IJCRR - 13(16), August, 2021
Pages: 198-206
Date of Publication: 30-Aug-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
In Silico Screening of Phytochemicals of Styrax Benzoin Against the Inflammatory Mediators
Author: Swathy B, Menaka M, Kiran G, Prabhakar Reddy V
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Inflammatory mediators are up-regulated during SARS-CoV-2 infection and also during injury and surgery. The wound is categorized as break down or opening of the skin, which could lead to malfunctioning of skin. Many physiological processes, protein targets, and cellular signalling pathways are involved in wound healing. Many inflammatory mediators are produced during injury and inhibition of the negative inflammatory mediators like 1RAK4 and NLRP3 inflammasome plays a key role in the wound healing process. Therefore, it could essential to find therapeutics for inhibiting the signalling pathways responsible for the release of negative inflammatory mediators. However, the conventional approaches to drug development are time-consuming and expensive. Objective: In the present study, we have adopted a computational approach to identify lead molecules from Styrax Benzoina�gainst the inflammatory mediators. Method: We have screened ligands from Styrax Benzoin library for their ability to bind and inhibit the two potential inflammatory targets such as IRAK4 (Interleukin-1 Receptor Associated Kinase-4) with Protein Data Bank (6F3I) and innate immune signalling receptor NLRP3 (NOD-, LRR-, and pyrin domain-containing-3) inflammasome with Protein Data Bank (6NPY). Results: We found that p-coumarin cinnamate 6 and coniferyl benzoate 12 could bind at the substrate-binding pocket of inflammatory targets with high binding affinity. Bioavailability properties and Pharmacophore features were also studied. Conclusion: The results suggest that the Phytoconstituents of Styrax Benzoin have the potential to be developed as novel inhibitors of inflammatory mediators. These inflammatory mediators are upregulated during SARS-CoV-2 infections. However, their clinical usage on wound healing is a subject of further investigations and clinical trials.
Keywords: Styrax Benzoin, Inflammatory Mediators, SARS-CoV-2, Wound, 1RAK4, NLRP3 inflammasome
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Inflammatory mediators are upregulated during SARS-CoV2 infections and also during injury and surgery. Viruses can affect the wound healing process by causing physiological changes. As per WHS (Wound Healing Society), wound is categorized as break down or opening of the skin, which could lead to malfunctioning of skin.1 The physiology stages of wound healing are primary and secondary interventions, smaller wounds heal by primary interventions and larger wound are heal by secondary interventions.2, 3 Among the different stages in wound healing the first stage is the inflammatory stage and is very essential phase in wound healing process.2, 4. These clots release monocytes and forms macrophages and further produce the cytokines.5When the tissue is injury that going to release inflammatory cytokines from the damaged tissue cells.6, 7 Neutrophils, also contribute in wound healing by releasing the cytokines and growth factors and also has phagocytosis functions which protect the wound against bacterial infections.8, 9. Therefore, it could essential to find therapeutics for inhibiting the signaling pathways responsible for release of negative inflammatory mediators. Inflammatory mediators like cytokines, chemokines and growth factors play the key role in wound healing by releasing fibroblasts and keratinocytes from cells and replace or restore the skin integrity.10, 11 NLRP3 (Nod-like receptor protein) inflammasome cellular pathway is involved in wound healing and various inflammatory skin diseases.12, 13Yimin Chai group have studied role NLRP3 expression in diabetic wounds in humans and the results demonstrates the higher expression of caspase1, NLRP3, IL-1β inflammatory mediators.14 These mediators could be the potential targets for the diabetic wound healing process. IRAK4 (interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4) is an important molecular target for the release of inflammatory substances.15, 16 IRAK inhibitors could be useful in the prophylaxis treatment of psoriasis, sclerosis, myocardial infarction, lupus erythematous, and arthritis.17, 18
