IJCRR - 13(15), August, 2021
Pages: 116-121
Date of Publication: 10-Aug-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Effect of Remnant Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Nitric Oxide in Young Coronary Heart Disease Subjects
Author: Thirunavukkarasu Jaishankar, Meera Shivasekar, V.M. Vinodhini, Sriram Veeraragavan
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The remnant lipoproteins Cholesterol are highly atherogenic, because of their lesser size along with high cholesterol content, and increased residence period in the blood which may not be reflected by the levels of LDL-C. Elevated Remnant lipoprotein cholesterol and decreased level of Nitric oxide is the novels atherosclerotic risk factors that stimulate the immune and inflammatory reactions associated with the progression of coronary heart disease. Aim and Objective: The study aims to assess the role of remnant lipoprotein cholesterol associated with nitric oxide in the development of coronary heart disease. Materials and Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted in SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre on subjects appearing the master health check-up and medicine OP. The study was conducted on 97 CHD patients and 97 healthy control in the age group of 30 to 55 years and was age and sex-matched. After overnight fasting body fluid samples were collected for analysis for Lipid Profile, Nitric oxide was measured by ELISA method and Lipid Profile is measured using Auto Analyser AU480. Statistical analysis was done using Student't' test and Pearson correlation analysis for the comparison between two groups. Result: The mean levels of FBG, Total cholesterol, Triglyceride, LDL-C, VLDL, TC/HDL-C Ratio, LDL-C/HDL-C Ratio, RLP-C, were significantly increased in CHD subjects when compared to controls. And the mean Nitric Oxide levels were decreased significantly in the CHD group compared to controls (P< 0.001). Conclusion: Decreased levels of Nitric oxide and the elevated levels of RLP-C in the arterial wall impairs endothelial function resulting in the progression of CHD.
Keywords: Coronary Heart Disease, High-Density Lipoprotein, Low-Density Lipoprotein, Nitric Oxide, Remnant lipoprotein cholesterol, Endothelial function
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The prevalence of Coronary Heart Disease in India is very high and has a maximum number of CHD patients in the world putting India in the state of a CHD epidemic. The high degree of mortality, morbidity, and prematurity of CHD has put a great burden on society and health care expenditure, and it is the most common cause of death worldwide.1 Coronary Heart Disease is one of the most common diseases and the major cause of death worldwide. Many traditional lipid markers such as lipoproteins (Total Cholesterol, TG, HDL, and LDL) and their subfractions helps for better diagnosis of CHD.2
Recently RLP-C and Nitric oxide are used as emerging risk markers which helps to rule out the CHD risk and predict cardiac events.3 Remnant cholesterol is the cholesterol content of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins that is IDL and VLDL in the fasting state, and chylomicron remnants in a non-fasting state.4 Remnant cholesterol acts as a potent contributor towards Coronary heart disease and stroke risk.5 Cholesterol in atherogenic particles other than the low-density lipoproteins (LDL-C) is currently emerging as a major risk factor for ischemic heart disease and is mostly found in fasting and non-fasting triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (TRLs).6 Surplus amounts of remnant lipoproteins present in plasma affect the lipoprotein metabolism cause obesity, diabetes, CVD and genetic variants.7
Alteration in the lipid profile (decreased HDL and Apo-A1) & (increased LDL, VLDL, and Apo-B 100) inhibits Nitric Oxide [NO].8Increase in RLP-C bind to scavenger receptor and uptake by macrophages from foam cell. All these cause oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in CHD patients.9 Nitric Oxide is a signal-transducing molecule and prominent free radical that maintains vasodilating tone, in-vitro modulation of lipid peroxidation, and alteration of pro-in?ammatory gene expression. LDL accumulation in arterial intima depicts an early stage in atherosclerosis.10Nitric Oxide produced from eNOS react with O2- ions and form ONNO- which induce biotin oxidation and uncoupled the eNOS resulting in decreased NO and increased O2- generation elevate the level of oxidative LDL.11Hypercholesterolemia is an essential pathogenic aspect of dysfunction in endothelium caused by impairment of endothelial nitric oxide (NO) production through mechanisms that remain poorly characterized. 12 Reduced NO level promotes endothelial dysfunction the earliest event in Coronary Heart Disease.13
Materials and Methods
Study design and population
This cross-sectional study was conducted from Nov 2019 to Feb 2020 at SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India on subjects attending the Cardiology and medicine outpatient. Totally 194 subjects were included who were age and sex match in the age group 30-55 years. 97 CHD subjects and 97 normal healthy subjects were selected as control. The control subjects were also taken from Master health check-up Programme and General Medicine OP in SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. This study obeys the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the institutional ethical committee at SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre (ECN: 1513/ICE/2018). Written informed consent was collected from all participants at the time of enrolment.
