IJCRR - 13(15), August, 2021
Pages: 09-13
Date of Publication: 10-Aug-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Analysis of Correlations among Cognition Function, Body Function, and Risk of Falling in Elders in Nursing Hospital
Author: Nam Seung-Min
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: As ageing progresses, all organs and tissues of the human body are degenerated and functionally lost. As the physical function decreases, the elderly increase instability during physical activity, increasing the risk of falls and fractures. Aims: This study was conducted to investigate the correlation between cognitive function, physical function, and fall risk of the elderly in the nursing hospital. Methodology: The subjects of the study were 38 elderly people in the nursing hospital. Tetrax was used to assess the risk of falls. To measure cognitive function, it was measured using the MMSE-K test. In addition, static balance, dynamic balance, walking ability, and lower extremity muscle strength were evaluated to measure physical function. Static balance was measured using Biorescue, the dynamic balance was time up and go, the walking ability was 10 MWT, and lower extremity muscle strength was measured using five times sit to stand test. Pearson's correlation analysis was used to analyze the correlation between cognitive function and physical function and the risk of falls. Results: As a result of the study, there was a non-significant correlation in the correlation between cognitive function and fall risk (p>.05), and in the correlation between physical function and fall risk, there was a significant correlation in static balance, dynamic balance, gait ability, and lower extremity muscle strength. Showed a relationship (p
Keywords: Risk of Falling, Cognitive Function, Balance Ability, Gait Ability, Lower Extremity Strength, Elders Nursing Hospital
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The elderly population in Korea continued to increase from 3.1% in 1970, and in 2019, the proportion of the elderly aged 65 and over entered 14.9%. As such, Korea's ageing population is advancing very rapidly, and it is expected to reach a post-aged society in 2025.1 In addition, due to the increase in the elderly population, medical expenses of the elderly population accounted for 40.8% of the total medical expenses in 2018.2 As such, medical expenditure and social expenditure for the elderly are increasing, and social interest in the elderly is increasing.
Generally, as ageing progresses, all organs and tissues of the human body are degenerated and functionally lost. As the physical function decreases, the elderly increase instability during physical activity, increasing the risk of falls and fractures.3 Fall means falling from the original position to the lower position or the floor, independent of one's intention, during one's daily life.4 This fall is a typical age-related accident, and the risk of falling is 10 times higher than other age groups.5 It has also been reported that falls can require significant rehabilitation costs, and even minor falls can cause serious damage and a life threat. As such, it is important to accurately evaluate the risk of falls in the elderly and to identify the risk factors that cause falls, and take measures to prevent and treat falls.6
Risk factors for falls are closely related to cognitive and physical functions following the ageing process. The first cognitive function is the ability to judge and decide by processing input information, which means mental and intellectual processes. It has been reported that in the elderly, cognitive function decreases as ageing progresses, especially attention is reduced, leading to difficulties in everyday life.7 It has also been reported that ageing of the nervous system is a major cause of falls, and it has been reported that cognitive impairment should be included in determining risk factors for falls because impairment of cognitive function is related to fall.8,9
The second physical function is the basis of physical activity and refers to the physical condition that maintains and promotes daily living performance. In general, bodily functions can be directly or indirectly evaluated bodily functions through evaluation of balance, gait, and lower extremity strength. Balance ability is the ability to maintain the body's centre of gravity on the support surface and plays an important role in preventing falls.10 In the elderly, the functions of the organs related to balance control such as vision, vestibular sense, and intrinsic water perception decrease, resulting in increased posture sway and reduced balance ability.11 It has also been reported that as the body's balance ability decreases, walking ability decreases and the risk of falls increases.12 In addition, to indirectly evaluate the level of functional independence of everyday life of the elderly, the lower extremity muscle strength is measured. Lower leg muscle strength has been reported to reduce body stability and mobility and to reduce the level of independence of everyday life, and lower leg muscle strength is an important factor in predicting the risk of falls.13,14
Although various risk factors can cause falls. There is a lack of research that has comprehensively investigated the association between the risk of falls and the various risk factors that cause falls. In addition, previous studies on the relationship between fall risk and risk factors were mainly conducted on normal elderly and community-dwelling elderly people, and research conducted on elderly people living in facilities is insufficient.
