IJCRR - 13(16), August, 2021
Pages: 88-93
Date of Publication: 30-Aug-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A Study of Pro Brain Natriuretic Peptide (PRO BNP) Levels in Asymptomatic Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Author: Ashutosh Arun Bandgar, Virendra Chandrashekhar Patil
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) is a thirty two-amino acid peptide. It is synthesized mainly in the left ventricle of the heart as a 108 amino acid prohormone pre-pro BNP (γ-BNP). Objectives: To measure pro Brain Natriuretic Peptide (pro-BNP) levels in subjects with Type 2 Diabetes mellitus. Methods: That we have used for the present study prospective, observational, non-interventional cohort study done in patients admitted in Krishna Hospital and Medical Research Centre, Karad with the diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Results: We have seen the Distribution of pulse rate, blood pressure, blood sugar, serum HbA1c and serum creatinine, Distribution of serum lipids, serum pro BNP and Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in the study population. Conclusion: The measurement of pro BNP level in a patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus will be valuable for early prediction of heart failure and its outcome.
Keywords: Pro Brain Natriuretic Peptide, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Pulse Rate, Blood Pressure
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION:
Diabetes mellitus is one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality globally. The development of diabetes mellitus requires corresponding amendments in the therapy and identification of the disease severity is therefore important for predicting prognosis, treatment, preventing complications, reducing complications and mortality.1 Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) is a thirty-two-amino acid peptide. It is synthesized mainly in the left ventricle of the heart as a 108 amino acid prohormone pre-pro BNP (γ-BNP). The hormone is an effective vasodilator and a natriuretic factor regulating salt and water homeostasis in the body. It is stored in the human cardiac tissue predominantly as BNP-32 with a smaller amount of the precursor pre-pro BNP. The circulating plasma forms of BNP are BNP-32 and the NH2-terminal portion pro-BNP (Nt-pro BNP). It is an easy measure for the assessment of cardiac function. As a response to myocardial wall stretch, pre-pro BNP is synthesized and processed to pro BNP; which is further processed to the biologically inactive NT-pro BNP fragment and the biologically active BNP fragment. These measurements can be useful for diagnosing heart failure, including left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction.
Relation between pro BNP and blood pressure
Anuva Mishra et al. observed that the mean systolic blood pressure (SBP) among his study population was 128.2±9.8 mm Hg and had a weak +VE correlation with the pro BNP levels (‘p’=0.46) whereas the mean DBP among them was 82±7.8 mm Hg and had a weak +VE correlation with pro BNP level (‘p’=0.56). A study conducted by Sasaki N et al, observed a strong +VE correlation of SBP and pro-BNP (‘p’<0.001) however a weak +VE correlation of DBP and pro BNP level was observed (‘p’=0.28). Kursat Dal et al. also reported that the mean SBP was 128.2±9.8 mm Hg and had a strong +VE correlation with the pro BNP level (‘p’<0.001); the mean DBP was 82±7.8 mm Hg and had strong +VE correlation with pro BNP level (‘p’<0.001).2,3
Masugata et al, analyzed the pro BNP levels with the blood pressure variability in Japanese population and reported that mean SBP 130±13 mm Hg while the mean DBP as 69±6 mm Hg. SBP had weak +VE correlation with pro BNP level (‘p’=0.59) and DBP was also having weak +VE correlation (‘p’=0.45). A study of Kumiko Hamano et al, too reported that the pro BNP had strong +VE correlation with SBP (‘p’=0.027) whereas DBP had weak +VE correlation (‘p’=0.45).4, 5
P Gaede et al, also reported strong +VE correlation (‘p’=0.002) between SBP and pro BNP while DBP had weak +VE correlation with pro BNP level (‘p’=0.39); Rosiak M et al reported that pro BNP level had a weak +VE correlation with SBP (‘p’=0.5), and weak +VE correlation with DBP (‘p’=0.33) respectively. Alain G Bertoni et al observed DBP and pro-BNP had a weak +VE correlation (‘p’=0.3). Thus the findings of the above studies are comparable with the present study. 6, 7, 8