Inclusion Criteria:
-
The CHD subjects were selected based on coronary angiography and subjects with chest pain, ECG changes, increased cardiac markers such as creatinine phosphokinase (CPK-MB) and troponin levels.
-
The control group consists of persons with no clinical and ECG evidence of CHD and negative history of the past of CHD or stroke, Diabetes mellitus, hypertension, smoking, dyslipidemia, and family history of CHD.
Exclusion Criteria:
The subjects who were on treatment for autoimmune diseases, pregnancy, arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, acute/chronic infection subjects were excluded
Anthropometric Measurement
Weight (Kg), height (meters), waist circumference (cm) and hip circumference (cm) were measured. The anthropometric indices, BMI and waist-hip circumference ratio were calculated.
Baseline measurement
Medical and demographic data were collected during the period of enrolment, and documents were de-identi?ed before investigation. Basic info on age, gender, a history of diabetes, hypertension, and the use of medications were collected using a questionnaire during the clinical appointment. Questionnaires were evaluated by an expert questioner for lost data and entirety, before shifting the data to a database. Arterial blood pressure was measured using standard methods in triplicate, and the averaged values were used for the analysis. Information on laboratory reports was noted for all the subjects. The fasting samples from cases and controls were taken in the morning taking all aseptic precautions from the antecubital vein. The blood was centrifuged for 15 minutes at 2500rpm; and serum was separated and used for the estimation of routine lipid profile, Nitric Oxide. Lipid Profiles were estimated using Direct Antibody Inhibition. Total Cholesterol and Triglycerides were estimated by the enzymatic end-point cholesterol esterase-peroxidase method (Beckmann Coulter AU480 Analyser).
The RLP-C was calculated using the formula: RLP-C=TC-(HDL-C+LDL-C). 14
Measurement of Nitric Oxide
