IJCRR - 2nd Wave of COVID-19: Role of Social Awareness, Health and Technology Sector, June, 2021
Pages: 210-214
Date of Publication: 11-Jun-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Drug Utilisation Study among COVID-19 Inpatients in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Eastern India
Author: Manjhi PK, Singh SK, Kumar R, Singh S, Priya A, Nishi
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) is a global pandemic without any specific treatment to date. Drug utilisation plays a vital role in helping the health care system to understand the pattern of drug use. Aim: To assess the prescribing trends among COVID-19 patients admitted to the hospital. Methodology: This was a retrospective cohort study conducted at a tertiary hospital dedicated to COVID-19 patients. Patients admitted in AIIMS, Patna from March 2020 to October 2020 were analyzed for WHO core prescribing indicators and was compared with the standard WHO values. Results: The median value of drugs prescribed was found to be 7 (IQR-6-8). The most common drugs prescribed for COVID-19 were Azithromycin (25.95%), hydroxychloroquine (23.88%) followed by paracetamol (20.17%) and Heparin (16.35%). The percentage of drugs prescribed by generic name was 77.72%. The average number of drugs from NLEM was 92.56%. Drugs were classified based on the Anatomical Therapeutic and Chemical Classification (ATC) and the majority of the drugs belonged to the J category which is the anti-infective group of drugs. The defined daily dose (DDD) /100 bed-days of azithromycin and cefixime was 5.2 and 0.092, respectively. Conclusion: Polypharmacy being the common finding, the concept of generic prescribing was practised well. There was a lesser number of prescriptions containing drugs from the National List of Essential Medicines, and the number of prescriptions containing antibiotics and injections was following criteria. The WHO prescribing criteria were met with moderate adherence.
Keywords: Drug utilisation, COVID-19, WHO prescribing criteria, Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification (ATC), De�fined Daily Dose (DDD), Polypharmacy
Full Text:
Introduction:
SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus causing Coronavirus disease 2019 originated in Wuhan, China in December 2019 and has spread rapidly across the world due to its high transmissibility and pathogenicity.1 It was shortly declared as a Public Health Emergency of International Concern and On March 11, a global pandemic was declared.2 Since then many drugs have been tried to treat COVID-19 infection but the effort has mostly been focused on repurposing existing medicines. The drugs that may be reused are from different pharmacological categories i.e. antimalarial, anthelmintic, anti-protozoal, anti-HIVs, anti-influenza, antineoplastics, neutralizing antibodies, immunoglobulins, and interferons.3 These drugs have been used as a single agent or in combination, unfortunately, no medicine has yet been officially approved to treat COVID-19. The treatment guidelines for COVID-19 vary from one country to another. However, the treatment protocols across the countries are almost similar and vary very slightly and include hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine phosphate, Remedesivir, azithromycin, tocilizumab and lopinavir/ritonavir.4 In India COVID-19 treatment guideline has been changed several times based on the latest research data. Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), New Delhi recommended hydroxychloroquine for prophylactic purposes in asymptomatic healthcare workers and household contacts of laboratory-confirmed patients.5 The Government of India, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Directorate General of Health Services (Emergency Medical Relief (EMR) Division), recommended lopinavir/ritonavir after proper informed expressed consent from the patient.6 The Government of India, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Directorate General of Health Services (Emergency Medical Relief (EMR) Division), recommended HCQ for mild to moderate case, low molecular weight heparin and steroid for moderate to severe case of COVID-19.7 Spanish Society of Hospital Pharmacy recommended lopinavir/ritonavir, Remdesivir, hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine, darunavir/cobicistat, tocilizumab interferon and alfa-2B,beta-1B.8,9 US FDA has not yet approved any drug for COVID 19 although some information regarding the drugs recommended for the treatment has been provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and includes Remdesivir, chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, and lopinavir/ritonavir.10 The drugs like Remdesivir, favipiravir, chloroquine phosphate, plasma, and traditional Chinese medicine was recommended by the National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China.11 At present there is the limited number of study which summarizes the drug Utilisation in corona infected patients in a tertiary care hospital in India. Drug utilisation focus on the factors related to the prescribing, dispensing, administering, and taking of medication, and the related events including medical and non-medical determinants of drug utilisation, the effects of drug utilisation, as well as how drug utilisation relates to the beneficial or adverse effects of drug use.12,13 Therefore this study has been designed to assess the prescribing trends among COVID-19 patients admitted to a tertiary care hospital in India. This study will be helpful to educate the prescribers, adherence towards rational drug therapy for safety and benefit to the patient.
