IJCRR - 13(16), August, 2021
Pages: 207-211
Date of Publication: 30-Aug-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A Clinical Study of Paediatric Tracheostomy: Our Experience in a Tertiary Care Hospital in North India
Author: Gupta R, Verma R, Anoop M, Nishad RK
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Tracheostomy is a surgical procedure to establish direct communication between the trachea and external environment by creating an opening into the anterior wall of the trachea and introducing a cannula into it. While performing pediatric tracheostomy, chances of complication are more especially in newborns and infants. In modern times, the long term outcome of tracheostomy is considered satisfactory due to more specific indications. Aims: Paediatric tracheostomy is a lifesaving procedure to secure airway, practised since ancient days. Paediatric tracheostomy is quite a less studied topic among literature. We took up this clinical study to assess its recent trends in terms of indications, complications, and management of its complications. Material and Methods: This is a prospective, observational study of 3 years duration, which was carried out in a tertiary care hospital of north India with the participation of Otorhinolaryngology, Paediatric and General surgery departments. Results: A total of 39 paediatric tracheostomies were included in this study. The major indications in this study were infective causes like Diphtheria (46%) and Tetanus (16%). The male to female ratio was 1.5: 1 and the rural to urban ratio was 4.5: 1. The most common complications were intraoperative haemorrhage, sudden apnea, secondary haemorrhage and difficult decannulations. The mortality rate in this study is found to be 46%. Conclusions: Upper airway obstruction due to infections like Diphtheria and Tetanus are the most common indications for paediatric tracheostomy in rural areas. Sound knowledge of the anatomy of the pediatric trachea combined with good surgical skills can reduce almost all the major complications associated with tracheostomy in children. Mostly, the higher mortality attributed to paediatric tracheostomy is due to the primary disease condition itself rather than related to complications arising out of tracheostomy procedure.
Keywords: Paediatric tracheostomy, Airway obstruction, Diphtheria, Tetanus, Complications
Full Text:
Introduction
Tracheostomy is a surgical procedure to establish direct communication between the trachea and the external environment by creating an opening into the anterior wall of the trachea and introducing a cannula into it. Many ancient texts described tracheostomies performed in ancient Egypt. Tracheostomy is considered one of the oldest surgical procedures.1While performing pediatric tracheostomy, chances of complication are more especially in newborns and infants.2 The indication of pediatric tracheostomy has changed over the years. In modern times, the long-term outcome of tracheostomy is considered satisfactory due to more specific indications.3 The main objective of the present study was to analyze the complications of pediatric tracheostomies in our institute and the methods used to tackle the complications.
Before the beginning of the twentieth century, tracheostomy was considered a very dangerous procedure with both patients and surgeons extremely worried about the outcome of the procedure. This scenario is changed only after the introduction of antisepsis and improved anaesthesia techniques in the early twentieth century. Nowadays, the technology of endotracheal intubation is very much improved and assisted by video laryngoscope and fiberoptic bronchoscope etc. due to which many upper airway emergencies can be managed by nasotracheal or orotracheal intubation or percutaneous tracheostomy. Intensivists are frequently performing bedside percutaneous tracheostomies now a day, due to these advances’ health care professionals of other branches are also facing problems of tracheostomy care and decannulation.4
Before the introduction of antisepsis and improved anaesthesia at the end of the nineteenth-century tracheostomy was an extremely hazardous procedure and was undertaken with a good deal of trepidation on the part of both surgeon and patient. In recent years, with improvements in the technology of endotracheal intubation, an increased number of upper airways emergencies can be managed with nasotracheal or orotracheal intubation or percutaneous tracheostomy. The growth of such techniques particularly that of percutaneous tracheostomy in the past ten years has meant that surgical management of upper airway obstructions is no longer the exclusive province of an otolaryngologist. The result is that more and more health care professionals are being confronted with the problems associated with tracheostomy care and decannulation procedures.4
Material and methods
This prospective observational study of 3 years duration (from December 2017 to November 2020) was conducted on pediatric patients, who underwent tracheostomies at a tertiary care health institute in northern India. Institutional Ethics Committee approval was taken and informed consent was obtained from the patient’s parents or legally acceptable relatives. The demographic details of each patient were recorded. The diagnosis, surgical procedures, complications and management of complications concerning pediatric tracheostomies were recorded and systematically analyzed.
