IJCRR - 13(14), July, 2021
Pages: 194-199
Date of Publication: 20-Jul-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A Comparative Study on the Effect of Kinesio taping with Rigid taping in Computer Professionals with Chronic Non-specific Low Back Pain
Author: Mohan P, Sudhan SG, A Thangamani Ramalingam, Dhasaradharaman K, Suresh A
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Abnormal posture leading to back pain is a major work-related health problem, especially in software and IT-enabled services. Objective: It is intended to find out the effect of Kinesio taping compared with rigid taping in alleviating pain and disability for work-related chronic low back pain in computer professionals. Method: Study was conducted on 26 computer professionals with chronic low back pain, divided into two groups randomly and intervened with Kinesio taping(KT) in one group and rigid taping(RT) in another group. The outcome of pain and disability was measured using the McGill pain questionnaire and the Oswestry disability index. Both groups were compared for the mean difference and effect size on pain and disability by using ANOVA and Cohen's. Results: statistical analysis showed that KT or RT useful in reducing symptoms but there was a significant difference of P ≤0.05 between the Kinesio tape group and the rigid tape group in terms of pain and disability. Conclusion: Kinesio taping was more effective than rigid taping in reducing pain and disability for computer users with chronic low back pain.
Keywords: Chronic low back pain, Kinesio tape, Rigid tape, Work-related musculoskeletal disorder, Computer professionals
Full Text:
Introduction
Work-related pain is quite common for computer users as working for more than 40 hours a week may lead to musculoskeletal pain due to abnormal body posture and the tendency to develop injuries to muscles, joints, ligaments, and tendons. Computer work has created a new type of occupational health problems such as work-related musculoskeletal disorder. Abnormal posture leading to back pain is a major work-related health problem; especially in the software services industries.1 Non-specific low back pain was defined as “not related to identifiable known specific pathology (e.g. infection, inflammatory process, tumour, osteoporosis, fracture or radicular syndrome).2 Chronic pain in the low back due to non-pathological origin is considered to be a complex multidimensional bio-psycho-social pain disorder, where precise aetiology remains undefined.3 Low back pain (LOW BACK PAIN) is a significant clinical, social, and financial problem with prevalence ranging from 8% to 56% in the USA and it is measured that 28% of people suffering from pain in low back sometime during their lives, 14% with episodes lasting at least two weeks, 8% throughout during employment in any given year.4 Among all sort of Musculoskeletal disorders the lower back pain is commonly seen in Information Technology employees. Low back pain is that the second commonest explanation for disability in adults who lost workdays in America, which was estimated to lose 149 million days of labour per annum which was further estimated to cost $200 billion annually to scale back the productivity.5
The presence of computer within the workplace results in a group of weird characteristics of the workstation which require the workers to remain during a static posture for long periods and its most often cited risk factors resulting in musculoskeletal disorders. The presence of imbalance and abnormal strain on the musculoskeletal structure caused by deviation. Further, more computer usage is linked to Low back pain. Specifically, sitting for quite long hours combined with awkward postures or frequently working during a forward bent position has been found to extend the likelihood of Low Back Pain.6 Studies also indicated that specific tasks performed while sitting in an ergonomically unfit chair for extended periods were also related to low back pain.7 A slouched posture may be a quite abnormal sitting posture with the flexed lumbar spine that occurs during day-to-day sitting activities. As a result of this prolonged flexed posture, the neutral position is lost and therefore the spine is potentially exposed to injury.
The risk of developing musculoskeletal injury for computer users significantly rises if their body mass index increases so employees with obesity are prone to develop low back pain due to postural abnormality.8 The McKenzie exercises are one among the foremost frequently used sort of physiotherapy for back pain. It is based totally on the identification of a directional preference for spinal movement and may form the idea for the prescription of exercises. Improvement in symptoms is subsequently assessed in terms of ‘centralization’ a phenomenon that has been quite well documented. A recent systematic review of six trials concluded that there's some evidence for the short term effectiveness of McKenzie approach for subacute and chronic back pain patients.9 Spinal stabilization exercises (including Pilates) for the management of back pain is gaining popularity, this exercise might help to improve postural control and correct imbalances of activity between more deeply placed stability muscles and more superficially placed mobilizing counterparts. Although intuitively a useful approach for non-specific low back pain patients, spinal stabilization exercises to date are supported by a number of pieces of evidence.
