IJCRR - 13(16), August, 2021
Pages: 129-137
Date of Publication: 30-Aug-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A Questionnaire Study on Assessing Newer Concepts and Diagnosis of Root Resorption Among Orthodontists and General Dentists- Knowledge, Awareness, Practice Survey
Author: Arvind Prasanna, Ramasamy Navaneethan
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Upcoming research necessitates a quantitative assessment of root resorption with trends pointing towards increased evidence of iatrogenic root resorption. Aims: This questionnaire survey aimed to assess the knowledge and working principles on the latest protocols of root resorption among orthodontists and general dentists Methodology: A total of 11 questions on root resorption were circulated through Google Forms. The questions evaluated participant's knowledge and grasp on the topic of root resorption along with awareness about the latest protocols for management. 188 responses were recorded of which 73 were orthodontists and 115 were general dentists. Results: Overwhelming majority noted root resorption with 80% of participants having observed root resorption at some point in time. Nearly 55% believe root resorption can be prevented from further progression if treated at the right time (p< 0.05). 79% believe diagnosing through IOPAs can provide adequate information (p< 0.05). Diagnosing root resorption through other modalities is lukewarm with 42% responding positively towards usage of CBCTs, histological sections (p< 0.05) Conclusion: Root resorption is a fairly common phenomenon with at least 70% of the participants concluding that they have observed it in practice and during orthodontic treatment. It is necessary to assess OIRR quantitatively to determine optimal force levels in different clinical scenarios. Despite its value, CBCT is not an ideal modality for identifying root resorption considering exposure to the patient and diagnostic ability. It would be prudent to utilize this modality in cases with existing lesions.
Keywords: Root resorption, Diagnosis and treatment planning, Orthodontics, Apical resorption, External resorption
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
External apical root resorption (EARR) is an acknowledged sequelae of fixed appliance therapy. Force concentration at the root apex during tooth movement is a mechanical effect that seems to trigger biologic events associated with root resorption especially in aberrant root shapes.1 Increased force levels can cause more destruction of cementoblasts by compression of cells and periodontal vessels, increasing root vulnerability to resorption.2 In extracted teeth analysed histologically, it has been found in up to 100% of orthodontically treated teeth but less often in teeth examined by panoramic or intraoral radiographs.3
Numerous investigators have reported that routine orthodontic treatment is associated with a risk of apical root resorption.4, 5 There is general agreement, however, that the presence of preexisting root absorption increases the risk factor and speculations prevail as to the involvement of a genetic predisposition. It is necessary to upgrade pre-existing information on current protocols regarding root resorption and improve diagnostic aids necessary for its prompt treatment.6The standard protocols for observing and monitoring OIRR include periodic periapical radiographs taken during orthodontic treatment.7However, 2D radiographs may not be sufficient to highlight all the surfaces of the tooth in question. Moreover, reproducibility of the radiographs is always questionable due to the difficulty in magnification standardization and angulation errors.8 Hence, the newer modalities of diagnosing root resorption such as cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT), Histological analysis have arrived.9,10 This survey aims to assess the awareness among orthodontists and general dentists regarding the key elements of root resorption.
Newer modes of diagnosis, research protocols have all started to focus on the effect of root resorption. Despite the absence of serious clinical effects, it is necessary for the operating dentist to adhere to the first rule of any treatment, which is to do no harm. Concepts of root resorption are constantly evolving with focused research avoiding confounding factors. Root resorption which is traditionally assessed with respect to only the apical area of the tooth has gradually started changing with researchers focusing on volumetric assessments including the cervical and middle-third of the tooth as well.11 This survey aims to assess the awareness among orthodontists and general dentists regarding the key elements of root resorption, its more recent methods of diagnosis and latest protocols on treatment of root resorption.
MATERIALS AND METHODOLOGY
This study was a knowledge, awareness, practice survey assessing the awareness of orthodontists and general dentists towards the newer advances and protocols followed in root resorption. The survey was prepared using Google forms and sent to the participants through mail or the web link of the survey.