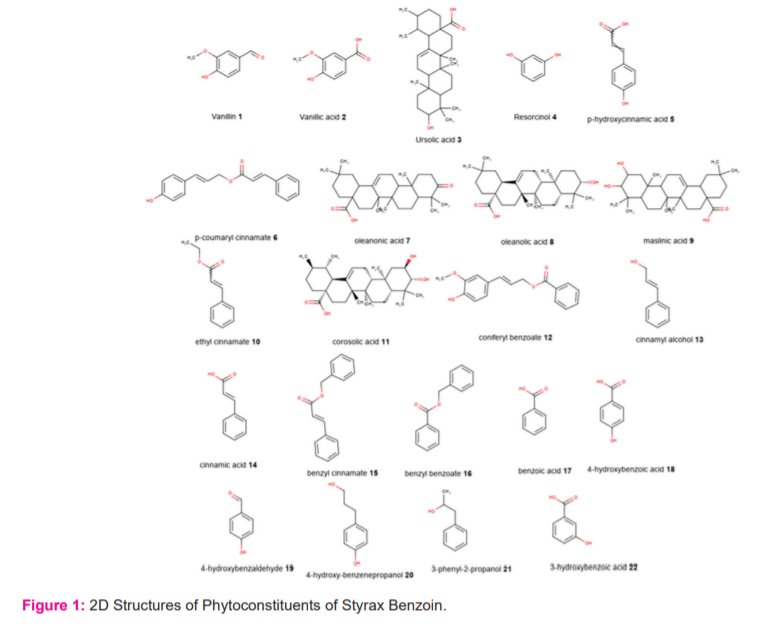
Styrax Benzoin (Latin: Benzoinum) is a balsamic resin and other species are Sumatra Benzoin and Siam Benzoin and belongs to family Styraceae.19 It is grown highly in tropical rain forests of South-Eastern Asia Countries like Indonesia, Thailand, China and Vietnam. (20) The plants grow up to 14 cm long and flowers are white in color and bell-shaped. Sumatra benzoin resin contains chemical constituents are balsamic acid which esters of benzoic and cinnamic acids.21 They also contains Triterpenoid acids like summaresinolic and siaresinolic acids are present.22 Whereas, Siam Benzoin about 76% of coniferyl benzoate is present as chief active constituent.23 The sytrax benzoin resin is prepared as tincture and used as expectorant, carminative, disinfectant and diuretic.24-27 It also has the biological uses in throat infection and upper respiratory tract infections.28 The aim of this study is to investigate the In Silico computational study of 22 Phytoconstituents of Styrax Benzoin against the inflammatory mediators 1RAK4 and NLRP3 inflammasome.
EXPERIMENTAL
Protein Preparation:
The present study is aimed to perform the computational studies of phytochemical analogs of Styrax Benzoin against COVID-19 negative immune regulators such as IRAK4 (Interleukin-1 Receptor Associated Kinase 4) with PDB ID: 6F3I and innate immune signaling receptor NLRP3 (NOD-, LRR-, and pyrin domain-containing 3) inflammasome with PDB ID: 6NPY.29,30The X-ray crystal structures of IRAK4 in complex with pyrrolotriazine inhibitor and NLRP3 bound to NEK7 were retrieved from Protein Data Bank (https://www.rcsb.org/structure/6F3I; https://www.rcsb.org/structure/6NPY). The protein targets were downloaded in PDB format and protein structural preparation in Macromolecule protocol was carried out in Discovery Studio software with default settings. Protein structures were cleaned and missing residues, Hydrogen’s were added and 3D protonation were carried out to the target protein and minimized for the selected active residues.
Ligand Preparation:
The important phytochemicals of Styrax Benzoin were collected from the literature survey and also from TCIM database. The canonical smiles were saved in .csv format and structures were generated by using Data warrior software and all the 22 Phytoconstituents were saved in SD file. All the ligand structures were energy minimized using CHARMm force field in Small-molecule Protocol and different conformers were generated.
Molecular Docking Studies:
Molecular docking were carried out for the 18 Phytoconstituents of Styrax Benzoin (1-22) to identify the molecular interactions between inflammatory targets 1RAK4 (PDB ID: 6F3I) and NLRP3 inflammasome (PDB ID: 6NPY).29, 30All the ligands were docked with by using Accelrys Discovery Studio version 3.5 with Libdocker and CDocker software. The protein structures were retrieved form protein data bank and the protein preparation and minimization were carried out with the default settings in Discovery Studio. The active site sphere generated from by ligand binding sites with current selection of Define and Edit Binding site in Receptor-Ligand Interaction tools. The binding site sphere specified based on the binding interactions of co-crystal ligand against the target protein, Docking Tolerance as 0.25, Docking Preferences as High Quality. The results were analysed and 3D and 2D interactions were obtained with Discovery studio Visualizer.
Pharmacophore Modelling.
