IJCRR - 13(15), August, 2021
Pages: 143-148
Date of Publication: 10-Aug-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Imaging Interpretation of Complications after Cesarean Section Delivery
Author: Jan Mohd. Suhail, Obaid Ashraf, Sumiaya Kiran
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Cesarean section delivery is one of the most common abdominal surgeries performed on women and saves the lives of both mother and fetus in many complicated cases. Aim: The aim of this study was early identification of post-cesarean section complications through various imaging studies. Methods: This was a retrospective cohort study conducted on the patients who were admitted for post-cesarean-section complications and underwent different imaging studies from January 2020 till November 2020. Our study group comprised of 140 women who had undergone elective or emergency C-sections and developed complications for which imaging was imperative. Result: Among the 140 Post C-Section patients which were sent for emergency USG abdomen or CT and even MRI in some cases, it was observed that complications were higher among emergency C-Section patients (60.7%) than elective C-section patients(28.5%). These patients had developed various symptoms after C-sections and were sent for imaging studies. It was observed that endometritis was the most common complication secondary to retained products of conception followed by a wound infection. Conclusion: The rate of increase of Cesarean section assisted deliveries have resulted from an increased rate of complications with infection seen as the most common (36%) complication among which Endometritis (20%) seen as the most common imaging finding.
Keywords: Cesarean section, Rates, Complications, Abnormal imaging features, Postpartum haemorrhage, Endometritis, Retained products of conception
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Cesarean deliveries are necessary surgical procedures in the advent of pregnancy and delivery complications.¹ Although the rise of caesarean deliveries is associated with reduced maternal and infant mortality in high risk groups, but recent evidence suggests that cesarean rates beyond 15% threshold given by WHO, may lead to increased perinatal mortality and morbidity.²,³ In one cross-sectional study done in India, of 699 686 adolescent girls and women aged 15 to 49 years, the cesarean birth rate was 17.2%( higher than the WHO threshold of 15%) in 2010 through 2016, with variations ranging from 3% to 70% according to regions and socioeconomic groups.? The most common acute post-CS complication, that are encountered, included; infections, hematomas, uterine dehiscence and rupture, pelvic vein thrombosis/thrombophlebitis with an overall rate of 14.5%.Infection is the commonest among these with Endometritis being the most common (6.6%), followed by wound infection (1.6%).? Severe complications like uterine rupture are uncommon. ?,? Patients who are anaemic or obese or had increased duration of labour or prolonged ruptured membranes are predisposed to postoperative morbidity.? Patients may complain of intermenstrual bleeding, pelvic or abdominal pain as symptoms of healed cesarean delivery scar. There is a relative increased chance of retained products of conception, placenta accrete, cesarean scar ectopic pregnancy, malpositioned intrauterine devices(IUDs), and endometriosis in successive pregnancies in such patients. ?,¹?,¹¹ Imaging modalities used to evaluate such chronic complications include US, Sono-hysterography, magnetic resonance imaging, and occasionally CT.
The normal postprocedural findings (Table 1) should be differentiated from early significant complications such as haematomas, infections, abscesses, uterine dehiscence and rupture, and pelvic thrombophlebitis. Patients usually present with fever, decreased hematocrit value, heavy vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain in the post-procedural period prompt for imaging studies. ¹²,¹³In the emergency setting ultrasonography (US) and computed tomography (CT)remain the mainstay imaging modality, while Magnetic resonance (MR) is limited in terms of acquisition time and availability. ?
AIM
The aim of this study was early identification of complications that developed after Cesarean section assisted deliveries and differentiate normal imaging findings from abnormal.
MATERIALS AND METHODS.
Study design
This retrospective cohort study was done on patients who were admitted for post-procedural complications and sent for imaging studies from Jun 2020 to November 2020. The study was conducted in SMHS Srinagar, which is a government tertiary care hospital.
Participants and inclusion/exclusion criteria
This study included 140(n=140) patients who developed symptoms like fever, heavy vaginal bleeding or odorous discharge, severe abdominal pain, deranged blood counts, reduced hematocrit after cesarean section delivery. These patients were sent for Usg or CT abdomen and in some disputable diagnostic cases for MRI abdomen for identification of complications.
The inclusion criteria was determined as being between the age of 20 to 45 years , not having undergone other abdominal surgery and the patient data being complete.
