IJCRR - 13(16), August, 2021
Pages: 184-189
Date of Publication: 30-Aug-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Descriptive Study on Prevalence of Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Diabetes, Hypertensive Patients
Author: Bomma Vijay Kumar, Ambati Rathna Kumari, Sravani Maryada, Shoban Babu
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The chronic diseases caused by genetics, lifestyle, the environment and ageing itself are the key factors that affect health today; hence, we should concentrate our attention on our patients' last years of life aimed at raising the number of elderly people in health, able to sustain their physical and mental functions. Aims: To study the incidence and degree of sensorineural hearing loss in diabetic, hypertensive patients. Materials and Methods: This is a prospective observational study done for 18 months. The study will be conducted on 50 subjects diagnosed with diabetes, 50 subjects diagnosed with hypertension and 50 subjects with both hypertension and diabetes and 50 normal subjects without hypertension and diabetes. All the subjects in the age group of 20-60 years with diagnosed diabetes, hypertension and normal subjects without hypertension and diabetes both males and females are included in the study. Results: Of 100 patients in the study age of the group with the associated disease is statistically higher in the group without the associated disease. It was found that out of 150 cases with hypertension or diabetes or both in the present study 138 were in the age group of 40- 60 and only 12 cases were between ages 20-40. Patients with hypertension (86%) were at a higher risk of developing SNHL when compared to controls (0%). Conclusion: The importance of preventive processes that may reduce the mechanisms that trigger hearing aid degeneration induced by circulatory problems especially high blood pressure and high blood sugar, and the need for much more information on the regulation of the effects of these comorbidities on hearing are highlighted.
Keywords: Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL), Hypertension, Diabetes, Ischemic damage, Dyslipidemias, Hypoglycemic drug
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION:
Hearing, also known as auditory perception, is the ability to sense vibrations and changes in the surrounding medium's pressure overtime via an organ such as the ear.1 Hearing is an essential part of how we communicate with others and become aware of sounds that happen in our immediate environment. Hearing loss, also known as hearing impairment, is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss is any degree of impairment of the ability to comprehend sound. Acquired hearing loss is defined as a loss of hearing function due to nongenetic causes, for example triggered by environmental agents such as chemicals, drugs and noise. Sensorineural hearing loss in which the root cause lies in the inner ear or sensory organ (cochlea and associated structures) or cranial nerve VIII or neural part. SNHL may arise from number of different etiologies. Damage of the auditory hair cells, supporting cells, spiral ganglion cells, and other cell types may arise from a variety of factors. Gene mutations, trauma, inflammation, tumors, structural abnormalities, and altered ion homeostasis such as in endolymphatic hydrops, all may result in SNHL Systemic disorders, especially systemic hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemias, are directly or indirectly implicated in the assessment of patients with sensorineural hearing loss. Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus (DM) and hypertension are increasing worldwide and it is more pronounced in India. This hypertension and diabetes causes SNHL by affecting the blood supply of cochlea as main path way.
The cochlea is provided with a terminal capillary bed and is not supplied by collateral vessels which could restore blood flow in ischemic regions. Moreover, since cochlear hair cells have a high metabolic activity, they are particularly vulnerable to hypoxic or ischemic damage. It has been demonstrated experimentally that cochlear tolerance to ischemia is very limited and that the action potential is impaired after 60 sec of anoxia, while after 1 hour of vessel obstruction, cochlear function does not recover . Hearing loss is a common public health problem that affects work productivity, functional status, social interactions, personal safety and well-being, and quality of life.2 The hearing loss (HL) is a factor that irrespective of the degree of commitment affects the quality of life and when acquired in adults, it appears gradually and may make the oral language receiving difficult. May cause psychosocial effects, like low self-esteem, isolation, depression and irritability, which can interfere with the quality of life of the individuals.
