IJCRR - 13(14), July, 2021
Pages: 184-188
Date of Publication: 20-Jul-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Comparative Evaluation of the Efficacy of 4% Articaine and 2% Lignocaine During Orthodontic Extraction: A Randomized, Double-Blind Study
Author: Jain M, Dogra N, Gupta M, Grover S
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Local anaesthetics block the peripheral nerves and are used to prevent pain, during surgical and dental procedures. The primary object of this investigation was to compare and evaluate the efficacy of 4% Articaine hydrochloride with 1:100000 adrenaline and 2% Lignocaine hydrochloride with 1:80000 adrenaline during orthodontic extraction of maxillary first premolar. Methods: This prospective randomized, double-blind study was conducted from February 2013 to September 2014 on 43 patients less than 40 years of age requiring bilateral maxillary first premolar extractions for orthodontic purposes. Each patient was randomly assigned to receive either 2% lignocaine hydrochloride or 4% articaine hydrochloride for premolar extraction of one side and another solution was administered for the premolar extraction of contralateral side spaced 1 to 3 weeks apart.In each patient, the difference in the pain levels,onset of anesthesia and duration of anesthesiawas assessed on the administration of lignocaine hydrochloride and articaine hydrochloride. Results: There was statistically no significant difference in pain levels between orthodontic extraction of maxillary first premolar between the Articaine and Lignocaine groups. (p>0.05).The Articaine group had an earlier onset of anaesthesia after buccal infiltration and palatal infiltration as compared to the lignocaine group. The mean duration of anaesthesia was longer in the articaine group as compared to the highly significant lignocaine group. Conclusions: Articaine can be used as a suitable alternative to lignocaine in the extraction of maxillary premolars for orthodontic reasons with clinical advantages like faster time of onset, longer duration, and greater diffusing property over lignocaine.
Keywords: Local anaesthetic, Lignocaine hydrochloride, Articaine hydrochloride, Orthodontic Extraction, Prospective study, Double blind study
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Ever since the introduction of synthetic local anesthetic agents in surgical practice, clinically adequate pain control with minimum side effects has been the goal and desirable prerequisite for painless procedures.1 The ability to provide safe, effective local anesthetic is the cornerstone of successful clinical and surgical practice. Local anesthetics form the backbone of pain control techniques in dentistry.2
The history of local anaesthesia dates back to 1859 when cocaine was isolated by Niemann. Since the introduction of cocaine local anaesthesia (1886), and the subsequent development of procaine (1904) and other related type anaesthetics, dentistry has prided itself on being as close to “painless” as possible. In the late 1940s a new group of local anaesthetic compounds, the amide was introduced. The initial amide local anaesthetic, lidocaine (Xylocaine), revolutionized pain control. A new class of local anaesthetic was synthesized in 1943called Lidocaine. It was marketed under the proprietary nameXylocaine and successfully replaced procaine. Lidocaine was found to have faster action of action, longer duration of anaesthesia as compared to the esters .3
In 1969, Carticaine was first prepared by Rushing and colleagues and had its generic name changed to Articaine when it entered clinical practice in Germany in 1976 as a local anesthetic.4Articaine differs from the previous amide local anaesthetic in being derived from a thiophene ring instead of the usual benzene ring which gives the molecule better diffusion properties as compared to lidocaine. It contains an additional ester group that is quickly hydrolyzed by plasma esterase which gives Articaine an elimination half-life of approximately 90 minutes.5,6
The objective of this study was to evaluate the anaesthetic efficacy of 4% ArticaineHCl with 1:100000 adrenaline and 2% Lignocaine HCl with 1:80000 adrenaline in bilateral extraction of maxillary premolars for orthodontic purposes and also to compare both local anaesthetic agents for the difference in the pain levels, onset for of anaesthesia and duration of anaesthesia.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This prospective randomized, double-blind study was conducted on 43 patients (28 females and 15 males), aged less than 40 years who reported bilateral orthodontic extractions of upper premolar teeth to the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, from February 2013 to September 2014.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The participants were selected under the following criteria - age less than 40 years, American Society of Anesthesiologists Grade- I patients (a healthy individual with no systemic disease), having cooperative behaviour for dental treatment under local analgesia. But the participants - were excluded from the study under the following criteria - Medically compromised patients, pregnancy, history of allergy to lignocaine/articaine or any of the constituents in local anaesthetic solutions, age more than 40 years, and children below the age of reasoning infection/ inflammation near the site of injection, smokers, alcoholics.