The patients who gave births under 20 weeks of gestation or 500g were excluded from this study .
Data formulation
140 patients met the required criteria. They were divided in two main groups, those who had emergency C-Section(group 1) and those who underwent elective procedures (group 2). Then it was categorized into the following sections,(a) according to abnormal imaging findings like overtly enlarged uterine size, features of endometritis, pelvic haematoma (bladder flap, Subfascial haematoma), pelvic collection, uterine dehiscence or rupture, retained products of conception, morbidity adherent placenta ;(b)according to demographic data i.e, maternal age, BMI, parity and gravidity; (c) clinical features like puerperal pyrexia, abnormal vaginal bleeding, odorous vaginal discharge ; (d)Finally the imaging characteristics were compared with the clinical picture and in some cases surgical intervention for relevance and standardization.
Ethical approval
Their authors faced no ethical issue while conducting this study. Also, all the identifiable variables were removed from this study to safeguard the privacy and confidentiality of the participants.
Statistical method
The data were coded, checked and entered into the Statistical Package for Social Sciences version 22 (IBM Corp, Armonk ). Categorical variables, including, imaging features, clinical features, mode of CS, type of anaesthesia, type of incision, and complications were described using frequencies. Continuous variables, including maternal age, body height, body weight, parity, gravidity, GA at delivery were described using mean and standard deviation (SD). Chi-Square and independent t-tests were used to assess the association between the variables of the study. For all statistical tests, p-values ≤ of 0.05 were considered significant.
RESULTS
The hospital records were reviewed and about 850 patients underwent cesarean section from June 2020 to November 2020 among which 140 patients developed various complications (16.4%). Two study groups were made, group 1, which underwent emergency C-Section (n=95) and group 2 which had elective C-sections (n=45).
Accordingly, the groups were distinguished based on abnormal imaging findings(table 2) and it was found that infection was overall the most common complication in both groups particularly endometritis with p-value of less than <0.001 followed by wound infection. Among pelvic haematomas subfascial haematoma was more prevalent in group 1(10.5%) (as they usually undergo longitudinal incisions ) than group 2(8.8%).Additionally uterine dehiscence and rupture were seen rarely in both the groups with p values of <0.001 and <0.042 respectively.
Among other complications like the retained products of conception and ovarian thrombosis, significant variations were not observed. (Figure 5)
Moreover, 10 patients (10.5%) among group 1 and 5 patients (11%) among group 2 showed normal imaging features (table 1). (Figure 1,2)
The demographic data [Table 3] was extrapolated in between the two groups and it was observed that females who had prenatal comorbidities like obesity and Increased maternal age had more frequency of post-procedural complications showing a p-value of <0.009 and <0.476 respectively. Also, group 1 showed higher percentages of females with GDM (2O%) and PROM (10.5%) compared to group 2 with 8.8% and 6.6% respectively in the given categories. Since the participants were admitted with clinical features of post-cesarean section complications it was observed puerperal pyrexia was the most common symptom seen, 16.8 % and 15.5% in groups 1 and 2 respectively followed by abnormal or odorous vaginal discharge.
Finally, the imaging characteristics were interpreted in the context of the clinical picture and in some cases with surgical findings like in pelvic haematomas or collections requiring surgical intervention. It was observed that bladder flap haematomas which were more than 5 cm where associated with uterine dehiscence and rupture. (Figure 3,4) Accordingly, among group 1 (7.3%) ,group 2(6.6%) required surgical evacuation. Also, endometritis which was the most common complication seen in both groups secondary to RPOC (17%) required evacuation and curettage. Uterine rupture and dehiscence were difficult to differentiate on CT alone due to imaging findings overlap and required additional MRI study.
DISCUSSION
Cesarean section is an important abdominal surgical procedure showing an increased rate throughout the world .¹? Thus, it becomes important for the radiologists to be able to identify normal post-C-Section imaging findings from abnormal ones and interpret data in the context of clinical picture for proper patient management.¹²,¹?
This retrospective study was aimed at identifying imaging characteristics of complications in Cesarean section and their prevalence in emergency and elective procedures
The study group helped to determine the relative frequency of different complications and their associated findings in the context of an appropriate clinical picture.