Relation of pro-BNP with a duration of diabetes mellitus
Kumiko Hamno et al, had reported mean duration of diabetes mellitus as 9±5 years and had a strong +VE correlation with pro BNP (‘p’=0029). A study conducted by Kursat Dal et al, reported that mean duration of diabetes was 7.5 ± 3.5 years and there was a significant decrease in pro BNP levels after improving the glycaemic control in the study population (‘p’<0.001). Misurata et al 4 also reported that the duration of diabetes mellitus had a strong correlation with pro BNP level (‘p’=0.05). Similarly, P. Gaede et al in their study reported that the duration of diabetes mellitus had strong correlation with pro BNP level (‘p’=0.003). Alain Bertoni et al, also observed strong correlation with duartion of diabetes mellitus and pro BNP (‘p’<0.05). 6, 5, 9, 7
Pro BNP and blood sugar levels
Ashok Sahu et al also studied the pro BNP levels in diabetic population in central India and reported that FBS had +VE correlation with pro BNP level (‘p’<0.001). Mishra A et al, also reported that FBS had strong +VE correlation with pro BNP level (‘p’<0.001). Similarly, Kursat Dal et al too in their study observed that mean fasting plasma glucose levels were 306.3 ± 119.4 mg/dL and it had strong association with serum pro BNP level (‘p’=0.002). Thus, the above studies were comparable with the present study. 2, 10, 9
Pro BNP and HbA1C
Kursat Dal et al, reported that the mean HbA1c level was 11.0 ± 2.5% and a significant decrease in pro BNP level was observed after improving glycemic control (‘p’<0.001). Masugata et al also reported that HbA1c had +VE correlation with pro BNP levels (‘p’=0.002). Anuva Mishra et al in their study too observed strong +VE correlation of serum HbA1c and serum pro BNP levels. Roisak M et al also reported high mean HbA1c levels were associated with high pro BNP values (‘p’<0.001). Alain G Bertoni et al, also reported that HbA1c level had strong +VE correlation with pro BNP level(‘p’<0.001) 7,8, 9
Pro BNP and LV functions
Amulya et al. reported that LV systolic dysfunction had strong +VE correlation with the pro BNP levels (‘p’<0.001). Hui Gong et al, also observed strong +VE correlation of LV systolic dysfunction and pro BNP level (‘p’<0.05) and strong +VE correlation of LV diastolic function and pro BNP level (‘p’=0.045). A study of Cartsten Taschö pe et al also had described that LV systolic dysfunction and LV diastolic dysfunction were +VEly associated with pro BNP levels [‘p’=0.09, ‘p’=0.001 respectively]. 11,12,13
OBJECTIVES
• To measure pro Brain Natriuretic Peptide (pro BNP) levels in subjects with Type 2 Diabetes mellitus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Type of study:-
This was a prospective, observational, non-interventional cohort study done in patients admitted in Krishna Hospital and Medical Research Centre, Karad with diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Sample size calculation:
According to a study conducted by Bertoni A .G et al, the prevalence of Congestive Heart Failure in patients of diabetes was found 11.8%.14
So, p = 11.8%
Using formula for sample size (n) calculation,
n = 4 x p x q
e2
Where, p = 11.8% = 0.118
q = 1 - p = 0.882
Taking e, absolute error of 10%, e = 0.1
So, n = 4 x 0.118 x 0.882
0.1 x 0.1
n = 41.63 ≈ 42
According to the formula, a total 42 subjects were taken in the present prospective observational study. The study population, therefore, is A total of 42 subjects admitted in wards and ICU were enrolled in the present study. This study was conducted over a period of 18 months (October 2018 to May 2020). This study was conducted on patients admitted with a diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus according to American Diabetes Association criteria at Krishna Hospital and Medical Research Centre, Karad.
Inclusion Criteria:
• Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus who were asymptomatic for heart failure were included in the study
• All gender between 18 to 70 years were included in the study
Exclusion Criteria:
• Patients with established heart failure, renal failure, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, liver cirrhosis, stroke, hyperthyroidism, septic shock, patients with nephropathy
• Patients with valvular heart disease, coronary artery disease
This study was approved by Institutional Ethics Committee (IEC).The written and informed consent was taken from all the participants in local and English language before including them in to the study.
