IJCRR - 7(21), November, 2015
Pages: 13-18
Date of Publication: 11-Nov-2015
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
STUDY OF CLINICO-PATHOLOGICAL AND BACTERIOLOGICAL PROFILE OF URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN GERIATRIC PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
Author: Bhumika Vaishnav, Arvind Bamanikar, Pragati Maske, Vivek Singh Rathore, Vinit Khemka, Deepshikha Sharma
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The elderly with type2 Diabetes Mellitus(DM) have a greater frequency and severity of urinary tract infections(UTIs) due to long duration of DM, its neurovascular complications, long term insulin use, aging and suppression of immune system. The term UTI encompasses asymptomatic bacteriuria (ABU), urethritis, cystitis, prostatitis and pyelonephritis. Aims: To study the clinical and microbiological profileof UTI in patients more than 60 years of age having type2 DM. To examine whether the presence of diabetes alters the risks and complication profile for UTI's in elderly. Materials and Methods: Cross-sectional, analytical study of elderly diabetic patients with UTI diagnosed on the basis of detailed clinical history and investigations. Results: Out of 60 study subjects, 24 were male and 36 were female with maximum incidence of UTI occurring in 65-69 years of age group. 66.67% of patients had diabetes for more than 10 years and more than 70% were on insulin therapy. HbA1c valu was greater than 8 in 66.67% subjects. Foul smelling urine, dysuria and urgency were the commonest symptoms. Escherchiacoli (E coli) was the commonest pathogen isolated in 70% patients. 26.67% subjects had complicated UTI's and acute kidney injury was the common complication Conclusion: E. Coli is the commonest organism causing UTI in elderly diabetics. There was no gender difference in the incidence of UTI. The possible risk factors for UTI in elderly diabetics are long duration of disease (more than 10 years), prolonged insulin therapy and high HbA1c values..
Keywords: Urethritis, Asymptomatic bacteriuria, Diabetes mellitus, E. coli
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a chronic disorder of carbohydrate and fat metabolism having multisystem involvement. Type 2 DM, which is more common, is charactersized by insulin resistance, impaired insulin secretion and increased gluconeogenesis in the liver[1]. Individuals with DM have a greater frequency and severity of infections [2]. Defective migration, phagocytic alterations of chemotaxis in polymorphonuclear leukocytes and impaired cytokine secretion are well documented in type 2 DM[3]. Urinary tract infections (UTIs), both upper and lower tract, are very common in diabetic patients. The term UTI encompasses asymptomatic bacteriuria (ABU), urethritis, cystitis, prostatitis and pyelonephritis. UTIs can be asymptomatic or symptomatic in diabetics. The population most likely to suffer from UTIs is the geriatric diabetic population (60+ years) due to increased duration of disease, long term insulin use, aging, and immune system suppression. Dysfunctional bladders, obstruction in urinary flow, and incomplete voiding are additional factorsin elderly diabetic patients which may cause recurrent UTIs. UTI is twice as common in diabetic females as in non-diabetic females [4][5][6]. UTIs, although uncommon in diabetic men, have higher incidence of complications [7]. Also, as DM is an immunocompromised state, early diagnosis and investigations can prevent dreaded complications such asascending infections including emphysematous pyelonephritis, renal and perirenal abscesses, acute kidney injury and septicaemia in elderly and thus reduce the morbidity[8].