188 participants responded to the survey. Out of this, 73 participants were orthodontists and 115 participants were general dentists. 11 questions were asked in the survey, and all needed to be answered compulsorily. The study participants were from different geographical areas of India and hence their racial characteristics, prevalence all could increase the diversity of the knowledge. The participant’s opinions regarding root resorption were recorded and subjected to statistical analysis.
Statistical Analysis
The data obtained through Google sheets was statistically analysed using IBM SPSS Software Version 20.0. Chi-square tests were used to determine association between orthodontists and general dentists regarding concepts. The p<0.05 level of significance was chosen for all tests.
RESULTS
188 participants recorded their responses in the survey. 73 participants were orthodontists and 115 were general dentists. The questions were framed in such a manner that the first 3 questions tested the knowledge of the participant, the next 2 tested the attitude of the participant towards the subject and the final 3 tested the observant practices of the participant.

Fig 1: The blue bar represents the participants responding yes and the green bar represents the participants responding no. 92% of the participants responded yes and 8% of the participants responded no
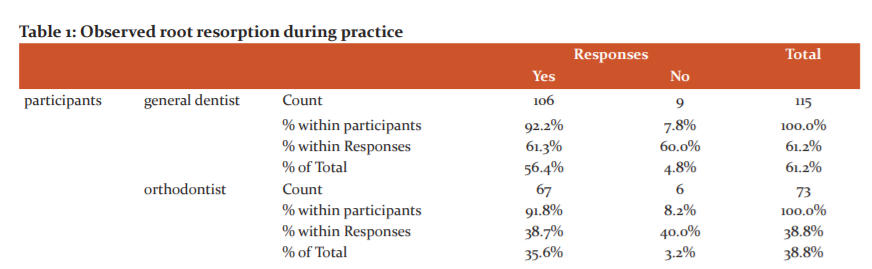
The first question enquired the participants about whether they have observed root resorption in clinical practice (Fig 1). An overwhelming majority of participants (92%) revealed that they had noted root resorption in everyday practice. Both orthodontists and general dentists showed equal observations within their groups (Table 1).
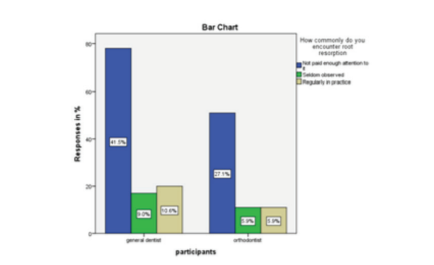
Fig 2: The blue bar represents the participants responding not paid enough attention to it, the green bar represents the participants responding seldom observed and the yellow bar represents participants responding regularly in practice. 68.6% of participants responded not paid enough attention to it, 14.9% of participants responded seldom observed and 16.5% of participants responded regularly in practice
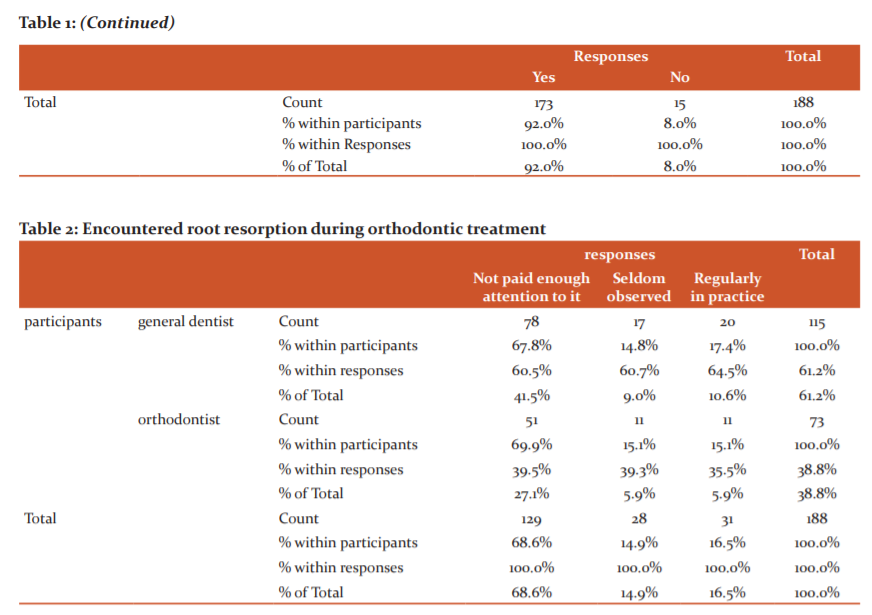
The second question was asked to evaluate the participant’s interest relating to the clinical significance of the survey (Fig 2). They were asked to check responses based on how commonly they encountered root resorption. Nearly 70% of the participants responded that they did not pay enough attention to it, but 16% observed that they were seen regularly in practice (Table 2)
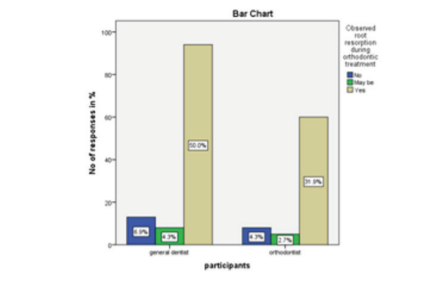