A detailed physical examination was done. The blood pressure was recorded using a well-calibrated mercury sphygmomanometer in the supine position (Diamond BP MR-120 Mercurial BP Deluxe). At least two readings were taken, with a one-minute intervals between them, and the average of the measurements was recorded. Other parameters such as pulse rate were checked in the radial artery for the whole one minute.
RESULTS
Distribution of pulse rate and blood pressure in study population
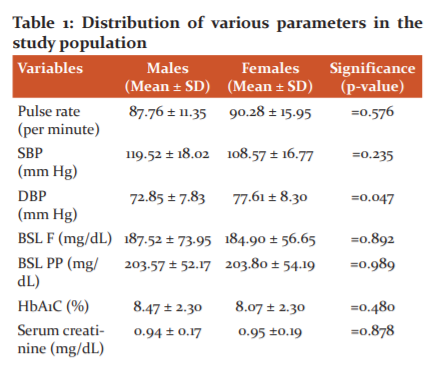
A total 42 subjects were enrolled in the present study. The pulse rate, systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure were measured in them. The mean pulse rate of males was 87.76 ± 11.35 per minute and mean pulse rate of females was 90.28 ± 15.95 per minute
(Table 1). The pulse rate of male and female subjects was not statistically significant (‘p’=0.576). The mean SBP of males was 119.52 ± 18.02 mm Hg and mean SBP of females was 108.57 ± 16.77 mm Hg. The mean SBP between males and females was statistically not significant (‘p’=0.235). The mean DBP of males was 72.85 ± 7.83 mm Hg and mean DBP of females was 77.61 ± 8.30 mm Hg. The mean DBP between males and females was statistically significant (‘p’=0.0475).
Distribution of blood sugar, serum HbA1c and serum creatinine level in study population
In the present study we assessed the fasting and post prandial blood sugar, serum creatinine and serum HbA1c levels. The mean fasting blood sugar level of males 187.52 ± 73.95 mg/dL, mean level of blood sugar in case of ladies when observing fast remained 184.90 ± 56.65 mg/dL. The mean post prandial fasting blood sugar level between males and females was not statistically significant (‘p’=0.989). The mean HbA1c of males was 8.47 ± 2.30 mg/dL and mean HbA1c of females was 8.07 ± 2.30. The mean HbA1c between males and females was not statistically significant (‘p’=0.480). The mean serum creatinine level of males was 0.94 ± 0.17 mg/dL and mean serum creatinine level of females was 0.95 ±0.19 mg/dL. The mean serum creatinine level between males and females was not statistically significant (‘p’=0.878). (Table 1)
Distribution of serum lipids in the study population
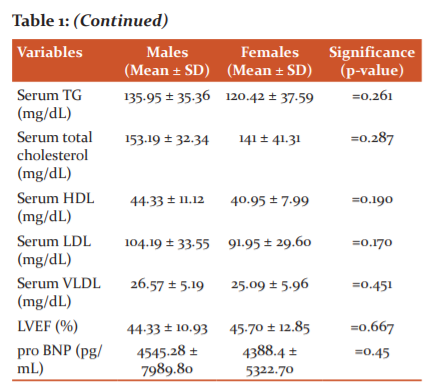
The mean serum triglyceride level of males was 135.95 ± 35.36 mg/dL and mean serum triglyceride level of females was 120.42 ± 37.59 mg/dL. The mean serum triglyceride level between males and females was not statistically significant (‘p’=0.261).The mean serum total cholesterol level of males was 153.19 ± 32.34 mg/dL and mean serum total cholesterol level of females was 141 ± 41.31 mg/dL. The mean serum total cholesterol level between males and females was not statistically significant (‘p’=0.287).(TABLE 1)
Distribution serum pro BNP and Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in the study population
The mean LVEF of males was 44.33 ± 10.93% and mean LVEF of females was 45.70 ± 12.85%. The mean LVEF between males and females was not statistically significant (‘p’=0.667).The mean serum pro BNP level of males was 4545.28 ± 7989.80 pg/mL and mean serum pro BNP level of females was 4388.4 ± 5322.70 pg/mL. The mean serum pro BNP level between males and females was not statistically significant (‘p’=0.45).Table 1
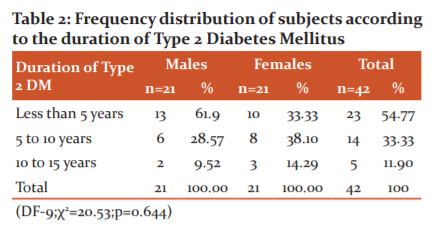
Distribution of the study population according to the duration of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
A total 42 subjects were enrolled for the present study. Total 23 (54.77%) subjects had duration of diabetes mellitus of less than 5 years of which 13 (61.9%) subjects were males and 10 (33.33%) subjects were females. Total 14 (33.33%) subjects had duration of diabetes mellitus of 5 to 10 years of which 6 (28.57%) subjects were males and 8 (38.10%) subjects were females, Total 5(11.90%) subjects had duration of diabetes mellitus between 10 to 15 years of which 2 (9.52%) subjects were males and 3 (14.29%) subjects were females. The was no statistical significance between the duration of diabetes mellitus of male and female subjects (‘p’=0.644). Table 2
DISCUSSION
The prevalence of diabetes mellitus is increasing day by day in developing countries like India. Heart failure is the leading cause of morbity and mortatilty in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.In this study we evaluated pro BNP as a marker in predicting heart failure in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and was compared with various other studies.