Variety of physical modalities used for back pain such as transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation), heat/cold, traction, laser, ultrasound, short wave diathermy, interferential therapy, corsets and collars. There’s limited evidence to suggest that electrotherapy (laser therapy, therapeutic ultrasound and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) isn't effective for reducing neck and back pain. However, the overall conclusions from systematic reviews are that there is insufficient evidence from good-quality studies to either support or refute the clinical use of physical modalities for patients with back or neck pain. The placebo effects of passive modalities may be a robust effect where both the therapist and the patient have faith within the treatment. However, dependency on physical modalities could encourage passivity, inactivity and disability behaviour.
In India, the occupational health personnel are working on this group of modern occupational diseases, which are slowly taking their roots among the Ing=formation Technology professionals. If these problems are ignored, can cause serious injuries and forcing one to change their job.10.According to Borenstein, low back pain patients require regular physical activity to enable them to receive the most beneficial effect.11 Acute back pain seems to respond well to simple treatment measures, although there is a lot of variation in the benefit for individual patients. Various treatment methods being considered for nonspecific low back pain but the effectiveness of each method vary due to external and internal factors. Even though some scientific study has proven Kinesio or rigid tape application were useful but need to obtain concrete evidence which one will be more effective in managing low back pain. This study intended to explore the effectiveness of Kinesio taping compared with rigid taping for work-related lower back pain patients along with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and exercise as common protocol. Thus, the objective of this study is to find out the effect of the Kinesio taping technique, along with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and Exercise in reducing pain and disability on work-related low back pain for computer professionals.
Methodology
Subjects
Employees who were working in medium and large scale information technology company were selected as the subject for the study who have more than 3 years of experience in a sitting job with computers for not lesson than 8 hours per day for 5 days a week. subjects with a history of chronic low back pain not less than 3 months 12,13were screened for Low back pain,26 Subjects who fulfilled inclusion criteria were recruited for this study and subjects with a history of disc prolapse, spondylolisthesis, SI Joint syndrome, recent surgical intervention, structural scoliosis and radiculopathy were excluded from the study. The subjects were blinded about the possible intervention effectiveness of Kinesio tape or rigid tape. Informed consent was taken from all subjects who participated in the study and allowed to withdraw at any time during the period of intervention on their own. 26 subjects were divided randomly into 2 groups as Group “A” (Kinesio Tape Group) and Group“B”(Rigid Tape group) consist of 13 subjects each. Ethical clearance was obtained from the institutional ethical committee with reference number EC/04-2019/PT/PhD-2 for this study.
Procedure
General clinical examination and musculoskeletal assessment were performed pain and disability measured by McGill pain questionnaire and Oswestry disability index respectively as baseline data before the intervention. Both groups underwent treatment for 2 weeks with 3 sessions per week, after the intervention post-test measurement was taken. Group A(KT) were given Kinesio tape long with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and back exercise program, similarly Group B(RT) was treated by rigid tape along with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and back exercise program. The exercise program includes strengthening abdominal muscles and core extensor muscles along with flexibility exercise. End of every session subjects was applied with Kinesio tape or Rigid tape in the lumbosacral region and asked to report every alternative day to the Department and retain the tape for 48 hours. Subjects were advised to do all the core stability and flexibility exercise at home. 14
Kinesio Tape Procedure.
KT tape is cotton elastic hypo allergic tape used for the intervention of Group A subjects. All subjects underwent allergic test before starting treatment whereas KT tape patch was applied in the anterior surface of the elbow and observed after 48 hours for any allergic reaction if anyone found allergic to KT tape were excluded from this study. The taping area was cleaned, free of hair and the lumbar spine was flexed to measure the required length of tape. Three I-Tapes were used whereas two vertical and one horizontal tape applied in the lumbosacral region. The first 4 cm to 5 cm of tape was removed from its backing, the base of the tape was applied to the origin of erector spinae to its insertion while the sacrum in the neutral position then the patient was asked to do a maximum flexion of the spine and the paper backing of the tape was removed, except final 4 cm to 5 cm the tape was applied on one side in the direction of the cranium, with a slight stretch of tape and at the end without stretch. The same procedure was then applied to the contralateral side. The third strip was applied horizontally where maximum pain was observed such as erector spinae or interspinous or quadratus lumborum muscle with more than 50% stretch. The tape was rubbed by hand several times to warm the adhesive film to attach with the skin surface the tape was retained for 48 hours before changing to the next session. 14
Rigid tape procedure.