Serum NO was measured as nitrite/nitrate levels in subjects using Griess reagent. Cayman’s Nitrate/Nitrite Colorimetric Assay Kit provides an accurate and convenient method for the measurement of total nitrate/nitrite concentration in a simple two-step process. The first step is the conversion of nitrate to nitrite utilizing nitrate reductase. The second step is the addition of the Griess Reagents which convert nitrite into a deep purple azo compound. Photometric measurement of the absorbance due to this azo chromophore accurately determines NO2- concentration. Absorbance is measured at 540 or 550 nm using a plate reader.
Statistical analysis
Data were analysed using a statistical package for social sciences (SPSS 25.0). The data collected from the study were shown as mean and standard deviation. Differences were considered as significant if the p-value was <0.05. Statistical significance for study group and control was analysed by Student ‘t’ test. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was calculated to find out the correlation between different parameters.
Results:
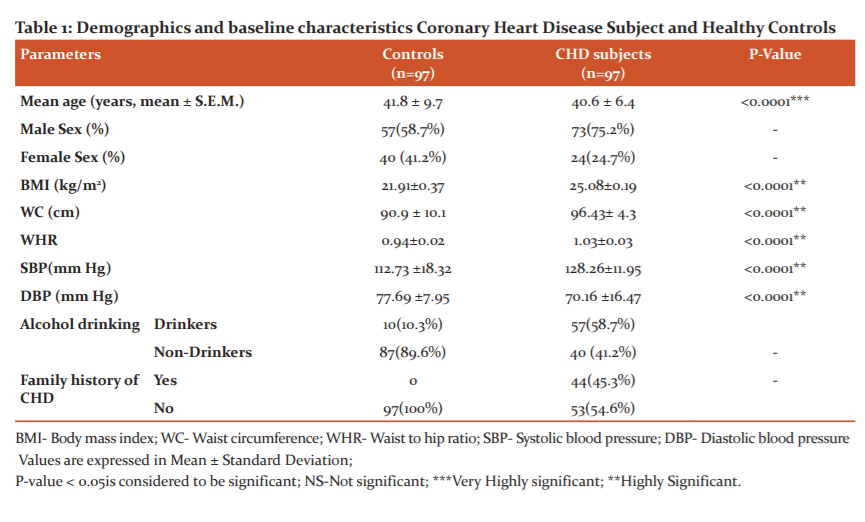
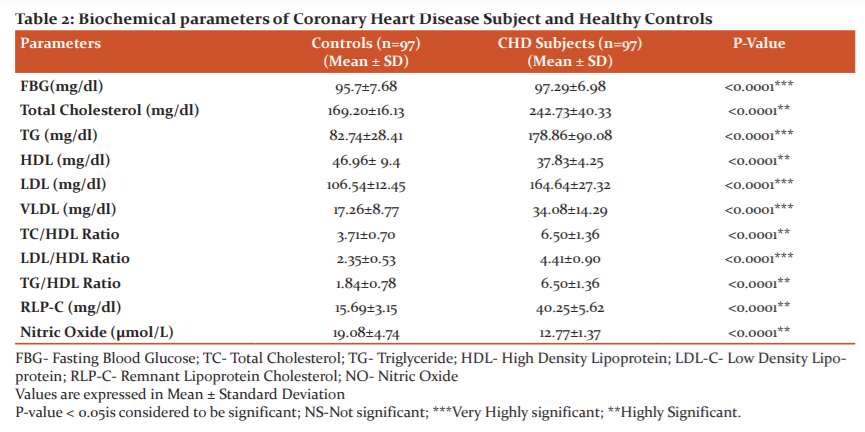
Among the 194 Participants 97 CHD subjects (73 males and 24 females) with average age 42.3 ± 10.5 and 97 Healthy Control (57 males and 40 females) with an average age of 41.8 ± 9.7 (Table 1). The Mean levels of FBG, Total Cholesterol, Triglyceride, LDL-C, RLP-C are significantly increased in subjects with CHD compared with the controls, whereas the mean levels of NO and HDL-C were significantly decreased in subjects with CHD compared with the controls (Table 2).
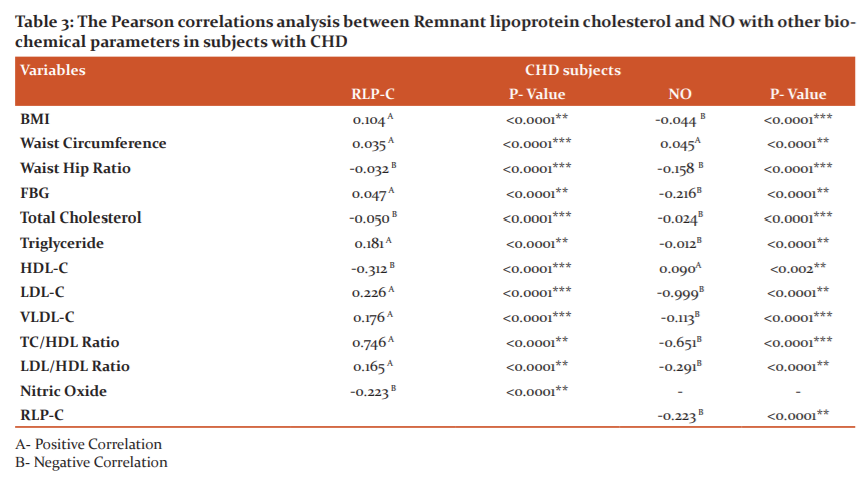
Remnant lipoprotein cholesterol is positively correlated with BMI, Waist Circumference, Waist Hip Ratio, Triglyceride, HDL-C, LDL-C, VLDL-C, TC/HDL ratio and LDL/HDL Ratio. And Remnant lipoprotein cholesterol is negatively correlated with FBG, HDL-C and Nitric Oxide.
Nitric oxide was is positively correlated with Waist Circumference, HDL-C. And Nitric oxide was negatively correlated with BMI, Waist Hip Ratio, FBG, Triglyceride, HDL-C, LDL-C, VLDL-C, TC/HDL ratio and LDL/HDL Ratio, Remnant lipoprotein cholesterol(Table 3).