Materials and methods:
This retrospective observational study was carried out at All India Institute of Medical Science (AIIMS), Patna, (Bihar) India. COVID-19 patients, admitted to AIIMS Patna from March 2020 to October 2020 were included in the study. Medical Records of (n = 300) COVID-19 patients from the Medical Record Department (MRD) were evaluated for 3 months. Data were recorded on a standardized format in which information on drug utilisation among COVID-19 patients which include patient’s demographic details (age, sex, duration of hospitalisation) and details of prescribed drugs (name, dose, therapeutic class, dosage form, route of administration, dosing frequency, etc.,) was retrieved from in-patient case files. Details of standard intravenous fluids, oxygen, vaccines and blood transfusion were not recorded. The prescription pattern was analysed using WHO’s core prescribing indicators. Drugs are divided based on pharmacological action on the organ or system and their therapeutic and chemical properties in the anatomical therapeutic chemical (ATC) classification.14The World Health Organization (WHO) Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology defines the defined daily dose (DDD) as a statistical measure of drug consumption. For grouping related drugs, it is defined in conjunction with the ATC Code drug classification system. The DDD allows for drug usage comparisons between different drugs in the same group or between different health care environments which were calculated by the following formula.15
DDD/ 100 bed -days =
Drug consumption in mg x 100
DDD (mg) x no. of days in study period x total no. of beds x occupancy index
The total number of beds used was 300 and the average occupancy index was 0.85. The occupancy index for every month was calculated by the Medical Records department. The occupancy index is the average monthly occupancy index for the three months of our study period.
Statistical analysis: Data were captured on Microsoft excel. The results were expressed as actual numbers, means, median (IQR) frequency (percentages) using SPSS software version 16.0., and were presented using tables.
Results:
Three hundred medical records of patients with confirmed COVID-19 patients were evaluated. The demographic and clinical characteristics of the patients are shown in Table 1. Of the total study population, 71.33% were male. A median number of seven medications (IQR, 6–8) were administered for the patients. Diabetes (21%) and hypertension (21%) was the most common comorbidity followed by hypothyroidism (14.28%) and hypercholesterolemia (8.4 %).


The analysis of drug utilisation using WHO core prescribing indicators revealed that the percentage of encounters with antibacterials and injectables was 15.63% and 11.82%, respectively. The percentage of drugs prescribed with a generic name and from the Essential Drug List of India was 77.72% and 92.56%, respectively (Table 2).

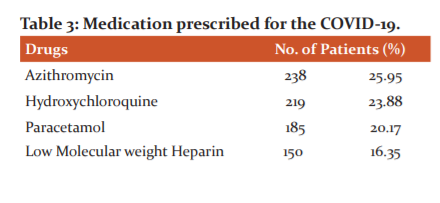
Looking at the individual drugs the most commonly prescribed drugs for COVID-19 patients include azithromycin (25.95%) hydroxychloroquine (23.88%), followed by paracetamol (20.17 %) and heparin (16.35%) from antimicrobial, analgesics, anti-inflammatory and an anticoagulant class of drugs, respectively.[Table 3]

The World Health Organization (WHO) defines polypharmacy as “the administration of many drugs at the same time or the administration of an excessive number of drugs”. Polypharmacy may be defined as the administration of five or more than five drugs simultaneously which is evident in our study. [Table 4]
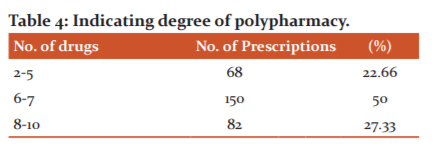
Table 5 shows the Defined daily doses (DDD) by anatomical therapeutic chemical (ATC) classification codes of various drugs utilized among COVID-19 inpatients.

Discussion:
Drug Utilisation study is an important tool for ensuring quality in hospital drug use. The WHO core indicators of prescribing practice assess healthcare providers' performance in key dimensions related to drug safety. As a result, the purpose of this study was to examine the prescribing indicator that will aid in the promotion of rational drug use to improve drug safety.
The average number of drugs per encounter in our study was 6.97, which was higher than the national average. WHO recommended range is 1.6-1.8.16 Our finding was higher than that of Hazra et al. (3.2)17 some international studies, such as Wang et al. (3.52),18 Bimo et al. (3.8)19, and other Indian studies, such as Rehan et al. (2.4)20 Tripathy et al.(2.9).21
The number of drugs prescribed in each encounter ranged from two to ten, with 27.33 % of encounters prescribing eight or more drugs, indicating a polypharmacy trend (Table 4). This was in line with Tripathy et al findings (30%).21 Polypharmacy has a variety of consequences, including adverse drug reactions, drug-drug interactions, therapeutic failure, and toxicity, reduces patient compliance, unnecessary drug costs, and the risk of bacterial resistance emergence when antibiotics from different classes are prescribed to the same patient without reason.