Fig 3: The blue bar represents participants responding no, the green bar represents participants responding maybe and the yellow bar represents participants responding yes. 11.2% of the participants responded no, 6.9% of the participants responded maybe and 81.9% of the participants responded yes
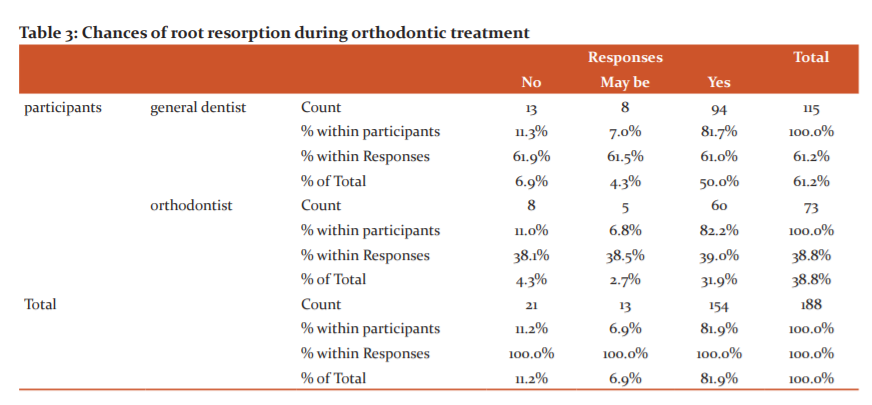
The third question evaluated the participant’s observation of root resorption during orthodontic treatment (Fig 3). An overwhelming 82% have noted root resorption during orthodontic treatment with general dentists contributing a fair share to it (50%) (Table 3)
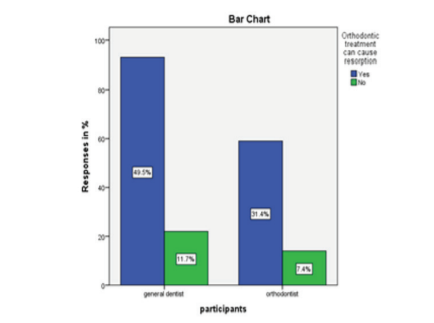
Fig 4: The blue bar represents the participants responding yes and the green bar represents the participants responding no. 80.9% of the participants responded yes and 19.1% of the participants responded no
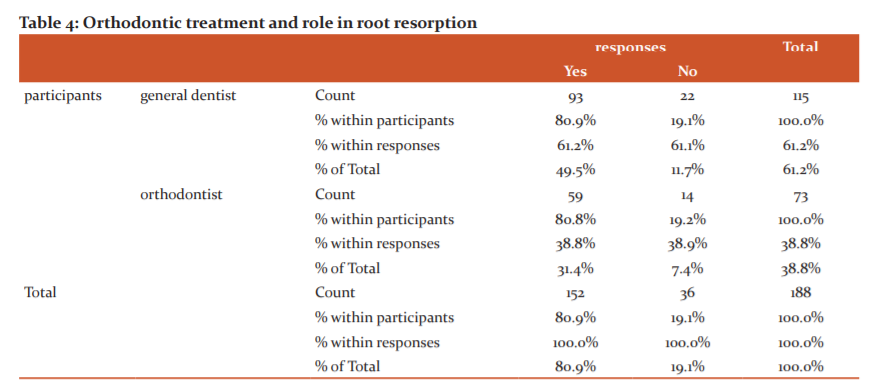
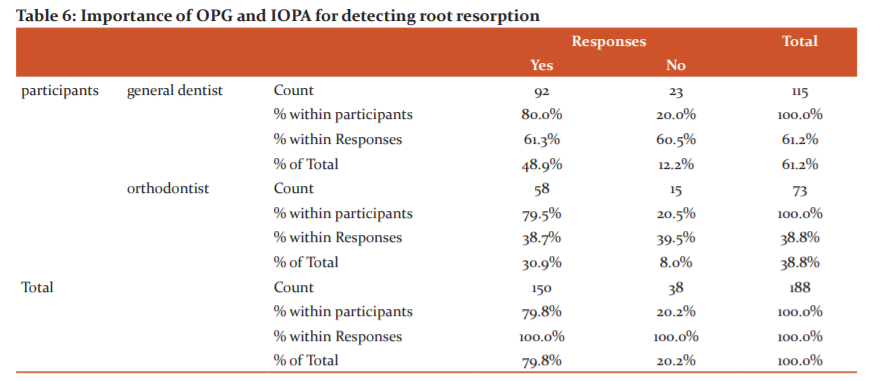
The fourth question was asked to analyse the attitude of the participants towards orthodontic treatment and its role in root resorption (Fig 6). Nearly 81% of the participants responded yes with general dentists contributing a fair majority (49.5%) (Table 6)

Fig 5: The blue bar represents the participants responding no and the green bar represents the participants responding yes.75.5% of the participants responded no and 24.5% of the participants responded yes
The fifth question was asked to assess the participants' awareness about newer protocols to deal with root resorption (Fig 7). Nearly 3/4th replied no with general dentists forming a majority number (Table 7)

Fig 6: The blue bar represents the participants responding yes and the green bar represents the participants responding no. 79.8% of the participants responded yes and 20.2% of the participants responded no
The sixth question evaluated common practices related to the subject (Fig 9). It questioned the participants on whether OPGs and IOPAs are sufficient to confirm root resorption. Nearly 80% replied yes with a majority of them being general dentists (Table 9)
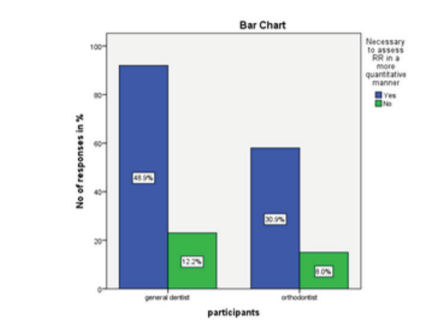
Fig 7: The blue bar represents the participants responding yes and the green bar represents the participants responding no.79.8% of the participants responded yes and 20.2% of the participants responded no
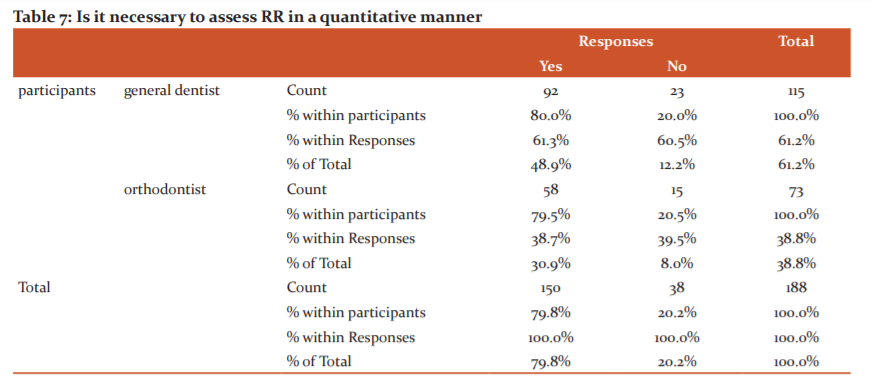
The seventh question asked the participants whether it was necessary to assess root resorption in a quantitative manner (Fig 10). 80% of the participants replied yes with a high number of responses from general dentists (Table 10)

Fig 8: The blue bar represents the participants responding no and the green bar represents the participants responding yes.71.3% of the participants responded no and 28.7% of the participants responded yes
