IJCRR - 13(14), July, 2021
Pages: 135-141
Date of Publication: 20-Jul-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Measurement of Oxidized LDL and Remnant Lipoprotein Cholesterol Associated with High-Sensitive C-Reactive Protein in Coronary Heart Disease
Author: Karini Keerthi, Thirunavukkarasu Jaishankar, Kasthuri Natarajan, Balasubramanian Kannan
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: LDL-C undergoes modification to form Oxidized LDL a crucial occurrence in the oxidation hypothesis of atherogenesis. Oxidized LDL and RLP-C stimulates the immune and inflammatory reactions and promotes atherosclerosis. Because of its lesser size along with high cholesterol content, and increased residence period in blood the remnant lipoproteins are highly atherogenic. Remnant lipoproteins enter into the arterial wall easily and taken up directly by macrophages lead to the formation of foam cells, thus initiating the lipid-laden plaque. Oxidized LDL along with remnant lipoprotein cholesterol and hs-CRP play a crucial role in the progression of coronary heart disease. Objective: The objective of the study is to measure the level of circulating Oxidized LDL and Remnant Lipoprotein Cholesterol associated with High-Sensitive C-Reactive Protein in Coronary Heart Disease Materials and Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted on 91 CHD patient and 91 healthy control in the age group of 25 to 55 years and were age and sex-matched. After overnight fasting body fluid samples were collected for analysis for Lipid Profile, oxidized LDL and hs-CRP. ox-LDL and hs-CRP measured by ELISA method and Lipid Profile are measured using Auto Analyzer AU480. Results: The mean level of oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein level in CHD was elevated (40.89\?8.69) and statistically significant (p-value < 0.001) compared to the normal healthy controls (16.6\?3.54). The mean RLP-C showed a significant increase (35.65\?16.11) in the CHD group when compared to controls (15.69\?12.15) (p < 0.001). hs-CRP level in CHD was (3.80\?1.35) and also shows a significant (p-value < 0.001) increase compared to the normal healthy controls (1.92\?0.47). Conclusion: Addition to conventional parameters, the estimation of ox-LDL, RLP-C and Hs-CRP can prove to be a valuable tool in risk assessment of population and management of the disease. Our results suggesting the link between the level of high ox-LDL along with remnant lipoprotein cholesterol and hs-CRP may consistent with atherogenesis in subject with CHD.
Keywords: Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein, Remnant lipoprotein cholesterol, Coronary Heart Disease, Glycosylated Hemoglobin, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
In developed and developing countries the prevalence of CHD is the most important cause of death in India by 2020. In the adult population, more than 7 million deaths are caused by CHD (21.9 % of total deaths, expected to increase to 26.3 % by 2030 worldwide. 1 Remnant lipoprotein cholesterol which is mostly found in fasting and non-fasting triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (TRLs). In fasting state as VLDL-C and IDL-C along with the non-fasting state as VLDL, IDL and chylomicron remnants.2Like LDL-C, Remnant cholesterol promoting inflammatory reaction and atherogenic process along with accumulating and infiltrating the endothelial barrier in the arterial wall. Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol along with remnant cholesterol are causally accompanying coronary heart disease.
Remnant particles are larger than LDL and carry ≤40 times as much cholesterol per particle and more atherogenic than LDL.3 Increased oxidative stress and formation of superoxide anion in vascular cells stimulate the alteration of LDL-C to atherogenic oxidized LDL.4 In the vessel wall, uptake of scavenger receptor on monocyte-derived macrophages caused by the elevated level of RLP-C and LDL oxidation, leads to foam cells accumulation along with fatty streak formation.5 In the Pathogenesis of coronary heart disease CRP plays a significant role. C- reactive protein is a pentraxin family of protein, an acute phase reactant with a molecular weight of 23kDa. It is a highly sensitive marker for inflammation.6The level of CRP rises drastically during the inflammatory process. The elevated concentration of hs-CRP directly implies subclinical inflammation in individual.7
Remnant lipoprotein cholesterol along with oxidation of LDL associated with local and systemic inflammatory reaction linked to the risk of CHD along with low-grade inflammation.8
We assessed each correlation between remnant lipoprotein cholesterol and ox-LDL associated with hs-CRP in the CHD subject.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This cross-sectional study was conducted from Jun 2019 to Dec 2019 at SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India on subjects attending the Cardiology and medicine outpatient. Totally 182 subjects were included who were age and sex match in the age group 25-55 years. 91 CHD subjects and 91 normal healthy subjects were selected as control. The control subjects were also taken from Master health check-up Programme and medicine OP in SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. This study follows the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the institutional ethical committee at SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre (ECN: 1513/ICE/2018). Written informed consent was collected from all participants at the time of enrollment. Based on coronary angiography, the CHD patients were selected. Serum glucose value is above the normal and below the diabetic level diagnosed both males and females coronary heart disease patient and patients with chest pain, ECG and ECHO, changes, increased cardiac markers such as creatinine phosphokinase (CPK-MB) and troponin level. The control group consists of Normal healthy individuals. The subjects who were on treatment for renal failure, cancer, autoimmune diseases, surgery, fever, alcoholics, smokers, pregnancy and patients with corticosteroids, estrogen, anti-retroviral drugs psychotropic medications. Thyroid, arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, acute/chronic infection patients were excluded
We did the study on both NGT & IGR subjects.
