IJCRR - 13(12), June, 2021
Pages: 243-246
Date of Publication: 22-Jun-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Effect of Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercise-Induced Progressive Positioning in Improving Pelvic Floor Muscle Strength
Author: Jenifer Augustina S, Prathap Suganthirababu, Vijayaraghavan Rajagopal, Kamalakannan M, Kamatchi Kaviraja
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The pelvic floor provides support for the pelvic organs, spine and pelvic girdle, and aid in urination, defecation and sexual function. In particular, these functions require relaxation and coordination of the pelvic floor muscles as well as the urine and anal sphincter muscles. Recent studies for improving Pelvic floor muscle strength contains vaginal cones, bladder training, pelvic floor muscle exercises, biofeedback and the electrical stimulation of pelvic muscles. Kegel exercises had become more popular as it is a non-invasive method of treatment and a perineometer is a quantitative tool used for both assessment and management of pelvic floor strength. Aim: This study had undertaken to intend to improve the pelvic floor muscle strength by improving the progression in different positions such as crook lying, sitting and standing. Methods: A study was conducted on 30 subjects among them 20 are illiterates and 10 are literates using a convenient sampling technique, based on inclusion and exclusion criteria. The brink scale is used as the outcome measure. The strength training program is performed in 3 positions and divided into 3 phases, phase-I is from week one to week three, phase II is from week four to week six and phase -III is from week seven to week nine Result: The statistical analysis of the study revealed that the post-test values of Phase-III had marked improvement due to increased duration and the improved position. The result of the study showed that the pelvic floor muscle strength can be progressed to a maximum of between 8 to 9 weeks. Conclusion: The study concluded that all the positions are equally important in the progression of pelvic floor strength.
Keywords: Biofeedback, Bladder training, Electrical stimulation, Kegal exercises, Pelvic floor, Perineometer, Vaginal cones
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION:
The pelvic floor is composed of bone, muscle and connective tissue. Together, these elements provide support for the pelvic organs, spine and pelvic girdle, and aid in urination, defecation and sexual function. In particular, these functions require relaxation and coordination of the pelvic floor muscles as well as the urine and anal sphincter muscles. Therefore, their impaired relaxation or paradoxical contraction can cause various symptoms, such as impaired urination or defecation, pelvic pain and sexual dysfunction. Pelvic Muscle Rehabilitation (PMR) is a multidisciplinary program involving many rehabilitation principles, such as muscle floor retraining, biofeedback, and electrical stimulation of the pelvic floor and functionally related muscle tissue. PMR therapeutic interventions modalities included using one or a combination of six possible therapeutic modalities. Modalities include Muscle Isolation, Discrimination Training, pelvic floor muscle strengthening resistance training down-training, electrical stimulation.1 Urinary incontinence (UI), faecal incontinence (FI), and pelvic organ prolapse (POP) are common conditions in women with a 20% lifetime risk of having a single operation for these floor conditions. A recent cross-section of the health survey mentioned that the symptoms of UI, FI and POP had a prevalence rate of 23.7% in women 20 years of age and older and 49.7% in women aged 80. There will be an increasing need for treatment of pelvic floor disorders (PFDs), according to the United States estimation percentage of women seeking care for these conditions will increase from 28.1 million to 43.8 million by 2050, parallel to demographic ageing. Recent studies for improving Pelvic floor muscle strength contains vaginal cones, bladder training, PFM exercises, biofeedback and the electrical stimulation of pelvic muscles.2,3,4,5,6,7 Kegel exercises had become more popular as it is a non-invasive method of treatment and the perineometer is a quantitative tool used for both assessment and management of pelvic floor strength.8, 9 Numerous studies have been done in past to improve pelvic floor muscle strength, this study aimed to analyse the effect of pelvic floor muscle exercise induce progressive positioning in improving pelvic floor muscle strength in various positions such as cooking sitting and standing. This study had undertaken to intend to improve the pelvic floor muscle strength by improving the progression in different positions such as cooking, sitting and standing. The strength is observed in all the 3phases by using the Brink scale as an outcome measure by documenting the pre and post-intervention values
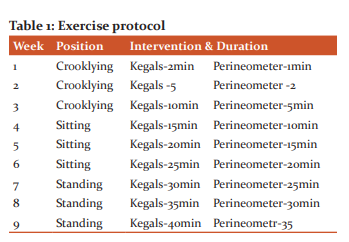
