IJCRR - 13(14), July, 2021
Pages: 156-160
Date of Publication: 20-Jul-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Preparation and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles of Nickel, Copper and Zinc
Author: Budde Kumara Swamy, Raju Bura, Ramreddy Godela, K. Venkata Ratnam, K. Suresh Babu
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Metal Oxide Nanoparticles can show distinctive physical and chemical properties due to their limited size. Metal oxide nanoparticles have been a hotspot in nanomaterials research due to the wide range of application in the pharmaceutical, biomedical, electronics, optics, energy storage industry and catalysis. Aim: To prepare the metal oxide nanoparticles of copper, nickel and zinc by the sol-gel method and evaluate their antibacterial and antifungal activity against the selected gram-positive, gram-negative bacterial strains and fungal strains respectively. Methodology: Three different variants of each metal oxide nanoparticles were obtained by employing an annellation of the In-situ generated metal hydroxide at temperatures 250, 450 and 6500C. Streptomycin (100\?g/ml) and Nystatin (10\?g/ml) were employed as reference standards for the evaluation of the antimicrobial and antifungal activity of the different variants of each metal oxide nanoparticles. Results: The experiments of antimicrobial assay revealed that the CuO nanoparticles possess the highest antibacterial activ�ity than the remaining metal oxide nanoparticles. ZnO and NiOnanoparticles have displayed better activity against the fungal strains. Relatively the nanoparticles produced at 450 and 6500C temperatures displayed superior antimicrobial activity than the pure metal oxides and nanoparticles produced at 2500C. Conclusion: The CuO nanoparticles calcinated at higher temperatures like 450, and 6500C were displaying higher antimicrobial activity relative to the pure metal oxides and those calcinated at 2500C.
Keywords: Metal oxides, Nanoparticles, Annellation, NiO, CuO, ZnO and Antimicrobial activity.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Research in the field of nanotechnology is existing for centuries and helped in the production of various types of materials at the nano scale. These materials are particulate substances with dimension < 100nm. The field of nanotechnology mainly encompasses biology, physics, chemistry and material sciences and it develops novel therapeutic nano-sized materials for biomedical and pharmaceutical applications.1 Metal oxide nanoparticles have been a hotspot in nanomaterials research due to the wide range of application. Progress in synthesizing metal oxide nanoparticles is phenomenal due to its application in electronics, optics, energy storage industry and catalysis.2-5 Since 1980, efforts have been made to invent synthetic methods for nanoparticles with desired properties. Synthesis of the nanomaterials is categorized into two types, the top-down approach and the bottom-up approach. Wet chemical synthesis approaches have been realized to produce the desired size and shape of metal oxide nanoparticles in a reproducible manner. Control over size and shape is achieved by a better understanding of elementary events, the mechanism by conversion of the precursor, surface stabilizing agent, and reagent in the system and its correlation with growth and nucleation rate.6The antimicrobial properties of silver oxide, copper oxide, zinc oxide and nickel oxide have been previously reported.7-10 The bactericidal effectiveness of metal nanoparticles has been suggested to be due to both their size and high surface-to-volume ratio. Such characteristics should allow them to interact closely with bacterial membranes, rather than the effect being solely due to the release of metal ions.11,12
Owing to the increasing importance of the metal oxide nanoparticles as anti-microbial agents as suggested by a handful of literature our group is vigorously involved in the development of new metal oxide nanoparticles at different temperatures that can be applied as anti-microbial agents with sub-micromolar activity against tested bacterial strains. This manuscript reports the synthesis, anti-microbial and antioxidant capacity of the NiO, CuO and Zn On a noparticles calcinated at different temperatures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Experimental
Synthetic grade Nickel Nitrate Hexahydrate (Ni(NO3)2·6H2O), Copper Nitrate Trihydrate (Cu(NO3)2·3H2O) and Zinc Nitrate Hexahydrate (Zn(NO3)2·6H2O) were procured from Merck, India. Sodium hydroxide purchased from SD fine chemicals, India. X-ray diffraction (XRD) of metallic and bimetallic nanoparticles was determined by using PANanalytical ‘X’PERT-PRO XRPD of Cu Ka radiation (l = 0.15406 nm) with a scanning rate of 20/min and 2? ranging from 100 to 800.