As there is increasing prevalence of diabetes and hypertension in the people, chance of sensorineural hearing loss may increase at an early age debilitating the persons day to day life. There are many studies on complications related to CAD, stroke, opthalmic complications due to hypertension and diabetes but less studies related to SNHL This study is done to evaluate the prevalence of sensorineural hearing loss in diabetes and hypertensive subjects.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This is a prospective observational study done for a period of 18 months from January 2018 to june 2019. The study will be conducted on 50 subjects diagnosed with diabetes, 50 subjects diagnosed with hypertension and 50 subjects with both hypertension and diabetes and 50 normal subjects without hypertension and diabetes. Study conducted in the department of Ear, Nose and Throat (ENT) of the Gandhi Medical College in association with audiologist. Ethical clearance was obtained from institutional board(IEC-17113002076D) and Informed Consent will be taken and complete history about duration of diabetes, hypertension and their medication history and any symptoms of hearing loss history is taken. Spot blood pressure in hypertensive patients is measured and >= 140/90 mmhg is considered as uncontrolled and HBA1C in diabetic patients are performed and > 7 is considered as uncontrolled. Pure tone audiometry is performed on all the subjects.
Inclusion criteria: All the subjects in the age group of 20-60 years with diagnosed diabetes, hypertension and normal subjects without hypertension and diabetes both males and females are included.
Exclusion criteria: Subjects under 20 and above 60 and with any congenital malformations causing hearing loss, conductive hearing loss and mixed hearing loss in patients, other causes of sensorineural hearing loss like Exposure to loud noise, Head trauma, Viral infections, Autoimmune inner ear disease, Hearing loss that runs in the family, Malformation of the inner ear, Meniere’s Disease, Otosclerosis, Tumors.
Questions regarding the duration of hypertension and diabetes, treatment history, and the associated complications were asked. Any complaints of hearing loss, duration was enquired. The study excluded patients with occupational noise sensitivity, ototoxic and chemotherapy drug use, serious head injury, family history of deafness, ear infection, ear surgery, head or neck radiotherapy, or upper respiratory tract infection in the previous month.
Identification data: name, age, gender was noted. Subjects with a history of physician diagnosed diabetes or who were taking oral hypoglycemic drugs or insulin were defined as diabetic. For those without a diagnosis of diabetes and not taking any antidiabetic medications, the value of fasting blood glucose was used to assess the presence of diabetes according to the American Diabetes Association guidelines (<126 mg/dl) [Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus, 1997]. Patients with a history of physician-diagnosed hypertension or who were taking medications for high blood pressure were considered with hypertension.
General ear examination was done using otoscopy. Pathologies related to external ear, Tympanic membrane are ruled out to exclude conductive hearing loss and any congenital defects.
Hearing function, as well as the degree, form, and configuration of any hearing loss, were determined through a general ear examination and Pure Tone Audiometry. The HbA1c levels of all diabetic subjects were then calculated. Normal laboratory procedures were used to draw 5ml of blood for the study of HbA1c concentration in the serum. Blood pressure was measured with a proper cuff and mercury gauge manometer. Blood pressure and Random blood sugars were done in non-hypertensive and nondiabetic subjects to confirm.
RESULTS
The sample size was 200 of which 50 cases are diabetic, 50 cases are hypertensive, 50 cases are both diabetic and hypertensive, and 50 cases are normal (controls) without any diabetes and hypertension.
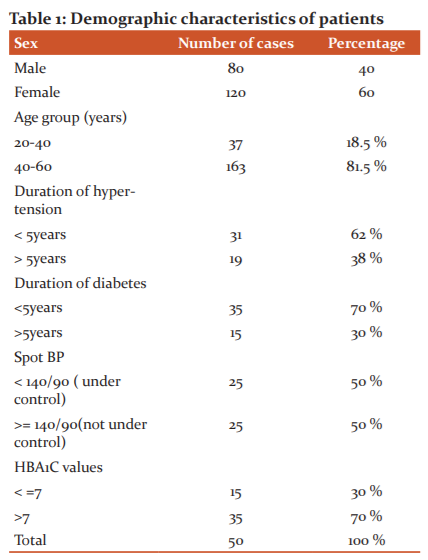
In the present study, it was found that the age of the group with associated disease is statistically higher in the group without associated disease. It was found that out of 150 cases with hypertension or diabetes or both in present study 138 were in the age group of 40- 60 and only 12 cases were between age 20-40. All the patients are on medical treatment for Hypertension from the time of diagnosis.