USG abdomen and CT abdomen with contrast-enhanced studies showed that endometritis was the most common complication observed( 20%) in the study group. Also, it was associated with puerperal pyrexia and abnormal vaginal discharge (14%) as the frequent clinical symptom. The severe complications of uterine dehiscence (9.6%), and uterine rupture (4.3%) were rare and had overlapping imaging features in many cases (2.2%). MRI helped to distinguish the two entities by showing intact serosal layer in uterine dehiscence (1.4%).
The demographics demonstrated that prenatal comorbidities especially high maternal age, obesity and having GDM increased the rate of complications by predisposing to emergency C-Sections in various settings and has a p-value of <0.476, <0.009, <0.029 respectively. High parity, with a history of previous Cesarean sections, increased complications especially RPOC (17%) and morbidly adherent placenta (0.5%) in these patients. The patients who had isolated finding of bladder flap haematoma <5 cm(4.5%) were followed by repeated imaging and showed resolution of symptoms and regression of haematoma over time . However, patients with large hematomas or associated pelvic infections required further surgical interventions and in some cases (1.2%) emergency postpartum hysterectomies. Patients with the imaging features of gonadal or pelvic vein thrombosis (8.5%) presented with pelvic pain (4.3%), abnormal vaginal discharge (7.9%) and were managed conservatively unless associated with necrosis. The study showed that 10.5 % of participants with post-procedural symptoms had normal imaging features.
Interpretation of certain imaging findings like large bladder flap haematoma and subfascial hematoma with pelvic collections prompted emergency surgical interventions in some cases (4.2%). The patients who had endometritis with soft tissue enhancing areas in the endometrial cavity (RPOC,17%) had to undergo emergency curettage. Some non-statistical complications like bladder injury, bowel injury were present in a few but they had an increased p-value of >0.700.
CONCLUSION