Preparation of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles
For the preparation of three different grades of metal oxide nanoparticles via the annellation of corresponding metal hydroxides, 0.1M concentration of precursors, Nickel Nitrate Hexahydrate (Ni(NO3)2·6H2O), Copper Nitrate Trihydrate (Cu(NO3)2·3H2O) and Zinc Nitrate Hexahydrate (Zn(NO3)2·6H2O) were reacted individually with 1M solution of NaOH. The resulted In-situ generated hydroxide form of three metals were subjected for annellation at temperatures 2500C, 4500C, 6500C to generate the different grades of respective metal oxides NiO, CuO, and ZnO.13,14,15,16
AntimicrobialAssay17
Test Microorganisms and Growth Media
The bacterial and fungal strains were obtained from the department of microbiology, Osmania University.StreptococcusPyogenes (MTCC 442), Bacillus cereus (MTCC 1305) Salmonella enterica (MTCC 1253) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MTCC 2453), Aspergillusniger and Candida albicans were chosen based on their clinical and pharmacological importance. Incubation of bacterial stock is done at 37°C for 24 hrs. on nutrient agar. The bacteria were grown on Mueller-Hinton agar plates at 37°C. The stock cultures were maintained at 4°C. For the growth of fungi, Potato Dextrose agar was used.
Procedure for Antimicrobial assay
Preparation of Discs:
Insert Whatman No. 1 filter of 5mm disc size in a clean and dry petri dish and then autoclaved. The discs were later soaked in the compound solution for 5 hrs and shade dried later. The concentration is about 0.1 gm/ 1 ml per disc. Carefully transfer the disc onto the cultured petri dish. We use paper disc dipped in ethanol as positive control are prepared and used as positive control and streptomycin in the concentration of 100μg/ml and Nystatin in the concentration of 10µg/ml were employed as negative controls for the Antibacterial and Antifungal activity respectively.
Testing of Antimicrobial activity
LB agar prepared and the medium is sterilized for 30 mins at 121°C for testing antibacterial activity. The test plates are prepared by pouring 10 ml of the medium into a petri dish of 10 cm diameter under aseptic condition. They were left undisturbed for 2 hrs to allow the medium for solidification. (containing suspension) of Streptococcus Pyogenes, Bacillus cereus, Salmonella enterica and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Aspergillusniger and Candida albicans was poured onto the plates separately containing solidified agar media. The prepared sterile filter paper discs were impregnated with the compound solution and shaken thoroughly and these test plates incubated for a period of 48 hrs in BOD at 37ºc for the development of inhibitory zones and the average of 2 independent readings for each organism in different compound solutions were recorded.
Measuring the diameter of inhibition zone
The measurement of inhibition zones is noted after one day at 37°C for bacteria. A plastic ruler is used to measure and record the diameter of the inhibition zone. 5 paper disc are placed on a single Petri plate.
RESULTS
Synthesis
Stable Nanoparticles of NiO, CuO and ZnO were synthesized at different temperatures by the annellation of corresponding metal hydroxides generated In-situ, in the reaction mixture using the Sol-gel method. Three different grades of the nanoparticles having variable size ranges were obtained based on the annellation temperature. The mean particle size of the synthesized nanoparticle and their FWHM and 2-THETAvalues were enumerated in Table-1.
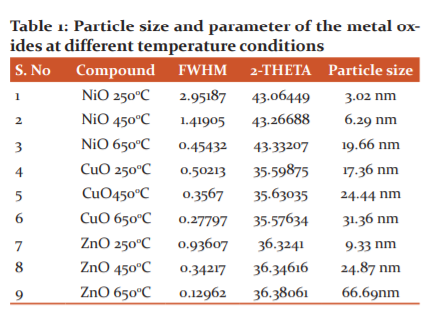
NiO nanoparticles resulted with a mean particle size ranges from 3.02 nm to 19.66 nm, CuO nanoparticles size ranges from 17.36 nm to 31.36 nm and ZnO nanoparticles size ranges from 9.33 nm to 66.69 nm. The XRD results proclaim that the annellation of the metal hydroxide at different temperature produced nanoparticles of varying sizes. This suggests that the temperature affect the size of nanoparticles produced via the Sol-Gel method. SEM analysis results provided the morphology of the synthesized nanoparticles. Results revealed that the nanoparticles annealed at 6500C provided spherical morphology while the annellation at temperatures 250 and 4500C produced the particle with irregular shapes.
