IJCRR - 13(16), August, 2021
Pages: 113-117
Date of Publication: 30-Aug-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A Review on Use of m-Health Interventions in Maternal Health
Author: Kaur Manpriya, Sheoran Poonam, Sarin Jyoti
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Effective maternal health care during pregnancy and after childbirth is a very crucial time for recognising and responding to obstetric complications. Most of the pregnancies result in normal birth but few may develop unpredicted complications. These complications can be prevented by using preventive strategies such as using m-Health interventions to educate the mothers on different aspects of antenatal care such as antenatal checkups, antenatal advice, birth preparedness and complication readiness, skilled birth attendant, early detection of risk, timely management of obstetrics complications and postnatal care. Methods: Peer-reviewed papers are included to assess the use of m-health applications that address maternal health issues. Randomised controlled trials, cluster-randomised trials, quantitative or mixed-methods papers which are published between January 2014 to May 2020 were included in this review. Peer-reviewed papers were identified using electronic databases via a combination of search terms. 11 relevant articles were identified. m-Health interventions were found useful, an effective and acceptable tools for pregnant/new mothers and community health care providers. Conclusion: m-Health intervention is an innovative strategy that may contribute to decreasing maternal and neonatal morbidities and mortalities and in developing countries, these strategies have proven to be more effective where resources are limited.
Keywords: m-health, Maternal health, Pregnancy, Mobile phone, m-Health interventions, Mobile health
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Mobile Health is defined by the World Health Organization as a public health tool that is based on wireless communication platforms such as Mobile phones, tablet computers, real-time patient monitoring devices and the use of Information and Communication Technologies.1
World Health Organization statistics showed that every day approximately 830 women die from pregnancy or childbirth-related complications globally. Approximately 303,000 women died during pregnancy and after childbirth and mostly the deaths were occurring in those settings where resources are limited.2 Data also revealed that the Maternal mortality ratio in developing countries in 2015 is higher 239/ 1 lakh live births as compared to 12/1 lakh live births in developed countries. Sample registration survey revealed that maternal mortality ratio in India is 130/1 lakh live births whereas in the states like Assam has maximum number of maternal deaths as Maternal Mortality Rate of 237/1 lakh live births, Uttar Pradesh has 201/1 lakh live births, Rajasthan has 199/1 lakh live births, Odisha has 180/1 lakh live births, Punjab state has 122/1 lakh live births, Haryana has 101 /1 lakh live births and least is in Kerala with 46/1 lakh live births.3
Deaths due to pregnancy and childbirth are common among women in the Reproductive age group. Globally, India being amongst the top fifth country accounts for more than one-fifth of all maternal deaths. 5 out of 1000 women who become pregnant die because of pregnancy-related causes and childbirth. The majority of maternal deaths are due to obstetric hemorrhage followed by anaemia, malaria, heart diseases, infections account for 15%, unsafe abortions 13% and around 8% of maternal deaths result due to prolonged or obstructed labour.4
Registration of pregnancy must be done as soon as the pregnancy is confirmed so that any medical complications can be easily identified or detected before they become life-threatening emergencies. Providing knowledge related to their health is a vital element, so as to aware the mothers regarding their own health status. There is huge evidence available that shows those women having adequate knowledge resulted in safe pregnancy and delivery outcomes.5 This is likely because if antenatal mother is equipped well with the knowledge, it will help her to take timely decisions about her health during pregnancy and childbirth.
The primary focus of modern obstetrical nursing is on the preventive care of pregnant women. If the mothers are well educated during antenatal period that can lead to safe childbirth. So, educating the primigravida mothers by using m-health technology is a strategy to improve her self-care practices during pregnancy and childbirth. This current review paper assesses the interventions targeted to increase antenatal care attendance, providing health education and studies evaluating other uses of m-Health. The present systematic review provides a more definitive picture of the state of evidence for m-Health interventions for maternal health.
AIMS AND OBJECTIVES The overall aim of this review is to identify, appraise, and synthesize quantitative research evidence on the use of m-health to improve maternal health care practices. This will allow us to identify the potential for using m-health strategies in national maternal health programs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
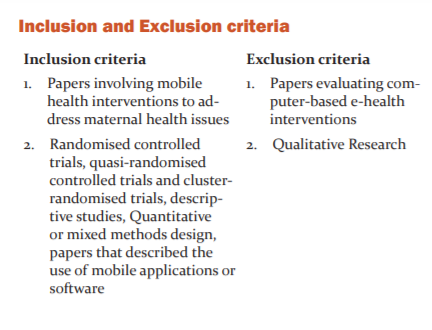
Search Strategy: This review includes Peer-reviewed papers that assess use of any mobile phone application that addresses maternal health issues. The study limited to randomized controlled trials, cluster-randomized trials, quantitative or mixed-methods papers which are published from January 2014 to May 2020 and therefore excluded the qualitative research and oral presentations. The literature search was conducted in Bio Med Central, Google scholar and various other electronic databases via a combination of search terms. Table 1 showed the search strategy using search terms.