The final question tested the participants on whether they were aware of the method of categorizing an individual at a high risk of root resorption (Fig 11). A high majority replied no (71.3%) with general dentists making up a majority of them (Table 11)
DISCUSSION
Many general dental practitioners and specialists believe that root resorption can be avoidable and hold the orthodontist responsible when it occurs during orthodontic treatment. It is therefore necessary to have knowledge regarding which orthodontic treatment factors contribute to root resorption, so that detrimental effects can be minimized.12
Over the years, there has been growing interest in evaluating the side effects of orthodontic treatment, particularly apical root resorption. Most studies have been conducted with the aid of intraoral radiography, which means that only root shortening and resorption on the mesial and distal aspects of the roots could be evaluated.13 Slanted surface resorption was found to be relatively common at buccal and palatal root surfaces—an interesting finding because these surfaces are not displayed on intraoral radiographs, and because such resorption eventually may result in root shortening.14,15 In attempts to identify patients at risk for severe root shortening, slanted surface resorption could be a relevant research topic in future studies of OIIRR with CBCT.16
Orthodontic treatment is predominantly completed over treatment duration of 1.5-2 years and naturally lends itself to iatrogenic side effects. Root resorption is one commonly noted adverse reaction and presents in various forms.17 Opinions on root resorption are varied in literature with different treatment protocols. Due to the absence of clinical effects, root resorption is neglected at times except in severe situations leading to many deleterious effects.18 Our study was conducted to determine the awareness on root resorption between orthodontists and general dentists. While orthodontists would be more equipped to deal with root resorption than other specialties, it is also necessary to understand that treatment of this condition is often chronic and unpredictable. A more accurate picture on root resorption and its harmful effects can be given by general dentists since they deal with other confounding factors as well.
Our study was framed such that the questions asked in the survey were not pointed and tested the participant’s learning on the subject about root resorption. The results of the survey make for interesting reading. A huge majority of the patients (92%) responded that they had noted root resorption during their clinical practice at some point of time or the other. The next question was asked about the prevalence of root resorption and the responses again were on the higher side with nearly 70% responding that they encountered root resorption quite commonly. A large majority of participants also responded that they could observe root resorption in most cases with fixed appliance therapy.