Discussion:
In our study, we observed a positive correlation between RLP-C and LDL-C. And the mean level of NO were decrease in subjects with CHD. Reduced levels of NO in CHD subjects are due to the formation of reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress. ROS quickly reduce the NO production cause peroxynitrite formation. Kuriyama et al. reported that higher levels of remnant lipoproteins in fasting serum predicted future coronary events in subjects with CHD independent of other risk factors.15 In overnight fasting serum, high levels of remnant lipoproteins causes enhanced hepatic secretion of VLDL or delayed clearance of the remnants, which may occur in hypertriglyceridemic patients.16Experimental studies have indicated that plasma remnants particles are found to be associated with impaired endothelial function and enhance the inflammatory reaction.17 Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins contain molecules of Apolipoprotein B (apo B) this is released into the circulation by the liver or intestine and binds to the surface of endothelial cells by the lipoprotein lipase (LPL). This yields a TG-depleted but cholesterol-rich remnant lipoprotein (RLP).18In our study we observed a positive correlation between RLP-C and LDL-C (0.4169) (<0.0001). High levels of both measured and calculated remnant cholesterol have been reported to be associated with increased all-cause mortality in subjects with heart disease, however, such association was not observed with increasing concentrations of LDL cholesterol. 19RLPs contain 5 to 20 times much more cholesterol as per particle than LDL and can cross the endothelial barrier. Importantly, unlike native LDL, RLPs can be taken up by scavenger receptors expressed by resident macrophages in the subendothelial space and facilitate foam cell formation and atherosclerosis.20The damaging effects of oxidative stress on the cardiovascular system regulate the dysfunction in endothelium by reduction in nitric oxide (NO) synthesis and bio-availability, inflammatory response and peroxidation of lipid.21
RLPs decreasing NO production from endothelium thereby inhibiting EDR. RLP is almost massively correlated to most LDL particles, it is especially bad because unlike LDL particles, which have to go through oxidation before they can be taken into the arterial intima by macrophage cells, RLP can be freely scavenged by macrophage cells even when they are not oxidized.22Once scavenged by a macrophage, RLP is converted into foam cells which are the building blocks of arterial plaque. Increased RLP has been found in survivors of myocardial infarction and individuals with significant coronary heart disease. Additionally, RLP contributes to endothelial dysfunction by damaging the vascular relaxation process as well as strengthening platelet aggregation.23
The endothelium is frequently active for various physiological molecules that may have a direct role in nitric oxide activities. Endothelial dysfunction and reduced production or bioavailability of NO is an important factor in the pathogenesis of vascular complications.24
As a result, remnant lipoproteins might cause dysfunction in the endothelial vasomotor and increase the risk of coronary heart disease in patients with hypertriglyceridemia. Endothelium-derived nitric oxide plays an essential protective role during the initial phases of coronary heart disease by inhibiting the adhesion of leucocytes. In atherosclerotic disease progression, NO may play an advantageous role in hemodynamically mediated coronary ischemia by causing coronary vasodilatation.25 Because the expression and activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) are dynamic to endothelial function, and latest data have implied a link between RLPs and eNOS.
Conclusion:
This manuscript suggests the hypothesis that RLPs might impair endothelial function via direct and indirect effects on eNOS. The current study demonstrated that increased levels of remnant lipoproteins in fasting serum predicts the development of clinical coronary actions in patients with CHD independently of other risk factors like NO. Calculation of RLP-C is not being widely practised and not much information is available in the Asian population. Raised levels of RLP-C can be dropped by adopting lifestyle changes. Lifestyle modifications might be useful to decrease remnant cholesterol by decreasing weight, reduced consumption of alcohol, decreased consumption of fat, avoidance of smoking and improved physical activity. RLP-C has to be encompassed as one of the lipid profile parameters for the subjects attending the hospital and in the health screening in our population. There is much work to be done to shed light on these scary cardiac blind spots.
Limitations: This study had some limitations. First, our results were limited by the relatively small sample size and cross-sectional nature of the study which demonstrates only the associations with CHD severity. A small sample size and more in-depth work on the role of NO and RLP-C are needed to evaluate for the prevention of future risk of CHD.
Acknowledgement: The authors acknowledge the Department of Cardiology and Department of Medicine for the permitting and support.
Conflict of Interest: I declare that no conflict of interest could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Source of Funding: This research did not receive any specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sector.
Ethical Approval: All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were by ethical standards. The study protocol was approved by the institutional ethical committee (ECN: 1513/ICE/2018).
Informed Consent: Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Authors’ Contribution
All authors have made important contributions to the research work reported in this manuscript.
Meera Shivasekar- Designing and drafting of the study
Thirunavukkarasu Jaishankar- data collection, data analysis and critical revision of the article
Sriram Veeraragavan- Statistical analysis and interpretation
Vinodhini V.M- Final inputs and approval of the article to publish.
References:
-
M.N. Krishnan. Coronary heart disease and risk factors in India on the brink of an epidemic? Indian Heart J. 2012; 64: 364-367.
-
Ravi Kant U, Perona, Javier S. Emerging Risk Biomarkers in Cardiovascular Diseases and Disorders. J lipids. 2015; 12(01): 971453-50.
-
Katsuyuki Nakajima, L.Adrienne C and Paulesh KS. Remnant-like particle (RLP) cholesterol is an independent cardiovascular disease risk factor in women: Results from the Framingham Heart Study. Atherosclerosis.1999; 154(1):229-36
-
Alan C, Henry N. Ginsberg, Tomas V. Remnants of the Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Disease. Diab. 2020; 69(4): 508-516.