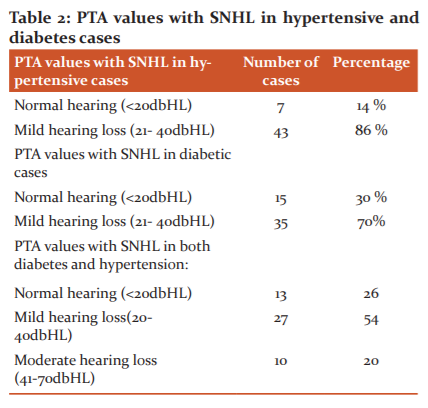
Patients with hypertension (86%) were at higher risk of developing SNHL when compared to controls. Effect of diabetes on the SNHL in comparision to controls which showed 70% chance of having SNHL in diabetic cases
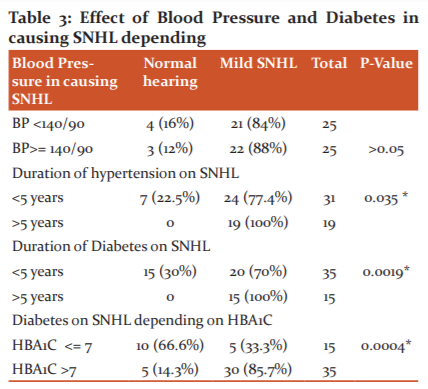
p value: 1 As the p value is more than 0.05, hence there is no difference in causation of SNHL between uncontrolled and controlled HTN.
p value: 0.035. As the p value is less than 0.05, hence there is causal relationship between effect of duration of HTN and occurrence of SNHL.
p value: 0.0019 As the p value is less than 0.05, hence there is relationship between increased duration of diabetes and occurrence of SNHL.
p value: 0.0004 As the p value is less than 0.05, hence there is causal relationship between effect of uncontrolled diabetes causing SNHL.
There is a chance of developing SNHL in patients with >5year (100%) diabetes than cases with <5 year (70%) diabetes.
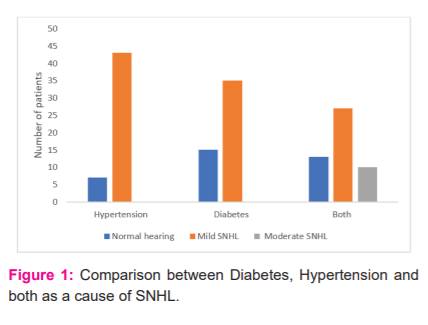
all the hypertensive and diabetic cases had only mild SNHL and no moderate or severe hearing loss. If they have both hypertension and diabetes they have moderate hearing loss.
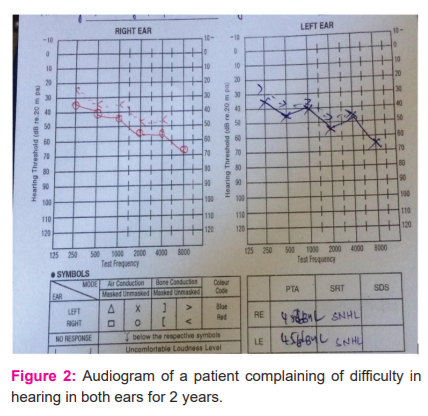
DISCUSSION:
Hearing loss is a dysfunction of hearing and it varies in severity ranging from mild; moderate; severe or profound. Hearing loss in general can be divided into conductive type, sensorineural type or mixed type. Sensorineural hearing loss results from lesions of cochlea, VIIIth nerve or central auditory pathway. Characteristically these patients have poor speech discrimination and difficulty in hearing in the presence of noise. The pathway for sound impulses from hair cells to inner ear to the auditory nerve and the brain is damaged It may be acute (sudden) or chronic sensorineural hearing loss. It has a multifactorial causation, is currently a public health concern. Several studies have been conducted in developed and developing countries regarding diabetes and hypertension as causative factors. The care taken in outlining the age factor, focusing on the age range of middle-aged individuals between 20 and 60 years, the strict exclusion criteria, excluding individuals with diseases and specific activities capable of causing hearing alterations, and the care taken in diagnosing their hearing loss and arterial hypertension are certainly methodological characteristics of this study. Despite memory biases during history taking and the use of ototoxic drugs, the results may have been influenced; despite, in studies about information reliability, such as metabolic and vascular alterations, or information biases, such as metabolic and vascular alterations biases still undiagnosed or not recorded by the patient, the results may have been influenced.