In our study, the percentage of drugs prescribed by generic names was 77.72%, which is less when compared to the standard WHO ideal value of 100%. It was higher than the findings of Chandelkar and Rataboli's study (0.05%)22, Rehan et al. (1.5%)20, Tripathy et al. (68 %),21 Hazra et al. (46.2 ),17 and other international studies.23,24
The analysis of two common expensive modes of drug administration such as antibiotics and injections showed that the percentage of encounters with antibiotics prescribed was 15.63%, which is less than the standard range of 20-26.8 % of the WHO prescribed values. The finding of other studies conducted in India such as Hazra et al. (72.8%),17 and Tripathy et al. (47.75 %) respectively.21 Lower rates of antibiotic prescribing in our study due to the viral origin of COVID-19.
The percentage of encounters with injections in our study was 11.82% which was lesser than the standard range of WHO ideal value (13.4-24.1%). It was higher to the findings from Tripathy et al. (8%)21 but very low compared to another region, South Ethiopia (38.1%)23 and Uganda (48 %).25
The percentage of drugs prescribed by the NLEM in our study was 92.56%, which was lower when compared to the ideal standard value of 100%. This finding was much more to findings from studies of other parts of India such as Hazra et al. (45.71%).17 The percentage of prescribing drugs from the essential drug list is lower in India17 compared to other countries such as Ethiopia (99%), South Ethiopia (99.6%),23 and Nepal (88%).19 This difference may be due to the lack of awareness of the essential drug list. Between the mean of the estimated parameters, demographic data, it is involved in all of this, is similar to the findings in other studies.26 Compared to studies from Dubai where the patient name was missing in 2.9%, age in 9.7%, and sex in 12%.27 Lack of demographic indicators will lead to the source of serious medication error such as dispensing of medication to the wrong patients. The diagnosis was mentioned in 100% of prescriptions which was slightly more than other study results Shipra et al. (64.66%).26 The doses of drugs were mentioned for 100% of the drugs which was similar to other study results such as Shipra et al. (100%).26 Dosage form was mentioned in 100% compared to other study results Shipra et al. (98.66%).26Duration of treatment was mentioned in 100% compared to 92.66% in Shipra et al.26 The DDD per 100 bed-days ranges from 23.96 to 0.03. Vitamin C was found to be the most commonly prescribed drug with DDD per 100 bed- days of 23.96 followed by antimicrobials 5.37. Among the antimicrobials, the defined daily dose (DDD) /100 bed-days of azithromycin and cefixime was 5.2 and 0.092, respectively. Our study reports the highest use of vitamin C. which plays a very important role as an immune modulator28,29 and since this study was performed during the COVID-19 pandemic where vitamin C was used very widely and this could be the possible reason behind the highest use. The DDD per 100 bed-days of azithromycin, cefixime and ceftriaxone, levofloxacin was found to be much lesser than other studies.30
This study has certain limitations as it is retrospective a time-bound study with a small sample size and among COVID- 19 patients. It was not possible to assess the rationality and quality of prescriptions. However, it helps to create a drug Utilisation database in a tertiary care teaching hospital of a developing country.
Conclusion: The WHO core prescribing indicators were met with moderate adherence. With the prevalence of polypharmacy, the concept of generic prescribing has been practised well. The prescription of NLEM drugs, antibiotics, and injections was within normal limits. Drug utilisation among covid-19 as well complied with AIIMS-Patna covid management protocol.
Acknowledgement: We thank all corona warriors of AIIMS Patna working at the front line against COVID-19. We acknowledge the medical record department staff of the hospital for cooperation in providing medical records.
Ethical Approval and informed consent: The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee, AIIMS Patna (Ref. No. AIIMS/Pat/IEC/2020/647 Dated 25/01/2021). Waiver of informed consent was granted as patient details were anonymized and only medical records of hospitalized COVID-19 patients were analyzed.
Financial support of the study: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared
Author’s contribution: Manjhi PK analyzed data and wrote the manuscript. Singh SK wrote the introduction and Kumar R analyzed data. Priya A. and Nishi collected data from Medical Record Department. All authors read this manuscript.
References:
-
Li H, Liu SM, Yu XH, Tang SL, Tang CK., Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): current status and future perspectives. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020;55(5):105951.
-
Sohrabi C, Alsafi Z, O'Neill N., World Health Organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) Int J Surg. 2020;76:71-76.
-
Rameshrad M, Ghafoori M, Mohammadpour AH, Nayeri MJD, Hosseinzadeh H., A comprehensive review on drug repositioning against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID19). Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020;393 (7):1137-1152.