50 cartridges each containing 1.8 ml of 2 % lignocaine hydrochloride with 1: 80,000 epinephrine and 50 cartridges each of 1.7 ml of 4 % articaine hydrochloride with 1:1, 00,000 epinephrine were masked by coloured tapes of two different colour (blue and green) by the independent observer to prevent identification. Randomization codes were held by the staff member who was responsible for giving masked cartridges but had no role in drug administration or in assessing outcomes. Neither the patient nor the surgeon had any knowledge of the identity of the solution so that the double-blind nature of the trial was ensured. In all patients, a thorough medical history and preoperative radiographs (OPG) were taken. After a brief examination, patients who met all the criteria had the first treatment visit for the extraction of the upper first premolar teeth of one side and were randomly assigned to receive either 2% lignocaine hydrochloride with 1:80000 adrenaline (Lignocaine special, Septodont India private health care) or 4% articaine hydrochloride with 1:100000 adrenaline (Septanest, Septodont India private health care)for the first procedure and the other solution was administered for the extraction of upper first premolar of contralateral sides at no less than one week (to eliminate possible carry-over effects) and not greater than three-week interval. Before administration of local anaesthesia, each patient was explained about the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS). The patient was asked to mark the scale from “0-10” numerical rating in the language (English or Hindi) which the patient understood (Figure 1 ). To interpret the data VAS scale was divided into 4 categories. No pain corresponding to “0” on the scale. Mild pain corresponding to score “1 to 3” on the scale whereas moderate and severe pain corresponding to “4 to 6” and “7 to 10” on the scale.
A standard maxillary infiltration injection containing either of the two solutions 0.8 ml solution of 1.7 ml of 4% articaine hydrochloride with 1:1,00,000 adrenaline or 1.8 ml of 2% lignocaine hydrochloride with 1:80,000 adrenaline was administered in the buccal vestibule using a self- aspirating syringe with 30-G needle ( {.31mm × 25mm} DENJECT disposable needle 30G -L ). The injection target site was centred over the buccal root apices of the maxillary premolar. The lip was gently retracted, and the needle was placed gently into the alveolar mucosa (needle insertion phase) with a bevel directed towards the bone and was advanced within 2-3 seconds until the needle was estimated to be at or just superior to the apices of the tooth (needle placement phase). The anaesthetic solution was deposited over 1 minute (solution deposition phase). Pain on injection was rated by asking the patient to mark a standard numeric VAS scale immediately after buccal infiltration was completed. After depositing the anaesthetic solution the time to anaesthetic effect on the buccal and palatal side was recorded as the time elapsed from the full withdrawal of needle until the patient indicated the first evidence of Vincent’s sign objectively. Subjective confirmation