Therefore, this study objectively evaluates the risk of falls using the Tetrax balancer, rather than the subjective evaluation tool that is mainly used in clinical practice for the elderly living in the nursing hospital, cognitive ability, static balance ability, dynamic balance ability, and gait The purpose of this study is to comprehensively study the correlation between ability, lower extremity muscle strength, and fall risk, to predict factors that cause fall, and to present information on fall prevention and treatment countermeasures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Subjects
This study was conducted on elderly people aged 65 and over who were admitted at S Nursing Hospital in Gyeongsangbuk-do in October 2019. After explaining the purpose and contents of the study to all study subjects, the experiment was conducted after obtaining consent to participate. The experimental procedure was approved by the Institutional Review Board (1040621-201711-HRBR-004-002). The selection criteria of the subjects were selected as the elderly who can stand and walk independently or using assistive devices, the elderly who have no abnormalities in the visual, auditory and vestibular organs, and conducted a study on the final 38 subjects.
Measurement tools and measurement methods
Fall risk measurement:
Tetrax balancer (Israel) was used to measure the risk of falls. The Tetrax balancer uses a total of four force plates, one on each heel and toes on both sides of the lower limb. The subject took off his shoes and placed his feet on the power plate and tested in a total of eight positions. First, the posture facing the front with the eyes open (normal eye open; NO), then the posture facing the front with the eyes closed (normal eye close; NC), and the posture facing the head with the eyes closed head right (HR), head left (HL), head up (HU), head down (HD). The test is performed with the foam-rubber pillow under the feet and the eyes open (PO) and eyes closed (PC) facing the front.15 There is a risk of falling when eyes are closed or standing on a soft support surface, so the examiner is allowed to stand around the subject. Through these eight postures, the degree of postural agitation was measured, and the risk of falls was measured. The risk of falling is comprised of 0-100 points, and the higher the value, the higher the risk of falling.16
Korean version, Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE-K):
The Korean version of the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE-K) is the most widely used dementia screening tool in Korea and has the advantage of being able to easily assess the intellectual condition and cognitive function of the subject in a short time.17 The Korean version of the MMSE-K consists of 12 questions, including five points of orientation relating to time, five points of orientation relating to place, three points about memory registration, three points to memory recall ability, five points to attention and computation, and nine points to understanding, judgment, and language. It consists of 30 points.
Biorescue:
The Biorescue biofeedback analysis system (Biorescue, France) is a device that measures the balance ability of various subjects such as patients, the general public, and athletes. It is a tool that can measure the length (mm) and average speed (cm/s). To evaluate the static balance ability, the limit of stability at the standing posture was measured. Of the eight directions indicated by the monitor, the total distance and area of the centre of gravity were measured for the weight movements before, after, left, and right. The device explained the measurement method through a monitor and first demonstrated it. The subject held a leg forward at 30° in the standing position, centred in a forward-looking position, and then used an ankle joint strategy to achieve maximum range without losing balance. The limit of their ability to move from their centre of gravity was measured.
Berg Balance Scale (BBS)
The Berg Balance Scale (BBS) can objectively assess the fall risk, static balance ability, and dynamic balance ability of the elderly by measuring the functional performance of their balance through sitting, standing, and posture changes.18 The scale is composed of 14 items, and if the task cannot be performed, the total score is 56, a maximum of four points being applied to each item if it is independently performed. In general, the higher the score, the better the balance ability, 0–20 points indicating balance disorder and 41–56 points indicating good balance.
10-Meter Walk Test (10 MWT)
The 10-meter walk test (10 MWT) is a test method that evaluates walking ability by measuring the walking speed of the examinee.19 No special equipment is required, so you can easily evaluate your walking ability in a short time. The method measures the time required to walk a distance of 10 m by taking into account acceleration and deceleration between the start and the end and measures a total of three times to obtain the average.
