IJCRR - 13(16), August, 2021
Pages: 30-37
Date of Publication: 30-Aug-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Antimicrobial Properties of Three Different Bioactive Compounds of Cassia Species Against S. mutans Serotype C (ATCC 25175). An Invitro Study
Author: Ann Polachirakal Tharakan, Madhura Pawar, Sonal Kale, Noreen Qazi, Rahul Deshpande, Suchita Abhay Gaikwad
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Cassia species (Caesalpinaceae) is a medicinal plant used in traditional Indian medicine for various ailments. In this study, three different bioactive compounds of two medicinal plant species Cassia tora and Cassia fistula were obtained and their antimicrobial properties were compared and evaluated against S.mutans serotype C (ATCC25175) and were conducted as a triple-blind study to identify their effectiveness. Aim: The study aims to evaluate and compare the antimicrobial properties of three different Bioactive Compounds of Cassia species and 0.2% chlorhexidine against S. mutans serotype C (ATCC 25175). Results: All the Bioactive Compounds had good antimicrobial activities based on their zones of inhibition; the highest zone of inhibition in mm was formed by Extract 8 which was Cassia Flower extract having a mean inhibitory zone of 9.93mm +0.76. Stastatistical analysis of the results with Kruskal Wallis and Mann Whitney Post Hoc test proved that at any concentration of Extract 8 the inhibition results are comparable to that of 0.2% chlorhexidine with p=0.05. The results confirmed the antimicrobial potential of the Bioactive Compound of Cassia Flower and hence it can be used as a preventive means for dental caries. Conclusion: The Bioactive Compound of Cassia Flower extract derived from cassia plants are only required in minute quantities as compared to their crude extracts. The study confirmed the antimicrobial potential of the plant at different concentrations can be used as preventive and therapeutic measures in preventive dentistry and due to its reduced potency can be used in children effectively.
Keywords: Bioactive compounds, Chlorhexidine, Cassia, Dental caries, Herbal medicines
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION:
The Global Burden of Disease Study in 2016 estimated that 2.4 billion people suffer due to dental caries of permanent teeth worldwide and an additional 486 million children suffer from caries of primary teeth. 1 Thus, prevention is important as it not only detrimentally impacts the quality of life but also becomes a financial drain due to the need for extensive treatments. Prevention can be achieved by maintaining the ecological balance of the naturally existing cell structures. Zaura et al. in 2014 reported that maintaining the stability of the oral biome is important to prevent ‘dysbiosis’ and according to the author acute infections of the oral mucosa occur but are rare. 2
The oral microbiota survives the daily chemo-mechanical insults from either food or oral hygiene practices which results in variations in temperature, pH or symbiotic microbes. By maintaining the state of dynamic equilibrium within a community of organisms subject to gradual changes an ecological homeostasis can be achieved.
According to He et al., 2011 and Schlafer et al., plaque microflorae have a symbiotic relationship with the host, acting as a barrier to opportunistic pathogens and carrying out metabolic processes that benefit the host.3,4 The emerging need is to target pathogenic microorganism thus shifts the focus towards maintaining the ‘holobiont’. 5
Bowden in 1996 reported that Mutans streptococci, particularly Streptococcus mutans as significant odontopathogens that are implicated to be highly associated with caries in humans.6 Streptococcus mutans being acidogenic and aciduric drives the microbial ecological shift that leads to dental caries and thus appears in primary tooth of children even under six years of age. 7, 8
Chemotherapeutic antimicrobial agents are known to be lethal for the normal commensals and cellular structures. Chlorhexidine is the commonly used potent agent with a proven efficiency which also targets the natural microflora. 9,10 It has a risk of developing skin injuries, such as skin erythema, burns, blisters discoloration of teeth and xerostomia in the mouth. 11,12 Naturally occurring organic substances have fewer disadvantages compared to synthetically obtained chemical plaque or caries inhibiting agent and are milder for use especially in children and infants.13
Cassia species (Caesalpinaceae) is a medicinal plant used in traditional Indian medicine for various ailments and grows annually in all tropical areas.14 Over 5000 species of cassia flowering plants exist and possesses significant anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial antifungal properties and antioxidant properties. 15,16
Bioactive Compounds are the main active ingredients or a chemical substance which may be found in all parts of the plant and have biologically beneficial effects.17 Thus, the aim of the study was to compare and evaluate the antimicrobial properties of three different Bioactive Compounds of Cassia species and 0.2% chlorhexidine against S. mutans serotype C (ATCC 25175).