Root resorption is commonly classified based on the area of interest: Apical, Middle-third and Cervical resorption. A majority of the participants in the affirmative regarding the types of root resorption.19 Information on these factors has shown changes. A recent study by Dudic et al, negates the multifactorial effects of root resorption in orthodontic treatment.9 It is well known that orthodontic force application induces aseptic local inflammation due to necrosis in the periodontal ligament (PDL) and that there is no tooth movement without this inflammation process. It is also well known that inflammation process is important for both bone as well cementum remodeling processes.20 If we consider these well known phenomena together, we can name the process related to orthodontic tooth movement, as well as the Inflammatory Root Resorption Concurrent with Orthodontics (IRRCWO), as ‘‘Orthodontitis’’. Orthodontitis is an aseptic local inflammation in the PDL induced by orthodontic forces. Root resorption is classified into two types: Instrumental Orthodontitits and Instrumental Detrimental Orthodontitits (Phase I and Phase II). These newer groups are helpful in determining volumetric loss of tooth area with respect to each one-third and are important for early focal resorption lacunae.21
Protocols to deal with root resorption are varied and dependent on patient-clinician factors. Awareness about newer protocols to deal with root resorption was still lacking with almost 75% of the participants responding no to the questions.22 Treatment of root resorption varies from usage of light forces, to using mild splints and in certain severe cases, fused crowns can also be used to prevent damage to the roots. Opinion was split on whether root resorption could be treated among the participants
Traditional 2D radiography has multiple issues when it comes to diagnosing and assessing orthodontic root resorption, including superimposition of adjacent structures, magnification, the ability to assess root resorption only on mesial and distal root surfaces that are perpendicular to the x-ray beam, and a general lack of reproducibility and sensitivity.9 These drawbacks of 2D imaging result in detecting only advanced root resorption and apical root loss. In our study though, 80% of the participants responded that IOPAs and OPGs were sufficient to detect root resorption.
