IJCRR - 13(14), July, 2021
Pages: 210-213
Date of Publication: 20-Jul-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A Clinico-epidemiological Study of Patterns of Homicidal Head Injuries at a Teaching Hospital in West Bengal: An Autopsy-based Study
Author: Partha Sarathi Hembram, Shobhan Roy, Mainak Tarafder, Saptarshi Chatterjee
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Homicide is a heinous crime with around 5,00,000 deaths per year worldwide. Head injuries are one of the most effective methods of homicide. The head is the vital and most vulnerable part of the body to sustain injuries. The type and size of intracranial haemorrhages, along with the association of skull fractures have an immense significance in the outcome of head injuries. Objectives: The present study is undertaken to analyse the profiles and patterns of head injuries in homicidal victims between 2008 to 2011. Methods: This is a cross-sectional descriptive study, which was conducted by analysing 59 cases of Homicidal Head Injuries, attended to Kolkata Police Mortuary for autopsy examination between 2008 to 2011. Results: The majority of the victims belonged to the 3rd and 4th decades, with male preponderance in all the age groups. Though the place of occurrence has got no significant implication on the pattern of homicidal head injuries, hard blunt weapons were most commonly used to inflict fatal blows. Basilar fractures of the anterior cranial fossa and the fissure fractures of the skull were most commonly encountered during the autopsy, with subdural haemorrhage being the most common among intracranial haemorrhages, being shortly followed by subarachnoid haemorrhages. Conclusion: The authors feel that homicide is an act of moment in mind, and to curb the menace of homicide, state and society should ensure education, employment and socioeconomic well-being, along with strict law enforcement.
Keywords: Skull fractures, Basilar Fractures, Intracranial haemorrhage
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Homicide is the heinous, the cruellest and the severest form of violent crime, where one human being deprives another human being of his fundamental right to live.1 Global rise of homicides is concerning nowadays, with around 5,00,000 deaths per year worldwide.2 It may be a result of arguments between acquaintances, domestic violence, drug addiction, robbery and terrorism. Violent deaths are from a spectrum of physical, sexual, mental and reproductive health problems. The most vulnerable are the young offenders who are becoming increasingly violent and that are causes for concern too.1,2
The head is the vital and most vulnerable part of the body to sustain injuries. Head injuries are one of the most effective methods of homicide. A craniocerebral injury due to blunt trauma causes more homicidal deaths, as compared to blunt trauma injury to other parts of the body.3 The type and site of intracranial haemorrhages, the presence or absence of skull fractures with their types are having imminent significance in the outcome of head injuries.3,4,5
Besides being a useful indicator of social stress, the pattern of homicide also provides useful information for law enforcement strategies. Investigation of homicidal deaths can never be complete without a detailed post-mortem examination. The detailed analysis and scientific interpretation of autopsy findings are imperative to reconstruct the crime scene.6
The present study is undertaken to analyse the profiles and patterns of head injuries in homicidal victims. The knowledge thus gained can be highlighted to reveal the magnitude of its impact on society, as well as to attempt a solution.7
MATERIAL AND METHODS
-
Place of study: Upgraded Department of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology, Medical College, Kolkata, West Bengal, India.
-
Period of study: 1st of January, 2008 to 31st of December, 2011
-
Study population: All the patients sent for autopsy examination at Kolkata Police Mortuary during the study period.
-
Sample size: All the victims of homicidal head injuries, attended to Kolkata Police Mortuary for autopsy examination between 2008 to 2011.
-
Homicidal deaths, due to any cause, other than head injuries.
-
Any case subjected for autopsy with an alleged or suspected history of homicide, but which were later registered as non-homicidal based on the autopsy findings, circumstantial evidence and police investigation.
-
Cases with incomplete or inadequate data
-
Study design: Cross-sectional descriptive study
-
Statistical analysis: All the data were manually checked and edited for completeness in a pre-determined format and were then coded for computer entry. Collected data were recorded in a Microsoft Excel worksheet and SPSS IBM 19. The data were collected, tabulated and statistically analyzed by applying a student’s t-test. The p <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
1. Incidence of homicidal head injuries in percentage
Homicidal head injuries (HHI) for the years 2008, 2009, 2010 and 2011 were 47.61, 56.25, 38.63 and 48.27 respectively.
2. Distribution according to gender
Of all the victims, 79.7% were males and the rest 20.3% were females.
3. Distribution according to age
The persons of age group 30-40 years were most affected, followed by the subjects of 20-30 years of age [Table I].