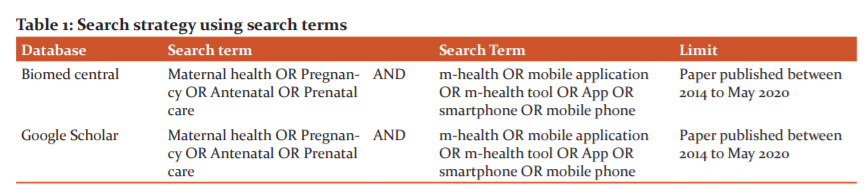
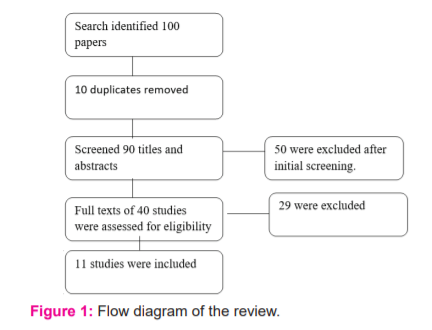
Study selection Study selections were depend on peer-reviewed original articles on m-health interventions for maternal health. Titles and abstracts of these articles were extracted from different database searches and then they were reviewed to ensure whether related to use of m-Health that addresses maternal health issues or not with the following inclusion and exclusion criteria. Our search identified 100 papers, in which we removed 10 duplicates and screened 90 titles and abstracts, of which 50 were excluded after initial screening. Full texts of 40 studies were assessed, 29 were excluded and 11 were included in this review. (Fig 1) All the included articles were reviewed twice by authors.

Outcome Measures
Primary Outcome
Number of Antenatal care visits, TT immunization, Early registration before 12 wks of gestation, Gain in weight and haemoglobin, Maternal knowledge regarding self care during pregnancy
Secondary Outcome
Maternal Outcomes- Institutional deliveries, maternal morbidities, early referral in case of identified complications, easy accessibility to skilled birth attendant for delivery
Infant outcomes-Decrease number of Low birth weight babies, preterm birth, still birth, Neonatal mortality
RESULTS
Three papers reported on interventions to improve antenatal attendance, 1 described use of m-health interventions for the purpose of Communication between health care facility, Community Health Worker, Pregnant women and new mothers, 2 papers reported use of m-health in the form of Health education and appointment reminders and 5 studies targeted antenatal mothers using mobile applications during pregnancy. Sample size range from 12-3000. Table 2 elaborated the characteristics of the papers included in the review.

Improving Antenatal care attendance. Three papers reported improving antenatal care attendance by using a mobile phone. A Randomized controlled trial was conducted among 1311 women in the intervention group and 1239 in the control group, who attended their first antenatal care visit at selected primary health care facilities and were followed until 42 days after delivery. The intervention involves sending mobile phone text-message on the antenatal mother’s phone along with distributing the voucher. Findings showed that the majority of the women received > four antenatal care visits in the intervention group as compared to the control group. Study recommended that mobile phone applications should be considered by policymakers as they may contribute towards improved maternal and newborn health.6
A similar study conducted for a period of 21 months on a sample of 204 registered antenatal women. The interventional group received mobile health support in addition to routine antenatal care and the control group received only routine antenatal care. The study findings revealed that the interventional group had maximum number of Antenatal Care visits, better correction of anemia, and only a few mothers were lost to follow-up.7
Another interventional study conducted among antenatal mothers using mobile phones was followed up to 28 days postpartum. 178 mothers and 206 antenatal mothers were included in the interventional and control group respectively. Results concluded that in the interventional group, there is an increase in antenatal attendance at the health facility, High risk pregnancies cases such as Hypertension, diabetes cases were detected earlier, increase in mean weight and hemoglobin was observed in the third trimester, more number of Institutional delivery and less prevalence of Low Birth Weight babies. Almost all the neonates in the interventional group were immunized with BCG and Oral Polio Vaccine within seven days compared to the control group.8
Communication between health care facility, Community Health Worker, Pregnant women and new mothers. In one study of provider to provider communication using a mobile Health tool that uses text messages to coordinate between health care facility, health worker, Pregnant women and new mothers. Results showed that all Community Health Workers agreed that this tool helped them easily tracking of pregnant woman. This study further recommended that incorporation of m-Health tools in Community maternal health programs will decrease the obstetric complications by improving the women adherence to Antenatal care and postnatal care. 9
Health education and appointment reminders. In a study conducted by Dalton showed similar findings of providing antenatal education for pregnant women through the Healthy e-baby App and sending appointment reminders to enhance Antenatal care visits.10 Another cluster Randomized Controlled Trial study was conducted in Bangladesh for 1 year period on sample size of 3000. Study interventional group i.e. 500 antenatal women received Mother and Child health Handbook along with text messages and 500 got health education through Maternal and child health book only. 1000 participants were in control group. This mobile phone-based intervention and handbook were more beneficial to improve maternal knowledge.11