Distribution of age in the study population and its association with pro BNP
Total 42 subjects were enrolled in the present study, majority of them were of age group 61 to 70 years (42.86%), followed by 51 to 60 years(26.19%) and then less than 40 years (16.67%). The mean age of the study subjects was 55.40 ± 11.42 years. It was observed that there was a weak +VE correlation with pro BNP levels and age of the study subjects. (‘p’ value = 0.031).
A study conducted by Hui Gong et al, reported that the mean age of the study population was 64 ± 8 years and there was a +VE correlation of pro BNP level and age of the subjects (‘p’<0.05).15 In the same way, Kumiko Hamano et al. also reported that the mean age of the study population was 64.3±12 years and its correlation with pro BNP level was strong +VE (‘p’=0.001).5 In a study done by P. Gaede et al it was observed that the mean age of the study population was 58±6 years and its correlation with pro BNP level was found to be strong +VE (‘p’<0.001).6 Carsten Taschö pe et al. had also reported the mean age of the study population as 49±13 years and its correlation with pro BNP level was weak +VE (‘p’=0.061). 13 Similarly, Rosiak M et al also reported the mean age of the study population as 64.4 ± 8.2 years and its correlation with pro BNP level as strongly +VE (‘p’<0.01). 8 Alain Bertoni et al, had described that the mean age of the study population was 59.5±6.8 years and it had a strong +VE correlation with pro BNP level (‘p’=0.05). 7 Thus findings of the above studies are comparable with the present study.9-12
Distribution of gender in the study population and its association with pro BNP
Total 42 subjects were enrolled in the present study, among them 21 (50%) subjects were males and 21 (50%) were females.The mean pro BNP level among reported among males was 4545.28±7989.80 pg/mL and among females it was 4296.09±5322.70 pg/mL and there was no statistical difference between the pro BNP levels among them (‘p’= 0.45). However a study reported by Kursat Dal et al. reported higher levels of pro BNP in females as compared to males. These findings were not comparable with the present study as population in the study of Kursat Dal et al. were predominantly females.13,14
Distribution of pulse rate in the study population and its association with pro BNP level
The mean pulse rate in the present study population was 89.02 ± 13.55 per minute and there was a weak +VE correlation with pro BNP level (‘p’ =0.854). A study of Kursat Dal et al. reported that the mean pulse rate was 72.8±10.4 per minute; Masugata et al, reported the mean pulse rate as 68±5 per minute and was weakly associated with pro BNP levels (‘p’=0.024). 4 Similarly, study of Ruihua Cao et al. reported a +VE correlation with pro BNP and pulse rate (‘p’=0.41).13 Thus observation of the present study was similar to previous studies and amplifies the importance pulse rate in diabetic patients.14
Distribution of systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and its association with pro BNP
In the present study, the mean SBP among males was 119.52±18.02 mm Hg while among females it was 108.57±16.77 mm Hg and there was no statistical significance among both (‘p’=0.23) however it had strong +VE correlation with pro BNP levels (‘p’=0.002) . The mean DBP among males was 72.85±7.83 while among females it was 77.61±8.30 mm Hg. There was a statistical significance between DBP of males and females and also DBP showed weak +VE correlation with pro BNP values (‘p’=0.72).