Hypo allergic under tape 50-mm strapping tape used over taping area before the rigid tape was applied. Subjects were in a lying prone or standing position whereas the Patient must be able to achieve a relaxed and pain-free extended lumbar posture (lordosis) while the tape was being applied and the tape was retained for 48 hours before changing to the next session. The spine is neutral to a slightly extended position with lumbar curvatures maintained, anchor strips were applied to the top and bottom of the area to be taped. An X was formed across the lumbar region from the top anchor to the bottom anchor, with the centre of the X overlying the L2–3 region. The top and bottom of the X were then re-anchored. Movements were assessed for pain-free range of motion in flexion and side flexion. 15
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) Procedure.
Transcutaneous electrical nervous stimulator stimulates peripheral nerves via skin surface electrodes at well-tolerated intensities which deliver the low-frequency current through superficial electrodes placed on the skin around the affected area which induce a tingling sensation and disrupt the pain signal in the surrounding area. The dual-channel transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation unit was used, out of which one channel is placed Para spinally at the level of origin of the sciatic nerve and the other two electrodes are placed at the inferior angle of the scapula. The machine Acupuncture –like transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation used, at low frequency (5-10Hz) for 30 minutes. 16
Exercise Protocol
Exercise program mainly concerned with strengthening core muscles such as the pelvic floor muscles, transverse abdominals, multifidus, internal and external oblique, rectus abdominis, erector spinae (sacrospinalis) especially the longissimus thoracic, and quadratus Lumborum. The exercise was taught and performed five sessions per week for about two weeks supine abdominal draw, with double Knee to Chest, supine twist, prone bridging on Elbows, side bridging on the elbow, quadruped opposite arm/leg raise, Supine Butt Lift with Arms at Side, above given exercise performed 10 to 20 repetition per session. 17
Outcome measure
The McGill Pain Questionnaire consist of a three-part pain assessment tool that measures several dimensions of the patient's pain experience.18 The first part consists of an anatomic drawing of the human form on which the patient marks where his or her pain is found. The second part of the MPQ permits the patient to record the intensity of his or her current pain experience. The third part of the MPQ would be a pain verbal descriptor inventory consisting of 78 descriptive adjectives. Subjects were informed to choose appropriate words matching his or her pain perception and circle it as every dimension was individually scored and summated for the total score. The score ranges from 0 to 78 as 0 is no pain and 78 maximum pain. The Oswestry Disability index Questionnaire (Fairbank, Couper, Davies & O’Brien, 1980) was developed in the late 1970s and has been widely used. Ten sections cover Pain, self-care, Lifting, Walking, Sitting, Standing, Sleeping, Sex Life, Social Life, and Travelling.19 All section had six statements describing the level of disability from 0 to 5 with the maximum score of 50 and the same was converted to a percentage score. 18,19
Statistical analysis
Baseline and post-intervention data were analysed by statistical software SPSS 18.0 for comparison of the mean difference between and within groups by ANOVA. The effect size of the intervention was calculated using cohen’s d formula (Mean difference/pooled standard deviation).
Results
26 subjects were assigned into 2 groups with 13 subjects each, Group A underwent Kinesio tape intervention long with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and exercise had 8 male participants and 5 female participants with a mean age of 31.8 and BMI of 24.5. Group B underwent rigid tape technique long with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and exercise had 7 male and 6 female with a mean age of 30.3 and Body Mass Index of 24.1. Table 1 shows the total number of subjects with gender in both groups with percentage. Table 2 shows the age and BMI of all subjects with standard deviation.