The age of the group with associated disease was found to be statistically higher than the age of the group without associated disease in the current research. It was found that out of 150 cases with hypertension or diabetes or both in present study 138 were in the age group of 40- 60 and only 12 cases were between age 20-40. This may be due to as age increases the comorbidities increases causing SNHL which is adding on to the SNHL caused due to age factor ( presbyacusis) In their study, Axelsson et al. had already described a worsening in the hearing loss with aging without, however, finding an association with diabetes control and duration. 3 Brohem et al. studied hypertensive patients complaining of hearing usually associated to their more advanced age. 4 Systemic arterial hypertension and advanced age were established as separate risk factors for sensorineural hearing loss by Marchiori et al.5 We couldn't distinguish the most advanced age as an isolated risk in patients with sudden idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss because the most advanced age coexisted with other diseases. According to some studies, sensorineural hearing loss is linked to microcirculatory insufficiency caused by vascular occlusion caused by emboli, haemorrhage, or vasospasm, and these occur as a result of a syndrome of hyperviscosity or microangiopathy caused by diabetes or hypertension, and the latter could cause the sensorineural hearing loss via histopathological mechanisms. 6,7
The gender factor is not taken into account as a factor in determining the cause of SNHL in this report. Many studies have found a connection between gender and hearing loss as people get older. After conducting a study that compared age, gender, and hearing acuity, Dubno et al. discovered that males had a substantial age-related decline in hearing acuity and speech comprehension, while females did not.8 Pearson et al. found a two-fold increase in the rate at which men lose their hearing as compared to women in a longitudinal study involving 681 men and 416 women without signs of serious hearing problems, unilateral or noise-induced hearing loss. 9This shows that age and gender are also linked to hearing loss even in groups without signs of noise-induced hearing loss. In the present study patients with hypertension (86%) were at higher risk of developing SNHL when compared to controls (0%).Marchiori et al, conducted a study in 2006, involving 154 cases and 154 controls, aged 45 to 64 years found that there is significant association between high blood pressure and hearing loss. 10
In our study duration of hypertension had a slight influence on developing SNHL as only 77% cases within 5 year duration had SNHL but 100% of cases with duration of hypertension more than 5 years had SNHL. Agarwal.et.al in his booked Neck Surgery also showed a strong relation between duration of hypertension and the development of SNHL.11 The longer duration of hypertension is postulated to increase the risk of ischemic damage to the cochlea due to vascular changes.Present study showed that there is no significant difference in the effect of controlled (84%) and uncontrolled (88%) hypertension on the occurrence of SNHL. Hypertension is a disease that compromises the adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients to cells. Such supply depends on the functional and structural integrity of the heart and blood vessels. Thus, hypertension may compromise the physiological mechanisms of the inner ear by increasing blood viscosity, resulting in decreased capillary blood flow and oxygen transport. The present study evaluated the effect of diabetes on the SNHL in comparision to controls which showed 70% chance of having SNHL in diabetic cases. Friedman et al. observed an incidence of 55% hearing loss in patients with diabetes. Which is the same as found in our study.12 Kakarlapudi et alnoted that patients with diabetes were more commonly known to have hearing loss (13.1%) when compared to the control group who were non-healthy subjects without diabetes.13
In our study there is a slightly higher chance of developing SNHL in patients with >5year (100%) diabetes than cases with <5 year (70%) diabetes. A study by Celik et al. noted that as diabetes duration raised to more than 15 years, the hearing loss incidence also increased.14 Our study showed higher chance of developing SNHL in diabetic cases with HBA1C >7(85%) than with HBA1C <7 . Thus showing increased chances of SNHL in uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. HbA1c level and hearing loss correlation indicates that good glycemic control can modify the progression of hearing loss in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus patients. Other studies conducted in India also found that T2DM patients with uncontrolled blood sugar levels increased the incidence of 76.6% of sensorineural hearing loss compared to patients with controlled blood sugar levels. In addition, another study said that patients with good HbA1c levels (HbA1c ≤ 7.5%) had a better hearing level in both ears compared to T2DM patients with poor glycemic control.
