of cases) and relative frequencies (percentages). Comparison of numerical variables between the two groups was done using the Mann Whitney U test for independent samples when comparing the two groups of non-normal data. Correlation between various variables was done using the Spearman rank correlation equation. A probability value (p-value ≤ 0.05) was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS:
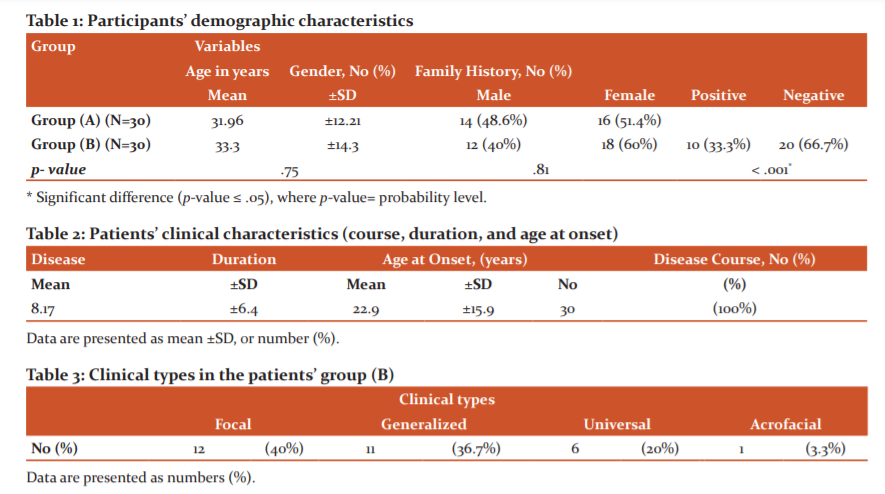
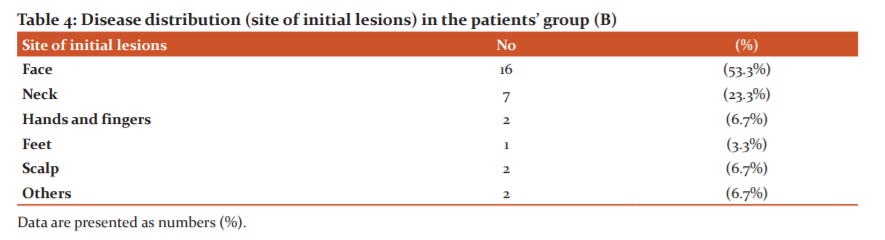
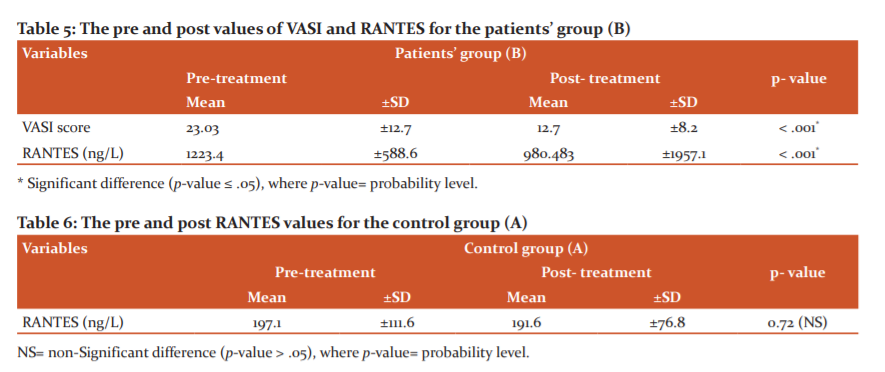
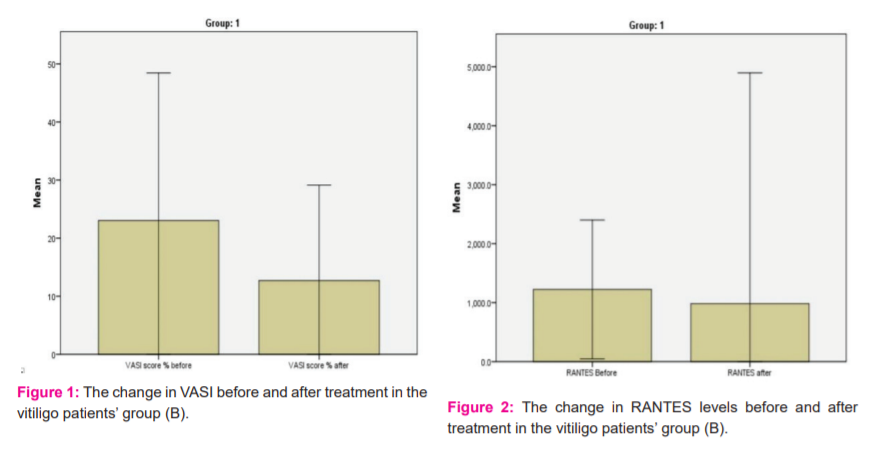
In the present study, 30 patients with vitiligo and 30 age and sex-matched controls were included. As shown in table 1of the participants’ demographic data, the mean age of the patients and the controls were 33.3 ±14.3 36 and 31.96 ±12.21 years, respectively, with 60% of patients were females. Almost 33% of the patients had a positive family history. There were no statistically significant differences between the patients’ group and the control group in terms of age (p=.75) and gender (p =.81). On contrary, there was a statistically significant difference between the patients’ group and the control group in terms of family history (p<.001). As illustrated in table 2, the mean patients’ disease duration was 8.17 ±6.4 years and the age at the disease onset was 22.9 ±15.9 years old, and all lesions were stationary. As indicated in table 3, the clinical type of vitiligo was focal in 40% of the cases, generalized in 36.7%, and universal in 20% of cases, with the face, was the most common site of the initial lesion (table 4). Before the interventions, the patients’ mean VASI score was 23.03 ±12.7 and the mean RANTES level was 1223.4 ±588.6 ng/L, while post-intervention, as shown in table 5, mean VASI score was 12.7 ±8.2 (Figure 1) and the mean RANTES level was 980.483±1957 (Figure 2), indicating statistically significant differences in both values in the patients’ group when comparing pre to post-study results (p <.001). Regarding the control group (A), there was no statistically significant difference when comparing results before and after 3 months of sun exposure (Table 6).
DISCUSSION
In the current study, the effect of fractional treatment using CO2 laser on the expression of circulating RANTES and vitiligo clinical outcomes in the form of VASI score in stable non-segmental vitiligo patients was explored. The study findings indicated a significant reduction in the serum RANTES level and a noticeable decrease in VASI score of vitiligo patients when they were treated using fractional CO2 laser, combined with sun exposure, 3 months after treatment, while sun exposure alone was not associated with a significant reduction in the serum RANTES level in the control group.