Criteria that we followed to rule out glucose status are
During the period of enrolment, Medical and demographic data were collected. By using a questionnaire during the clinical appointment the basic info on age, gender along with the history of diabetes, hypertension, and the use of medications were collected. Before shifting the data to the database. Questionnaires were assessed by an expert questioner for lost data and its entirety. Information on laboratory reports was noted for all the subjects. The physical examination consists of the 12-lead relaxing electrocardiogram. In the morning, fasting samples from cases and healthy controls were taken from the antecubital vein. At 2500 RPM the blood was centrifuged for 15 minutes; and serum was separated and used for the assessment of glucose and routine lipid profile includes plasma total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), TC/HDL-C ratio, LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and HbA1c were measured. BMI was calculated as weight in kilograms/(height in meters)2. Lipid Profiles were estimated using Direct Antibody Inhibition. TC was estimated by the enzymatic end-point cholesterol esterase-peroxidase method. Triglycerides were estimated by the enzymatic end-point glycerol oxidase-peroxidase method (Beckmann Coulter AU480 Analyzer). By using High-pressure liquid Chromatography, the levels of haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) were measured.
The RLP-C was calculated by using the formula: RLP-C=TC-(HDL-C+LDL-C) [9]. Ox-LDL and High sensitive C - reactive protein were measured by ImmunoTurbidometry in Marketable ELISA Kit.
Statistical Methods
By using a statistical package for social service (SPSS 16.0) the Data were analyzed. The data from the study were shown as mean and standard deviation. p-value was <0.05 were considered as statically significant if Statistical significance for study group and control was analyzed by Student’s ‘t's test. To find out the correlation between different parameter Pearson’s correlation coefficient was calculated. By simple linear regression analysis, the correlation between the two parameters was determined.
OBSERVATION AND RESULTS
Demographic characteristics of the study subjects
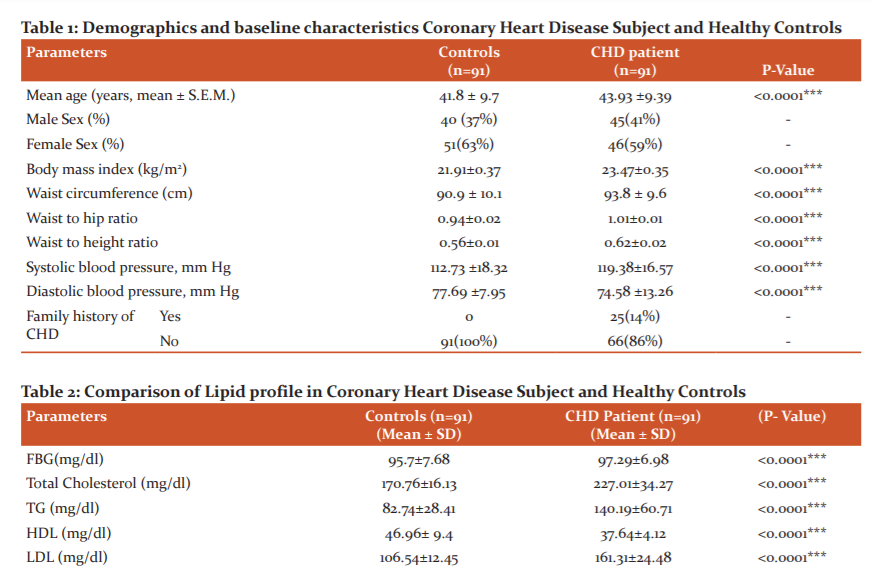
Totally 182 subjects were included who were age and sex match in the age group 30-55 years 91 CHD subject (45 males and 46 females) with average age 43.93 ±9.39 years and 91 healthy control (40 males and 51 females) with the average age of 41.8 ± 9.7. The majority of Non-Diabetic CHD subjects are in the age group of 40-50 years and Diabetic Subjects with CHD in the age group of 40-50 years. While most of the control subjects fall in the age group of 30-45 years. In the subject group, 27 Non-Diabetic CHD subjects having a Family history of CHD and 20 Diabetic CHD subject having a Family history of CHD. BMI, Waist Circumference, Waist Hip Ratio, systolic blood pressure were significantly increased (p<0.05) in Diabetic and Non-Diabetic CHD patients compared to controls as depicted in [Table 1].