-
Børge GN and Anette V. Triglyceride-rich Lipoprotein Cholesterol (Remnant Cholesterol) as a Therapeutic Target for Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Therapy Lipidology. 2020; (12): 139-158
-
Hermans MP, Ahn SA, and Rousseau MF. Novel unbiased equations to calculate triglyceride-rich lipoprotein cholesterol from routine non-fasting lipids. Cardio Diabet. 2014; 13, 56. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2840-13-56
-
Hirano, Tsutomu. Pathophysiology of Diabetic Dyslipidemia. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2018; 25(9):771-782. doi:10.5551/jat.RV17023
-
Brites F, Martin M, Guillas I, Kontush A. Antioxidative activity of high-density lipoprotein (HDL): Mechanistic insights into potential clinical benefit. BBA Clin. 2017 Aug 19;8:66-77. doi: 10.1016/j.bbacli.2017.07.002. PMID: 28936395; PMCID: PMC5597817.
-
Ooi BK, Goh BH and Yap WH. Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Diseases: Involvement of Nrf2 Antioxidant Redox Signaling in Macrophage Foam Cells Formation. Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 5;18(11):2336. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112336. PMID: 29113088; PMCID: PMC5713305.
-
Bloodsworth A, O'Donnell VB, Freeman BA. Nitric oxide regulation of free radical- and enzyme-mediated lipid and lipoprotein oxidation.Arteriosclerosis, Thromb Vasc Bio. 2000 July;20(7):1707-15. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.20.7.1707. PMID: 10894807.
-
Zou MH, Cohen R, Ullrich V. Peroxynitrite and vascular endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Endo. 2004 Mar-Apr;11(2):89-97. doi: 10.1080/10623320490482619. PMID: 15370068.
-
Olivier F, Chantal D and Stephane M. Hypercholesterolemia decrease nitric oxide production by promoting the interaction of caveolin and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. J Clin Invest. 1999; 103(6):897-905.
-
Minako Y-T. Endothelial Function for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Management. Int J Cardiol. 2017; (4):103.
-
Kuriyama K, Doi H, Takazoe K. Remnant lipoprotein levels in fasting serum predict coronary events in patients with coronary artery disease. Circul. 1999 Jun 8;99(22):2858-60.
-
Elena B, Mariarosaria N, Kathleen MB. Postprandial Lipid Metabolism: The Missing Link between Life-Style Habits and the Increasing Incidence of Metabolic Diseases in Western Countries. Open Transl Med J. 2010; (2): 1-13.
-
Galicia-Garcia U, Benito-Vicente A, Jebari S. Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. In. J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 30;21(17):6275. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176275. PMID: 32872570; PMCID: PMC7503727.
-
Ramasamy, Indra. Recent advances in physiological lipoprotein metabolism. Clin Chem Lab Med. (CCLM) 2014;52(12): 1695-1727.
-
Anette V, Marianne B, Anne T-H.Elevated Remnant Cholesterol Causes Both Low-Grade Inflammation and Ischemic Heart Disease, Whereas Elevated Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Causes Ischemic Heart Disease Without Inflammation. Circulation. 2013; (128):1298–1309.
-
Ruth McPherson. Remnant Cholesterol: “Non-(HDL-C + LDL-C)” as a Coronary Artery Disease Risk Factor. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013; 61 (4): 437–439.
-
Cristina M.SenaAna M.PereiraRS. Endothelial dysfunction — A major mediator of diabetic vascular disease. BBA Molec Basis Disease. 2013;1832(12): 2216-2231.
-
Zhang Y, Zhang W, Edvinsson L. Apolipoprotein B of low-density lipoprotein impairs nitric oxide-mediated endothelium-dependent relaxation in rat mesenteric arteries. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014; 725(Jan 18), 10-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.01.008
-
Herrero-Fernandez B, Gomez-Bris R, Somovilla-Crespo B, Gonzalez-Granado JM. Immunobiology of Atherosclerosis: A Complex Net of Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019 Oct 24;20(21):5293. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215293. PMID: 31653058; PMCID: PMC6862594.
-
Schulz, E., Gori, T. and Münzel, T. Oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in hypertension. Hypertension Res. 2011; 34, 665–673.
-
Paolo S, Andrea D'A and Mariateresa P. Ischemic Heart Disease Pathophysiology Paradigms Overview: From Plaque Activation to Microvascular Dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci.2020; 21(21): 8118.
-
Ren X, Ren L, Wei Q. Advanced glycation end-products decrease expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase through oxidative stress in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Cardioid Diab. 2017 Apr 20;16(1):52. DOI: 10.1186/s12933-017-0531-9. PMID: 28427390; PMCID: PMC5397770.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License