was done with a standard probe every 30 seconds until no response was recorded for 10 minutes on the buccal and palatal side using a stopwatch in minutes. Palatal infiltration was administered 10 minutes after buccal infiltration when it was observed that palatal anaesthesia was not achieved with buccal injection. If the patient complained of pain on the buccal or palatal side then the need for re-anaesthesia was considered. After palatal injection patient was again asked to mark the VAS scale to record the pain on palatal injection. The onset of palatal anaesthesia was checked on every 30 seconds till 10 minutes until no response was observed. After the successful anaesthesia had been achieved the tooth was extracted using a standard forceps’ technique under sterile aseptic conditions and a pressure pack was placed. Post-operative instructions were given and only analgesics (Tab. Ibugesic plus TDS × 3 days) was prescribed. The duration of anaesthesia was recorded as the time from initial pain perception of the anaesthetic effect to the moment in which the effect began to fade. Patient marked fliers distributed to them representing the loss of intensity of heaviness (+ + + + + + to -), as the time elapsed from 30 minutes to 6 hours, after extraction, of 15-minute interval. This was also confirmed by a telephone conversation with the patient. Postoperative complications if present were observed.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
The data were entered in the Microsoft Excel spreadsheet 2013. The student’s unpaired t-test analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Version 24.0 (Armonk, NY: IBM Corp.). The VAS scores by t-test were calculated. P-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
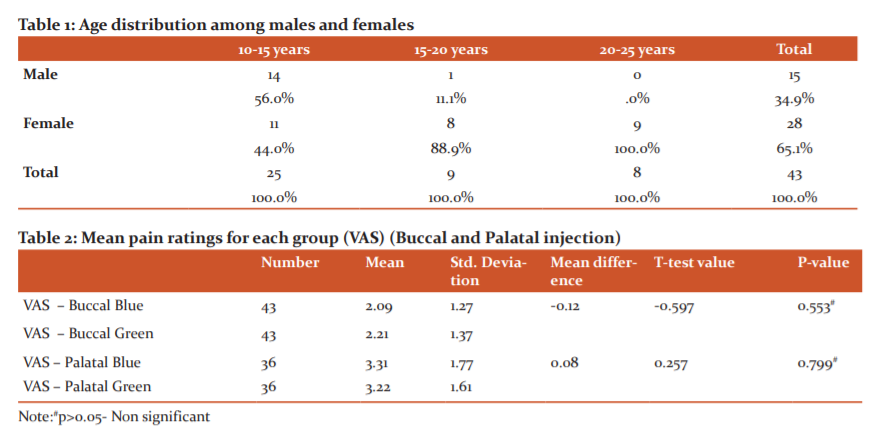
Table 1 illustrates the age distribution among males and females. Out of 43 patients included in the study, 34.9% of patients were male and 65.1% of patients were females. 14 patients in the male group were in the age group of 10-15 years and 1 in the age group of 15-20 years. 11 patients in the female group were in the age group of 10- 15 years, 8 in the age group of 15-20 years of age, and 9 in 20 – 25 years of age.
Pain on buccal and palatal injections was compared between blue (Articaine group) and green (Lignocaine) groups using Paired T-test. Table 2 shows that there was statistically no significant (p-value>0.05) difference between the Blue (Articaine) and Green (Lignocaine) groups for pain on injection on the buccal and palatal sides.
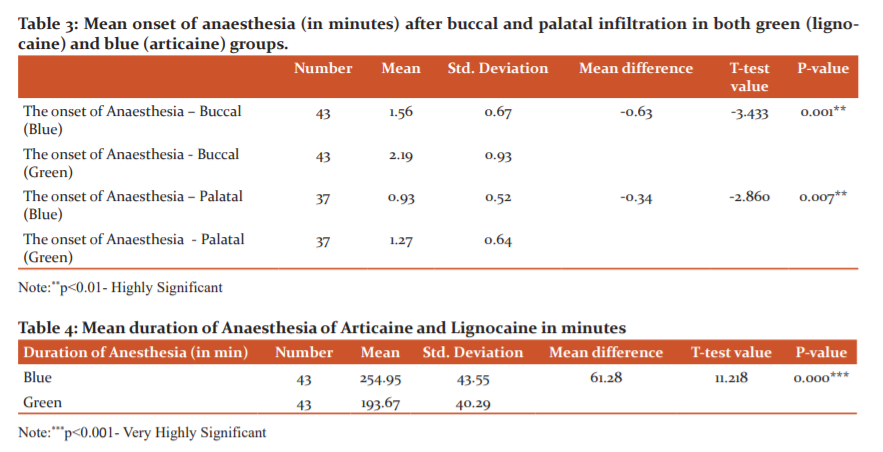
The mean for the onset of anaesthesia was calculated by paired T-test. Table 3 shows the mean onset of anaesthesia after buccal infiltration in the green (lignocaine) group which was 2.19 minutes as compared to the blue (articaine) group which was 1.56 minutes and the difference was statistically significant (p-value<0.05). Mean onset of anaesthesia after palatal infiltration in the green group (lignocaine) was 1.27 minutes as compared to that of the blue group (articaine) which was 0.93 minutes and the difference was statistically significant (p-value<0.05).