METHODS:
This study was approved by the Institutional ethics committee of Dr DY Patil Vidyapeeth Pune, Maharashtra, India (ref: DPU/R&R(D)/32(21)/19) and was conducted as a triple blind study. The aim was to evaluate and compare the antimicrobial properties 3 different bioactive compounds at three concentrations (200mcg, 400mcg, 600mcg) and 0.2% chlorhexidine gluconate against S. mutans serotype C (ATCC 25175).
Extract Preparation: 18
The extracts of cassia species were obtained from the scientist which were from the two medicinal plant species Cassia tora and Cassia fistula from Western Pune Maharashtra, India, shade dried authentication was done by comparing with herbarium specimens preserved in Botanical Survey of India, Pune (Maharashtra). Authentication no of Cassia tora BSI/WC/Cert/2015/SG01, Cassia fistula is BSI/WC/Cert/2015/SG02.18 The extracts were then finely pulverized and exactly weighed plant material was utilized to prepare extracts with measured volumes of solvents like ethyl acetate, acetone, ethanol, methanol and distilled water then removed under pressure. Weighed amounts of the extracts marked at Extract 6, Extract 7 and Extract 8 were then collected from the scientist and utilized for the study.
Microbiological assay laboratory processing: 19
Well diffusion method was used to determine zone of inhibition of 3 bioactive extracts in the concentration of (200µg , 400µg, 600µg) against mutans serotype C (ATCC 25175). All the tests were performed under sterile conditions in triplicate by standard norms and protocols . 0.2% chlorhexidine against S. mutans serotype C (ATCC 25175) was used as positive control. Adequate amount of Mueller Hinton Agar was evenly distributed over the surface of 15 cm diameter petri-dish to a thickness of 5 mm and allowed to solidify under aseptic conditions. Streptococcus mutans serotype C (ATCC 25175) was inoculated with a sterile spreader on the agar medium. Standard wells were made with a cupborer (9.0mm)
Then 0.2% chlorhexidine gluconate, bioactive Compounds of cassia species with concentration of 200µg , 400µg, 600µg in 0.5ml DMSO solvent was inserted in separate wells of agar plates inoculated with Streptococcus mutans serotype C (ATCC 25175). The plates were incubated at 37 ± 0.1? C for 24 hours. The same procedure was followed for different concentrations of bioactive compounds. After incubation, the plates were observed for zone of inhibition and measured in millimeters.
RESULTS:
The zones of inhibition in mm was obtained. The results were compared statistically with chlorhexidine in the form of mean and standard deviation. The p values were obtained. Kruskal Wallis and Mann Whitney Post Hoc test was conducted to analyze the data.
The below tables and graphs projects the mean and standard deviation of inhibition zones at 200µg, 400 µg, 600µg for the three Bioactive compound extracts- Extract 6, Extract 7, Extract 8 and 0.2%chlorhexidine gluconate against S. mutans serotype C (ATCC 25175) and their comparison.