The etiology of resorption of roots in orthodontic treatment is complex and still remains unclear, including genetic predisposition and environmental factors.23, 24 The genetic predisposition makes resorption of roots associated with orthodontic treatment more predictable. The factors relevant to root resorption can be divided into biological and mechanical factors. Mechanical factors include the tooth movement type, force magnitude, duration and type of force and so on. For the biological factors, root morphology, a genetic susceptibility, systemic disease, gender, age and medication intake have been demonstrated to influence root resorption.2 Hence a quantitative method might be appropriate to determine any volumetric loss occurring in response to orthodontic force. Usage of better diagnostic aids such as CBCT may help us in detecting incipient root losses at the start of treatment itself or in cases of existing lesions.
Slanted root resorption was found in up to 15% of palatal root surfaces and could be evaluated only on tomographic images. A CBCT technique thus can provide more valid and accurate information about root resorption and may be of value in research.9-11 Conservative therapeutic treatment exists and resorting to extraction is still the exception. For the orthodontist, it is essential to temporarily or even indefinitely stop treatment in cases of apical resorption in order to halt the process of resorption. In cases of cervical resorption, the orthodontist should intervene as soon as resorption is detected given its invasive and evolving nature when directly exposed to the oral environment.3, 6 Orthodontists, dentists and endodontists will have to collaborate in order to improve the prognosis of the most difficult clinical situations. Informing the patients and obtaining their informed consent, a thorough medical history and an evaluation of risk, routine screening and early and accurate detection with the use of cone beam technology, and finally, collaborative and multidisciplinary management of therapeutic treatments therefore represent the key elements for the management of orthodontically induced apical and cervical resorptions.7 However, presently, we are still unable to completely eliminate the occurrence of OIIRR even though Brezniak and Wasserstein optimistically hope that future research will make it possible.21
CONCLUSION
Root resorption is a fairly common phenomenon with at least 70% of the participants concluding that they have observed it in practice and during orthodontic treatment. It is necessary to assess Orthodontically-induced root resorption (OIRR) in a quantitative manner to determine optimal force levels in different clinical scenarios. Despite its value, CBCT is not an ideal modality for identifying root resorption considering exposure to the patient and diagnostic ability. It would be prudent to utilize this modality in cases with existing lesions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Nil
SOURCE OF FUNDING
The authors received no funding for the study
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
The first author (P.A.) conducted the survey, drafted the manuscript and analyzed the results. The second author (N.R.) verified the results obtained and cross-checked the statistics done along with general review of the manuscript.

References:
1. Aryal N, Jing M. Root Resorption in Orthodontic Treatment: Scoping Review. Orthod J Nepal. 2017 Dec 31; 7(2):47-51.
2. Weltman B, Vig KW, Fields HW, Shanker S, Kaizar EE. Root resorption associated with orthodontic tooth movement: a systematic review. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010 Apr 1; 137(4):462-76.
3. Abass SK, Hartsfield Jr JK. Orthodontics and external apical root resorption. Semin Orthod 2007 Dec 1 (Vol. 13, No. 4, pp. 246-256)
4. Linge L, Linge BO. Patient characteristics and treatment variables associated with apical root resorption during orthodontic treatment. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1991 Jan; 99(1):35–43.