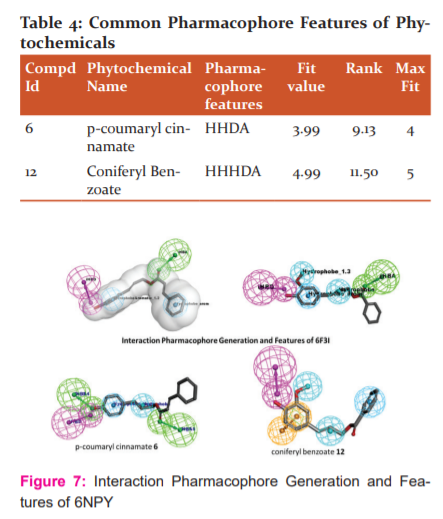
Pharmacophores features are generated between receptor-ligand using Interaction Pharmcophore generations in DS Protocol. Different molecular interactions like HBA (hydrogen bond acceptor), HBD (hydrogen bond donor), HY (hydrophobic center) and PI (Positive ionisable) were generated for receptor-ligand complex. The study was done for best docked pose of p-coumaryl cinnamate6 and coniferyl benzoate12 for 1RAK4 and NLRP3 complex proteins.
In Silico Absorption Distribution Metabolism Excretion (ADME) and Toxicity Prediction:
All the Phytoconstituents of Styrax Benzoin(1-22) were predicted In silico ADME properties and Toxicity analysis were carried out using Discovery Studio, pKCSM web server and Data Warrior Software.31,32
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Molecular Docking Studies
The molecular docking studies were carried out in Discovery Studio Docking software. The 3-dimensional proteins (PDB: 6F3I and 6NPY) were retrieved from the protein data bank. All the proteins were prepared and their energies were minimized by the protein preparation wizard. The receptor sphere around their co-crystal ligands were generated using current selection of co-crystal ligand interactions. All the selected 22 Phytoconstituents of Styrax Benzoinwere downloaded from Pubmed (Figure-1). The molecular docking using normal mode was carried out and results were analyzed.
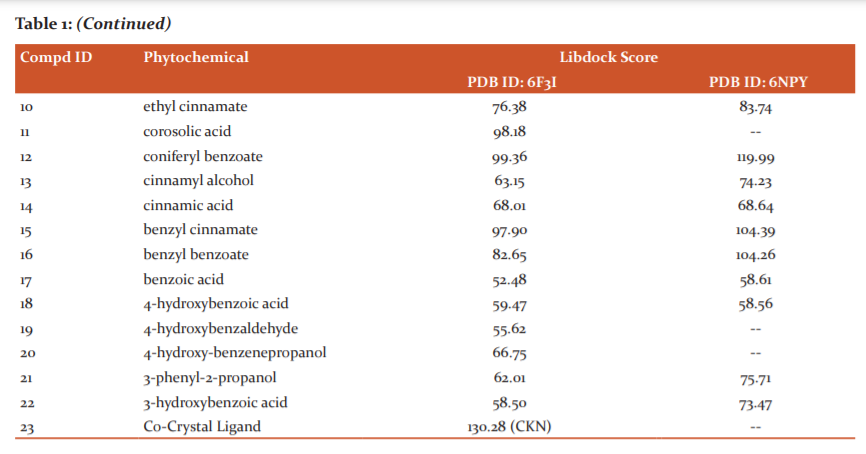
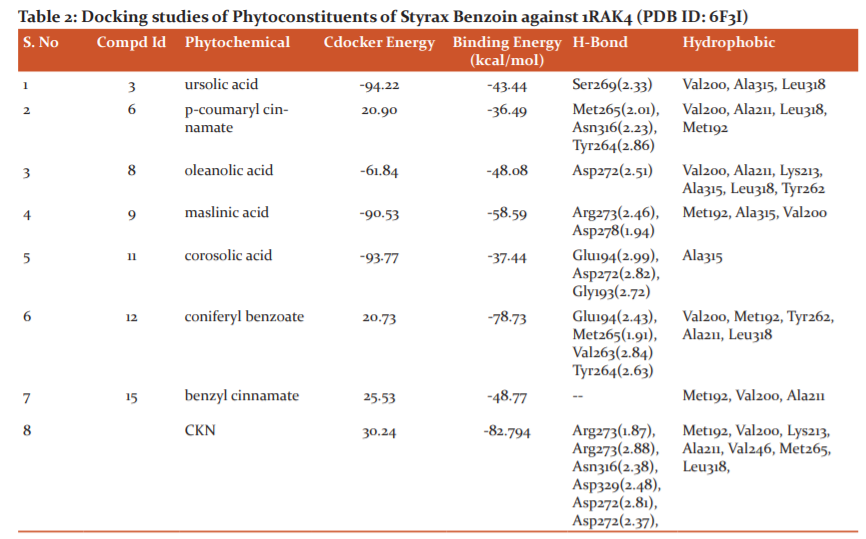
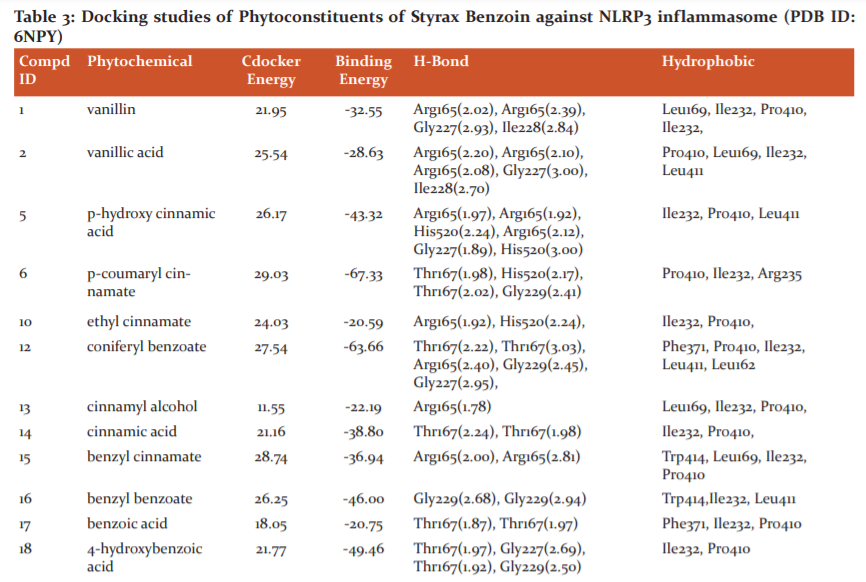
The initial rationale molecular docking studies of all 22 Phytoconstituents of Styrax Benzoin (1-22) in the active site of 1RAK4 (PDB ID: 6F3I) and NLRP3 inflammasome (PDB ID: 6NPY)were carried out in order to predict the binding efficiencies. The molecular docking scores are summarized in (Table:1-3). Initially the docking studies were carried out for all ligands with Libdock which High Throughput Screen-based software and best ligand poses were further docked with CDocker.

Molecular Docking Studies with 1RAK4 (PDB ID: 6F3I):