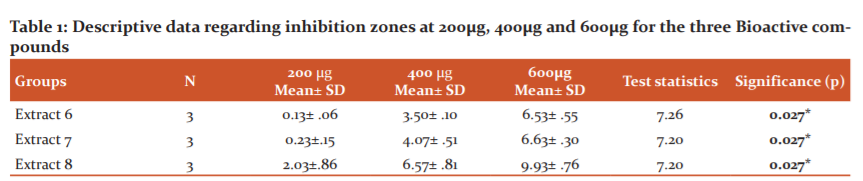
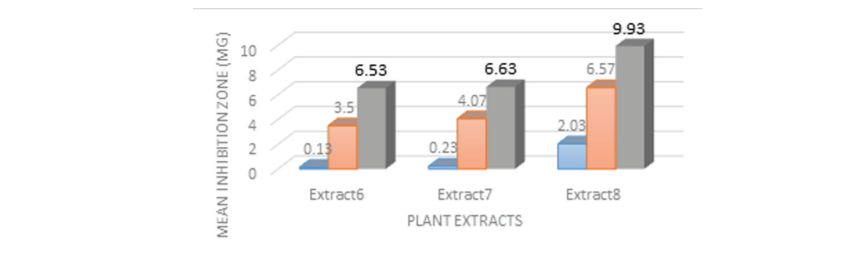
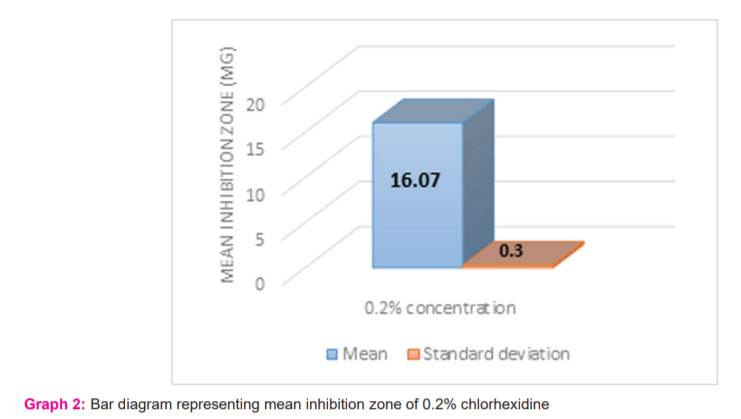
The Table no.1, Graph no.1 showed the extracts with inhibition zones at 200µg, 400 µg, 600 µg for the three Bioactive compound extracts- Extract 6, Extract 7, and Extract 8 were compared and evaluated against S. mutans serotype C (ATCC 25175). At 200µg concentration the highest zone inhibition in mm was formed by Extract 8 concentration having mean inhibitory zone of 2.03mm ±0.86. At 400µg concentration the highest zone inhibition in mm was formed by Extract 8 concentration having mean inhibitory zone of 6.57mm±0.81. At 600µg concentration the highest zone inhibition in mm was formed by Extract 8 concentration having mean inhibitory zone of 9.93mm +0.76. At all concentrations extract 8 showed the highest zone of inhibition. For all concentrations of Extracts 6, 7,and 8 at 200µg, 400µg and 600µg there was a significance of p= 0.027.The mean inhibition zone against S. mutans serotype C (ATCC 25175) formed by 0.2% chlorhexidine which was 16.07±0.30 (Graph 2).
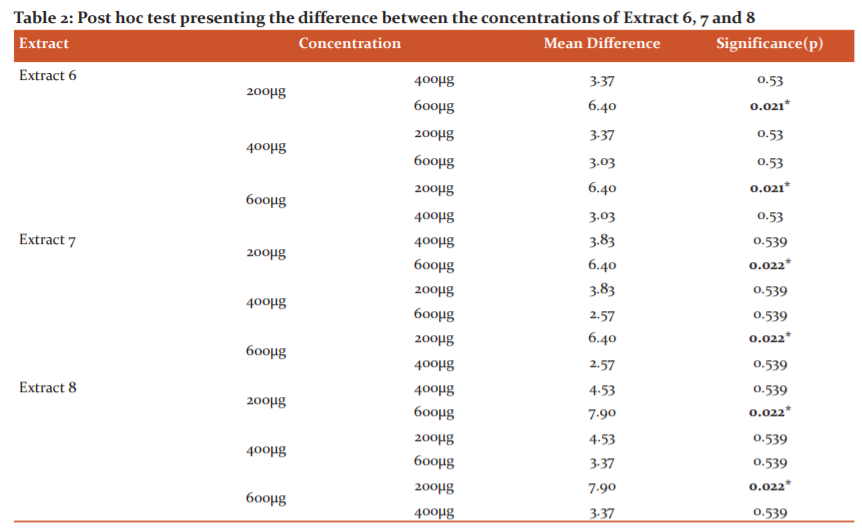
The Table no.2 depicts the Post hoc test of Kruskal Wallis and Mann Whitney presenting differences between the extracts 6, 7 and 8 at concentration of 200µg, 400 µg, 600 µg revealed that a significant difference was present between 200µg and 600µg concentrations with p=0.021. A significantly large inhibition zone was formed against S. mutans serotype C by 600 µg concentration as compared to 200 µg concentration. No significant difference was found between 200 µg and 400 µg concentration as well as 400 µg and 600 µg concentration.