-
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Epidemiology, virology, clinical features, diagnosis, and prevention (2020) up to date. Available from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19#H1354847215.
-
National Taskforce for COVID-19 Advisory on the use of hydroxy-chloroquine as prophylaxis for SARS-CoV-2 infection 2020. Available from: https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/AdvisoryontheuseofHydroxychloroquinasprophylaxisforSARSCoV2infection.pdf
-
Government of India Ministry of Health & Family Welfare Directorate General of Health Services (EMR Division). Guidelines on Clinical Management of COVID – 19 dated 17th March 2020.
-
Clinical Management Protocol: COVID-19. Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India directorate general of health services (EMR division), Available from: https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/ClinicalManagementProtocolforCOVID19.pdf
-
Spanish Society of Hospital Pharmacy (SEFH) - Hospital pharmacy procedures for the management of antiviral treatment in the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 disease (COVID-19).
-
EAHP: COVID-19 Resource Centre. Available from: https://www.eahp.eu/hp-practice/hospitalpharmacy/eahp-covid-19-resource-centre
-
Centres for disease control and prevention: Information for Clinicians on Therapeutic Options for COVID-19 Patients. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019ncov/hcp/therapeutic-options.html
-
National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. 2020. Potential Treatments for COVID-19. Available from: http://en.nhc.gov.cn/2020-03/19/c_77977.htm
-
World Health Organization. Introduction to drug utilisation research. Oslo: World Health Organization, 2003.
-
Lunde PK, Baksaas I., Epidemiology of drug utilisation basic concepts and methodology. Acta Med Scand Suppl 1988;721:7-11.
-
WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology: Guidelines for ATC classification and DDD assignment. Oslo: World Health Organisation, 2020.
-
WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology: ATC index with DDDs 2020. Oslo: World Health Organisation, 2020.
-
Isah AO, Ross-Degnan D, Quick J, Laing R, Mabadeje AF., The Development of Standard Values for the WHO Drug use Prescribing Indicators. ICUM/EDM/WHO. Available from: http://www.archives.who.int/prduc2004/rducd/ICIUM_
-
Hazra A, Tripathi SK, Alam MS., Prescribing and dispensing activities at the health facilities of a non-governmental organization. Natl Med J India. 2000;13(4):177-82.
-
Wang H, Li N, Zhu H, Xu S, Lu H, Feng Z., Prescription pattern and its influencing factors in Chinese county hospitals: A retrospective cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e63225.
-
Bimo., Report on Nigerian field test, INRUD news. In: How to Investigate Drug Use in Health Facilities. Vol. 3. Geneva: WHO; 1992. p. 9-10.
-
Rehan HS, Singh C, Tripathi CD, Kela AK., Study of drug utilisation pattern in dental OPD at the tertiary care teaching hospital. Indian J Dent Res. 2001;12(1):51-6.
-
Tripathy R, Lenka B, Pradhan MR., Prescribing activities at district health care centres of Western Odisha. Int J Basic Clin Pharmacol. 2015;4:419-21.
-
Chandelkar UK, Rataboli PV., A study of drug prescribing pattern using WHO prescribing indicators in the state of Goa, India. Int J Basic Clin Pharmacol. 2014;3:1057-61.
-
Desalegn AA., Assessment of drug use pattern using WHO prescribing indicators at Hawass university teaching and referral hospital, South Ethiopia: A cross-sectional study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2013;13:170.
-
Menik HL, Isuru AI, Sewwandi S., A survey: Precepts and practices in drug use indicators at Government Healthcare Facilities: A Hospital-based prospective analysis. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2011;3:165-9.
-
Bannenberg WJ, Forshaw CJ, Fresle D, Salami AO, Wahab HA., Evaluation of the Nile Province Essential Drug Project. Geneva: WHO; 1991.
-
Shipra J, Zafar YK, Prerna U, Kumar A., Assessment of prescription pattern in a private teaching hospital in India. Int J Pharm Sci. 2013;3(3):219-22.
-
Sharif S, Al-Shaqra M, Hajjar H, Shamoun A, Wess L., Patterns of drug prescribing in a hospital in Dubai, United Arab emirates. Libyan J Med. 2008;3(1):10-2.
-
Carr AC, Maggini S., Vitamin C and Immune Function. Nutrients. 2017 Nov 3;9(11):1211.
-
Chambal S, Dwivedi S, Shukla KK, John PJ, Sharma P., Vitamin C in disease prevention and cure: an overview. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2013;28(4):314-328.
-
Mittal N, Mittal R, Singh I, Shafiq N, Malhotra S., Drug utilisation study in a tertiary care centre: recommendations for improving hospital drug dispensing policies. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2014;76(4):308-314.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License