Antimicrobial activity
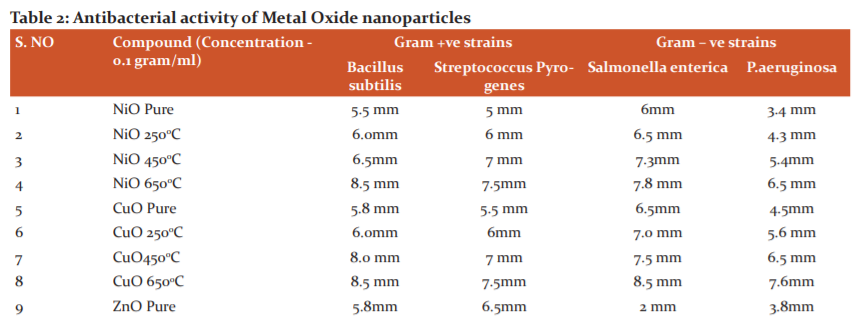
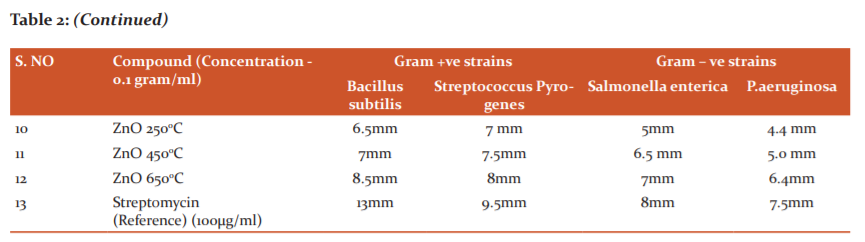
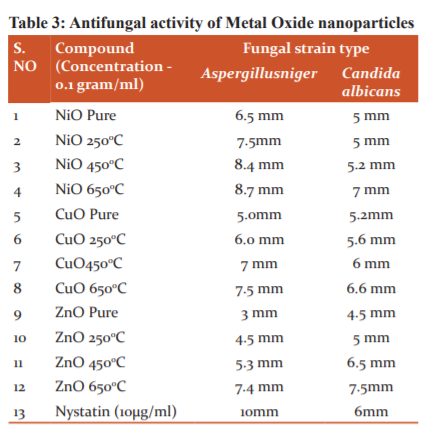
The compounds were screened for their antibacterial activity (zone of inhibition) against Streptococcus Pyogenes (MTCC 442), Bacillus cereus (MTCC 1305) Salmonella enterica (MTCC 1253) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MTCC 2453), along with Antifungal activity againstAspergillusniger and Candida albicans strains using disc diffusion method according to the literature protocol. The antibacterial activity of the synthesized metal oxide nanoparticles was compared with standard drugs treptomycin at a concentration of 0.1gram/ml and the results of Antibacterial and Antifungal activity (zone of inhibition) have been presented in Table 2 and 3 respectively.
-
Antibacterial studies using CuO, ZnO and NiO nanoparticles against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative bacteria
Based on the test results, it is evident that the CuO nanoparticles have displayed superior antibacterial activity than the remaining NiO and ZnO nanoparticles on both gram-positive and gram-negative strains. Cu nanoparticles especially those nanoparticles calcinated at the temperature of 6500C (CuO 650) has possessed the highest antibacterial activity against all bacterial strains tested. ZnO and NiO particles disclosed antibacterial activity majorly against gram-positive strains. Zone of inhibition data of all the tested nanoparticles displays that the nanoparticles have superior inhibition capacity on all bacterial strains when compared to the pure forms of metal oxides. Based on earlier studies.18 The reasons might be whenever nanoparticle enters into the bacterial cell, the death of bacteria is due to either high production of ROS inside the bacterial cell leads to the creation of high oxidative stress or binding of copper nanoparticle to functional groups like carboxyl or amino present in peptidoglycan which is a component of the cell wall of bacteria. In the present study, we propose that the reason for the superior antibacterial activity of copper nanoparticles might be there is a strong affinity towards the functional groups like amino or carboxyl or mercapto. Results suggest that the nanoparticles are calcinated at temperature 4500C and 6500C were possessed more antibacterial activity potential than the pure metal oxides and are synthesized at 2500C. This increased activity can be comprehended and attributed to the decreasing size and spherical shape of the nanoparticles generated at much higher temperatures. The compounds CuO 250, CuO 650 showed good activity against bacterial strains salmonella and pseudomonas also. The results were shown in Table-2
Possible mechanisms of invade of Nanoparticles (NPs) on Bacteria19