Lower limb strength
Five Times Sit to Stand Test (FTSST) is a test method that starts from a sitting position on a chair and measures the time to perform the sitting and sitting motion five times. FTSST is a measure that predicts the recurrence of falls and the independence of daily life performance by measuring functional aspects of the lower extremity strength.20 Subject was instructed to wake up five times as soon as possible and then sit down.
Statistical analyses
The results of the experiments obtained in this study were described as mean±standard deviation (Mean±SD). Pearson's correlation analysis was conducted to analyze the correlation between the level of cognitive function and physical function in the elderly and the risk of falls. Statistical processing was analyzed using SPSS 23.0 for Windows, and all statistical significance levels (?) were set to 0.05.
RESULTS
General characteristics of subjects
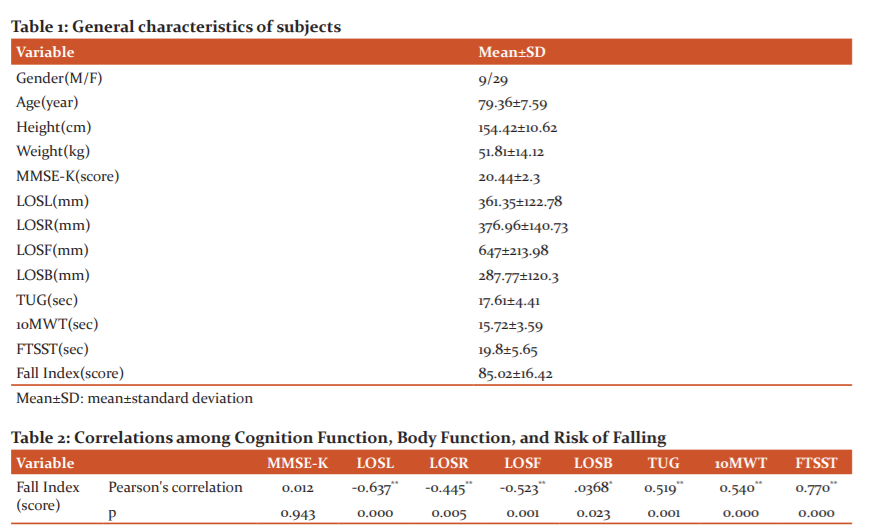
A total of 38 subjects participated in this study, and the general characteristics of the subjects are shown in Table 1. As a result of analyzing the correlation between cognitive function and fall risk, there was no statistically significant relationship (p>.05).
Correlations among Cognition Function, Body Function, and Risk of Falling
As a result of correlation analysis between physical function and fall risk, there was a statistically significant relationship between static balance ability, dynamic balance ability, gait ability, lower leg strength level and fall risk, static balance ability, dynamic balance ability, gait ability, lower leg strength The risk of falls increased with decreasing levels of (p<.05) (Table 2).
DISCUSSION
Fall is a typical senile accident, and the number of fall patients is increasing with the increase in the elderly population.5 Therefore, it is important to manage the risk factors that cause falls to prevent and treat falls. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to predict the risk factors that cause fall by studying the correlation between cognitive function, physical function, and fall risk for the elderly.
As a result of the analysis of the correlation between cognitive function and fall risk, there was no statistically significant difference. However, according to a previous study that measured cognitive function by dividing it into fall experience and no fall experience, the cognitive function of the elderly group who experienced fall was lower than that of the elderly group who did not fall, and the elderly group who experienced fall. The results were not consistent with the reported study of cognitive decline.21 In addition, according to previous studies, the MMSE-K score of the fall risk group averaged 17.28 points, and the MMSE-K score of the non-fall risk group averaged 22.13.22 As such, cognitive function is considered to have a high association with falls when it is at the level of severe cognitive impairment, and in this study, the MMSE-K score is 20.44 points on average, and it is considered that there is no high association with falls. In future studies, it is considered necessary to study the risk of falls according to the level of cognitive impairment.