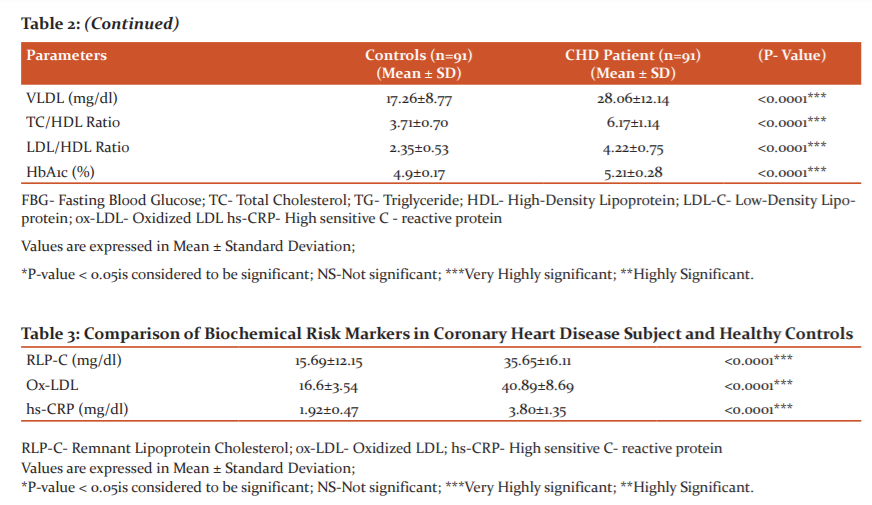
The study shows FBG, Total cholesterol, Triglyceride, LDL-C, VLDL-C, LDL-C/HDL-C ratio, Total Cholesterol/HDL ratio and HbA1c are significantly elevated in the patients compared to control. Among the two groups, the mean levels of HDL-C levels did not vary significantly.
Plasma RLP-C values were significantly increased (35.65±16.11) mg/dl in CHD subject when compared (15.69±12.15) mg/dl with controls (p< 0.001). Serum ox-LDL show a statistically significant increase (40.89±8.69) U/L in CHD subject when compared (16.6± 3.54) U/L with controls (p< 0.001). Serum hs-CRP values were significantly increased (3.80±1.35) U/L in the CHD subject when compared (1.92±0.47) with controls (p< 0.001)[ Table 2 and 3].