METHODS: A Quasi-Experimental study was conducted on 30 subjects among them 20 are illiterates and 10 are literates using a convenient sampling technique, the inclusion criteria for the study was 25-45-year-old women who had a history of vaginal delivery and the strength of the pelvic floor muscle should score only 3 according to brink scale.1 The exclusion criteria for the study was women who underwent vaginal hysterectomy or pelvic floor repair and who had vaginal infections. Ethical clearance was obtained from HEC (009/09/2019/IEC/SMCH) of SIMATIC. After receiving an informed consent form, the women were explained about the Brink scale for pelvic floor muscle. The strength of the pelvic floor is measured by using the BRINK scale, the scale has 3criteria i.e., pressure, moving the fingers in the horizontal plane and time and each criterion has 4degrees where the minimum score is 3 and the maximum is 12.8 To find the strength of the pelvic floor muscle the subject should be in crook lying position by completely relaxing the perineal area, two fingers are inserted into the vagina and asked to contract her pelvic floor muscles as she holds the urine and should try to pull the finger upward inward, the subject with score -3 are selected for the study.The strength training program is performed in 3 positions and divided into 3 phases, phase-I is from week one to week three, phaseII is from week four to week six and phase -III is from week seven to week nine. In this study, the subjects were taught to perform kegal exercise with a hold of 5seconds and relax of 5sec for 2 minutes in crooklying position per session per day for 6 days in 1st week. Then the pelvic floor strengthening is performed by using a perineometer, subject is taught to contract the transducer of the perineometer for 1minuteproperly during 1st week in the crooklying position. During the 2nd week the kegel exercise is performed for a period of 5minutes and strength training is performed by using a perineometer for a period of 2minutes incrooklying position and in 3rd week the Kegels is performed for 10 minutes and strength training by using perineometer is performed by using 5minutes in crooklying position and sitting position during 4th-week kegals for 15minutes and pelvic floor strengthening by usingperineometer for 10min is performed. During the 5th week in sitting position Kegels is performed for 20minutes and perineometer isused for 15minutes,in the 6th week of progression Kegels is performed for 25minutes and the perineometer is used for 20minutes in the position of sitting.In the week of 7th, the progression is increased by performing Kegels for 30 minutes and perineometer for 25minutes in standing position.During the 8th week of progression in standing position,Kegels is performed for 35 minutes and a perineometer is used for 20minutes to improve the strength. Finally, the progression is done in a standing position by performing Kegels for 40minutes and a perineometer is used for 35 minutes for strength training. The strength is observed in all the 3phases by using the Brink scale as an outcome measure by documenting the pre and post-intervention values ( Table 1).9
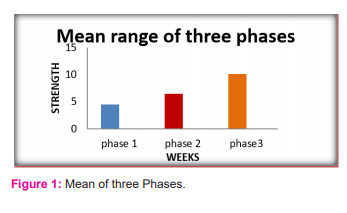
Result: In the total of 30 subjects, the strength of the pelvic floor reached to maximum score by the end of 9weeks.The statistical analyses of phase-I, phase- II and Phase -III revealed that the pre-test means value in phase -I from week 1 to 3 is 3 and the post-test mean value is 4.47, In the phase-II that is from week 4 to 6 the pre-test mean value is 4.47 and the post-test mean value is 6.4. In the finale phase -III from week 7-9 the pre-test mean value is 6.4 and the post-test mean value is 10.7.The post-test mean values of all the 3 phases revealed that the post meansthe value of Phase-III showed a great improvement in pelvic floor muscle strength compared to phase-I and phase-II. So the result of the study showed that the pelvic floor muscle strength can be progressed to a maximum between 8to 9weeks ( Figure 1).
Discussion: Pelvic floor muscle strength plays a crucial role in maintaining the quality of life in women. It is very important to strengthen them and the progression of the strength training helps the women to improve their quality of life.10,11,12 In our study we concentrated on the progression of the pelvic floor muscle in different positions. There are many devices to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles like vibrancekegel devices and vaginal cones and biofeedback, there are studies that kegel exercises will help in strength training and also improve sexual life and some studies state that the pelvic floor muscle exercise also helps in reducing low back pain.13 This study focused on knowing the effect of pelvic floor muscle exercise-induced progressive positioning in improving pelvic floor muscle strength.The study showed that there is no significant difference between the groups, we observed an improvement in phase-3 compared to phase-2 and phase -1. Pelvic floor dysfunction is common among women after vaginal delivery and pelvic floor muscle strength plays a crucial role in maintaining the quality of life in women, it is very important to strengthen them and progression of the strength training helps the women to improve their quality of life.14 In this study we observed that three positions have their importance and all the positions help in the good progression of the pelvic floor muscle strengthening as we selected 30 subjects who reached maximum strength after completing 9 weeks of strength training and the statistical analysis of the study revealed that the posttest values of Phase-III had marked improvement due to increased duration and the improved position.15 In our study we focused more on the strength training program as it plays a vital we focused on progression in 3 positions such as cooking, sitting and standing and performed strength training in 3 phases that is phase-I from week 1to3, phase-II from 4 to 6 and phase-III from week 7 to 9 and pre and posttest values are documented by using Brink scale as the outcome measure. Women are not able to participant in all the 3 phases continuously due to the influence of the menstrual cycle.16 In this study both illiterates and literature have participated and our study did not reach the understanding capacity of illiterates here we recommend that future studies should be done to reach the understanding capacity of illiterates without readings or calculations, which provides the pelvic floor strength knowledge.