For Extract 7 at 200 µg Post hoc test revealed that a significant difference was present in inhibition zone when compared to 600µg extract the significance was p = 0.022. No significant difference was found between 200 µg and 400 µg concentration as well as 400 µg and 600 ug concentration.
For Extract 8 at 200µg extract, 400µg extract and 600µg Post hoc test revealed that a significant difference was present between 200µg and 600µg with p= 0.022. A significantly large inhibition zone was formed against S. mutans serotype C by 600 µg concentration. No significant difference was found between 200 µg and 400 µg concentration as well as 400ug and 600 ug concentration.
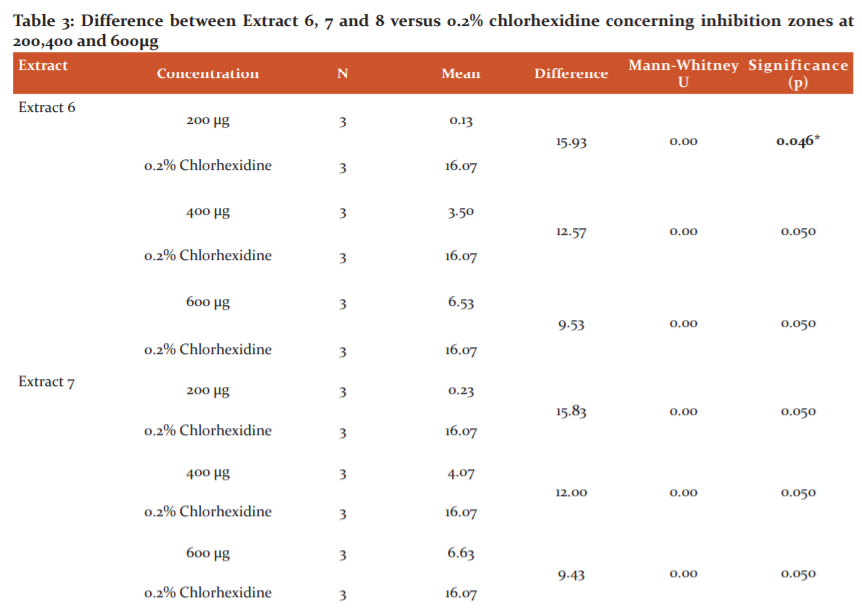
The Table no.3 showed the difference between the inhibition zones of Extract 6, 7 and 8 at different concentrations 200µg ,400 µg, 600µg and 0.2% chlorhexidine. The mean inhibition zone against S. mutans serotype C (ATCC 25175) formed by 0.2% chlorhexidine which was 16.07±0.30 (Graph 2).
For Extract 6 a significant difference was found between 200µg extract concentration and 0.2%chorhexidine with p=0.046. No significant difference was found between 400ug and chlorhexidine, 600ug and chlorhexidine indicating that the higher concentration of bioactive compounds showed a comparable action as that of chlorhexidine. The difference between 600 µg of Extract 6 and 0.2 % chlorhexidine was 9.53+0.050 with p=0.05.