Pearson’s correlationanalysis between ox-LDL with various biochemical parameters in Coronary Heart Disease subject
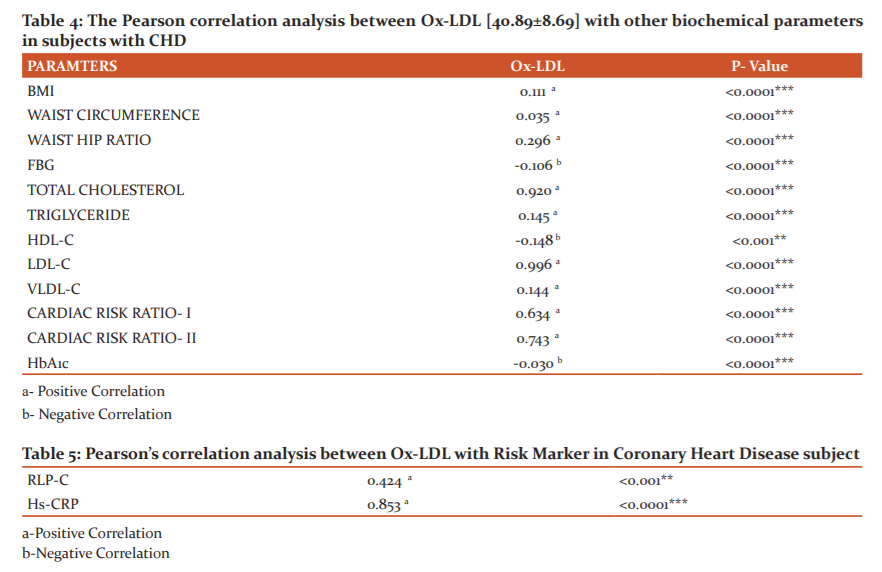
ox-LDL positively correlated with BMI (r = 0.111), Waist Circumference (r = 0.035), Waist Hip Ratio (r = 0.296). Total Cholesterol (r = 0.920), Triglyceride (r = 0.145), LDL-C (r = 0.996), VLDL-C (r = 0.144), TC/HDL ratio (r = 0.634), LDL/HDL ratio (r = 0.743)
And ox-LDL negatively correlated with FBG (r = -0.106), HDL-C (r = -0.148), HbA1c (r = -0.030) [Table 4].
Pearson’s correlation analysis between ox-LDL with Risk Marker in Coronary Heart Disease subject
ox-LDL positively correlated with RLP-C (r = 0.424) and hs-CRP (r = 0.853)[Table 5].
Pearson’s correlation analysis between Remnant lipoprotein cholesterol with various biochemical parameters in Coronary Heart Disease subject
Remnant lipoprotein cholesterol is positively correlated with FBG (r = 0.2008), BMI (r = 0.183), Waist Circumference (r = 0.050), Waist Hip Ratio (r = 0.195). Total Cholesterol (r = 0.721), Triglyceride (r = 0.277), LDL-C (r = 0.416), VLDL-C (r = 0.278), TC/HDL ratio (r = 0.483), LDL/HDL ratio (r = 0.477)
And Remnant lipoprotein cholesterol are negatively correlated with HDL-C (r = -0.395), HbA1c (r = -0.007) [Table 6].
Pearson’s correlation analysis between Remnant lipoprotein cholesterol with Risk Marker in Coronary Heart Disease subject
Remnant lipoprotein cholesterol are positively correlated with ox-LDL-C (r = 0.424) and hs-CRP (r = 0.330) [Table 7].
DISCUSSION
In our study WC and BMI were directly linked with RLP-C, ox-LDL along with CRP showed that blood pressure and BMI, Waist Circumference, waist-to-hip ratio were significantly elevated in CHD subjects when compared with healthy controls. The study done by INTERHEART stated that compared to BMI the waist-hip ratio is a more significant predictor for myocardial infarction.10 Similarly, our study showed that the high BMI values subjects have a higher RLP cholesterol concentration. Holvoet et al stated that for evaluating the concentrations of circulating ox-LDL, BMI act as the strongest predictor.11
This study shows the significant difference in TC, LDL-C, HDL-C and triglyceride, however, the plasma level of LDL-C cholesterol, RLP-C, ox-LDL and hs-CRP were significantly elevated in CHD patients compared to controls an essential risk factor in the progression of atherosclerosis.
In our study, we found a negative correlation between oxidized LDL and HDL-C. The levels of HDL cholesterol is conversely related to the risk of CHD because it prohibits atherosclerosis by degenerating the stimulatory action of oxidized LDL on monocyte aggression.