The main objective of the present study was to analyze the various types of complications related to pediatric tracheostomies and their management. The age pattern, sex pattern and populations distributions of these patients were also analyzed. The study group includes patients who were under 18 years of age and underwent tracheostomies. Patients above 18 years of age, previous history of tracheostomy, bleeding disorders and congenital heart disease were excluded from the study.
All paediatric tracheostomies were accomplished by senior otolaryngologists under monitored anaesthesia care either bedside or in the operation theatre. All tracheostomies were performed according to departmental S.O.P. (Standard Operative Procedure) for tracheostomy. The indication and timing of tracheostomy were decided by the treating physician. Decannulation was planned when the child is off inotropes, hemodynamically stable and maintaining oxygen saturation on room air. The decannulation protocol involves downsizing of the tracheostomy tube and then gradual occlusion of it. After discharge patients were followed up fortnightly for one month and monthly thereafter for at least 6 months.
Results
Among 43 pediatric tracheostomies conducted at our institute during the study period, 39 were included in this study. Three cases were excluded due to the previous history of tracheostomy and one due to the non-willingness of guardians to give consent for this study.
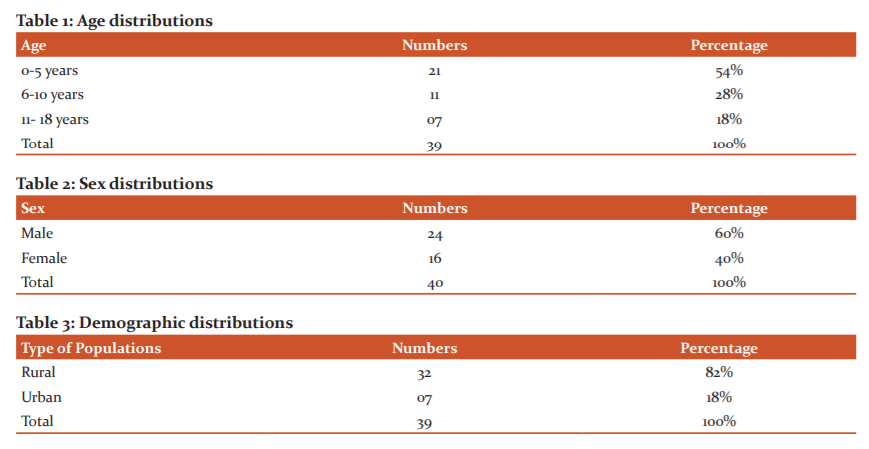
Most of the patients who underwent tracheostomy were under 5 years of age, the median age at tracheostomy was 5 years (Table:1). There was no statistically significant difference between the median age at the time of tracheotomy between children who developed Intraoperative (5 years), early (4.5 years), late (5 years) or no complications (5.5 years) using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test (P>0.05). The male to female ratio in this study was 1.5:1 and the rural versus urban ratio was 4.5:1(Table 2 &3).
The most common causative factor for pediatric tracheostomy was diphtheria (18 patients) followed by ventilatory dependent respiratory failure (11 patients), tetanus (6 patients) and congenital anomaly (4 cases) (Figure:1).