Similar to the present study, Anuva Mishra et al observed that the mean SBP among his study population was 128.2±9.8 mm Hg and had a weak +VE correlation with the pro BNP levels (‘p’=0.46) wheras the mean DBP among them was 82±7.8 mm Hg and had a weak +VE correlation with pro BNP level (‘p’=0.56).2 A study conducted by Sasaki N et al, observed a strong +VE correlation of SBP and pro BNP (‘p’<0.001) however a weak +VE correlation of DBP and pro BNP level was observed (‘p’=0.28).3 Kursat Dal et al, also reported that the mean SBP was 128.2±9.8 mm Hg and had strong +VE correlation with the pro BNP level (‘p’<0.001); the mean DBP was 82±7.8 mm Hg and had strong +VE correlation with pro BNP level (‘p’<0.001).9 Masugata et al, analysed the pro BNP levels with the blood pressure variablity in Japanese population and reported that mean SBP 130±13 mm Hg while the mean DBP as 69±6 mm Hg. SBP had weak +VE correlation with pro BNP level (‘p’=0.59) and DBP was also having weak +VE correlation (‘p’=0.45). 4 A study of Kumiko Hamano et al, too reported that the pro BNP had strong +VE correlation with SBP (‘p’=0.027) whereas DBP had weak +VE correlation (‘p’=0.45).5 P Gaede et al, also reported strong +VE correlation (‘p’=0.002) between SBP and pro BNP while DBP had weak +VE correlation with pro BNP level (‘p’=0.39).6 Rosiak M et al reported that pro BNP level had weak +VE correlation with SBP (‘p’=0.5), and weak +VE correlation with DBP (‘p’=0.33) respectively. 8 Alain G Bertoni et al observed DBP and pro BNP had weak +VE correlation (‘p’=0.3). 7 Thus the findings of above studies are comparable with present study.
Distribution of duration of diabetes mellitus and its association with pro BNP
In the present study, 42 study subjects were enrolled. Majority of them 23(54.77%) had a duration of less than 5 years of diabetes mellitus and among 19 (45.23%) subjects with the mean duration of diabetes mellitus as 4.6 ± 4.32 years. The mean pro BNP level in subjects with duration of diabetes mellitus less than 5 years was 1235.08 ± 1217.54 pg/mL and the mean pro BNP level in subjects with duration of diabetes mellitus more than 5 years was 8276.94 ± 8483.48 pg/mL. There was statistical significant correlation with subjects who had duration of DM less than 5 years and who had more than 5 years (‘p’=0.01). There was moderate +VE correlation of duration of DM and pro BNP (‘r’=0.63)
Similar to present study Kumiko Hamno et al. had reported mean duration of diabetes mellitus as 9±5 years and had strong +VE correlation with pro BNP (‘p’=0.029).5 A study conducted by Kursat Dal et al. reported that mean duration of diabetes was 7.5 ± 3.5 years and there was significant decrease in pro BNP levels after improving the glycaemic control in the study population (‘p’<0.001). 9 Masugata et al. also reported that duration of diabetes mellitus had strong correlation with pro BNP level (‘p’=0.05). 4 Similarly, P. Gaede et al in their study reported that the duration of diabetes mellitus had strong correlation with pro BNP level (‘p’=0.003).6 Alain Bertoni et al. also observed strong correlation with duartion of diabetes mellitus and pro BNP (‘p’<0.05).7 Thus the above studies were comparable with the present study.
CONCLUSION
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a major risk factor for heart failure. With the increase in the number of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in India it is evident that the burden of heart failure in the Indian population will be the mirror of the global picture in future. Considering this, in the present study the association between serum pro BNP levels and various factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus was evaluated. There was a significant correlation of pro BNP levels with systolic and diastolic blood pressure, duration of diabetes mellitus, glycosylated hemoglobin levels, impaired fasting and postprandial blood sugar levels, triglyceridemia, albuminuria, glycosuria and retinopathy as determined by linear regression analysis. There was a negative correlation with LVEF and pro BNP and a +VE correlation with pro-BNP and grades of diastolic dysfunction. Thus we can conclude that the measurement of pro BNP level in patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus will be valuable for early prediction of heart failure and its outcome.