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study was conducted in the medicine department of a tertiary care hospital. Both inpatients and outpatients were included in the study which was carried out over a period of three months. All patients more than 60 years of age with type 2 DM diagnosed with UTIs (urine showing significant bacteriuria ≥105 CFU/ml of urine) were included in the study. A total of 60 subjects were included in the study. After an informed consent from the patients, they were subjected to a detailed history, physical examination and relevant clinical investigations. Selection criteria for type 2 DM were: a)Fasting blood sugar more than 126 mg/dl OR b) Post-prandial blood sugar more than 200 mg/dl OR c) Patients on drug treatment for diabetes. Patients having age less than 60 years, hypertension, chronic kidney disease, Type 1 DM or known anatomical or surgical defects in the genitourinary tract were not included in the study. Diagnosis of urinary tract infection was made on the basis of clinical history, symptoms and detailed clinical examination. Biochemical investigations of blood and urine were done to confirm the diagnosis. The study subjects, after giving proper instructions, were asked to submit a midstream urine sample which was transported to the microbiology laboratory of the hospital immediately. After ensuring that the urine sample was uncontaminated (by normal vaginal/urethral flora), it was centrifuged and examined under a microscope(×400 magnification). Presence of pyuria (≥ 10 leukocyte/hpf) with a positive leukocyte esterase and/or nitrite tests was considered as a positive urinalysis. The collected samples were then subjected to gram staining and culture testing to identify the species of the pathogens. Significant bacteriuria (SB) was defined as presence of ≥ 105 colony forming units (CFUs) of isolated organisms per millilitre of urine sample in urine culture. Presence of significant bacteriuria with urinary symptoms was diagnosed as UTI. Presence of SB in two consecutive urine samples collected at a seven day interval but without classic urinary symptoms was diagnosed as asymptomatic bacteriuria (AB). Positive history of UTI within past six months was diagnosed as recurrent UTI. Pyelonephritis was diagnosed by presence ofsymptoms of UTI with fever, abdominal pain, leukocytosis and associated with SB. The following investigations were carried out: a)Complete Hemogram - Hemoglobin (Hb in gm/dl); total and differential leukocyte count (TLC, DLC in lac/cumm); erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (by auto-analyser); b) Urine routine including pH, specific gravity, proteins and albumin, sugar. In Microscopic examination pus cells, epithelial cells, red blood cells, bile salts, bile pigments. c) Urine culture and Blood culture; d) Renal function tests including blood urea (mg/dl), serum creatinine (mg/dl); e)Blood sugar level profile including fasting blood sugar (mg/dl), post prandial blood sugar (mg/dl) (by Glucose Oxidase – Peroxidase method); f) Glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1C) (by Resin method); g) Ultrasound of abdomen and pelvis and X-ray kidney, ureter, bladder (KUB) as and when required. Data was analyzed using statistical package SPSS version 16. The mean was the primary statistical measure used. The chi-square statistical test was used and a p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
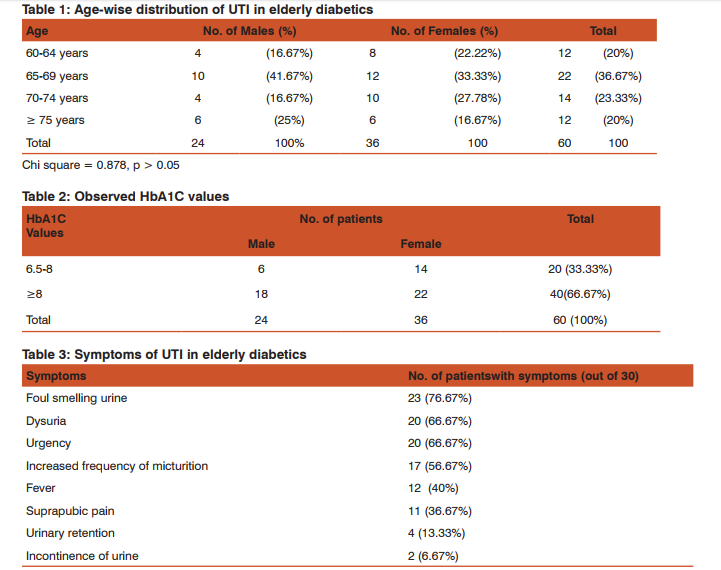
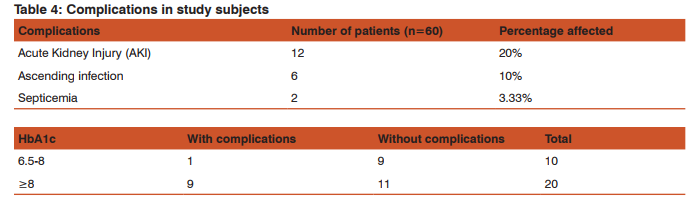
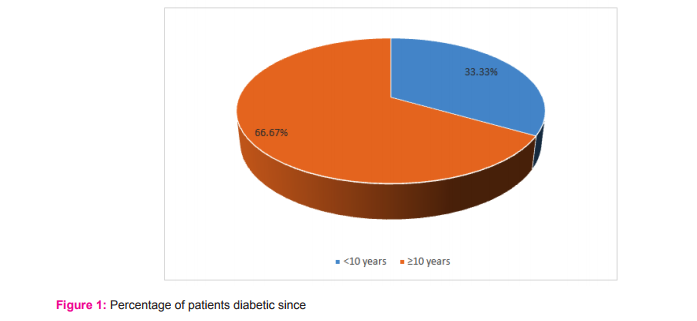
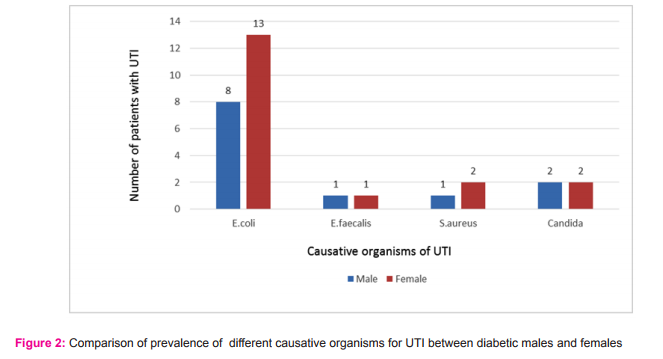
Out of 60 patients, 24 were males and 36 were females. Maximum incidence of UTI occurred in age group of 65-74 years (60%). The mean age of the study subjects was 68.2 years. Chi-square test showed non-significant relationship between different age groups and gender (Table 1). This shows that UTI occurred with similar frequency in both genders in different age groups. A majority of the study subjects had DM for more than 10 years (Fig. 1) with HbA1c value more than 8(66.67%) (Table 2). There was a non-significant relationship between different levels of HbA1C and gender (p-value >0.05). This shows that both the genders are equally distributed among different levels of HbA1C. At the time of enrolment in the study, 70% subjects were on insulin therapy and remaining 30% were on oral hypoglycaemic drugs. 34(56.67%) diabetic patients had their first episode of UTI whereas 26 (43.33%) had recurrent bouts of UTI in the study. The odds for occurrence of recurrent episodes in females were 1.12 which shows that there is 1.12 times more risk for developing recurrent episodes in females than males. But it was statistically not significant (p> 0.05). 76.67% patients had foul smelling urine, which was the most common presenting symptom, followed by dysuria and urgency (66.67%) (Table 3). Lower UTI i.e. urethritis (36.67%) and asymptomatic bacteriuria (33.33%) were commonly found in the subjects. Urethritis was more common in older females (44.44%) as compared to males (25%). Asymptomatic bacteriuria occurred with equal frequency in both males and females. Cystitis accounted for 13.33% cases of UTI and Pyelonephritis accounted for 16.67% cases. E.coli was the commonest organism isolated from the urine of elderly diabetics accounting for 70% infections, followed by candida species which was found in 13.33% cases. The remaining 16.67% of pathogens were E.faecalis and S.aureus. The difference in incidence of isolation of E.coli in both genders is statistically not significant (Fig. 2). Acute kidney injury was the commonest complication of UTI in elderly diabetics (20%) followed by pyelonephritis (10%) and septicaemia (3.33%) (Table 4). UTI was complicated in 33.33% cases. Mortality rate was 1.67% and cause of mortality was septicemic shock secondary to urosepsis with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus.