Remnant Lipoprotein Cholesterol related with Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein along with Lipid Profile
Circulating oxidized LDL-C and RLP-C were positively correlated with Total Cholesterol, Triglyceride, LDL-C, VLDL, TC/HDL Ratio and LDL/HDL Ratio and negatively correlated with levels of HDL-C cholesterol. More studies stated that Ox-LDL is the major cause for hyperlipidaemia which triggers CHD.12 Nishi et al stated that LDL undergoes oxidation in plaque and that high concentrations of ox-LDL and triglyceride.13 After modi?cation of Apo B, oxidized LDL and triglyceride-rich lipoprotein undergoes lipolysis by lipoprotein lipase and release of cholesterol-rich remnant lipoprotein. 14 Sampson et al., found that there is still a considerable residual risk of reoccurring cardiovascular events even after reduction in LDL cholesterol to suggested concentration Although stains lowers LDL-C and it has a small effect on triglycerides. Therefore the concentration of triglycerides increased thus increase remnant cholesterol. Compared to LDL-Cholesterol the remnant lipoprotein cholesterol are two times more associated with coronary heart disease.15 RLP-C crosses the barrier of endothelium and uptake by macrophages leads to the formation of foam cell. As a result, remnant lipoproteins might cause dysfunction in the endothelial vasomotor and increase the threat of coronary heart disease in patients with hypertriglyceridemia.16Hypertriglyceridemia are significantly related to endothelial dysfunction.17 Kugiyama et al., stated that RLP-C levels were linked with abnormal endothelium-dependent vasomotor stated that for inhibitory effects of remnant lipoproteins the reduction in the bioactivity of coronary nitric oxide might be responsible for the progression of coronary heart disease.18
Remnant Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein-associated with hs-CRP
The innovative finding of our present study shows remnant lipoprotein cholesterol and ox-LDL was positively correlated with inflammatory biomarker high sensitivity C-reactive protein. In our study elevated hs-CRP is signi?cant compared to the control group. Ridker et al. reported that healthy individuals with elevated hs-CRP values are 4 times possible to have coronary heart disease.19 Ndrepepa et al., stated that raised hs-CRP level is linked with the threat of future adverse cardiovascular events in healthy persons and subjects with stable coronary heart disease.20 The fasting serum revealed that increased levels of remnant lipoprotein cholesterol can predict the progression of clinical coronary actions in patients with CHD independently along with other risk factors such as ox-LDL and hs-CRP. In our study, we observed a positive correlation between RLP-C and hs-CRP. Recent genetic studies done with very large samples by Varbo et al. found that elevated remnant cholesterol and ox-LDL is related to low-grade inflammation, but the elevated level of LDL-C causes ischemic heart disease without inflammation.21 Zhang et al found that OX-LDL and hs-CRP were positively correlated and it can directly lead to the occurrence of inflammatory reaction.22 Study by Hong et al., stated that remnant lipoprotein cholesterol was positively associated with the most important inflammatory biomarker hs-CRP.23 Toward our information, there are no previous studies on defining whether the baseline levels of remnant lipoprotein cholesterol along with ox-LDL is qualified as a useful independent predictor as traditional prognostic variables for adverse outcomes.
Conclusion:
CHD has been a subject of research for decades. Finding of its relation with remnant lipoprotein cholesterol, ox-LDL, Hs-CRP, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and DM have now become emerging areas of concern.
The current study concludes that assessment of RLP-C, ox-LDL and hs-CRP may contribute to the early finding of coronary heart disease may reduce the morbidity and mortality risk.
LIMITATIONS
A small sample size and more in-depth work on the role of ox-LDL, Remnant Lipoprotein Cholesterol and hs-CRP are needed to evaluate for the prevention of future risk of CHD.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors acknowledge the Department of Cardiology and Department of Medicine for permitting and supporting
Conflict of Interest: There is no conflict of interest
Funding: Self-funding
Ethical Approval: All procedures performed by human participants were involved in this study are performed following the ethical standards. The study protocol was approved by the institutional ethical committee (ECN: 1513/ICE/2018).
Informed Consent: Informed consent was taken from all the participants involved in the study.
References:
-
Krishnan MN. Coronary heart disease and risk factors in India - on the brink of an epidemic? Indian Heart J. 2012;64(4):364–367. doi:10.1016/j.ihj.2012.07.001
-
Vinodhini VM, Keerthi K, Kumar JS and Subramaniyam G. Assessment of Remnant Lipoprotein Cholesterol (RLP-C) Levels and its Correlation with Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Insulin Resistant Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. J Clin Diagn Rese. 2019 May, Vol-13(5): BC29-BC31
-
Varbo A, Benn M, Nordestgaard BG. Remnant cholesterol as a cause of ischemic heart disease: Evidence, definition, measurement, atherogenicity, high-risk patients, and present and future treatment. Pharmacol Ther. 2014;141:358–67.