The molecular docking study was carried out for 22 phytoconstituents of Styrax Benzoin (1-22) into the active site of 1RAK4 (PDB ID: 6F3I). IRAK family (IRAK1-4) plays a central role in positive and negative inflammatory responses by regulating the expression of genes in immune cells.33 These signals which stimulus the various inflammatory mediators and plays key role for elimination of pathogens like virus, bacteria and carcinogenic cells, as well as for wound healing.
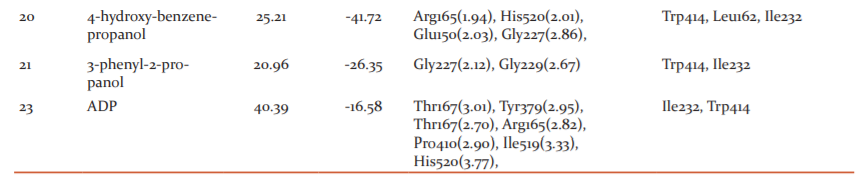
Among the ligands docked against IRAK-4, coniferyl benzoate (12) has showed excellent free energy binding with Lib dock score 99.36 and with Cdock score -20.73 and with binding energy value of -78.73 kcal/mol. Coniferyl benzoate(12) exerted H-bond interactions and bond distance in Å with Glu194(2.43), Met265(1.91), Val263(2.84) Tyr264(2.63) amino acid residues and hydrophobic interactions with Val200, Met192, Tyr262, Ala211, Leu318 residues. Similarly, p-coumaryl cinnamate has exhibited H-bond interactions with Met265(2.01), Asn316(2.23), Tyr264(2.86) residues and hydrophobic interactions with Val200, Ala211, Leu318, Met192 amino acid residues with Libdock Score 105.19and Cdock score -20.90and binding energy value of -36.49 kcal/mol. (Table-1 & 2)
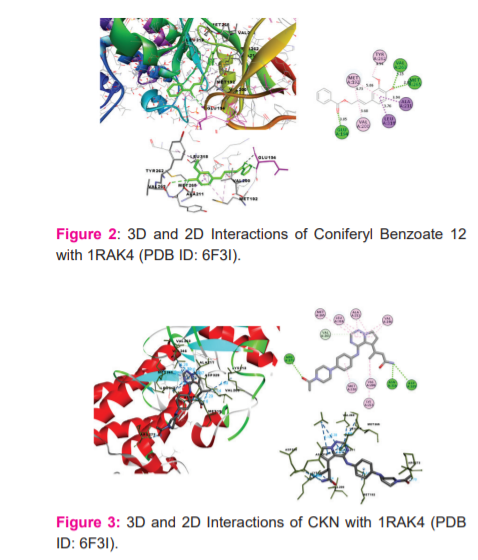
Whereas, Crystal ligand CKN (Pyrrolotriazine) has involved key interactions with residues forming H-bond with Arg273(1.87), Arg273(2.88), Asn316(2.38), Asp329(2.48), Asp272(2.81), Asp272(2.37), and hydrophobic interactions with Met192, Val200, Lys213, Ala211, Val246, Met265, Leu318, residues with Libdock Score 130.28 and Cdock score 30.24 and binding energy value of -82.79 kcal/mol. It signifies that Coniferyl benzoate(12) is occupying the same residues of active site of crystal ligand. (Figure: 2 & 3)
Molecular Docking Studies with NLRP3 inflammasome (PDB ID: 6NPY):
The molecular docking study was carried out for 22 phytoconstituents of Styrax Benzoin (1-22) into the active site of NLRP3 inflammasome (PDB ID: 6NPY). NLRP3 inflammatory signalling pathway plays a key role in release of inflammatory mediators, on activation of NLRP3 abrupt the cytochrome storms viz Interlukins (IL-1β, IL-6) and TNF-αand causes inflammatory in lower respiratory tract.34 On inhibition of NLRP3 will stops the release of negative inflammatory mediators.