The increased C-Section assisted deliveries above the WHO threshold of 15% is associated with raised complications. Infections (Endometritis =20%) was the most common complication observed in both emergency and elective procedures. Furthermore, prenatal comorbidities like obesity, high maternal age, GDM predisposed the patients to develop complications.
Imaging studies can help to promptly identify various complications thereby decreasing maternal mortality and morbidity. However, proper standardization of imaging features is required which necessitates further studies.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors declare that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors wish to acknowledge the contribution of dept of radiodiagnosis, dept of obstetrics and gynaecology GMC Srinagar in conducting this study.
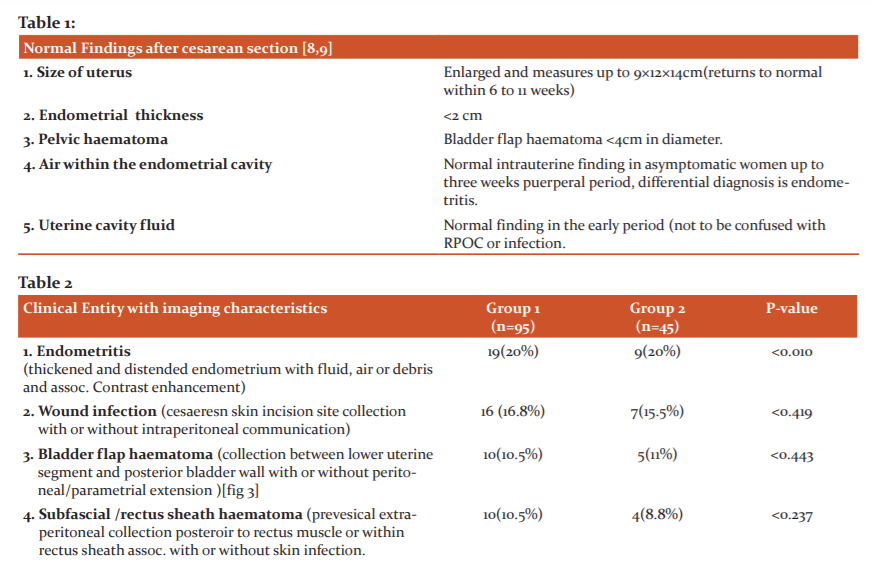
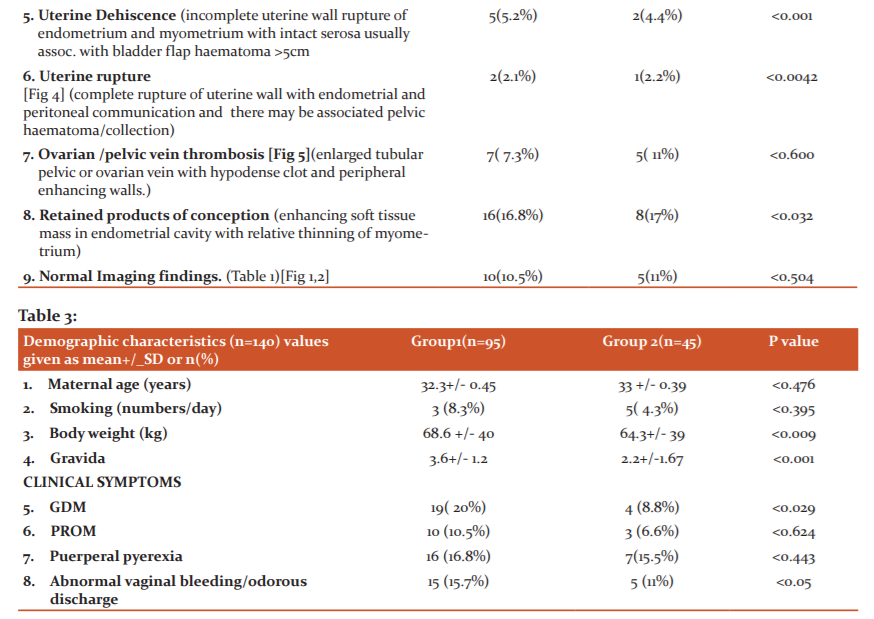
Fig 1: Normal post-operative finding of the uterus on the US, 3rd-day post-CS; thin stripe of an anechoic area(arrow) and linear echogenic stripes (clots)normally seen in the endometrial cavity in an enlarged uterus with heterogeneous myometrium (cross).
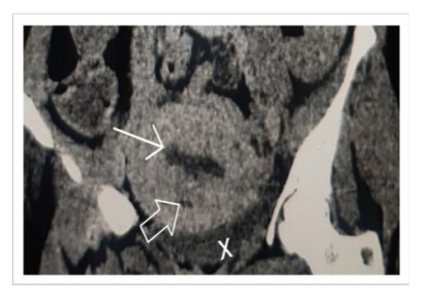
Fig 2: Normal coronal reformatted CT image of a 7-day post-CS uterus showing a low attenuation linear area(white block arrow) in the lower uterine segment in the incision area and a mild amount of fluid in the pelvic cavity( cross) and mild fluid in the endometrial cavity (arrow).
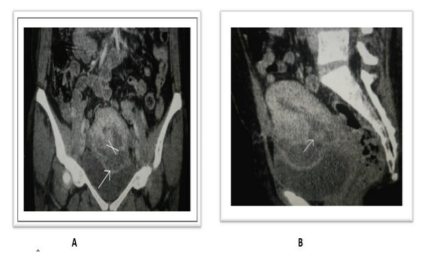
FIG 3:Normal coronal reformatted CT image of a 7-day post-CS uterus showing a low attenuation linear area(white block arrow) in the lower uterine segment in the incision area and a mild amount of hyperdense fluid in the pelvic cavity( cross)[bladder flap haematoma] and mild fluid in the endometrial cavity
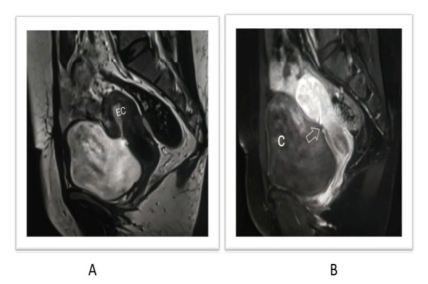

Fig 4: Uterine rupture with pelvic collection in a 37-year-old following an emergency C-section presenting with heavy vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain showing a mixed intensity collection in the anterior aspect of the uterus on T2-W image (A) communicating with the endometrial cavity (EC) through a large interruption (block arrow) of the ventral uterine wall. (B) Post-contrast T1-W images show a linear hypointense area in the ventral lower uterine wall communicating with the collection.