To the best of the current knowledge, several studies used fractional ablative CO2 laser in the treatment of vitiligo. Also, earlier studies have evaluated chemokines in the serum and tissues of vitiliginous patients and showed their importance in vitiligo pathophysiology. Still, no studies have been conducted to understand and correlate the relationship between the beneficial effect of fractional Co2 laser in treating vitiligo and both the chemokines’ level in the serum as well as improved vitiligo clinical outcomes.
To explain the underlying mechanism by which CO2 laser could positively affect vitiligo outcomes, various theories are proposed. For instance, First, a CO2 laser causes an immediate shrinkage of the tissue contraction that produces narrowing the vitiligo lesions’ size. Also, the wound healing process involves the secretion of multiple cytokines and growth factors from nearby intact tissues and hair follicles, serving as proteins to help melanocytes’ division. Another explanation is that laser fractional treatment enhances the penetration of both ultraviolet rays and other topical agents through the epidermal layer, boosting their effects.14
The results of this work matched those from a study with a similar design done by Shin et al.15 which showed vitiligo lesions’ improvement, but with a longer duration of the application. Also, many studies approved that fractional CO2 laser was better to be combined with other approaches as narrowband ultraviolet B and medications for more effective treatment outcome.16,17,18
However, the exact effect of a fractional CO2 laser remains elusive, as contradicting results were reported by Esme et al.19 who suggested that treating non-segmental vitiligo lesions using combined therapy of both phototherapy and CO2 laser is not superior to phototherapy alone in terms of their effectiveness in re-pigmentation, as they found non-significant differences between the two modalities when used separately in treating the patients’ lesions, with one half of the body treated by phototherapy and the other half with CO2 fractional laser, three times/ week for 4 months.
Regarding the effect of laser therapy added to sun exposure, it was previously studied by Helou et al.20 who examined the effects of fractional CO2 laser followed by sun exposure on generalized stable vitiligo and found a greater recovery of the lesions, when treated with both fractional CO2 laser beside sun exposure compared to sun exposure alone.