Besides, the above findings interestingly raise some facts about the behaviour of nanoparticles to bacteria. The first one is, by comparing the zone of inhibition by Gram-positive to Gram-negative bacteria concerning the use of different types of nanoparticles, the results dig out NPS shows high bactericidal activity on Gram-positive than Gram-negative bacteria. Based on earlier reports, this is due to a structural difference in the cell wall of bacteria and it plays a crucial role in the binding of nanoparticle to the cell surface which confirms the complexity of the cell wall of Gram-negative higher than Gram-positive bacteria. Anyhow in Gram-negative bacteria having Lipoproteins(LPS), phospholipids etc form a strong barrier which repels NPs and in another way the Gram-positive bacteria possess a high negative charge on the surface which helps to attract NPs resulting metal NPs, from metal Oxide NPs, enters into the cell through diffusion using porins as ionic channels and shows strong bactericidal effect. The second one, by comparing of results of zone inhibition data (table-3) to particle size (table 1), we confirm that the small size nanoparticles shows high bactericidal effect. This size effect of NPS explained that the adsorption of nanoparticles increases with a decrease in size, resulting from a high bactericidal effect. In general, nano-size renders more surface area which facilitates high adsorption. Hence NPs enters into the cell through adsorption leads to damage of enzyme activity, affecting the normal physiological processes like protein synthesis, DNA replication, and finally inhibiting the bacteria. Meanwhile, there is direct interaction of NPs with functional groups carboxyl (–COOH) groups, amino (–NH) and mercapto (-SH) is possible for inhibition of enzyme meant for the certain physiological process. Ultimately based on results, we confirm that extent of the zone of inhibition of bacterial growth depends on either variability in the cell wall of bacteria or the size of the nanoparticle or both.
-
Antifungal studies using CuO, ZnO and NiO nanoparticles
The results of Antifungal activity evaluated on the fungal strains Aspergillusniger and Candida albicans displayed in Table 3. Results disclose that NiOnanoparticles synthesized at temperatures 4500C and 6500C (NiO450 and NiO 650) exhibited the highest activity against Aspergillusniger with a zone of inhibition of 8.4 mm and 8.7 mm respectively and CuO 650 also showed good inhibition of 7.5mm. Against Candida, albicansZnOnanoparticles synthesized at temperatures 4500C and 6500C (ZnO 450 and 650) displayed a superior activity zone of inhibition of 6.5 mm and 7.5 mm respectively and the compound NiO 650 and CuO 650 also displayed good inhibition against Candida albicans ( Table 3).
DISCUSSION
Out of the three metal oxides, NiO nanoparticles produced with relatively low sizes. Comparatively, metal hydroxides calcinated at 6500C produced the lowest sizes of the metal oxide nanoparticles concerning all metals employed concerning the other annellation temperatures 4500C and 2500C. CuO nanoparticles have shown greater antibacterial activity than the remaining NiO and ZnO nanoparticles on both gram-positive and gram-negative strains. The compounds CuO 250, CuO 650 and NiO 450 showed the highest Antifungal activity against strains when compared with the standard drug Nystatin. Among all the synthesized nanoparticles NiO 650 exhibited the highest activity against both fungal strains (Table-3). The highest activity of the NiO nanoparticles against fungal strains might be due to their relatively low particle size, and spherical shape that can easily penetrate the fungal cell wall.