5. Turkkahraman H, Yuan X, Salmon B, Chen C-H, Brunski JB, Helms JA. Root resorption and ensuing cementum repair by Wnt/β-catenin dependent mechanism. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2020 Jul; 158(1):16–27.
6. Consolaro A. Extensive orthodontically induced dental resorption: What to do? Dental Press J Orthod. 2020 Mar; 25(2):18–23.
7. Apajalahti S, Peltola JS. Apical root resorption after orthodontic treatment—a retrospective study. Eur J Orthod. 2007 Aug 1; 29(4):408–12.
8. Sameshima GT, Sinclair PM. Predicting and preventing root resorption: Part I. Diagnostic factors. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2001 May; 119(5):505–10.
9. Dudic A, Giannopoulou C, Leuzinger M, Kiliaridis S. Detection of apical root resorption after orthodontic treatment by using panoramic radiography and cone-beam computed tomography of super-high resolution. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009 Apr; 135(4):434–7.
10. Samandara A, Papageorgiou SN, Ioannidou-Marathiotou I, Kavvadia-Tsatala S, Papadopoulos MA. Evaluation of orthodontically induced external root resorption following orthodontic treatment using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Orthod. 2019; 41(1):67–79.
11. Kapila SD, Nervina JM. CBCT in orthodontics: assessment of treatment outcomes and indications for its use. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2015 Jan; 44(1):20140282.
12. Li X, Xu J, Yin Y, Liu T, Chang L, Tang Z, et al. Association between root resorption and tooth development: A quantitative clinical study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2020 May; 157(5):602–10.
13. Leach HA, Ireland AJ, Whaites EJ. Radiographic diagnosis of root resorption in relation to orthodontics. Br Dent J. 2001 Jan 13; 190(1):16–22.
14. Graber LW, Vanarsdall RL, Vig KWL, Huang GJ. Orthodontics - E-Book: Current Principles and Techniques. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2016. Jul 15.
15. Segal GR, Schiffman PH, Tuncay OC. Meta-analysis of the treatment-related factors of external apical root resorption. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2004; 7(2):71–8.
16. Lund H, Gröndahl K, Hansen K, Gröndahl H-G. Apical root resorption during orthodontic treatment. A prospective study using cone-beam CT. Angle Orthod. 2012 May 1; 82(3):480–7.
17. Marques LS, Junior P, Jorge M, Paiva SM. Root resorption in orthodontics: An evidence-based approach. Orthodontics-Basic Aspects and Clinical Considerations. 1th ed. InTech: Shangai. 2012 Mar 9:429-46.
18. Kunimatsu R, Kimura A, Tsuka Y, Horie K, Yoshimi Y, Awada T, et al. Baicalin inhibits root resorption during tooth movement in a rodent model. Arch Oral Biol. 2020 Aug; 116:104770.
19. Janson GR, De Luca Canto G, Martins DR, Henriques JF, De Freitas MR. A radiographic comparison of apical root resorption after orthodontic treatment with 3 different fixed appliance techniques. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2000 Sep; 118(3):262–73.
20. Vineet RV. Root resorption: Pathophysiology & Management. diplom.de; 2015. Dec 23.
21. Brezniak N, Wasserstein A. Defining and framing orthodontitis: a new term in orthodontics. Angle Orthod. 2014 May; 84(3):568–9.
22. Kjaer I. Root resorption: Focus on signs and symptoms of importance for avoiding root resorption during orthodontic treatment. Dental Hypotheses. 2014 Apr 1; 5(2):47.
23. Al-Qawasmi RA, Hartsfield JK Jr, Everett ET, Flury L, Liu L, Foroud TM, et al. Genetic predisposition to external apical root resorption. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003 Mar; 123(3):242–52.
24. Lopatiene K, Dumbravaite A. Risk factors of root resorption after orthodontic treatment. Stomatologija. 2008; 10(3):89–95.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License