Conflict of Interest: There is no conflict of Interest
Source of Funding: No Source of Funding
Authors Contribution: This is a collaborative work among all authors. Dr. Ashutosh Arun Bandgar, Dr. Virendra Chandrashekhar Patil performed the statistical analysis, wrote the protocol, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Dr. Ashutosh Arun Bandgar managed the literature searches. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
References:
1. Kenny HC, Abel ED. Heart failure in type 2 diabetes mellitus: impact of glucose-lowering agents, heart failure therapies, and novel therapeutic strategies. Circ Res. 2019 Jan 4;124(1):121-41.
2. Mishra A, Bhanja SS. An Interrelationship between Nt Pro-Bnp Level, Glycemic Control And Myocardial Ischemia in Type 2 Diabetes Without Overt Cardiac Disease. IOSR j. biotechnol. Biochem. 2018;4(2): 2455-2458
3. Sasaki N, Yamamoto H, Ozono R, Fujiwara S, Kihara Y. Association of N-Terminal Pro B-Type Natriuretic Peptide With Blood Pressure and Pulse Pressure in Elderly People?- A Cross-Sectional Population Study. Circ J. 2018;82(5):2049-2054.
4. Masugata, Hisashi, Senda, Shoichi, Inukai, Michio, Himoto, Takashi, Hosomi, Naohisa, et al. Analysis of association between brain natriuretic peptide levels and blood pressure variability. Exp Ther Med. 2014;8(4):21-24.
5. Hamano K, Nakadaira I, Suzuki J, Gonai M. N-terminal fragment of probrain natriuretic peptide is associated with diabetes microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes .Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2014;10(10):585-589.
6. Gaede, Peter , Hildebrandt, P , Hess, G , Par,ing, H.-H , Pedersen, Oluf. Plasma N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide as a major risk marker for cardiovascular disease in patients with Type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria. Diabetologia. 2006;48(10). 156-63.
7. Bertoni AG, Hundley WG, Massing MW, Bonds DE, Burke GL, Goff DC Jr. Heart failure prevalence, incidence, and mortality in the elderly with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004 ;27(3):699-703.
8. Belagavi AC, Rao M, Pillai AY, Srihari US. Correlation with NT proBNP and left ventricular ejection fraction in elderly patients presenting to emergency department with dyspnoea. Indian Heart J. 2012;64(3):302-304.
9. Dal K, Ata N, Yavuz B, Sen O, Deveci OS, Aksoz Z, et al. The relationship between glycemic control and BNP levels in diabetic patients. Cardiol J. 2014;21(3):252-6.
10. Sahu Ashok , Gupta T, Kavishwar, A, Sarkar PD, R.K.Singh. Diagnostic Role of NT Pro BNP in Diabetes Type 2 Patients Associated with Cardiovascular Disease Risk, A Study from Central India. J Med. 2010;11(1):33-38
11. Rosiak M, Postula M, Kaplon-Cieslicka A, Trzepla E, Czlonkowski A, Filipiak KJ, Opolski G. Metformin treatment may be associated with decreased levels of NT-proBNP in patients with type 2 diabetes. Adv Med Sci. 2013;58(2):362-8.
12 Carsten Tscho¨pe, Mario Kas?ner, Dirk Westermann, Regina Gaub, Wolfgang C. Poller, Heinz-Peter Schultheiss. The role of NT-proBNP in the diagnostics of isolated diastolic dysfunction: correlation with echocardiographic and invasive measurements. European Heart J. 2005;26(6), 2277–2284
13. Tschöpe C, Kašner M, Westermann D, Gaub R, Poller WC, Schultheiss HP. The role of NT-proBNP in the diagnostics of isolated diastolic dysfunction: correlation with echocardiographic and invasive measurements. Eur Heart J. 26(21), 2277-2284.
14 Dobson M. Nature of the urine in diabetes. Medical Observation Enquiries. World J Diab .2016;7(1):1-7
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License