Conclusion: The progression of pelvic floor strengthening can be achieved between 8 to 9 weeks in crook lying, sitting and standing and the study concluded that all the positions are equally important in the progression of the pelvic floor strength. The main issue to be addressed in the study is that as we included the illiterate women in the study they are not able to notice the perineometer readings, so research has to be done in a way to meet the understanding capacity of rural or illiterate women in pelvic floor strength.
Acknowledgement: Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of interest: Nil
Funding: Nil
Authors contribution:Study conception and design: S. Jenifer Augustina, Acquisition of data: S. Jenifer augustina, Prathap Suganthirababu, Analysis and interpretation of data: S. Jenifer Augustina, Kamalakannan. M, Drafting of ManusAcript: S. Jenifer Augustina, R.Vijayaraghavan, Kamatchi Kaviraja
References:
[1] Kari BO, Sherburn M, Evaluation of Female Pelvic-Floor Muscle Function and Strength, Phys Ther. 2005; 85(3): 269–282
[2] Hallock JL, Handa VL. The Epidemiology of Pelvic Floor Disorders and Childbirth: An Update. Obst GynecolClin North Am. 2016; 43(1):1-13.
[3] Pereira VS, Cofloor Rreia MV, Drissusso P, Individual and group pelvic floor muscle training versus no treatment in female stress urinary incontinence: a randomized controlled pilot study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2011;159(2):465-471.
[4] Pereira VS, de Melo MV. Vaginal cone for postmenopausal women with stress urinary incontinence: randomised, controlled trial. Climact. 2012; 15(1): 45-51.
[5] Zanett M.R.D, De Aquino Catro R., Rotta A.L, dos Santos P.D, “Impact of supervised physiotherapeutic pelvic floor exercises for treating female stress urinary incontinence,” Sao Paulo Med J,2007;125(5): 265-269.
[6] FloratosDL, Sonake GS, Rapidou CA. Biofeedback vs verbal feedback as learning tools for pelvic muscle exercises in the early management of urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy. BJU international, 2020; 89(7):714-719.
[7] Castro RA, Arruda RM, Zanetti MR. Single-blind, randomized, controlled trial of pelvic floor muscle training, electrical stimulation, vaginal cones and no active treatment in the management of stress urinary incontinence. Clinics, 2008;63(4): 465-472.
[8] Seong-Hi Park, ChangB. Effect of kegel exercises on the management of female stress urinary incontinence: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Adv Nurs, 2014;640262:(10): 261.
[9] Van K, Delft R. Thakar AH. Sultan, Pelvic floor muscle contractility: digital assessment vs transperineal ultrasound. Ultras Obst Gynec. 2015; 45,( 2): 217-222.
[10] Andrea Marques, Lynn Stothers and Andrew Macnab The status of pelvic floor muscle training for women. Can Urol Assoc J. 2010; Dec; 4(6): 419–424.
[11] Woodley S.J, Boyle R, Cody J.D, Mørkved S, Hay-Smith EJC. Pelvic floor muscle training for prevention and treatment of urinary and faecal incontinence in antenatal and postnatal women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017; 12(12).
[12] TengAlk Ong, Su Yen Khong, Keng Limn G using the vibrancekegal device with pelvic floor muscle exercise for stress urinary incontinence:Arandomised controlled pilot study, female urology,2015,Sep;86(3):487-91.
[13]. Kondo A, Yamada Y, Niijima R. Treatment of stress incontinence by vaginal cones: short- and long-term results and predictive parameters. Br J Urol. 1995,Oct;76(4):464-6.
[14] Berghmans LC, Frederiks CM, de Bie RA, Efficacy of biofeedback, when included with pelvic floor muscle exercise treatment for genuine stress incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn. 1996;15;37-52.
[15] Sobhgol SS, Priddis H, Smith C.A, Dahlen HG. The Effect of Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercise on Female Sexual Function During Pregnancy and Postpartum: Sex Med Rev. 2019 Jan;7(1):13-28.
[16] Mohammad A. Mohseni- Bandpei, The effect of pelvic floor muscle exercise on women with chronic low back pain.J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2011; 15(1): 75-81.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License