CONCLUSION
By annealing at three different temperatures (250, 450, and 6500C) CuO, NiO, and ZnO nanoparticles were synthesized employing the sol-gel method from the metal hydroxides. The antibacterial and antifungal activities of the synthesized nanoparticles were evaluated against different gram-positive, gram-negative and fungal strains. CuO nanoparticles possessed higher activity against bacterial species while NiOnanoparticles displayed good Antifungal activity. Results suggest that the nanoparticles calcinated at higher temperatures like 450, and 6500C were displaying higher antimicrobial activity relative to the pure metal oxides and those calcinated at 2500C.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are very much thankful to the Secretary of MLR group of Educational Institutions Sri MarriRajashekar Reddy for his constant help, support and encouragement to the academics generally and research particularly. The authors are also thankful to him for providing a suitable research lab facility at MLR Institute of Pharmacy College, and Mari Laxman Reddy Institute of Technology and management, Dundigal, R.R.District, Hyderabad. We would also like to thank the department of microbiology, Osmania University, Hyderabad for providing bacterial and fungal strains for Anti-micro bacterial studies.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No conflict of interest from all the authors
SOURCE OF FUNDING
No funding was granted from any authority. It is a self-financed research work
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTION
Kumara SwamyBudde has prepared a plan of work and execution. Dr.VenkataRatnam has supported and suggested the activity-related information. Raju BuraSureshBabuK and Ramreddygodela were helped in the preparation of nanoparticles and their evaluation of activity behaviour.
References:
-
Laurent S, Forge D, Port M, Roch A, Robic C, Vander Elst L et al. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem Rev. 2010;10: 2574–2574
-
Franke ME, Koplin TJ Simon U.Metal and metal oxide nanoparticles in chemiresistors: does the nanoscale matter? Small, 2006;2(1):36-50.
-
Brovelli S, Chiodini N, Lorenzi R, Lauria A, RomagnoliMand PaleariA.Fully inorganic oxide-in-oxide ultraviolet nanocrystal light-emitting devices. Nature Communic. 2012; 3: 690.
-
Zhang H, Yu X and BraunPV.Three-dimensional bicontinuous ultrafast-charge and -discharge bulk battery electrodes. Nature Nanotech. 2011; 6(5): 277-281.
-
Zhang Z, Dong C, Yang C, Hu D, Long J, Wang L, Li H, Chen Y and KongD. Adv Synth Catal. 2010; 352: 1600-1604.
-
Skrabalak SE andBrutchey RL. Going with the Flow: Continuous Flow Routes to Colloidal Nanoparticles. Chem Mat. 2018; 28; 4: 1003-1005.
-
Sondi I andSalopek-Sondi B. Silver nanoparticles as an antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for gram-negative bacteria. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2004;275:177–82.
-
Cioffi N, Torsi L, Ditaranto N, Tantillo G, Ghibelli L and Sabbatini L. Copper nanoparticle polymer composites with antifungal and bacteriostatic properties. Chem Mater. 2005;17:5255–62.
-
Emami-Karvani Z and Chehrazi P. Antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticle on gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Afr. J Microbiol Res. 2011; 5(12): 1368–1373.
-
Oussalah M. Facile synthesis of nickel oxide nanotubes and their antibacterial, electrochemical and magnetic properties. Food control. 18; 5: 414- 420.
-
Li Z, Lee D, Sheng X, Cohen RE and Rubner MF. Two-level antibacterial coating with both release-killing and contact-killing capabilities. Langmuir. 2006; 33:9820–9823.
-
Morones JR, ElechiguerraJL, Camacho A, Holt K, Kouri JB and Ramirez JT. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotech 2005;16:2346–53.
-
Cho S, Jung SH and Lee KH.Morphology-Controlled Growth of ZnO Nanostructures Using Microwave Irradiation: from Basic to Complex Structures. J Phys Chem C. 2008; 112(33): 12769–12776.
-
Tang H, He Y, Li B, Jung J, Zhang C, Liu X and Lin Z et al.Continuous crafting of uniform colloidal nanocrystals using an inert-gas-driven microflow reactor Nanoscale. 2015;7: 9731-9737.
-
Xu JF, Ji W, Shen ZX, Tang SH, Ye XR and Jia DZ. Preparation and characterization of CuO nanocrystals. J Solid State Chem. 1999;147:516–19.
-
Stoimenov PK, Klinger RL, Marchin GL and Klabunde KJ. Metal oxide nanoparticles as bactericidal agents. Langmuir, 2002;18:6679–86.
-
Ericsson HM, Sherris JC, Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing. Rep Int Collab Study Acta Pathol Microbiol Microbiol Immunol. 1971; 217-223.
-
Avinash P. Ingle, Nelson Duran and Mahendra Rai. Bioactivity, mechanism of
action, cytotoxicity of copper-based nanoparticles: Review Appl Microbiol Biotech. 2014;98(3):1001-1009.
-
Linlin W, Chen H and Longquan S.The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: present situation and prospects for the future. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017; 12:1227–1249.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License