Hearing loss associated with diabetes is a progressive, bilateral, and sensorineural disorder with a gradual onset and generally points a higher frequency. Sensorineural hearing loss is caused by chronic and persistent hyperglycemia. When hyperglycemia status is controlled in diabetic patients, the severity of hearing loss will be minimal. Hearing loss should be assessed earlier in T2DM patients to prevent the severity of hearing loss which can also occur due to age.15
In present study all the cases had only mild SNHL and no moderate or severe hearing loss. A study conducted by Rajendran et al showed a result similar to our study, The patients with diabetes reviled a high-frequency loss which was bilateral and severity was from mild to moderate of sensorineural type and it was significant (73.3%) as compared to controls of similar age. Whereas Weng et al noted that in 67 patients with diabetes who were examined, 44.8% of them had hearing loss which was profound.16 Many studies were conducted to observe the pathogenesis of this sensorineural loss observed in diabetics. During this course many studies suggested that diabetes is a cause of hearing loss. The probable mechanisms suggested were microangiopathy in the inner ear, neuropathy of cochlear nerve, or even a combination of both. Outer hair cell dysfunction and disruption of endolymphatic potential were noted in some studies. Some effects of diabetes on body tissue are thought to be correlating with the polyol pathway, where glucose is broken down to sorbitol.
Generally the accumulation of Sorbitol is observed in neuropathy as it causes a reduction in myo inositol levels which further leads to reduction in Na+ K+ ATPase activity Makishima and Tanaka demonstrated atrophy of the spiral ganglion over basal lamina and the middle turns of cochlea were severe in individuals with diabetes along with hearing loss which was sensorineural type. `17 It was also noted that in the 8th nerve changes were present in the myelin sheath, which denoted degeneration and fibrosis of perineurium.
Van den Ouweland et al observed mutational changes in the mitochondrial RNA. It was also observed that in a minor subset of patients, with diabetes inherited maternally showed some degree hearing loss which was sensorineural type.18 Lisowska et alin their study noted that in diabetic patients, there was abnormality in the function of outer hair cells in auditory brain stem responses.19 Fukushima et al proposed that patients with type 2 Diabetes had changes in cochlea, leading to atrophy of stria vascularis and basal turn which was significant and which could be the likelihood of hearing loss in these patients.20 The present study also showed that there is an increased chance of acquiring moderate degree of SNHL in patients with both diabetes and hypertension than with individual comorbidities. Given the results found in this research, it is evident the need to investigate and monitor the hearing of patients with DM, HTN and especially individuals with both diseases, since they constitute a population at higher risk for hearing impairment. In addition, it is important to note that the greater the chances of hearing rehabilitation of the individual, the sooner such changes are detected.
CONCLUSION
Chronic diseases induced by genetics, lifestyle, the environment, and ageing itself are the major factors affecting health today; therefore, we should concentrate our attention on our patients' final years of life in order to increase the number of healthy elderly capable of sustaining their physical and mental functions until near to death. The new problem is chronic aging-related diseases, many of which can be detected and prevented as early as middle age, and which are currently being treated in a variety of health-care specialties.
To live a disease-free life, it is important to follow concepts and strategies for preventive care and health maintenance that are specifically tailored to each patient's needs, with the goal of enhancing their quality of life. We should take note of the onset of the many complications that arise from arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus, including hearing loss, as part of such preventive care. Our present study confirms that there is a possible association between hypertension and diabetes increase in hearing threshold. Patients with hypertension and diabetes have greater increase in hearing threshold as compared to those without these comorbidities. Such association between hearing loss and arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus has been an important object of research in recent decades.