As a result of correlation analysis between physical function and fall risk, a statistically significant correlation was found between static balance ability, dynamic balance ability, walking ability, lower extremity muscle strength and fall risk. First, the LOS measured to evaluate the static balance ability showed a negative correlation with the risk of falls as the length decreased, and the TUG measured to evaluate the dynamic balance ability increased the risk of falls with time. An increasing amount of correlation was shown. Previous studies have reported that the incidence of falls increases when the balance ability decreases with age, and the instability of the balance secondary causes fear of falls and lack of confidence, causing physical activity to fall and independent daily life performance It has been reported to decrease.10 It was also consistent with the results of previous studies that showed a decrease in static and dynamic balancing ability in the falling risk elderly group than in the falling non-risk elderly group.22
In addition, the 10MWT measured to evaluate the walking ability showed a positive correlation with the risk of falling as time increased. Previous studies have reported that elderly people who have experienced falls have a narrower stride length, slower walking speed, and differences in gait patterns than those who have not experienced falls.23 In this study, as the walking speed slowed, the risk of falling significantly increased, which was consistent with the results of previous studies. Walking is the most basic movement for the movement of the human body and is an essential element in everyday life. According to previous studies, it is considered that in the elderly, it is difficult to control the central nervous system and maintain the balance of the body, and as the balance ability decreases, the walking ability decreases, thereby increasing the risk of falls.12
Lastly, the FTSST measured to evaluate the lower extremity muscle strength showed a positive correlation with the risk of falling as time went on. Previous studies have reported that older adults have reduced functional independence in their daily lives as FTSST increases, and the risk of falls increases as time increases based on 15.62 seconds.24 It was also consistent with the results of previous studies that showed a significant difference in the muscle strength of the lower extremity flexors when comparing the elderly with non-experienced fall.25
In summarizing the results of this study, it is necessary to accurately assess the risk of falls, and regularly balance and gait training, and exercise to strengthen lower extremity muscles for the elderly and general elderly patients who have experienced a fall.
The limitations of this study are as follows. First, the number of subjects was 38. It is considered that it is necessary to further expand the subjects in future studies. There is a limit to generalizing the results of this study to all the elderly in the second general facility. In future studies, it is considered that it is necessary to compare the elderly in the facility with the elderly in the community. In addition, it is considered that there is a need for research that analyzes the correlation by stratification according to characteristics such as classification according to age group and cognitive function level.
CONCLUSION
This study was conducted to investigate the correlation between cognitive and physical functions and risk of falls in 38 elderly patients admitted to nursing hospitals. As a result of this study, there was a significant correlation between static balance ability, dynamic balance ability, gait ability, lower extremity muscle strength level and risk of falls, and there was no significant relationship between cognitive function and fall risk. In other words, balance training, gait training, and lower extremity muscle strengthening exercises should be performed for the elderly in hospitals and communities. It is thought that it will be effective in preventing falls of the elderly and improving their ability daily life.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by Uiduk University Foundation Grant, 2021
Conflict of Interest: NIL
Source of Funding: NIL
*p<.05, **p<.01
Mean±SD: mean±standard deviation
MMSE-K: Korean version Mini-Mental State Examination
LOSL: Limit of Stability Left
LOSR: Limit of Stability Right
LOSF: Limit of Stability Forward
LOSB: Limit of Stability Back
TUG: Time Up & Go
10MWT: 10-Meter Walk Test
FTSST: Five Times Sit to Stand Test
References:
1. Korea S. Resident registration demographics. Seoul: Statistics Korea; 2019 [cited 2020 September 30].
2. Korea S. 2018 Health Insurance Statistics Yearbook. Seoul: Statistics Korea; 2019 [cited 2020 September 30].
3. Andersen CK, Wittrup-Jensen KU, Lolk A, Andersen K, Kragh-Sørensen P. Ability to perform activities of daily living is the main factor affecting quality of life in patients with dementia. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2004;2(1):1-7.