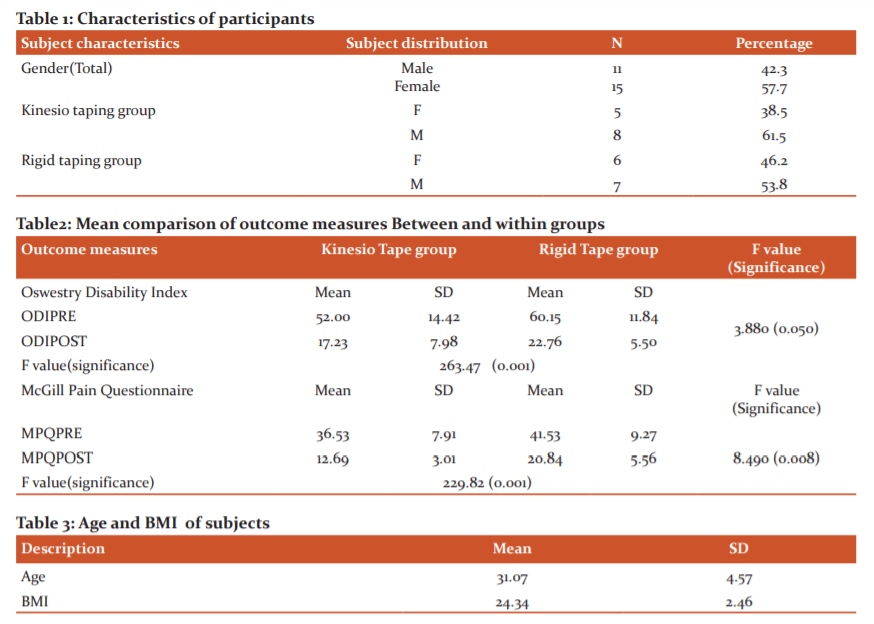
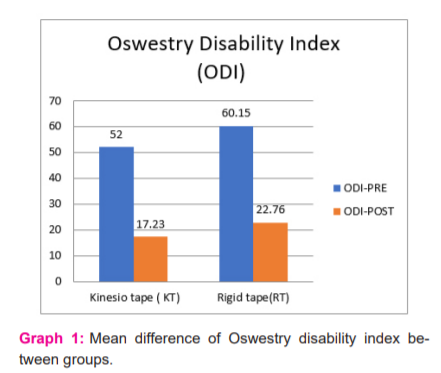
In Group A the mean value of baseline data for McGill pain score was 36.5and post-test measure was 12.7 when both data were compared for mean difference there was a high statistical significance P = 0.001 was found, similarly the disability score Oswestry Disability Index mean of baseline value was 52 and the post-test measure was 17 when both data were compared for the differences the P= 0.001 and it showed pain and disability considerably reduced after intervention of Kinesio taping. In Group B treated by rigid taping had a mean value of 41.5 and the post-test measure was 20.8 for pain score similarly the Oswestry Disability Index score of pre-test were 60 and post-test was 22.7 when both data were compared for differences it showed statistical significance in both parameters P=0.001 for pain and disability that indicates rigid tape group was helpful managing pain and disability. Table 3 Describes meaning comparison of pain and disability within and between the Kinesio taping group and Rigid taping group.
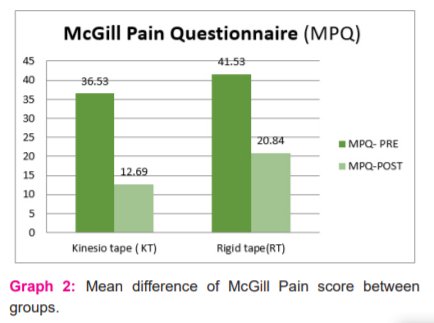
When both groups were compared for statistical difference in pain and disability Kinesio tape group was better than the rigid tape group in reducing pain and disability as the level of significance between the group for McGill pain score P = 0.008 and Oswestry Disability Index score P = 0.05 it indicates Group A Kinesio taping along with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and exercise was effective in work-related low back pain for computer professionals. Graph 1 shows the mean of pre and post measurements of Disability for the KT and RT group. Graph 2 shows the mean of pre and post measurements of pain for the KT and RT group.