For Extract 7 at 200µg, 400µg, 600µg and 0.2% chlorhexidine no significant difference was present between any of the extracts and chlorhexidine indicating that at any concentration of Extract 7 the inhibition results are comparable to that of 0.2% chlorhexidine with p=0.05. The difference between 600 µg of Extract 7 and 0.2 % chlorhexidine was 9.43+0.050.
For Extract 8 at 200 µg, 400 µg 600µg and 0.2% chlorhexidine no significant difference was present between any of the extracts and chlorhexidine indicating that at any concentration of Extract 8 the inhibition results are comparable to that of 0.2% chlorhexidine with p=0.05. The difference between 600 µg of Extract 8 and 0.2 % chlorhexidine was only 6.13+0.050.
DISCUSSION:
Current evidence suggests that the cariogenic factors that drive streptococcus mutans to be virulent is its potential to thrive in acidic environment’s, its ability to lower the pH, ferment simple sugars, synthesize sucrose, promote its adhesion and buildup the plaque-ecology especially for those having a low socioeconomic status with limited access to healthcare.20 Milsom et al. described that children with an already existing caries lesion have a 5–6 times higher incidence of developing new caries lesions compared to previously caries-free children. 20
Peterson et al (2014) concluded with next-generation sequencing (NGS) that Streptococcus-species was found to be the most abundant genus (>50% of the microorganisms)in the microbial composition of the dental plaque.21 Damle et al (2016) concluded that the number of s mutans colonies increases with increasing age and it is more in children with lesions that can be seen clinically and the amount of S. mutans in the saliva is directly proportional to the colonized surfaces. 22
In this study chlorhexidine(CHX) was used as the control as it is the most extensively used anti-plaque and anti-bacterial agent and it is highly active against the s. mutans strain. Among the available chemotherapeutic agents, chlorhexidine mouthwash is considered as the “gold-standard” due to its proven efficiency, but it exhibits cytotoxic activity on ectodermal cells causing altered taste sensation and extended used causes xerostomia, brown-staining of teeth and fillings. 23
Therefore, the nature-based alternatives with less side effects would be beneficial than the chemically prepared agents. They also have a two-fold advantage of minimal side-effects and being alcohol-sugar free. Nature-based plant products like Aloe vera, Bloodroot Garlic and Propolis have several advantageous properties anti-microbial, wound healing, anti-helminthic, anti-inflammatory, anti-fungal properties of medicinal plants. 24
In this study Cassia plant species was selected for their anti-inflammatory, hypoglycaemic, antiplasmodial properties. 25 Thus can be used as a broad-spectrum antibacterial agent that is nature based . It is easily obtainable, in Asia, South Africa, Mexico, China, East Africa and Brazil thus making it cost effective. 26
Bioactive compounds are substances are present within all part of the plant such as flavonoids which includes a huge group of naturally occurring organic compounds. It is found in a large variety of plants including fruits, seeds, grains, tea vegetables, nuts, and wine. 26
The Microbiological assay of well diffusion method was used to determine zone of inhibition and after incubation at 37ºC for 24 hours as per standard protocols. The diameters of inhibition zones produced by the plant extract were measured in mm.
Statistical analysis of the results with Kruskal Wallis and PostHoc Mann Whitney Test and concluded that the mean and standard deviation of inhibition zones at 600µg for the three Bioactive compounds extracts- against S. mutans serotype C (ATCC 25175) identified that the highest zone inhibition in mm was formed by Extract 8 concentration having mean inhibitory zone of 9.93mm +0.76 followed by Extract 7 was 6.63 mm+0.30 inhibition zone. The least effective concentration of Bioactive compound of cassia species was found with Extract 6 which formed a small zone of 6.53 mm+0.55.
The three bioactive compounds provided by the scientist were Quercetin (Extract 6), Gallic acid (Extract 7), and Cassia flower (Extract 8). All three bioactive compounds have antimicrobial properties based on their zones of inhibition, but the extract labelled as number 8 which is Cassia flower (Tora and Fistula) showed the highest antimicrobial zone when compared to the three extracts.