The mean duration of anaesthesia was compared in both groups using a paired “t” test. Table 4 illustrates the mean duration of anaesthesia of 193.67 minutes with the green (lignocaine) group and 254.95 minutes with the blue group (articaine) group. The difference was statistically significant (p-value<0.05) giving the inference that the blue (articaine) group has a longer duration of anaesthesia compared with the green (lignocaine) group.
DISCUSSION
Lignocaine is, today the ‘Gold Standard’ local anaesthetic agent against which all new local anaesthetics are compared .1 Lignocaine 2% combined with a vasoconstrictor in a 1:1, 00,000 concentration provides reliable and profound pulpal anaesthesia for approximately 60 minutes with a duration of soft tissue anaesthesia ranging from 3 to 5 hours. Lignocaine is also supplied as a 2% solution with 1:50,000 epinephrine. Although this concentration may be useful to provide surgical hemostasis by local infiltration, its routine use for primary operative or surgical anaesthesia should be avoided because of the possibility of an acute epinephrine reaction, which may often manifest as hypertension or tachycardia in susceptible patients.7In 1969, Ruschinget al.,synthesizedArticaine hydrochloride with the name of articaine and in 1976 it was marketed in Germany. The pharmacological characteristics of this anaesthetic are responsible for its main advantages concerning other local anaesthetics and include a substitution of the aromatic ring that increases the lipid solubility of the drugs as well as potency (1.5 times greater than of the lignocaine).8
No difference was observed in the intensity of pain on injection on buccal infiltration in both groups. However, palatal infiltration in both groups was more painful than their buccal counterparts. These results were by the findings of Malamed et al., who found no significant difference in VAS pain scores between subjects receiving articaine with epinephrine and those receiving lignocaine with epinephrine .4
Onset and duration periods must be considered when comparing two or more local anaesthetic agents. An ideal agent must have a shorter onset and should last for a sufficient time to allow the completion of the desired procedure. 9
In our study mean onset of anaesthesia after buccal injection had a significant difference between articaine and lignocaine groups. The lignocaine group had higher mean onset of anaesthesia as compared to the articaine group suggesting a shorter onset of action in the articaine group. Costa et al. reported a higher mean onset for lignocaine (2.8 minutes), followed by 4% articaine with 1:200000 epinephrine ( 1.6 minutes) and 4% articaine with 1:100000 epinephrine (1.4 minutes). 9
Kambalimath et al. also reported similar results with a mean onset time of 4 % articaine as 2-3 minutes when compared to 3 minutes for the lignocaine group.10 Similar findings were reported by Colombini et al. and Rebolledo et al. 11,12 Shorter mean onset of anaesthesia in articaine group could be attributed to smaller dissociation constant (pKa = 7.8) of articaine as compared to lignocaine which has greater dissociation constant (pKa = 7.9)
In this study, the mean duration of anaesthesia achieved with the articaine group was longer than that achieved with the lignocaine group. Similar results were reported by Rebolledo et al., Sreekumaret al., and Bansal et al.12,8,13 The duration of the effect of an anaesthetic depends upon its degree of protein binding. The injection site or concentration of vasoconstrictor present in the anaesthetic solution also affects the duration of the effect of the local anaesthetic among other factors. Among all amide local anaesthetics, Articaine has the highest protein binding percentage. This in turn implies a longer duration of the anaesthetic effect.
Further controlled clinical trials with similar local anaesthetic agents in other areas of the oral cavity in the form of infiltration and nerve block are necessary to evaluate the safety and efficacy of articaine.