Enhancing awareness regarding different aspects of pregnancy. A cross-sectional survey was conducted among 193 pregnant women to explore the use of pregnancy-related mobile applications. Findings suggested that more than half of the pregnant women were using mobile apps related to pregnancy, birth, or child care. There is a significant difference in the use of mobile App among Primigravida mothers. This study further recommended that there is a need of developing credible pregnancy care applications and its content must be prepared by experts in the field of health.12
Another study to evaluate the mobile usability of Amila Pregnancy app, a mobile assistive app for pregnant women and expectant mothers and the results showed that most of the participants like the mobile Amila Pregnancy app and found acceptable, usable and useful during pregnancy.13
Another similar study on mobile applications i.e. BenEssere Mamma App (Pregnancy App) had features of providing meditation and guided imagery exercises to the selected antenatal mothers. 12 study subjects were selected for a total of four weeks. This App was perceived very easy to use and guided imagery exercises were assessed as pleasant and quite effective.14 Another study was conducted on usage of Smartphone Apps. Pregnant and young mothers from various hospitals and scan centres were the study subjects. The researcher found that the women who were pregnant and new expecting mothers were more enthusiastic in knowing their health and infant development. The result of the study revealed that middle-class and lower-middle-class women uses a smartphone and its applications more frequently during their pregnancy period as compared to the women in the upper-middle class and higher-income women.15 Another study project was donefor pregnant women to develop an Android application on self-care management to control gestational weight gain. This Android application enhances self-care practices and awareness and brings convenience to pregnant women in order to maintain a healthy weight gain during their pregnancy stages.16
DISCUSSION The current review showed that m health interventions have been widely used in maternal health in order to improve the maternal and neonatal outcomes. Review studies showed that m-health interventions provide promising findings such as health education, appointment reminders, sending text messages to improve Antenatal care visits and better communication strategy between health care facility, Community health workers and pregnant mothers. m-Health strategy is very effective in tracking and timely referring the high risk-pregnancies. In survey results, 94% of pregnant women reported that smartphones had changed their life in many ways such as the availability of information related to pregnancy anytime-anywhere.17 Even this service can be accessed from rural areas where transportation and medical services are limited. Easy availability and affordable prices of mobile phones makes huge contribution towards the development in the field of m-Health.
m-health applications helps pregnant and new mothers to reduce the time of traveling to health facility, free of access to information and hence, it overcomes the issues of inadequate financing, poor access to information and limited resources. m-Health is an effective educational communication tool between pregnant/ new mothers and community health care providers.7Antenatal mothers m-health registration should be done early in first trimester to avoid less number of Antenatal care visits. However, there were barriers associated with the engagement of antenatal mothers in using m-health such as free wi-fi was not available at the time of registration so they were not able to download the application on their mobiles. Another factor is difficult to understand the user interface/ language could impact the usage of m-Health interventions.10 In order to overcome the barriers adequate training to community health workers about m-Health application usage is necessary and if the application is provided in their local language then it will be easy for the antenatal mother to understand various aspects of antenatal care such as antenatal advices, exercises, about diet in pregnancy, minor ailments of pregnancy, birthing process and breastfeeding. The present review agreed with other reviews that there is a need of higher-quality studies which are focussing on m-health interventions addressing maternal health issues. But still there is a need to review full text of large number of papers to know more about the m-health interventions. There is a need for comprehensive review as the new papers on m-health are publishing very fast. Currently the number of women accessing the complete antenatal care package (to monitor the foetal development and to know about maternal well-being) is quite low which results in delay in reaching the health facility and ultimately increases the risk of complications to both mother and baby.