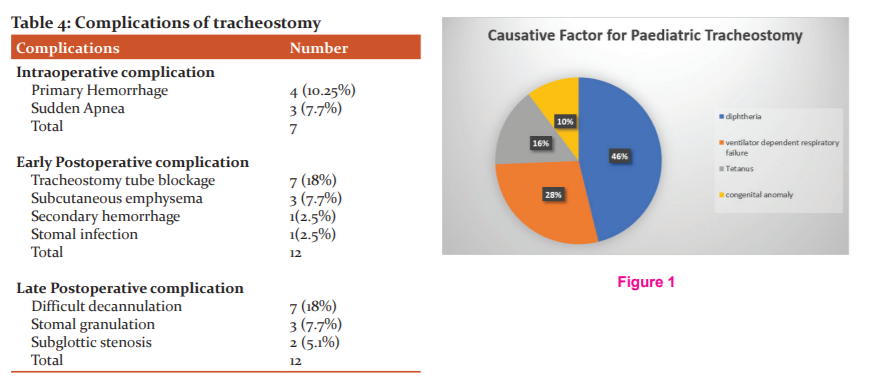
Among 39 patients 24 patients (61.53%) developed complications. The complications were classified according to time of occurrence as intraoperative, early postoperative and late postoperative complications. In this study 31 complications were developed in a total of 24 patients. Some patients developed more than one complication as shown by data (Table:4).
In this study, two types of Intraoperative complications were noticed i.e. primary haemorrhage and sudden apnea. Four patients developed bleeding during dissection which was controlled successfully by ligating the bleeding vessels and in three cases patients developed sudden apnea immediately after opening the trachea.
Tube blockage was the most common complication in the early postoperative period, seen in seven patients. Three patients developed subcutaneous emphysema in the neck and upper part of the chest which was subsided within two days. One patient developed a secondary haemorrhage, the wound was immediately explored at the bedside and bleeding vessels were ligated. Infection of the stomal site was seen in one patient.
Difficulty in decannulation was the most common late complication with seven patients having multiple failed decannulation attempts. All patients who had failed decannulation attempts were undergone bronchoscopic examination under general anaesthesia, among them two patients were found to have subglottic stenosis. Both of these subglottic stenosis patients were managed with the bronchoscopic placement of silicon airway stent. Both of these airway stents were successfully removed after 1year follow-up. So, to date, all surviving patients of this study were successfully decannulated. The Decannulation rate of this study was 54%. Granulation at the stomal site was seen in three patients.
Mortality was high in this study after one month follow up 18 patients (46%) died and 21patients (54%) survived. In this study, mortality was associated with primary disease conditions and none died due to complications of tracheostomy.
Discussion
Tracheostomy is a surgical procedure that involves creating a temporary or permanent opening in the anterior wall of the trachea to place a tube to communicate to the external environment. The credit for the first tracheostomy goes to the Asclepiades of Rome in 2ndcentury BC. Antonio M. Brasovala an Italian physician successfully performed a tracheostomy on a patient with an abscess of the trachea in the 16th century AD.5In 1766, Caron had done a tracheostomy on a seven-year-old child for removing a foreign body. This is supposed to be considered the first paediatric tracheostomy in the history of ENT practice.6 In 1833, Trousseau saved nearly 50 children with diphtheria by doing paediatric tracheostomies. It also described postoperative care after paediatric tracheostomy.6 In 1921, Chevalier Jackson demonstrated a reduction in mortality due to paediatric tracheostomy by following standard protocols of performing it.7 Chevalier Jackson contributed tremendously to standardized paediatric tracheostomies, thereby, reducing complications and increasing its tolerance. The next major development to its increasing usage came when Galloway reported using paediatric tracheostomy with children with poliomyelitis.8
Embryologically larynx develops from the cranial most part of the laryngotracheal tube. The trachea develops from the intermediate part of the laryngotracheal tube that lies between the points of its bifurcation into branchial or lung bud and the larynx. With the caudocranial extension of the tracheoesophageal septum, the trachea elongates. At birth the bifurcation of trachea lies at the level of lower border of 4th thoracic vertebra.9 A study was conducted by Anne Dsouza et al on 28 spontaneously aborted / still born human fetuses to found that during second and third trimester of gestation tracheal length increase significantly but not the diameter.10
Tracheostomy is a speedy, safe, effective lifesaving procedure practised since ancient times. Pediatric tracheostomy differs significantly from the adult one. Sound knowledge of pediatric airway, greater care and skill are required for performing a pediatric tracheostomy.