4. Place of occurrence
In 37.3% of cases, the place of occurrence was outdoor and in 40.7% was indoor, with the rest being doubtful. However, statistically, no significant difference was found between the place of occurrences.
5. Type of weapon
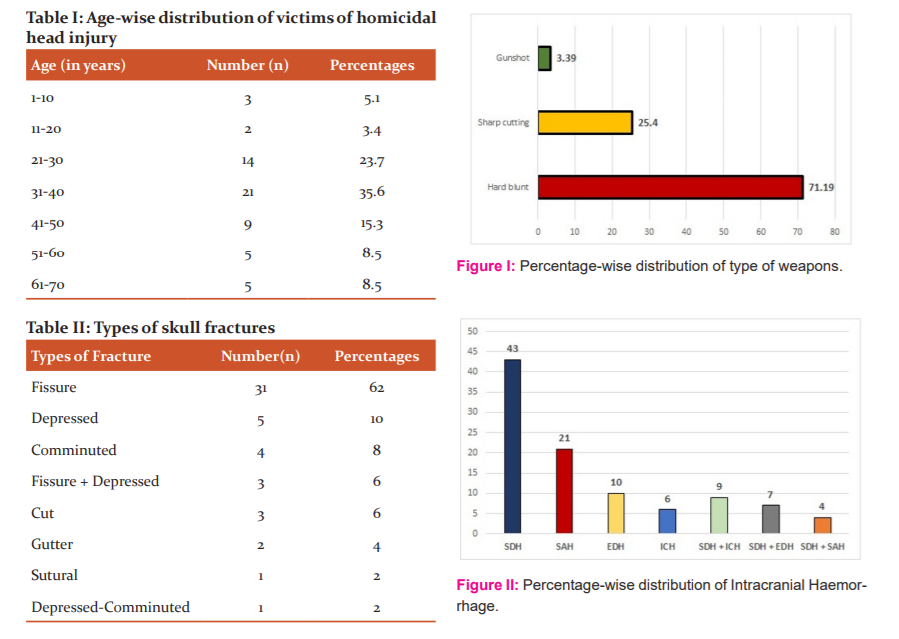
Hard blunt weapons were mostly used to inflict fatal blows, as compared to sharp cutting weapons [Figure I].
6. Distribution according to the location of the basilar fracture
Among the 59 Homicidal Head Injuries (HHI), 15 victims (25.4%) presented with basilar fractures of the skull. Fracture of anterior cranial fossa was observed in 60% of cases, followed by middle cranial fossa in 33.33%. The posterior cranial fossa seemed to be the least affected with 6.67%.
7. Type of skull fracture
50 victims (84.74%) out of 59 of HHI came with skull fractures. Fissure fractures were most common followed by Depressed and Comminuted fractures [Table II].
8. Types of Intracranial haemorrhage
Subdural haemorrhages, followed by subarachnoid haemorrhages were most commonly encountered during autopsy [Figure II].
DISCUSSION
Homicidal deaths are a challenging task to investigating authorities, as well as to the judiciary. At this step, autopsy examination by forensic medicine specialist is of immense importance to recognise the medicolegal injuries in the right perspective and further help the investigating officers and the judiciary in their legal conclusions. The incidences of homicidal head injuries in our study for the years 2008 to 2011, replicated similar findings to the studies conducted by Mishra and Singh in Bhopal, Central India.4
Males by nature are aggressive due to which they tend to indulge in violent activities and revenge. Our study results proliferate the view as majority of the victims were males, which is consistent with the observation of Buchade and Mohite.5
Similar to the results in the other parts of the world, the age group of 20-50 years, in this study population, constituted more than 70% of the affected.6 In this era of competitive world, the most aspirant and active age group are 21-30 years, who begin to mount their responsibilities of earning and marriage and can usually materialize it by age 40 through enormous struggles with fast-changing cultural, social and economic trends. These predispose persons of this age to superfluous interactions, frustrations and addictions, making them the most vulnerable to violence.8,9
The maximum number of victims of homicidal head injury got affected in their residence or indoors only, which implies that these homicides were mostly premeditated as the assailants were aware of the victim’s whereabouts and motive being financial dispute or murder for gain, followed by outdoors, which were due to gang rivalry, revenge murders and arguments arising while under the influence of alcohol or other substances. However, the statistically insignificant difference between the two, calls for more researches in this field of criminal psychology. Our results are in continuation to the study conducted by Hugar and Chandra.7
In our study, blunt weapons were commonly used, followed by sharp cutting weapons. This observation is similar to the study by Dhaval in Chhattisgarh,8 though it contradicts the study in Bhavnagar by Dhaval and Bhagora.1 Sharp weapon usage in homicidal cases can be attributed to the availability of such weapons in the area, but its exclusive use also points towards premeditated crime. The use of only blunt weapons for homicide could be the unpremeditated aggressive and explosive response.10
Fractures of the base of the skull are associated with high fatalities. As the vital centres are situated in the midbrain and brain stem, if the force of impact is transmitted to the base thus causing fracture, it is likely to cause damage to the vital centres. Basilar fractures also point towards the use of strength by the assailant(s) is maximum during the material moment to make sureness of the death of the victims. In our study, the anterior cranial fossa was mostly fractured. This can be explained by the fact that the anterior cranial fossa consists of the thin orbital plate and the cribriform plate, where chances of fracture are getter. Our findings are in concordance to the results of another study from Varanasi, India.9
The dominant type of skull fracture found was linear (fissure) fracture, followed by depressed and comminuted fractures in a study by Rupani and Verma,10 which is consistent with the findings of the present study. Manish and Jyothi from Davangere, in their study, reported that the linear fracture (38.8%) was the commonest, followed by comminuted fracture and depressed fracture,11 contrary to the findings of our study.