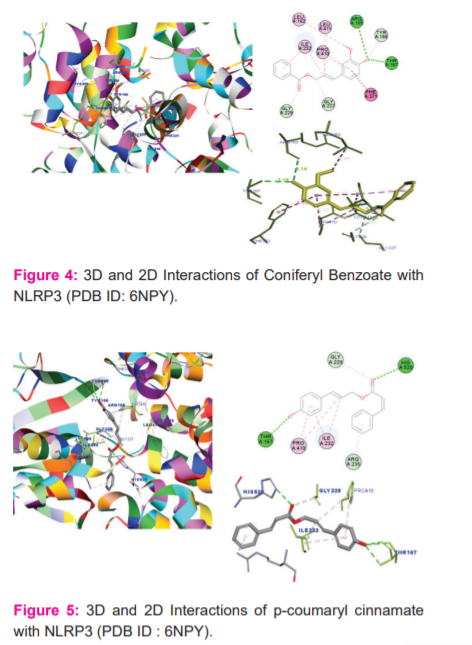
Among the ligands docked against IRAK-4, coniferyl benzoate (12) has showed excellent free energy binding with Lib dock score 119.99and with Cdock score -27.54 and with binding energy value of -63.66 kcal/mol. Coniferyl benzoate(12) exerted H-bond interactions and bond distance in Å with Thr167(2.22), Thr167(3.03), Arg165(2.40), Gly229(2.45), Gly227(2.95), amino acid residues and hydrophobic interactions with Phe371, Pro410, Ile232, Leu411, and Leu162 residues. Similarly, p-coumaryl cinnamate(6) has exhibited H-bond interactions with Thr167(1.98), His520(2.17), Thr167(2.02), Gly229(2.41) residues and hydrophobic interactions with Pro410, Ile232, Arg235 amino acid residues. (Table 1 & 3)
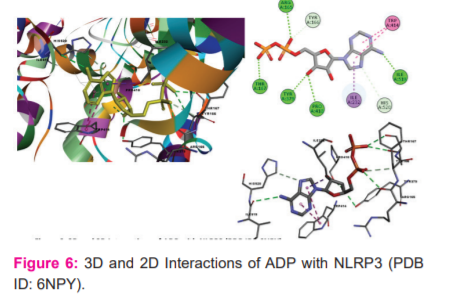
Whereas, Crystal ligand CKN has involved key interactions with residues forming H-bond with His163 and Glu166 with a bond distance 2.06 Ao and 2.18 Ao, respectively and hydrophobic interactions with His41, Met49 and Met165 residues. It signifies that p-coumaryl cinnamate(6) and Coniferyl benzoate(12) is occupying the same residues of active site of crystal ligand. (Figure: 4-6)
Structure-Based Pharmacophore: The best protein-ligand pose of docking were further analysed for Pharmacophore features using Interaction Pharmacophore Generation Protocol. Table-4 give the details about Common Pharmacophore Feature for ligand p-coumaryl cinnamate 6 has HHDA pharmacophore feature and fit value 3.99 and rank 9.13 and whereas, coniferyl benzoate 12 has HHHDA pharmacophore features with fit value 4.99 and rank 11.50 which shows better features. The interaction pharmacophore features for receptor-ligand complex among the result coniferyl benzoate-6F3I complex has 10 pharmacophore models with H-bond interactions Glu194, Val263, Tyr264, Met265 and with hydrophobic interactions Met192, Val200, Ala211, Tyr262, Leu318. Similarly, with coniferyl benzoate-6NPY complex has 10 pharmacophore models with H-bond interactions Arg165, Thr167, Gly227 and hydrophobic interactions Leu162, Ile232, Phe371, Pro410, Leu411. The interaction pharmacophore features are shown in Figure-7.