CONCLUSION To fulfil the needs of pregnant mothers, pregnancy-related credible m-health applications should be developed in local language and managed by qualified health professionals, so that there will be quick provision of credible professional information for pregnant mothers. Policy makers must ensure to include m-health services in the national health programs to achieve Sustainable Developmental Goals of reducing maternal and newborn mortality and morbidity rates. Future researchers must conduct more studies on m-health to prove its role in delivering maternal and new born health care.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT Authors acknowledge the immense help received from scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Ethical clearance: None
Informed consent: NA
Source of funding: None
Conflict of interest: NIL
Author’s Contribution:
Conceptualization: MK,PS,JS Methodology: MK,PS,JS Results: MK,PS Writing-Original draft preparation: MK Writing- review and editing: MK,PS,JS Supervision: PS,JS
References:
-
WHO Global Observatory. mHealth: new horizons for health through mobile technologies: second global survey on eHealth. Switzerland[Internet]. World Health Organization; 2011[cited 2021 Jan 8]. 14p. Available from: https://www.who.int/goe/publications/goe_mhealth_web.pdf
-
Maternal Mortality. [Online].; 2021 [cited 2021 Jan 8]. Available from: http://www.who-int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/material-mortality
-
National Institute of Transforming India.[Online] [cited 2021 Jan 8]. Available from: Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) (per 100000 live births) | NITI Aayog.
-
World Health Organization. [Online].; 2021 [cited 2021 Jan 8]. Available from: https://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/estimates_child_cod_2000 _2012/en/
-
Zohra S L, Mansoor T, Rehana A S, Das J K, Bhutta ZA. Essential pre-pregnancy and pregnancy interventions for improved maternal, newborn and child health. Reproductive Health 2. 2014; 11(1):1-19
-
Stine L, Birgitte BN, Maryam H, Ida MB, Azzah S, Khadija SM, Makungu H et al. Mobile phones improve antenatal care attendance in Zanzibar: a cluster randomized controlled trial. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth. 2014; 14(29):14-29.
-
Basavanapalli M, Vasundhara K, Vijaya SM. The role of m-health in providing antenatal care in rural areas. International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2017 Sep; 6(9):4059-4064.
-
Mudey DA, Khapre DM, Mudey DG,Goyal DR. An Innovative Approach of Mobile E-Health Intervention in Tracking Antenatal Mothers & Neonates in Selected Rural Areas of a District in Central India: An Ice Breaking Footstep for Revolution. Int. J. Epidemiol.2015 Sep; 44(1):95-96.
-
Ivy M, Chibulu L, Casey IH, Yanis BA. Evaluation of the impact of a mobile health system on adherence to antenatal and postnatal care and prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV programs in Kenya. BMC Public Health. 2015 Feb; 15(102):1-16
-
Julia AD, Dianne R , Michael W , Sal H, Andrew S , Claire TR et al. The Health-e Babies App for antenatal education: Feasibility for socially disadvantaged women. PLoS ONE. 2018 May; 13(5):1-18.
-
Ruoyan GT, Syed EH, Kiyoko I, Rintaro M. Mobile-health tool to improve maternal and neonatal health care in Bangladesh:a cluster randomized controlled trial. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth. 2018; 18(102):1-7.
-
Yeonkyu L, Mikyung M. Utilization and Content Evaluation of Mobile Applications for Pregnancy, Birth, and Child Care. Healthcare Informatics Research. 2016 April; 22(2): 73-80.
-
Hussain A, Emmanuel M, Najdawati MF, Norhasizasuriati MH. The UX of amila pregnancy on mobile device. In The 2nd International Conference on Applied Science and Technology; 2017: AIP Publishing.
-
Carissoli C, Villani D, Triberti S, Riva G. User experience of BenEssere Mamma, a pregnancy app for women wellbeing. Annual Review of CyberTherapy and Telemedicine. 2016; 14(1):195-98.
-
Jayaseelan R, Pichandy C, Rushandramani D. Usage of Smartphone Apps by Women on their Maternal Life. Journal of Rawalpindi Medical College. 2015; 5(7):1-6.
-
Saw YC. My pregnancy care mobile health monitoring application system Malaysia: Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka, 2014.
-
Pradhan N. Use of Mobile health applications in obstetric care: A review. BMC Pregnancy and childbirth 2017:18-46
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License