Quercetin (Extract 6) was isolated and found from both Cassia tora L as well as Cassia Fistula. 26 Quercetin is the main bioflavonoids known for its anti-inflammatory, anti-hypertensive, vasodilator effects, anti-obesity, anti-hypercholesterolemic and anti-atherosclerotic activities.26 It is a naturally occurring flavonoid pigment present in many fruits and vegetables. It is antioxidant rich and plays an important role in helping the body. It is not only an antioxidant but also has anti-inflammatory, and anticancer activities.27 Quercetin induces apoptosis by inducing the dissociation of Bax from Bcl-xL, activating caspases, and inhibiting phosphorylation. 27 It is metabolized immediately by enzymes in the epithelial cells and further metabolized by the liver. Thus quercetin has proven effects that benefit the oral health. 27 This study proved that Quercetin has an antibacterial effect with a zone of inhibition of 6.53 mm+0.55. This was compared to the zone of inhibition of 0.2% chlorhexidine which was 16.07mm. The zone of inhibition was also compared to the other extracts and was found to be the least.
Gallic acid (GA) is in the group of hydroxybenzoic acids. 28 Many plant extracts have been found to inhibit the growth of oral bacteria , particularly s.mutans and thus may prevent the formation of dental caries. It is the most popular of trihydroxybenzoic acids. An important source of gallic acid is also tea containing up to 4.5 g/kg fresh weight in tea leaves it also occurs mostly in certain red fruits, black radish, and onions. Apart from its phytochemical role, gallic acid is also used in tanning, ink dyes, and the manufacture of paper. 28 Effects include antihyperglycemic, antilipid peroxidative, antioxidant antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, cardioprotective, gastroprotective, and neuroprotective effect.29 Gallic acid can inhibit motility, adherence and biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus mutans, Chromobacterium violaceum, and Listeria monocytogene. 29 In this study the zone of inhibition of Gallic acid on streptococcus mutans serotype C (ATCC 25175)was evaluated at the 600µg concentration the zone was 6.63 and compared with 0.2% chlorhexidine which was 16.07. The zone of inhibition in mm for Extract 7 (Gallic Acid) was more when compared to bioactive compound of cassia species Extract 6 (Quercetin) .
Cassia flower also known as the ‘Golden Shower’ is widely grown as a decorative tree for its beautiful bunches of yellow flowers. Cassia plants have bright yellow flowers of characteristic- bell shape drop. 30 Cassia provides dyes and is widely used for its medicinal properties. The plant has antipyretic and analgesic effect.31 It was found that extracts of Cassia fistula flowers contained tannins, flavonoids, and anthraquinones compounds in higher amount.32 Cassia flowers has known antibacterial and antifungal activity. In the present work, the extracts are obtained from Cassia fistula flowers. All the Bioactive Compounds had good antimicrobial activities based on their zones of inhibition but of all the three; the extract of cassia flower showed the highest zone inhibition in mm was formed by Extract 8 (Cassia Flower) concentration having mean inhibitory zone of 9.93mm +0.76. Mann Whitney test revealed that at any concentration of Extract 8 the inhibition results are comparable to that of 0.2% chlorhexidine with p=0.05. The difference between 600 µg of Extract 8 and 0.2 % chlorhexidine was only 6.13+0.050.
The Cassia flower extract can be an excellent substitute for chlorhexidine which can be can prepared in various forms like mouthwashes, gels, sustained release forms, intracanal medicaments, lollipops etc. The bioactive compound extract of cassia flower has a possibility to be used as new antimicrobials for children and adults as well as for prevention of dental caries. Nowadays, the patients are more aware of the harmful effects of synthetic formulations and prefer a natural herbal alternative that is well tolerated by the body. Thus, these natural herbal formulations with their bioactive compound extract can offer a non- potent resolution with minimal adverse effects to improve the oral health of children.