In Silico ADMET Prediction:
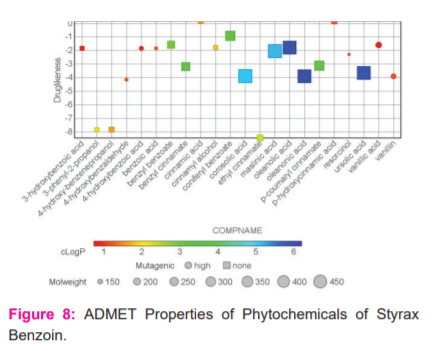
In Silico Prediction of ADME and Toxicity parameters were analysed for the Phytoconstituents of Stryax Benzoin by using Discovery Studio, pKCSM webserver and Data Warrior Software. All the phytochemicals has obeyed Lipinski’s rule of 5 in which the Mol. Wt is below 500, logP <5, No of Hydrogen Bond Donors is <5 and Acceptors < 10 and Molar refractivity (2) between 40-130. Almost all the phytochemicals have not deviated the rule of 5 and hence they potential for oral absorption and less toxicity. (Figure-8).
Some of the potential Phytochemicals (1-7, 9, 11-16, 20) which have shown good binding affinity with the docking studies were analysed for ADMET using pKCSM webserver(Table-5). Absorption properties of the compounds are studied by Caco-2 permeability, human intestinal absorption, skin permeability, and p-gp substrate or inhibitor. Predicted value >0.90 indicates high Caco-2 permeability. Vanillin 1, vanillic acid 2, ursolic acid 3, resorcinol 4, p-OHcinnamic acid5, p-coumaryl cinnamate 6, oleanonic acid 7, masilinic acid9, corosolic acid 11, coniferyl benzoate12, cinnamyl alcohol13, cinnamic acid14, benzyl cinnamate15, benzyl benzoate16, 4-hydroxy-benzenepropanol20 were predicted to have highCaco-2 permeability. All phytochemicals have good intestinal absorption. In terms of skin permeability if the compounds has logKp > -2.5 consider to be low skin permeability. Among analysed compounds, cinnamyl alcohol13 was consider to have low skin permeability with logKp = -1.70.
None of the phytochemicals are substrate for p-glycoprotein which is an efflux transporter which excretes chemicals or drugs from the cells. All phytochemicals have apparent volume of distribution the limits are VDss is low if log VDss <-0.15 and high if logVDss >0.45. For Blood-Brain Barrier permeability, compound with logBB > 0.3 consider to cross the BBB and logBB < -1 are impermeable to brain. Phytoconstituents 12-16 & 20 will cross the BBB as predicted values are logBB>0.3. Regarding CNS permeability, phytochemicals 6, 7, 9, 11, 13, 14, 15, 16 & 20 have high CNS permeability (logPS > -2).
Cytochrome P450 is important enzyme for biotransformation of drugs in liver and inhibitors of CYP450 will affect the pharmacokinetic properties of drug. All phytochemicals are not substrate for CYP2D6, Compound 12, 13,
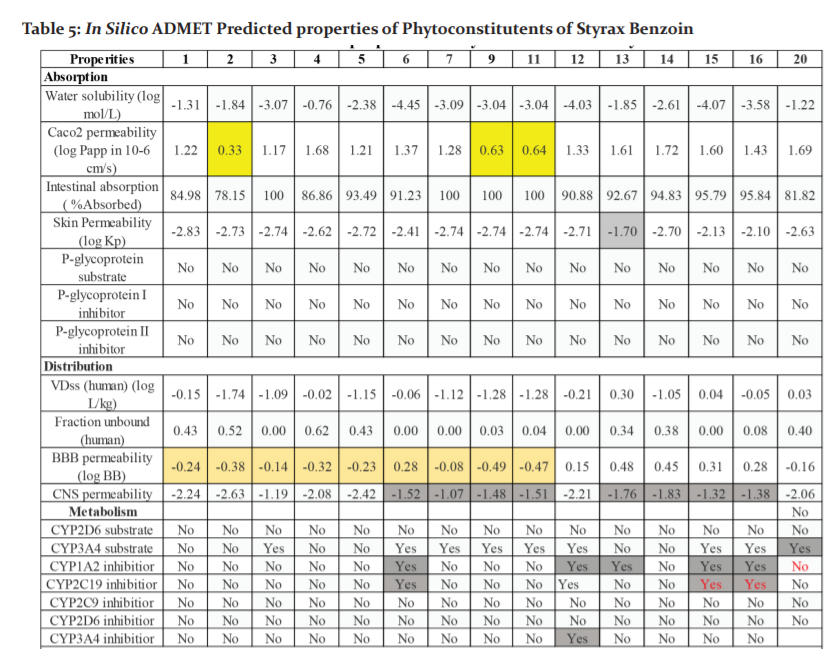
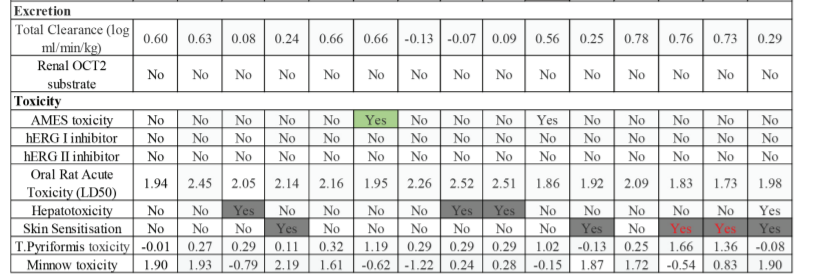
16 & 20 are substrate for CYP3A4. Compound 6, 12 & 13 are inhibitors for CYP1A2 inhibitor.
Regarding toxicity compound 6 has Ames toxicity, and compounds 3, 9, 11 have hepatoxicity, 4, 13, & 20 has skin sensitisation problems. All phytochemicals have hERG toxicity and are free form cardiotoxicity. From these observations it could revealed that all phytochemicals of Styrax Benzoin have shown good drug-like properties viz., no toxicity, good oral absorption, metabolism and excretion and no interaction with cytochrome P450 enzymes and free from cardiotoxicity.