-
Jezovnik MK and Poredos P. Oxidative stress and atherosclerosis. e-journal of the ESC Coun Card Pract. 2007; 6(6):97-107
-
Kathryn J. Moore and Mason W. Freeman. Scavenger Receptors in Atherosclerosis Beyond Lipid Uptake. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, Vascular Biol. 2006;26:1702–1711
-
Nicola R. Sproston and Jason J. Ashworth. Role of C-Reactive Protein at Sites of Inflammation and Infection. Front Immunol. 2018; 9: 754.
-
Sanjay K. Singh, Madathilparambil V. Suresh, Voleti B, and Agrawal A. The connection between C-reactive protein and atherosclerosis. Ann Med. 2008; 40(2): 110–120.
-
Varbo A, Benn M, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, Jorgensen AB, Frikke-Schmidt R,Nordestgaard BG. Remnant cholesterol as a causal risk factor for ischemic heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61:427–36.8.
-
Langsted A, Freiberg JJ, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, Schnohr P, Jensen GB, [11]Nordestgaard BG. Nonfasting cholesterol and triglycerides and association with risk of myocardial infarction and total mortality: the Copenhagen City Heart Study with 31years of follow-up. J Intern Med. 2010,270; 65-75.
-
Sabah M, Khandker MD. Body mass index and waist/height ratio for prediction of severity of coronary artery disease. BMC Res Note. 2014; 7:246. 17 Apr. 2014, doi:10.1186/1756-0500-7-246
-
Holvoet P, Mertens A, Verhamme P. Circulating oxidized LDL is a useful marker for identifying patients with coronary artery disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001;21:844–8.
-
Rafieian-Kopaei M, Setorki M, Daudi M, Baradaran A, Nasri H. Atherosclerosis: process, indicators, risk factors and new hopes. Int J Prev Med. 2014;5(8):927-946.
-
Nishi K, Itabe H, Uno M, Kitazato KT, Horiguchi H, Shinno K, Nagahiro S. Oxidized LDL in carotid plaques and plasma associates with plaque instability. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002; 22: 1649–1654.LinkGoogle Scholar
-
Dallinga-Thie GM, Kroon J, Borén J, Chapman MJ. Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins and Remnants: Targets for Therapy?. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2016;18(7):67. doi:10.1007/s11886-016-0745-6
-
Sampson UK, Fazio S, Linton MF. Residual cardiovascular risk despite optimal LDL cholesterol reduction with statins: the evidence, aetiology, and therapeutic challenges. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2012;14(1):1–10. doi:10.1007/s11883-011-0219-7
-
Xiao-Yan Zheng and Liu L. Remnant-like lipoprotein particles impair endothelial function: Direct and indirect effects on nitric oxide synthase. J Lipid Res. 48(8):1673-80. DOI: 10.1194/jlr.R700001-JLR200.
-
Chowienczyk PJ, Watts GF, Wierzbicki AS, Cockcroft JR, Brett SE, Ritter JM: Preserved endothelial function in patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia and low functional lipoprotein lipase activity. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997; 29:964-968
-
Kuriyama K, Doi H, Motoyama T, Soejima H, Misumi K, Kawano H, Nakagawa O. Association of remnant lipoprotein levels with impairment of endothelium-dependent vasomotor function in human coronary arteries. Circul. 1998; 97:2519-2526
-
Ridker PM. Inflammation, aspirin, and the risk of cardiovascular disease in apparently healthy men. N Engl J Med. 1997; 336: 973-979.
-
Ndrepepa G. N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide and C-reactive protein in stable coronary heart disease. Am J Med. 2006; 119: 355.e1-355.e8.
-
Varbo A, Benn M, Tybjaerg-Hansen A and Nordestgaard BG. Elevated remnant cholesterol causes both low-grade inflammation and ischemic heart disease, whereas elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol causes ischemic heart disease without inflammation. Circulation. 2013;128:1298–1309. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.003008. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
-
Zhang YC, Tang Y, Chen YS. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein and C-reactive protein have combined utility for better predicting prognosis after acute coronary syndrome. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014;68:379–85.
-
Hong LF, Song-H, Yang B, Li JJ. Predictive value of non-fasting remnant cholesterol for the short-term outcome of diabetics with new-onset stable coronary artery disease. J Lip Health Dis. 2015;16(10): 192-197.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License