DISCUSSION
In this study, 60 diabetic patients above the age of 60 years with symptoms suggestive of UTI were included and investigated. Their clinical profile and laboratory data were analyzed to determine the spectrum of presenting clinical features, complications and common causative organisms for UTI. In the current study, the incidence of UTI in elderly diabetics was the maximum in the age group of 65-69 years (36.67%). 20% of the patients were of more than 75 years of age. A study by Geerlings et al. has shown similar results, i.e. the incidence of UTI increases with ageing in type 2 DM patients.[4] Females (60%) had a higher incidence of UTI than males (40%) in this study. Premenopausal female diabetics commonly have UTIs due to urinary tract contamination by vaginal bacterial flora.[9] But the current study showed that even postmenopausal and elderly diabetic women have a higher incidence of UTI compared to elderly males. Evidence from study by Boyko et al. have shown similar results. [5] Longer duration of type 2 DM (> 10 years in 66.67% subjects), insulin therapy (70% subjects), uncontrolled DM (HbA1C > 8 in 66.67% subjects) were all striking clinical parameters associated with increased incidence of UTI in the study. The findings of a study carried out on south Indian subjects were similar.[10] However, in another study by Schmitt et al., longer duration of diabetes but not glycaemic control (HbA1c values), was associated with higher incidence of UTI.[11] A study by Boyko et al. did not find any significant association between the degree of glycaemic control as assessed by HbA1c level and odds of UTI.[5] Our study also did not find any significant association between HbA1C levels and odds of developing complicated UTI. Thus, the association between glycaemic control as determined by HbA1c levels and UTI among diabetic patients is controversial. In the current study, 43.33% subjects had a history of recurrent UTI with a minor degree of female preponderance. But there was no significant statistical association between DM type 2 and recurrent UTI in elderly females (p>0.05) which was similar to a study by Raz R et al., where DM type 2 was not found to be a risk factor for recurrent urinary tract infections in postmenopausal women.[12] In this study, elderly patients presented with various symptoms but foul-smelling urine was the commonest symptom (76.67%), followed by dysuria, urgency (66.67%) and frequency (56.67%). These findings are in accordance with the observations of a study by Marques et al.[13] A few patients had no symptoms suggestive of UTI and were admitted for uncontrolled diabetes but were found to have asymptomatic bacteriuria on routine examination of urine. Only 40% patients presented with fever in this study showing that in aged diabetic patients, UTI may be present in the absence of fever. Thus, a high index of suspicion for UTI should be kept while evaluating an elderly diabetic with atypical symptoms like urinary retention (13.33%) and incontinence (6.67%) which were also presenting symptoms of a few patients in this study. Urethritis was the commonest form of UTI followed by asymptomatic bacteriuria. However, urethritis occurred with increasing frequency in elderly females compared to males possibly due to shorter urethra and concomitant vaginitis. Complicated pyelonephritis was present in 16.67% patients. This high prevalence of upper UTI can be due to ascending infection, impaired host defences, late presentation of elderly diabetics. Upper urinary tract infections (UTIs) are also a frequent result of bladder colonisation. These findings corresponded well with those of some other studies.[6] As a point of difference, the incidence of pyelonephritis was very high in the current study as compared to the study conducted by Marques et al. where the incidence was only 2.02%. However, the latter study was carried out on community-dwelling elderly women without DM.[13] Thus, type 2 DM is an independent risk factor for developing upper UTI. E.coli was the pathogen isolated in 70% of the study subjects. It occurred with nearly equal frequency in males and females, which is in concordance with other studies.[2,10] Other Gram-negative bacilli like Klebsiella Spp., Proteus Spp., and Citrobacter Spp. were not isolated in the current study. This may be due to the smaller sample size of the current study. In another study from India, it was found that E. coli was the most commonly grown organism (64.3%), followed by Staphylococcus aureus (21.4%) and Klebsiella pneumoniae (14.3%).[14] In a study by Geerlings SE et al., it was noted that increased adherence of E. coli (with type 1 fimbriae) to uroepithelial cells correlated positively with high HbA1C. Higher adherence of E. coli to the uroepithelium was found in patients with poorly controlled diabetes.[15]Candida was isolated from 13.33% subjects in the current study. Prolonged hospitalisation, urethral catheterisation and long term parenteral antibiotic therapy predispose elderly diabetics to candida infections.[16]Gram-positive cocci play a lesser role in UTIs. In the current study, Staphylo-coccus aureus accounted for 10% of UTI. Another common Gram-positive cocci is Staphylococcus saprophyticus which causes UTI in younger females. Complicated UTIs due to Enterococci and S. aureus are quite common, particularly in patients who have received antibiotic treatment or who have undergone instrumentation of the urinary tract. Enterococcus Faecalis was isolated in 6.67% elderly diabetic subjects with UTI in this study. Most of these subjects had a recent history of receiving antibiotic therapy for other infections. Acute kidney injury (AKI), ascending infection to kidneys from lower urinary tract and septicaemia were few complications seen in the study subjects with UTI. However, majority of elderly DM –type 2 patients had an uncomplicated UTI (66.67%). Thus, although UTI occurred with higher frequency in elderly diabetics, the rate of complications was low. AKI was also the commonest complication in a study done by Aswani SM et al.[16]
CONCLUSION
Indiais known as the ‘diabetes capital of the world’ because of Asian-Indian phenotype i.e. high waist to hip ratio. Type 2 DM forms the major burden causing great morbidity due to recurrent infections like UTI and other microvascular and macrovascular complications. India also has a large population of age above 60 years - 8% (according to Census India 2011), many of whom are diabetics. They are prone to recurrent and complicated UTI which causes significant healthcare burden on the society. The current study was aimed at identifying causative micro-organisms of UTI in elderly diabetics and to study their clinical presentation and complications. The results were compared with other similar studies done within and outside India. E.coli was the commonest micro-organism causing UTI followed by candida. Thus, the distribution of organisms found in the urine of patients is similar to that in other populations. There was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of recurrent UTI between male and female subjects in the study. None of the study subjects had HbA1c0.05) Substantial research has been done involving a study group of post-menopausal diabetic female populations. But very few studies have been done on elderly male diabetic subjects. This is the distinguishing feature of the current study. Investigation of asymptomatic or symptomatic bacteriuria in aged diabetic patients for urinary tract infection is important for treatment and prevention of renal complications. However, the sample size in the current study was small and was done for a limited period in a single hospital. Hence, larger study population studied for a longer duration in multiple hospitals will be required to strengthen and confirm our conclusions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors acknowledge the immense help received from scholars whose articles are cited and included in the references to this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J; Diabetes mellitus, Harrison’s principles of internal medicine, 18th edition, chap. 344, pg no.2974.