Conclusion:
InSilico computational studies like molecular docking, pharmacophore mode, ADMET prediction could provide helpful information for rapid design of drugs. Wound infection causes cytokine storm and release negative inflammatory mediators such as 1RAK4 and NRLP3. Therefore, it could essential to find therapeutics for inhibiting the signaling pathways responsible for release of negative inflammatory mediators. To find potent inhibitors for inflammatory targets 1RAK4 and NRLP3 inflammasome we performed molecular docking studies for 22 Phytoconstituents of Styrax Benzoin using Libdocker and Cdocker. The results shown p-coumaryl benzoate 6 and coniferyl benzoate 12 have high binding affinity against the protein targets. A detail pharmacophore features were also generated against these docked complexes. ADMET prediction studies indicate that all the Phytoconstituents are having good oral absorption and less toxicity. The results suggest that the Phytoconstituents of Styrax Benzoin have the potential to be developed as novel inhibitors of inflammatory mediators. These inflammatory mediators are upregulated during SARS-CoV-2 infections. However, their clinical usage against inflammatory mediators is a subject of further investigations and clinical trials.
References:
1. WHS 2019 Abstracts. Wound Repair and Regeneration. 2019;27(3): A1-A40.
2. Velnar T, Bailey T, Smrkolj V. The wound healing process: an overview of the cellular and molecular mechanisms. J. Int. Med. Res. 2009;37(5):1528-42.
3. Bertone AL. Principles of wound healing. Vet. Clin. North. Am. Equine. Pract. 1989 Dec 1;5(3):449-63.
4. George Broughton I, Janis JE, Attinger CE. The basic science of wound healing. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;117(7S):12S-34S.
5. Gillitzer R, Goebeler M. Chemokines in cutaneous wound healing. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2001;69(4):513-21.
6. Fara A, Mitrev Z, Rosalia RA, Assas BM. Cytokine storm and COVID-19: a chronicle of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Open. Biol. 2020;10(9):200160.
7. Bai B, Yang Y, Wang Q, Li M, Tian C, Liu Y, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome in endothelial dysfunction. Cell. Death. Dis.. 2020;11(9):1-18.
8. Werner S, Grose R. Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines. Physiol.Rev. 2003.
9. Fujiwara N, Kobayashi K. Macrophages in inflammation. Curr.Drug.Targ-Inflam Allergy. 2005;4(3):281-6.
10. Raja SK, Garcia MS, Isseroff RR. Wound re-epithelialization: modulating keratinocyte migration in wound healing. Front. Biosci. 2007;12(3):2849-68.