Concerning the findings of the current study, patients’ group (B) showed a significant decrease in RANTES levels. Previous reports demonstrated that the laser reduced the oxidative stress markers and increased the antioxidant capacity as well.21 Also, the laser was proved to enhance cytokine and chemokine expression via mitochondrial biogenesis, thus it could be considered as an efficient boosting agent for immunity in vitiligo treatment.22
The findings of the present study regarding the decrease in VASI score also agreed with the results from Abu Zeid et al.23 who found that treating patients with stable vitiligo with the fractional laser before applying tacrolimus ointment yielded significant improvement in form of decreased VASI scores, especially for acral areas and newly affected patches.
Having a controversial view about the exact role the fractional CO2 laser plays in vitiligo treatment,23,24,25 the current study provides evidence on its positive effect in the circulating chemokines and clinical measures of vitiligo. Also, using blood sampling to assess the serum RANTES was more convenient and easily accepted by patients than taking skin biopsy, though the latter could provide direct evidence for local skin immune responses. Moreover, the results of the present study are not affected as any change of the immune cells in circulation reflects the status of homeostasis of the peripheral immune system.
The current study provides objective data with statistically significant differences. Still, there are some limitations to it. While the study achieved the desired effect size, a larger sample would be more suitable for generalizing the results. Also, additional studies for RANTES (CCL5), their receptor CCR5, and other cytokines present in the circulation as well as skin are needed to provide better insight into the role of RANTES chemokine in the pathogenesis of vitiligo and other autoimmune disorders, and how inhibiting its production may provide therapeutic benefits via disruption of the chemokine-receptor axis. Similarly, the validation of factors associated with RANTES concentrations in vitiligo patients requires further investigation.
CONCLUSION
Based on the findings of that work, we can conclude that fractional treatment of vitiligo using CO2 laser could effectively decrease the serum RANTES level, a key chemokine in the vitiligo pathology, as well as reduce VASI score leading to better clinical outcomes in vitiligo patients after three months of treatment.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS: All the authors want to thank all individuals who participated in this study.
Conflict of Interest: All authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
Funding sources: None (this work did not receive any funding).
References:
-
Bergqvist C, Ezzedine K. Vitiligo: a focus on pathogenesis and its therapeutic implications. J Dermatol. 2021; 48(3): 252-70. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.15743
-
Zhang Y, Cai Y, Shi M, Jiang S, Cui S, Wu Y, et al.The prevalence of vitiligo: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2016; 11(9): e0163806.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0163806
-
Bhandarkar SS, Kundu RV. Quality-of-life issues in vitiligo. Dermatol Clin. 2012; 30(2): 255-68. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2011.11.013.
-
Kundu RV, Mhlaba JM, Rangel SM, Le Poole IC. The convergence theory for vitiligo: a reappraisal. Exp Dermatol. 2019; 28(6): 647-55. doi: 10.1111/exd.13677
-
Said-Fernandez SL, Sanchez-Domínguez CN, Salinas-Santander MA, Martinez-Rodriguez HG, Kubelis-Lopez DE, Zapata-Salazar NA, et al. Novel immunological and genetic factors associated with vitiligo: a review. Exp Ther Med. 2021; 21(4): 312. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.9743
-
Kandaswamy S, Akhtar N, Ravindran S, Prabhu S, Shenoi SD. Phototherapy in vitiligo: assessing the compliance, response and patient's perception about disease and treatment. Indian J Dermatol. 2013; 58(4): 325. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.113944
-
Yasmeen S, Khan T. Laser Carbon Dioxide Resurfacing. [Updated 2020 Aug 15]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
-
Omi T, Numano K. The role of the CO2 laser and fractional co2 laser in dermatology. Laser Ther. 2014; 23(1): 49-60. doi: 10.5978/islsm.14-RE-01
-
Kim WI, Kim S, Lee SH, Cho MK. The efficacy of fractional carbon dioxide laser combined with narrow-band ultraviolet B phototherapy for non-segmental vitiligo: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lasers Med Sci. 2021; 36(1): 165-73. doi: 10.1007/s10103-020-03069-0.
-
Yang L, Yang S, Lei J, Hu W, Chen R, Lin F, et al. Role of chemokines and the corresponding receptors in vitiligo: a pilot study. J Dermatol. 2018; 45(1): 31-8. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.14004
-
Locati M, Bonecchi R, Corsi MM. Chemokines and their receptors: roles in specific clinical conditions and measurement in the clinical laboratory. Am J Clin Pathol. 2005; 123 (1): S82-95. doi: 10.1309/M6U4B8L6TNAK4G9L.