Discussion
The present study included subjects not less than 3 months of chronic LBA. Kinesio taping along with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and exercise was effective in work-related low back pain for computer professionals. The statistical difference in the improvement of pain and disability was better in Kinesio tape than in the rigid tape group. Lower back pain was disabling and debilitating disorders for professionals who are working with desktop or laptop for more than 8 hours unless there was the attention given to prevent curate and rehabilitate, it's going to affect the employees in terms of productivity lead to loss of Compensation for the employers. Low back pain is more in industrialized Western countries that is the second commonest problems.20 The latest pieces of evidence of low back pain are of mechanical origin and initially occurs between 25 and 55 years aged. There are lot of interventions found to be effective for the management of work-related pain in computer professionals but the specific and superior techniques which yield better result are under investigation for a longer duration. In this present study, the attempt was made to identify whether the conventional method of back pain treatment such as exercise program and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation along with Kinesio tape was effective. The afferent neural structure is stimulated through transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation induces analgesia and additionally decreases the inflammation induces dorsal horn sensitisation (Sabino 2008), neurotransmitters like gamma-aminobutyric acid and glycine which are also involved in inhibition of nociceptive traffic, and modulation of the activity of the cells by supporting structure(glial cells) in the medulla spinalis, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation may produce all above effects to control pain.21,22,23
The combination of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and core stability exercise program along with the application of Kinesio tape or rigid tape was effective for chronic low back pain who are in a sedentary job. Kinesio tape supports injured muscles and joints and helps to relieve pain by lifting the skin by improved blood and lymph flow. A research study suggested that the Kinesio taping with a regular home exercise program for strengthening and flexibility reduces pain and disability.24 This present study found out rigid taping technique used for 2 weeks in lower back region Reduced pain and disability effectively, Rigid tape help to support lower lumbar region and stabilise Paraspinal muscles in contrast Kinesio tape helps to facilitate the back muscles and also reducing inflammation and promoting healing by improving blood circulation and lymphatic drainage. 24,25 Kinesio tape believed to reduce paravertebral muscle fatigue so it may be assumed to reduce musculoskeletal injury in computer professionals and also, facilitatory application provide adequate anticipatory postural control in back muscles to maintain correct posture during working hours.26
Conclusion
Both the kinesio tape group and rigid tape group were helpful to reduce pain and disability for subjects with work-related chronic low back pain in Computer professionals but the Kinesio tape group was better than the rigid tape group when compared for effectiveness.
Conflict of interest: No conflict of interest
Acknowledgement: The authors thank the management of Garden city University to carry out this study.
Funding Source: Self-financing – No external funding source
Author contribution:
1. Prasanna Mohan - Conception and design of the study, analysis, and interpretation of data & Drafting the manuscript
2. Sudhan SG - Study design & Acquisition of data, Drafting of the manuscript
3 A Thangamani Ramalingam - Revision of the manuscript & data analysis
4 Kannan Dhasaradharaman-Data acquisition & analysis
5. Anjali Suresh -Revision of the manuscript
References:
1.Bhuyar P, Banerjee A, Pandve H, Padmanabhan P, Patil A, Duggirala S, et al. Mental, physical and social health problems of call centre workers. Indian Psychiatry J. 2008;17:21–5.
2. Burton AK, Balagué F, Cardon G, Eriksen HR, Henrotin Y, Lahad A, Leclerc A, Müller G, van der Beek AJ; COST B13 Working Group on Guidelines for Prevention in Low Back Pain. Chapter 2. European guidelines for prevention in low back pain: November 2004. Eur Spine J. 2006 Mar;15 Suppl 2(Suppl 2): S136-68.
3.Borkan J, Van Tulder M, Reis S, Schoene ML, Croft P, Hermoni D. Advances in the field of low back pain in primary care: a report from the fourth international forum. Spine.2002;27(5):E128-32.
4. Manchikanti L. Epidemiology of low back pain. Pain physician. 2000;3(2):167-92.
5.Katz JN, Lumbar disc disorders and low-back pain: socioeconomic factors and consequences. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88 (2) 21- 24 6.
6.Spyropoulos P, Papathanasiou G, Georgiadis G, Chronopoulos E, Koumoutsou F. Prevalence of low back pain in Greek public office Workers. Pain Physician. 2007;10:651-9.