CONCLUSION
The efficacy of 4% articaine with 1:1, 00,000 epinephrine based on the Visual Analogue Scale was better than 2% lignocaine with 1:80,000 epinephrine, indicating that articaine provides adequate analgesia for the procedure to be performed. The efficacy of 4% articaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine was found to be comparable to 2% lignocaine with 1:80,000 epinephrine. The Onset of anaesthetic action of 4% Articaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine was found to be shorter than 2% lignocaine with 1:80,000 statistically significant epinephrine. 4% Articaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine was found to have a longer duration of action than 2% lignocaine with 1:80,000 epinephrine thus adding to the patient comfort after the extractions by increasing the pain-free duration. This difference was statistically highly significant.ThusArticaine can be used as a suitable alternative to lignocaine in the extraction of maxillary premolars for orthodontic reasons with clinical advantages like faster time of onset, longer duration, and greater diffusing property over lignocaine. Thus more studies in the future with a larger sample size must be performed where the difficulty of extraction and complications are recorded in addition to evaluation of the efficacy of the Articaine over lignocaine.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest: Nil
Financial support: Nil
Author’s contribution
Dr. Meenu Jain: Concepts, design of the study, investigation, and statistical analysis, Dr. NamrataDogra: Definition of intellectual content, and statistics.Dr. Manish Gupta: Manuscript editing and review of literature: Dr. Seema Grover: Writing results.

References:
-
Dugal A, Khanna R, Patankar A. A comparative study between 0.5% centbucridineHCl and 2% lignocaine HCl with adrenaline (1:200000). J Maxillofac Oral Surg.2009 ;8(3):221-223.
-
Malamed SF, Gagnon S, Leblanc D. Articaine hydrochloride: the study of the safety of a new amide local anesthetic. J Am Dent Assoc.2001;132(2):177-185.
-
Malamed SF. Local anesthetics: dentistry's most important drugs, clinical update 2006. J Calif Dent Assoc. 2006; 34(12):971-976.
-
Malamed SF, Gagnon S, Leblanc D. Efficacy of Articaine: A new amide local anesthetic: J Am Dent Assoc. 2000;131:635-642.
-
McLure HA, Rubin AP. Review of local anaesthetic agents. Minerva Anestesiol. 2005; 71(3):59-74.
-
Malamed SF, Gagnon S, Leblanc D. A comparison between articaine HCl and lidocaine HCl in pediatric dental patients. Pediatr Dent. 2000 ; 22(4):307- 311.
-
Giovannitti JA, Rosenberg MB, Phero JC. Pharmacology of local anaesthetics used in oral surgery. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2013;25(3):453-465.
-
Sreekumar K, Bhargava D. A Prospective double-blind study to assess the latency and efficacy of articaine and lignocaine in surgical removal of impacted mandibular third molars in Indian patients. J Stomat Occ Med. 2012; 5: 10-14.
-
Costa CG, Tortamano IP, Rocha RG, Francischone CE, Tortamano N. Onset and duration periods of articaine and lidocaine on maxillary infiltration. Quintessence Int. 2005;36(3):197-201.
-
Kambalimath DH, Dolas RS, Kambalimath HV, Agrawal SM. Efficacy of 4 % Articaine and 2 % Lidocaine: A clinical study. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2013 ;12(1):3-10.
-
Colombini BL, Modena KC, Calvo AM, Sakai VT, Giglio FP, Dionísio TJ, Trindade AS Jr, Lauris JR, Santos CF. Articaine and mepivacaine efficacy in postoperative analgesia for lower third molar removal: a double-blind, randomized, crossover study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;102(2):169-74.
-
Sierra Rebolledo A, Delgado Molina E, BeriniAytís L, Gay Escoda C. Comparative study of the anaesthetic efficacy of 4% articaine versus 2% lidocaine in inferior alveolar nerve block during surgical extraction of impacted lower third molars. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2007;12(2): E139-144.
-
Bansal SK, Kaura S, Sangha PK, Kaur P, Bahl R, Bansal S. Comparison of anaesthetic efficacy of 4% articaine versus 2% lignocaine. Indian J Dent Sci. 2018;10:92-97.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License