CONCLUSION:
Nature-based cassia plant species is available in all seasons and easily obtainable in many countries and hence provides a novel therapeutic future for combating oral diseases like caries in especially in children. Based on the findings of the study, it was concluded that: (1)The bioactive components of cassia flower extracts appears promising against Streptococcus mutans serotype c (ATCC 25175) and can be used effectively as a novel compound especially in children due to the nature based non synthetic properties for combating dental caries. (2) Future studies are needed to determine the antimicrobial activity of Cassia flower plant extract against Streptococcus mutans on whole saliva to understand its efficacy against polymicrobial or mixed culture. (3) Lastly toxicological investigations of Cassia plant extract also need to be found out to confirm its safety[A1] for human trials.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS:
We acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. We are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
There was No Funding or Financial support and No Conflict of interest.
*Significance at p<0.05
A significant difference is present between 200 and 600µg, with Extract 6
A significant difference is present between 200 and 600µg with Extract 7
A significant difference is present between 200 and 600µg with Extract 8
 *Significance at p<0.05
*Significance at p<0.05
For Extract 6- A significant difference is present in inhibition zone between 200µg and 0.2% Chlorhexidine
For Extract 7- No significant difference is present in inhibition zone between 200µg and 0.2% Chlorhexidine, 400µg and 0.2% Chlorhexidine, 600µg and 0.2% Chlorhexidine
No significant difference is present in inhibition zone between 200µg and 0.2% Chlorhexidine, 400µg and 0.2% Chlorhexidine, 600µg and 0.2% Chlorhexidine.

References:
-
Collaborators GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017; 390: 1211–1259
-
Zaura E, Nicu EA, Krom BP, Keijser BJ. Acquiring and maintaining a normal oral microbiome: current perspective. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014 Jun 26(4):85.
-
He X, Hu W, He J, Guo L, Lux R, Shi W: Community- based interference against integration of Pseudomonas aeruginosa into human salivary microbial biofilm. Mol Oral Microbiol 2011; 26: 337–352.
-
Schlafer S, Ibsen CJS, Birkedal H, Nyvad B: Calcium-phosphate-osteopontin particles reduce biofilm formation and pH drops in in situ grown dental biofilms. Caries Res. 2017; 51: 26–33.
-
Philip N, Suneja B, Walsh LJ. Ecological approaches to dental caries prevention: paradigm shift or shibboleth. Caries Res. 2018;52(1-2):153-65.
-
Bowden GH. Mutans streptococci caries and chlorhexidine. J Can Den Ass. 1996 Sep;62(9):700-3.
-
Takahashi N, Nyvad B. The role of bacteria in the caries process: ecological perspectives. J Den Res. 2011 Mar;90(3):294-303.
-
Pitts NB, Baez RJ, Diaz-Guillory C, Donly KJ, Alberto FC, McGrath C, Phantumvanit P, Seow WK, Sharkov N, Songpaisan Y, Tinanoff N. Early Childhood Caries: IAPD Bangkok Declaration. J Dent Chil (Chicago, Ill.). 2019 May 15;86(2):72.
-
Kocak MM, Ozcan S, Kocak S, Topuz O, Erten H. Comparison of the efficacy of three different mouthrinse solutions in decreasing the level of streptococcus mutans in saliva. Eur J Dent. 2009 Jan;3(01):57-61.
-
Mathur S, Mathur T, Srivastava R, Khatri R. Chlorhexidine: The gold standard in chemical plaque control. Nat J Phys Pharm Pharmac. 2011 Jul 1;1(2):45.
-
Vanzi V, Pitaro R. Skin Injuries and Chlorhexidine Gluconate-Based Antisepsis in Early Premature Infants: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. J Perinat Neonatal Nurs. 2018;32(4):341-350.
-
Lakade LS, Shah P, Shirol D. Comparison of antimicrobial efficacy of chlorhexidine and combination mouth rinse in reducing the Mutans streptococcus count in plaque. J Ind Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2014 Apr 1;32(2):91.