-
Vrijman C, Linthorst Homan MW, Limpens J, van der Veen W, Wolkerstorfer A, Terwee CB, et al. Measurement properties of outcome measures for vitiligo: a systematic review. Arch Dermatol. 2012; 148(11): 1302-9. doi: 10.1001/archdermatol.2012.3065.
-
Hamzavi I, Jain H, McLean D, Shapiro J, Zeng H, Lui H. Parametric modelling of narrowband UVB phototherapy for vitiligo using a novel quantitative tool: the vitiligo area scoring index. Arch Dermatol. 2004; 140(6): 677-83. doi: 10.1001/archderm.140.6.677.
-
El-Zawahry MB, Zaki NS, Wissa MY, Saleh MA. Effect of combination of fractional CO2 laser and narrow-band ultraviolet B versus narrow-band ultraviolet B in the treatment of non-segmental vitiligo. Lasers Med Sci. 2017; 32(9): 1953-8. doi: 10.1007/s10103-017-2290-y
-
Shin J, Lee JS, Hann SK, Oh SH. Combination treatment by 10 600 nm ablative fractional carbon dioxide laser and narrowband ultraviolet B in refractory nonsegmental vitiligo: a prospective, randomized half-body comparative study. Br J Dermatol. 2012; 166(3): 658-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10723.x.
-
Ghasemloo S, Gauthier Y, Ghalamkarpour F. Evaluation of using fractional CO2 laser plus NB-UVB versus NB-UVB alone in inducing marginal repigmentation of vitiligo lesions. J Dermatolo Treat. 2019; 30(7): 697-700. 10.1080/09546634.2018.1564232
-
Liu L, Wu Y, Zhang J, Gu H, Luan Q, Qian L, et al. Ablative fractional Co2 laser aided delivery of long-acting glucocorticoid in the treatment of acral vitiligo: a multicenter, prospective, self-bilateral controlled study. J Dermatolog Treat. 2019; 30(4): 320-7. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2018.1509048.
-
Doghaim NN, Gheida SF, El-Tatawy RA, Mohammed Ali DA. Combination of fractional carbon dioxide laser with narrowband ultraviolet B to induce repigmentation in stable vitiligo: a comparative study. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019; 18(1): 142-9. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12553
-
E?me P, Gür Aksoy G, Elçin G. No additional benefit of combining fractional carbon dioxide laser with narrow-band ultraviolet b phototherapy for vitiligo: a randomized prospective study with half-body side comparison. Dermatol Surg. 2019; 45(12): 1627-34. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000001890.
-
Helou J, Maatouk I, Obeid G, Moutran R, Stéphan F, Tomb R. Fractional laser for vitiligo treated by 10,600 nm ablative fractional carbon dioxide laser followed by sun exposure. Lasers Surg Med. 2014; 46(6): 443-8. doi: 10.1002/lsm.22260
-
De Oliveira HA, Antonio EL, Arsa G, Santana ET, Silva FA, Júnior DA, et al. Photobiomodulation leads to reduced oxidative stress in rats submitted to high-intensity resistive exercise. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018; 2018: 5763256. doi: 10.1155/2018/5763256.
-
Chen W, Zhou Y, Huang FR, Luo D, Wang DG. Preliminary study on the treatment of vitiligo with carbon dioxide fractional laser together with tacrolimus. Lasers Surg Med. 2018; 50(8): 829-36. doi: 10.1002/lsm.22821
-
Abu Zeid OM, Omar N, El Sharkawy D. The efficacy of combining fractional CO2 laser and tacrolimus ointment in the treatment of vitiligo. J Egypt Women's Dermatologic Soc. 2020; 17(1): 25-30. doi:10.4103/JEWD.JEWD_41_19
-
Mahmoud ES, Abd el-baky AM, Said OM, Hussein HG. Low-level diode laser therapy on wound healing post gingivectomy. J Life Sci Biomed. 2020; 10(6): 80-6. doi:10.51145/jlsb.2020.10
-
Kim HJ, Hong ES, Cho SH, Lee JD, Kim HS. Fractional carbon dioxide laser as an "add-on" treatment for Vitiligo: a meta-analysis with systematic review. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018; 98(2): 180-4. doi: 10.2340/00015555-2836.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License