The majority of the cases, being traumatic, were mixed with intra-cranial and extra-cranial lesions. Most commonly found intra-cranial haemorrhage happens to be subdural haemorrhage followed by subarachnoid haemorrhages, which is consistent with the findings by other researchers in Central Asia.12
CONCLUSION
Homicide is a vast varied and intricate topic, yet our study is a tangible attempt of exploring certain physical aspects of injuries. The majority of the victims belonged to the 3rd and 4th decades, with male preponderance in all the age groups. Though the place of occurrence has got no significant implication on the pattern of homicidal head injuries, hard blunt weapons were most commonly used to inflict fatal blows. Basilar fractures of the anterior cranial fossa and the fissure fractures of the skull were most commonly encountered during the autopsy, with subdural haemorrhage being the most common among intracranial haemorrhages, being shortly followed by subarachnoid haemorrhages.
Education, employment, socio-economic well-being and strict law enforcement can decrease the number of homicidal deaths. But authors feel that homicide is an act of moment in mind, so any decision made under excitement or incitement is the real culprit. Therefore, we would like to wrap up this by suggesting to improve the ability to think over any problem, with a balanced and reasonable tolerance.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest is associated with this work.
Ethical clearance
Taken
Source of funding
None declared
Informed consent
After taking the ethical clearance the study was conducted on Fatal Homicidal Head Injuries at an autopsy centre, without the need for Informed consent.
References:
-
Parmar DJ, Bhagora LR, Parmar RD. Recent trends of homicidal deaths in Bhavnagar region - A two-year retrospective study. Ind J Res. 2015;2(8):45-54.
-
Reza A, Mercy JA, Krug E. Epidemiology of violent deaths in the world. Ind J Res. 2019;8(3):39-40.
-
NaikSG, NaikRK.Evaluation of head injuries with skull fractures in Homicidal deaths. Ind J Res. 2019;8(3):39-40.
-
MishraPK, Singh S. Fatal head injury in homicidal deaths in Bhopal region of Central India. Int J Pharm Bio Sci 2013;3(4):1103-8.
-
Buchade D, Mohite S. Pattern of injuries in Homicidal cases in Greater Mumbai: a three-year study. J Int For Med. 2011;33(1):46-49.
-
Kasmaei VM,Asadi P, Zohrevandi B.An epidemiological study of traumatic brain injuries in the emergency department. Emergency 2015;4:266-74.
-
Hugar BS, Harish S. Pattern of Homicidal Deaths. J Int For Med. 2017;32(3):194-98.
-
PateDJ. Analysis of Homicidal Deaths in and around Bastar region of Chhattisgarh. J Int For Med. 2012;34(2):139-42.
-
Chattopadhyay S, Tripathi. Skull fracture snd haemorrhage pattern among fatal and nonfatal head injury assault victims - a critical analysis. J Inj Violence Res 2010;2(2):99-103.
-
Rupani R, Verma A, Rathore S.Pattern of skull fractures in cases of Head Injury by blunt force. J Int For Med. 2013;35(4):336-38.
-
ManishK, JyothiNS, GuruduttaSP. Fatal head injuries in road traffic accidents in and around Davangere. Ind J For Med Path. 2012;5(2):61-65.
-
Al-Qazzaz MA, Jabor MA. Medico-legal study of intra-cranial causes of death. Egy J For Sci. 2014;4(4):116-23.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License