4. Tinetti ME, Speechley M, Ginter SF. Risk factors for falls among elderly persons living in the community. N Engl J Med. 1988;319(26): 1701-1707.
5. Miller CA. The connection between drugs and falls in elders. Geri Nurs. 2002;2(23):109-110.
6. Schoenfelder DP, Rubenstein LM. An exercise program to improve fall-related outcomes in elderly nursing home residents. Appl Nurs Res. 2004;17(1):21-31.
7. Kami?ska MS, Brodowski J, Karakiewicz B. Fall risk factors in community-dwelling elderly depending on their physical function, cognitive status and symptoms of depression. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015;12(4):3406-3416.
8. Evans D, Hodgkinson B, Lambert L, Wood J. Falls risk factors in the hospital setting: a systematic review. Int J NursPract. 2001;7(1):38-45.
9. Jensen J, Nyberg L, Gustafson Y, Lundin?Olsson L. Fall and injury prevention in residential care effects in residents with higher and lower levels of cognition. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51(5):627-635.
10. Gang TW, Kim BR. Comparison of Task-oriented Balance Training on Stable and Unstable Surfaces for Fall Risk, Balance, and Gait Abilities of Patients with Stroke. Kor Soc Phys Med. 2019;14(2):89-95.
11. Hurley MV, Rees J, Newham DJ. Quadriceps function, proprioceptive acuity and functional performance in healthy young, middle-aged and elderly subjects. Age Ageing. 1998;27(1):55-62.
12. Unsworth J, Mode A. Preventing falls in older people: risk factors and primary prevention through physical activity. Br J Community Nurs. 2003;8(5):214-220.
13. Moreland JD, Richardson JA, Goldsmith CH, Clase CM. Muscle weakness and falls in older adults: a systematic review and meta?analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52(7):1121-1129.
14. Schenkman M, Hughes MA, Samsa G, Studenski S. The relative importance of strength and balance in chair rise by functionally impaired older individuals. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1996;44(12):1441-1446.
15. Kohen-Raz R. Application of tetra-ataxiametricposturography in clinical and developmental diagnosis. Percept Mot Skills. 1991;73(2):635-656.
16. Kim TH, Yi JH, Oh SG. Static posture stability evaluation of female elderly using stability evaluation device. J Kor Skill. 2011;12(12):5518-5524.
17. Tombaugh TN, McIntyre NJ. The mini?mental state examination: a comprehensive review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1992;40(9):922-935.
18. Morris S, Morris ME, Iansek R. Reliability of measurements obtained with the Timed “Up & Go” test in people with Parkinson disease. Phys Ther. 2001;81(2):810-818.
19. Dean CM, Richards CL, Malouin F. Walking speed over 10 metres overestimates locomotor capacity after stroke. Clin Rehabil. 2001;15(4):415-421.
20. Bohannon RW. Reference values for the five-repetition sit-to-stand test: a descriptive meta-analysis of data from elders. Percept Mot skills. 2006;103(1):215-222.
21. Ruchinskas R. Clinical prediction of falls in the elderly. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2003;82(4):273-278.
22. Cuevas-Trisan R. Balance problems and fall risks in the elderly. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2017;28(4):727-737.
23. Wang S, Varas-Diaz G, Dusane S, Wang Y, Bhatt T. Slip-induced fall-risk assessment based on regular gait pattern in older adults. J Biomech. 2019;96(11):1-7
24. Nam SM, Kim SG. Effects of a Five Times Sit to Stand Test on the Daily Life independence of Korean Elderly and Cut-Off Analysis. J Kor Soc Phys Med 2019;14(4):29-35.
25. Chung JW, Choi HJ. Functional fitness and asymmetry on lower body muscle strength of elderly women with fall experience. Asian J Kinesiol. 2009;11(2):65-72.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License