In our study, 39 pediatric tracheostomies were done in a study period of 3 years from December 2017 to November 2020. The mean age group in this study was 5 years. In other studies, by Carron et al11 Ang et al12 and Ozmen et al13 the mean age was 3.2 years, 3.24 years and 2.25 years respectively. In our study mean age group was comparatively on the upper side. Maximum patients were in the age group 0 to 5 years. The male to female ratio was [1.5:1] which is comparable to a study conducted by Carron et al in which the male to female ratio was 1.2:1. This slight male preponderance could be due to the increased susceptibility of male children to congenital and acquired diseases.
In this study, the most, common indication for performing pediatric tracheostomy was infection leading to upper respiratory obstruction. It was diphtheria (46%) followed by tetanus (16%). These were compared with the study done by Ozmen13 and the one by Kremer et al.14 Children with prolonged ventilatory support (28%) and congenital anomaly (10%) added to the rest of the figures. In this study, a smaller number of patients with congenital anomalies could be due to lack of early recognition, lack of awareness by the parents, lack of prenatal and perinatal screening procedures. The mortality rate was slightly higher in our study. 18 patients (46%) who underwent pediatric tracheostomy died and 21 patients (54%) survived. The mortality in this study was fully attributable to primary disease condition and none died due to surgical procedure or complication of pediatric tracheostomy. The higher mortality could be due to the late presentation of children at an advanced stage of disease and ignorance among the rural population. Mortality due to diphtheria was higher than due to tetanus, even though both are the vaccine-preventable disease.
There is enough description in pediatric literature for diphtheria being a disease-causing higher mortality. The diphtheria toxins are very potent, poor socio-economic background of children, poor host response to diphtheria antiserum are a few to mention.15,16,17
In this study 24 patients (61.53%) developed complications. The complications were studied as three subsets i.e. intraoperative, early postoperative and late postoperative complications. Total 31 complications developed in a total of 24 patients. Some patients developed more than one complication. The percentage of complications of this study (61.53%) was a little higher compared to other studies by Carron et al. (44%) and Ozman et al (18%). The possible explanation for the higher rate of complication in this study could be the lack of ideal operating facilities in the pediatric intensive care unit, where most of the bedside tracheostomies are done. The complications were noticed more in male patients.
Haemorrhage while performing tracheostomy was the most common intraoperative complication noticed in this study. Four patients developed intraoperative haemorrhage. It is controlled by ligating the bleeding vessels the commonest vessel causing bleeding while performing tracheostomy could be the anterior jugular vein, thyroid vein, thyroid ima artery.18
Sudden apnea was the other intraoperative complication three patients developed. Sudden apnea was recovered spontaneously. One patient needed carbogen inhalation
Tube blockage (18%) was the most common early postoperative complication noticed. seven patients developed tube blockage which was comparable to the study done by Wetmore et al19 where the tube blockage contributed (16%).
In this study, all surviving patients (54%) were successfully decannulated. The Decannulation rate was 82% in a study conducted by Sharma and Vinayak.20
Conclusions: The indications of pediatric tracheostomies are showing a change in its trend in recent years due to the better availability of neonatal ICUs and neonatologists skilled in endotracheal intubation. Still, in rural setups, upper airway obstruction due to infections like Diphtheria and Tetanus are the most common indications for paediatric tracheostomy. Sound knowledge of the anatomy of the pediatric trachea combined with good surgical skills can reduce almost all the major complications associated with tracheostomy in children. Mostly, the higher mortality attributed to paediatric tracheostomy is due to the primary disease condition itself rather than related to complications arising out of tracheostomy procedure.
Acknowledgement: We express our sincere gratitude to Dr. Gaurav Khandelwal Professor & HOD Department of ENT, Dr. Avinash Saxena Professor & HOD Department of Surgery and Dr. Sonia Bhat Professor & HOD Department of Pediatrics for their constant support for this study.
Conflict of Interest: Ritu Gupta, Reetu Verma, Anoop M and Rajeev Kumar Nishad declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval: Approval was taken from F.H. Medical College Institutional Ethics Committee (IEC No.138 dated 16th Nov.2017) before starting the project.