11. Baum CL, Arpey CJ. Normal cutaneous wound healing: clinical correlation with cellular and molecular events. Dermatologic surgery. 2005;31(6):674-86.
12. Weinheimer-Haus EM, Mirza RE, Koh TJ. Nod-like receptor protein-3 inflammasome plays an important role during early stages of wound healing. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0119106.
13. Shen H-H, Yang Y-X, Meng X, Luo X-Y, Li X-M, Shuai Z-W, et al. NLRP3: a promising therapeutic target for autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2018;17(7):694-702.
14. Zhang X, Dai J, Li L, Chen H, Chai Y. NLRP3 inflammasome expression and signaling in human diabetic wounds and in high glucose-induced macrophages. J Diabetes Res. 2017;2017.
15. Katsuyama E, Miyamoto H, Kobayashi T, Sato Y, Hao W, Kanagawa H, et al. Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-4 (IRAK4) promotes inflammatory osteolysis by activating osteoclasts and inhibiting formation of foreign body giant cells. J.Bio.Chem. 2015;290(2):716-26.
16. Patra MC, Choi S. Recent progress in the molecular recognition and therapeutic importance of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4. Molecules. 2016;21(11):1529.
17. Borges T. Clinical Approach to Systemic Autoinflammatory Disorders: Classification, Disease Phenotypes and Management. Curr. Imm. Rev. 2018;14(2):105-19.
18. Zarrin AA, Bao K, Lupardus P, Vucic D. Kinase inhibition in autoimmunity and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2020:1-25.
19. Sankaralingam R, Sengottuvelan B, Venkat P, Selvaraj M, Arunachalam V, Natarajan J. Experimental investigation on varying flame characteristics of benzoic resin solid fuel pellets. Renewable Energy. 2020;147:1500-10.
20. Saputra MH, Sagala SAH, Lee HS, editors. Species Distribution of Styrax sumatrana in North Sumatra using Maxent Modelling Approach. Forum Geografi; 2020.
21. Falzon CC, Balabanova A. Phytotherapy: An Introduction to Herbal Medicine. Prim Care. 2017 Jun;44(2):217-227.
22. Wang F, Zhang L, Zhang Q, Chen A, Wang S, Fang Z. Two new phenylpropanoids from the resin of Styrax tonkinensis (Pierre) Craib ex Hartw. J Nat Med. 2020:1-6.
23. Tra NT, Anh TD, Van Cuong P, Ha NTT, Anh LTT, Cham BT, et al. Chemical constituents from the leaves of Styrax annamensis Guill. Vietnam J. Chem. 2020;58(5):630-6.
24. Nurwahyuni I, Situmorang M, Sinaga R. Plant Regeneration through Callus Cultures from Leaf Explant of Sumatra Benzoin (Styrax benzoin). Int J Forestry Res. 2020;2020.
25. Jaradat N. Phytochemistry, traditional uses and biological effects of the desert plant Styrax officinalis L. J.Arid. Env. 2020;182:104253.
26. Atia Sharif HN, Rehman R, Mushtaq A, Rashid U. A review on bioactive potential of Benzoin Resin. Int. J. of Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2016;10(1):106-10.
27. Du J, Singh H, Yi TH. Antibacterial, anti-biofilm and anticancer potentials of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using benzoin gum (Styrax benzoin) extract. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2016;39(12):1923-1931.
28. Parkman C. Integrating CAM into traditional health care. The Case. Manager. 2000;11(3):27-9.
29. Degorce SL, Anjum R, Dillman KS, Drew L, Groombridge SD, Halsall CT, et al. Optimization of permeability in a series of pyrrolotriazine inhibitors of IRAK4. Bioorg. Med.Chem. 2018;26(4):913-24.
30. Sharif H, Wang L, Wang WL, Magupalli VG, Andreeva L, Qiao Q, et al. Structural mechanism for NEK7-licensed activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Nature. 2019;570(7761):338-43.
31. Pires DEV, Blundell TL, Ascher DB. pkCSM: Predicting Small-Molecule Pharmacokinetic and Toxicity Properties Using Graph-Based Signatures. J. Med. Chem. 2015;58(9):4066-72.
32. Sander T, Freyss J, von Korff M, Rufener C. DataWarrior: An Open-Source Program For Chemistry Aware Data Visualization And Analysis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015;55(2):460-73.
33. Su L-C, Xu W-D, Huang A-F. IRAK family in inflammatory autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020;19(3):102461.
34. Sendler M, van den Brandt C, Glaubitz J, Wilden A, Golchert J, Weiss FU, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome regulates development of systemic inflammatory response and compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndromes in mice with acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(1):253-69. e14.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License