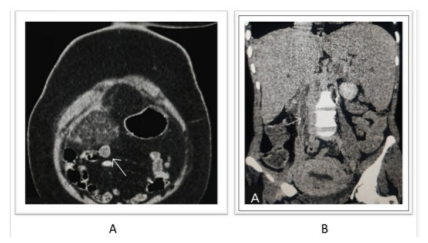
Figure 5: 40-year-old female who underwent a c-section about 20 days back presented with fever, vomiting and lower abdominal pain. On post-contrast axial and coronal CT images, there is thrombophlebitis of the right ovarian vein in mid-portion and appears as enhancing the dilated hypodense tubular structure of about 4 cm with surrounding fat stranding. There is bilateral pelvic congestion with engorged enhancing pelvic veins.
References:
-
MacDorman MF, Menacker F, Declercq E. Cesarean birth in the United States: epidemiology, trends, and outcomes. Clin Perinatol. 2008 Jun 1;35(2):293–307. doi: 10.1016/j.clp.2008.03.007. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
-
Ye J, Zhang J, Mikolajczyk R, Torloni MR, Gülmezoglu AM, Betran AP. Association between rates of caesarean section and maternal and neonatal mortality in the 21st century: a worldwide population-based ecological study with longitudinal data. Bri J Oor Gynacol. 2016;123(5):745-753. doi:10.1111/1471-0528.13592 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
-
Molina G, Weiser TG, Lipsitz SR. Relationship between cesarean delivery rate and maternal and neonatal mortality. J Am Med Ass. 2015;314(21):2263-2270. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.15553 [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
-
JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Mar; 2(3): e190526.Published online 2019 Mar 22. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.0526PMCID: PMC6583298 PMID: 30901040Christophe Z. Guilmoto, PhD1 and Alexandre Dumont, MD, PhD1
-
Nielsen TF,Hökegård KH. Postoperative cesarean section morbidity: a prospective study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1983;146(8):911–916. Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
-
Rivlin ME, Carroll CS Sr, Morrison JC. Infectious necrosis with dehiscence of the uterine repair complicating cesarean delivery: a review. Obstet Gynecol Surv 2004; 59:833–837
-
Auh YH, Rubenstein WA, Schneider M, Recker JM, Whalen JP, Kazam E. Extraperitoneal paravesical spaces: CT delineation with US correlation. Radiology 1986;159(2):319–328. Link, Google Scholar
-
Rodgers SK, Kirby CL, Smith RJ, Horrow MM. Imaging after cesarean delivery: acute and chronic complications. Radiogr. 2012; 32(6):1693–1712.
-
Hoveyda F, MacKenzie IZ. Secondary postpartum haemorrhage: incidence, morbidity and current management. Bri J Org Gynocol 2001; 108:927–930
-
Sadan O, Golan A, Girtler O. Role of sonography in the diagnosis of retained products of conception. J Ultrasound Med. 2004; 23:371–374
-
Weydert JA, Benda JA. Subinvolution of the placental site as an anatomic cause of postpartum uterine bleeding: a review. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006; 130:1538–1542
-
Grivell RM, Reid KM, Mellor A. Uterine arteriovenous malformations: a review of the current literature. Obstet Gynecol Surv 2005; 60:761–767 Paspulati RM, Dalal TA. Imaging of complications following gynecologic surgery. Radio Graphics. 2010; 30(3):625–642Shamash AH, Ahmed AG, Abdel Latif MM, Abdullah SA. Routine postpartum ultrasonography in the prediction of puerperal uterine complications. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2007; 98:93–99
-
Ustunyurt E, Kaymak O, Iskender C, Ustunyurt OB, Celik C, Danisman N. Role of transvaginal sonography in the diagnosis of retained products of conception. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2008; 277:151–154
-
Gedikbasi A, Akyol A, Bingol B, Cakmak D, Sargin A, Uncu R, Ceylan Y. Multiple repeated cesarean deliveries: operative complications in the fourth and fifth surgeries in urgent and elective cases. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2010 Dec 1;49(4):425–431. doi: 10.1016/S1028-4559(10)60093-9.
-
Rodgers SK, Kirby CL, Smith RJ, Horrow MM (2012) Imaging after cesarean delivery: acute and chronic complications. Radiograp. 32(6):1693–1712.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License