We emphasise the importance of preventive processes that may reduce the mechanisms that trigger hearing apparatus degeneration caused by circulatory problems, especially high blood pressure and high blood sugar, as well as the need for further research into the regulation of these comorbidities' effects on hearing.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of interest-Nil
Financial support-Nil
References:
-
Plack, C. J: The Sense of Hearing. Psychology Press Ltd. :2014: ISBN 978 1848725157.
-
Yavuz E, Morawski K, Telischi FF, Ozdamar O, Delgado RE, Manns F et al: Simultaneous measurement of electrocochleography and cochlear blood flow during cochlear hypoxia in rabbits: J Neurosci Methods 2005; 147: 55–64.
-
Axelsson, S.E. Fargerberg: Auditory function in diabetics Acta Otolaryngol., 66 (1968), pp. 49-64.
-
BrohemV.M.A. , CaovillaH.H. , Ganança M.M.: Dos sintomas e achados audiológicos e vestibulares em indivíduos com hipertensão arterial Acta AWHO., 15 (1) (1996), pp. 4-10.
-
MarchioriL.L.M. , FilhoE.A.R. , MatsuoT. Hipertensão como fator associado à perda auditive Braz J Otorhinolaryngol., 72 (4) (2006), pp. 533-540
-
Carrasco VN, Prazma J, Faber JE: Cochlear microcirculation effect of adrenergic agonists on arteriole diameter. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1990;116:411–417.
-
Gates GA, Cobb JL, D′Agostinho RB, Wolf PA: The relation of hearing in the elderly to the presence of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular risk factors: Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1993;119:156–161.
-
Dubno JR, Lee FS, Matthews LJ, Mills JH: Age-related and gender-related changes in monaural speech recognition. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 1997;40(2):444–452.
-
Pearson JD, Morrell CH, Gordon-Salant S, Brant LJ, Metter EJ, Klein LL et al: Gender differences in a longitudinal study of age-associated hearing loss. J Acoust Soc Am :1995, 97(2):1196–1205.
-
de Mores Marchiori LL, de Almeida Rego Filho E, Matsuo T: Hypertension as a factor associated with hearing loss. Braz Otorhinolaryngol ; 72(4): 533-40.
-
Agarwal S, Mishra A, Jagade M: Effects of hypertension on hearing Indian J Otolaryngol. 2013; 65 (suppl 3) 614- 618).
-
Friedman SA, Schulman RH, Weiss S: Hearing and diabetic neuropathy. Arch Intern Med. 1975 ;135(4):573-6.
-
Kakarlapudi V, Sawyer R, Staecker H: The effect of diabetes on sensor neural hearing loss. Otol Neurotol. 2003;24(3):382-6.
-
Celik O, Yalçin S, Celebi H, Oztürk A: Hearing loss in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Auris Nasus Larynx.1996;23:127-32.
-
Dalton DS, Cruickshanks KJ, Klein R, Klein BE, Wiley TL: Association of NIDDM and hearing loss. Diabetes Care 1998;21:1540-4.
-
Weng SF, Chen YS, Hsu CJ, Tseng FY: Clinical features of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in diabetic patients. Laryngoscope.2005;115(9):1676-80.
-
Nakashima, K., Tanaka, K: Pathological changes of the inner ear and central auditory pathways in diabetics. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol.1971;80:218-288.
-
Van den Ouweland JM, Lemkes HH Gerbitz KD, Maassen JA: Maternally inherited diabetes and deafness (MIDD): A distinct subtype of diabetes associated with a mitochondrial tRNALeu(UUR) gene point mutation. Muscle Nerve. 1995;3:S124-30
-
Lisowska G, Namyslowski G, Morawski K, Strojek K: Otoacoustic emissions and auditory brain stem responses in insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Otolaryngol Pol. 2002;56(2):217-25.
-
Fukushima H, Cureoglu S, Schachern PA, Paparella MM, Harada T, Oktay MF: Effects of type 2 diabetes mellitus on cochlear structure in humans. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006; Sep;132(9):934-8
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License