Informed Consent: Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in this study
Source of Funding: None
Author Contributions
Ritu Gupta, Conception and design, literature research, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data
Reetu Verma, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data, supervision, draft writing;
Anoop M, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data, critical revision of the manuscript, administrative and technical support;
Rajeev Kumar Nishad, literature research, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data, critical revision of the manuscript, final approval of the manuscript, Corresponding author.
References:
-
Frost EA. Tracing the tracheostomy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1976 Sep-Oct;85(5 Pt.1):618-24. doi: 10.1177/000348947608500509. PMID: 791052.
-
Wilson DP. Paediatric Tracheostomy. Grand Rounds. Philadelphia, PA: Philadelphia University,1997. pp. 454–63.
-
Ghosh T, Yewale V, Parthsarthi A, Shah NK. Paediatrics Infectious Diseases. Indian Academy of Pediatrics series (Under IAP Action Plan 2006)
-
Pracy Paul, Tracheostomy; in Michael Gleeson, George G, Browning, Martin J Burton et al: Scott-Brown’s Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Volume 2, Seventh edition, 2008, Hodder Arnold London. 2292-95
-
Wetmore RF. Tracheotomy. In: Bluestone CD, Stool SE, Alpes CM, Arjmand EM, et al., editors. Pediatricotolaryngology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2003.p. 1583-98.
-
Gooddal EW. The story of tracheotomy. Br J Child Dis. 1934;31:167-76.
-
Jackson C. High tracheotomy and other errors: the chief causes of chronic laryngeal stenosis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1921;32:392-8.
-
Galloway TC. Tracheotomy in bulbar poliomyelitis. J Ame Med Ass. 1943;123:1096-7.
-
Subhadra Devi V, Respiratory system, body cavity and diaphragm, In Inderbir Singh’s Human Embryology Eleventh Edition Jaypee, 2018, New Delhi: 215-19
-
Dsouza Anne, AnkolekarVrinda Hari, Hosapatna Mamatha, Dsouza Antony Sylvan. Dimensional changes of the trachea in second and third trimester fetuses-An anatomical study. Int J Cur Res Rev. 2013: 05(19): 126-131
-
Carron JD, Derkay CS, Strope GL, Nosonchuk JE, Darrow DH. Pediatric tracheostomies: Changing indications and outcomes. Laryngoscope 2000;110(7):1099–104.
-
Ang AH, Chua DY, Pang KP, Tan HK. Pediatric tracheotomies in an Asian population: the Singapore experience. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005;133(2):246–50.
-
Ozmen S, Ozmen OA, Unal OF. Pediatric tracheostomies: a 37-year experience in 282 children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2009;73(7):959–61.
-
Kremer B, Botos-Kremer AI, Eckel HE, Schlöndorff G. Indications, complications, and surgical techniques for pediatric tracheostomies—an update. J Pediatr Surg. 2002;37(11):1556–62.
-
Sachdev HPS, Choudhury P, Bagga A, Chugh K, Ramji S, Puri RK (Eds.). Principles of Pediatric and Neonatal Emergencies, 2nd edn. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd, 2004. pp. 689–94.
-
Ghai OP, Paul VK, Bagga A (Eds.). Pediatric critical care. In: Essential Pediatrics, 7th edn. New Delhi: CBS Publishers, 2013:686–712.
-
Gaudet PT, Peerless A, Sasaki CT, Kirchner JA. Pediatric tracheostomy and associated complications. Laryngoscope. 1978; 88(10):1633–41.
-
Hardy KL. Tracheostomy: indications, technics, and tubes. A reappraisal. Am J Surg. 1973 Aug;126(2):300-10. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(73)80167-9. PMID: 4721553.
-
Wetmore RF, Handler SD. Postic WP. Pediatric tracheostomy. Experience during the past decade. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1982;91(6 Pt 1):628–32
-
Sharma P, Vinayak N. A single centre experience of pediatric tracheostomy. Indian Pediatr. 2018;55:1091–2. [PubMed]
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License