2. Bonadio M, Costarelli S, Morelli G, Tartaglia T. The influence of diabetes mellitus on the spectrum of uropathogens and the antimicrobial resistance in elderly adult patients with urinary tract infection. BMC Infect Dis. 2006: 17(6),54.
3. Brauner AM, Flodin U, Hylander B, Östenson CG. Bacteriuria, Bacterial Virulence and Host Factors in Diabetic Patients, Diabetic Medicine; 1997:10(6), 550–554.
4. Geerlings SE, Stolk RP, Camps MJ, Netten PM, Hoekstra JB, Bouter KP. Asymptomatic bacteriuria may be considered a complication in Women with diabetes mellitus Utrecht Study Group. Diabetes Care; 2000:23(6), 744-749.
5. Boyko EJ,Fihn SD, Scholes D. Diabetes and the Risk of Acute Urinary Tract Infection Among Postmenopausal Women. Diabetes Care; 2002: 25(10), 1778-1783.
6. Gilbert GG, Donders MD. Lower genital tract infections in diabetic women. Current Infectious Disease Reports; 2002: 4(6), 536-539.
7. Hoepelman AIM, Meiland R, Geerlings SE. Pathogenesis and management of bacterial urinary tract infections in adult patients with diabetes mellitus. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents; 2003:22(2), 35–43.
8. Patterson JE, Andriole VT. Bacterial urinary tract infections in diabetes. Infect Dis Clin North Am; 1995: 9(1), 25-51.
9. Minardi D, d’Anzeo G, Cantoro D, Conti A, Muzzonigro G. Urinary tract infections in women: etiology and treatment options. Int J Gen Med. 2011; 4: 333–343
10. Janifer J, Geethalakshmi S, Satyavani K, and Viswanathan V. Prevalence of lower urinary tract infection in South Indian type 2 diabetic subjects. Indian J Nephrol; 2009; 19(3): 107–111.
11. Schmitt JK, Fawcett CJ, Gullickson G. Asymptomatic bacteriuria and hemoglobin A1c. Diabetes Care. 1986;9:518– 20.
12. Raz R, Gennesin Y, Wasser J, Stoler Z, Rosenfeld S, Rottensterich E, et al. Recurrent urinary tract infections in post menopausal women. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;30:152–6.
13. Marques LP, Flores JT, Barros Junior Ode O, Rodrigues GB, MourãoCde M, Moreira RM. Epidemiological and clinical aspects of urinary tract infection in community-dwelling elderly women.Braz J Infect Dis: 2012;16(5):436-41.
14. Goswami R, Bal CS, Tejaswi S, Punjabi GV, Kapil A, Kochupillai N. Prevalence of urinary tract infection and renal scars in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diab Res Clin Pract.2001;53:181–6.
15. Geerlings SE, Meiland R, van Lith EC, Brouwer EC, Gaastra W, Hoepelman AIM. Adherence of type 1-fimbriaeted E. coli to uro epithelial cells: More in diabetic women than in control subjects. Diab care. 2002;25:1405–9.
16. Aswani SM, Chandrashekar U, Shivashankara K, Pruthvi BC. Clinical profile of urinary tract infections in diabetics and nondiabetics; Australas Med J.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License