7.Ferguson SA, Marras WS. Work Place design guidelines for asymptomatic and low back injured workers. Applied Ergonomics. 2005;36:85-95.
8. Mohan P, Sudhan S. G Dhasaradharaman K, Suresh A. Work-related Musculoskeletal Injury Risk Assessment and its relevance to Body Mass Index for Computer Professionals. Biomed Pharmacol J. 2020;13(2): 843-48
9.Kjellman G, Oberg B. A randomised clinical trial comparing general exercise, McKenzie treatment and a control group in patients with neck pain. J RehabilMed. 2002;34:183–90.
10. Choudhary SB, Sapur S, Deb PS. Awkward posture and development of RSI (Repetitive strain injury) in computer professionals. Indian J Occup Environ Med. 2002;6:10–2.
11. Borenstein DG. A clinician's approach to acute low back pain. Am J Med. 1997;102(1A):16-22.
12. Airaksinen O, Brox JI, Cedraschi C, Hildebrandt J, Klaber-Moffett J, Kovacs F, Mannion AF, Reis S, Staal JB, Ursin H, Zanoli G; COST B13 Working Group on Guidelines for Chronic Low Back Pain. Chapter 4. European guidelines for the management of chronic nonspecific low back pain. Eur Spine J. 2006 Mar;15(2): S192-300.
-
Gordon W. The Back Pain Revolution. 2 ed: Churchill-Livingstone; 2004:182-85
-
Fahad AlBahel, Ashraf , Ramadan Hafez, Abdul Rahim Zakaria,Abdulaziz Al-Ahaideb, Syamala Buragadda ,Ganeswara Rao Melam. Kinesio Taping for the Treatment of Mechanical Low Back Pain. World Appl Sci. 2013; J.22 (1): 78-84.
-
Rose MacDonald. Taping Techniques: Principles and Practice.London:2nd Revised edition, Elsevier Health Sciences2004.142-143
-
Claydon LS, Chesterton Am. Does transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) produce 'dose-responses'? A review of systematic reviews on chronic pain. Phys Ther Rev.13:6, 450-463.
-
Akhtar MW, Karimi H, Gilani SA. Effectiveness of core stabilization exercises and routine exercise therapy in the management of pain in chronic non-specific low back pain: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Pak J Med Sci. 2017;33(4):1002-1006.
-
Melzack R. The McGill Pain Questionnaire: major properties and scoring methods. Pain. 1975;1(3):277-299.
-
Fairbank JC, Couper J, Davies JB, O'Brien JP. The Oswestry low back pain disability questionnaire. Physio. 1980;66(8):271-273.
-
Dettori JR, Bullock SH, Sutlive TG, Franklin RJ, Patience T. The effects of spinal flexion and extranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation exercises and their associated postures in patients with acute low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20(21):2303-2312.
-
Sabino GS, Santos CM, Francischi JN, de Resende MA. Release of endogenous opioids following transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation in an experimental model of acute inflammatory pain. J Pain. 2008 Feb;9(2):157-63.
-
Somers DL, Clemente FR. Contralateral high or a combination of high? and low?frequency transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation reduces mechanical allodynia and alters dorsal horn neurotransmitter content in neuropathic rats. J Pain 2009;10(2):221?9
-
Matsuo H, Uchida K, Nakajima H, Guerrero AR, Watanabe S, Takemura N, et al. Early transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation reduces hyperalgesia and decreases activation of spinal glial cells in mice with neuropathic pain. Pain 2014;155(9):1888?901.
-
Uzunkulao?lu, A., Güne?Aytekin, M., Ay, S., &Ergin, S. (2018). The effectiveness of Kinesio taping on pain and clinical features in chronic non-specific low back pain: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Turk J Phys Med Rehabil.64(2), 126–132.
-
Trobec K, Peršolja M. Efficacy of Kinesio taping in reducing low back pain. J Health Sci.2017;7(1):1-8
-
Bae SH, Lee JH, Oh KA, Kim KY. The effects of Kinesio taping on potential in chronic low back pain patients anticipatory postural control and cerebral cortex. J Phys Ther Sci 2013;25(11):1367-71.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License