-
Mondal M, Hossain MM, Rahman MA, Mubarak MS, PK MM, Islam MS, Pervin R, Rahman M, Morad RU, Chowdhury MM, Das N. Cassia fistula Linn: a review of phytochemical and pharmacological studies. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2014 Jun;5(7):2125-21230.
-
Bhalodia NR, Shukla VJ. Antibacterial and antifungal activities from leaf extracts of Cassia fistula l.: An ethnomedicinal plant. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2011;2(2):104.
-
Luximon-Ramma A, Bahorun T, Soobrattee MA, Aruoma OI. Antioxidant activities of phenolic, proanthocyanidin, and flavonoid components in extracts of Cassia fistula. J Agric Food Chem. 2002;50(18):5042-5047.
-
Srividhya M, Hridya H, Shanthi V, Ramanathan K. Bioactive Amento flavone isolated from Cassia fistula L. leaves exhibits therapeutic efficacy. 3 Biotech. 2017 May 1;7(1):33.
-
Sasidharan S, Chen Y, Saravanan D, Sundram KM, Latha LY. Extraction, isolation and characterization of bioactive compounds from plants’ extracts. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2011;8(1),1-10.
-
Gaikwad SA. Phytochemical investigation of bioactive Emodin and quercetin in Cassia fistula and Cassia tora plant parts by HPTLC. J Pharmac Phytochem. 2018;7(5):892-897.
-
Tanner AC, Kressirer CA, Rothmiller S, Johansson I, Chalmers NI. The caries microbiome: implications for reversing dysbiosis. Adv Den Res. 2018 Feb;29(1):78-85.
-
Milsom KM, Blinkhorn AS, Tickle M. The incidence of dental caries in the primary molar teeth of young children receiving National Health Service funded dental care in practices in the North West of England. Bri Den J. 2008 Oct;205(7): 462-465.
-
Alejandra BM, Daniel OM. Virulence Factors of Streptococcus mutans Related to Dental Caries. In Staphylococcus and Streptococcus. Intech Open. 2020;11(4): 732-737.
-
Karpi?ski TM, Szkaradkiewicz AK. Chlorhexidine–pharmaco-biological activity and application. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015 Apr;19(7):1321-6
-
Petti S, Hausen H. Caries-preventive effect of chlorhexidine gel applications among high-risk children. Caries Res. 2006; 24(2): 514-521
-
Cheng L, Li J, He L, Zhou X. Natural products and caries prevention. Caries Res. 2015;49(1):38-45
-
Shekar BR, Nagarajappa R, Suma S, Thakur R. Herbal extracts in oral health care-A review of the current scenario and its future needs. Pharmacognosy Revi. 2015 Jul;9(18):87.
-
Sankari SL, Babu NA, Rani V, Priyadharsini C, Masthan KM. Flavonoids–Clinical effects and applications in dentistry: A review. J Pharm Bioal Sci. 2014 Jul;6(1):S26
-
Corega C, Vaida L, Festila DG, Rigoni G, Albanese M, D'Agostino A, De DS, Pardo A, Nocini PF, Bertossi D. The benefits of Quercitin for dentistry and maxillofacial surgery: a systematic review. Minerva stomatologica. 2014;10(4):264-269.
-
Nowak R, Olech M, Nowacka N. Plant polyphenols as chemopreventive agents. InPolyphenols in human health and disease 2014;13(5):1289-1307
-
Erukainure OL, Sanni O, Islam MS. Clerodendrum volubile: phenolics and applications to health. InPolyphenols: Mechanisms of Action in Human. Heal. Dise. 2018: 2(1):53-68.
-
Chaudhary HSD, Kumar P, Chandoria RK. The potency of Cassia fistula extracts as antibacterial agents against multidrug resistant bacteria. J Pharm Res. 2011;4(10):3756-8.
-
Lavanya B, Maheswaran A, Vimal N, Vignesh K, Uvarani KY, Varsha R. An overall view of cassia species phytochemical constituents and its pharmacological uses. Int J Pharm. Sci. Res.. 2018;3:47-50.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License