IJCRR - 13(14), July, 2021
Pages: 113-118
Date of Publication: 20-Jul-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
What is the Understanding of Antibiotics among Parents of Young Children? Findings of a Cross-sectional Study Conducted in a Tertiary Care Hospital in South India
Author: Aishwarya STY, Ganesan DK, Jain T
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Antibiotics were considered the greatest invention in the 20th century. Antibiotic resistance is an alarming issue in developing countries and the major reason contributing to this is the irrational use because of the lack of knowledge. Aim: To understand the level of knowledge and the usage pattern of Antibiotics among Parents of Young Children attending a Tertiary care Hospital Methodology: The present study was a cross-sectional study conducted among the parents of children attending the Pediatric Out-patient department in a tertiary care hospital in Kancheepuram district, Tamil Nadu. A total of 133 participants were surveyed using a semi-structured and a pre-tested questionnaire to find out their understanding of Antibiotics. Results: Among the 133 participants, around 23.4% of parents correctly identified antibiotics are used against bacterial infections, and only 16.6% of people knew about the term antibiotic resistance. About 60% of parents said that they never used leftover antibiotics. People with low socio-economic status were found to have a lack of knowledge regarding antibiotics and they misuse them without knowing the consequences. Conclusion: We need to invest more time in educating and creating awareness regarding the judicial use of antibiotics and to check unprescribed dispensing of antibiotics.
Keywords: Antibiotic resistance, Attitude, Knowledge, Practice
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Antibiotics were considered to be the greatest invention in the 20th century for treating bacterial infections.1 However, rampant and irrational use of antibiotics for any clinical condition will emerge as a worldwide issue of antibiotic resistance in the future. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines antimicrobial resistance as a microorganism’s resistance to an antimicrobial drug that was once able to treat an infection by that microorganism. Resistance arises as a consequence of mutations in microbes and selection pressure from antibiotic use that provides a competitive advantage for mutated strains.2 A person cannot become resistant to antibiotics. Resistance is a property of the microbe, not a person or other organism infected by a microbe.WHO has warned about the excessive use of antibiotics, where minor infection and injury won’t be manageable with the help of antibiotics in the future.
There is increasing bacterial resistance due to improper management and weak implementation of Health policy.3 The major cause of mortality in children in developing countries like India is Acute Respiratory Infections (ARI). Upper respiratory tract infections are the most common case where antibiotics are prescribed in the Pediatrics Age group.4 There should be an awareness of the consequences of unnecessary prescription of antibiotics among Physicians, and the General public should also be conscious of this matter.5 Viral infections are the most common (which do not require antibiotics) and bacterial infections carry less than 5% complicated problems, therefore, antibiotics should be used judiciously.
Knowledge of antibiotics is well known to be poor among the general public. As India is ranked the world’s largest consumer of antibiotics for human health, the misuse of antibiotics is striking in India. The rules by the Drugs and Cosmetics Act stated only qualified medical practitioners can prescribe medicine, but it is not practised everywhere instead, without valid prescription the people who do not hold any formal degree and are not trained in allopathic medicine prescribe drugs and misuse it as part of their regular practice.6 The rate of self-medication is found to be rising around the world including India.7 Because of these factors, it is necessary to investigate and prevent these detrimental practices. Thus, the present study was undertaken to find out the current understanding of antibiotics.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Study Design: This is a Hospital-based cross-sectional study conducted among parents of children who attended the pediatric outpatient department (OPD) of a Tertiary Care Hospital in Kancheepuram district, Tamil Nadu.
Ethical Clearance number: SMC/IEC/2020/03/407
Study period:
The study was conducted for 2 months between February and March 2020.
Study Population:
We included the Parents of Children who attended the Pediatric OPD of a Tertiary care hospital during the above-mentioned study period. Children who were accompanied by guardians and grandparents were not included in our study. Parents who refused to participate were also excluded from the study.
Sample size: 133 willing parents of young children were included in our study.
Study procedure:
Approval from the Institutional Health Research Ethics Committee was obtained before the commencement of the study. The interview was conducted in the OPD and this was done after the parents sought consultation from the doctors for their child. Before the interview began, verbal consent was obtained by informing them about the nature and purpose of the study. Face-to-face interaction with each participant was done to collect data. If both the parents of the child were present then whoever was willing among them was taken for the data collection. Counselling & Health education was given about the knowledge of Antibiotics and their resistance to the parents after the completion of the interview.
Study tool:
The study tool consisted of the semi-structured pretested questionnaire which consisted of questions that were adopted from previous studies. 8,9 A pilot study was undertaken with 10 participants to test the validity and reliability of the data collection tool and to identify possible field problems and modifications were made accordingly. The questionnaire consists of several sections: Socio-demographic characteristics; Knowledge; Attitude, and Practice.
Data Analysis:
Data were entered in an Excel spreadsheet (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA). Data were analyzed using Statistical Package for Social Sciences version 20 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Proportions were used to describe the socio-demographic variables and the Chi-square test was used to measure the association between the variables. p-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
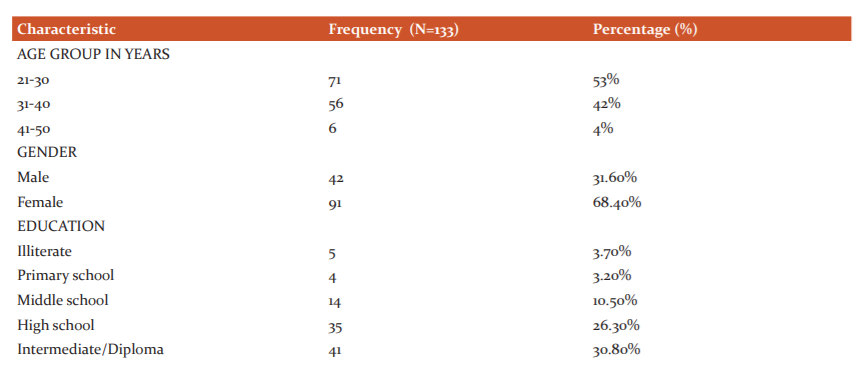
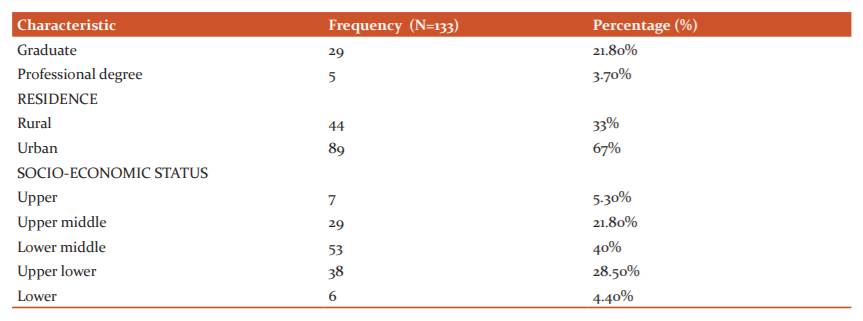
A total of 133 participants participated in the interview. Out of the 133 participants,68.4% were females and 31.6% were males. The majority (53%) of the participants were between the age group of 21-30 years and very few (4%) in the age group of 41-50 years. Education level was grouped as Illiterate, Primary school, High school, Intermediate/diploma, Graduate and then, Professional degree, of these 133 respondents, 3.7% were Professional degree holders, 21.8% were graduates.1/3rd (33%) of parents were residing in a rural area and the remaining 67% were from an urban area. The majority (40%) of participants belonged to the lower-middle-class group in the Socioeconomic status classification. [Table:1].
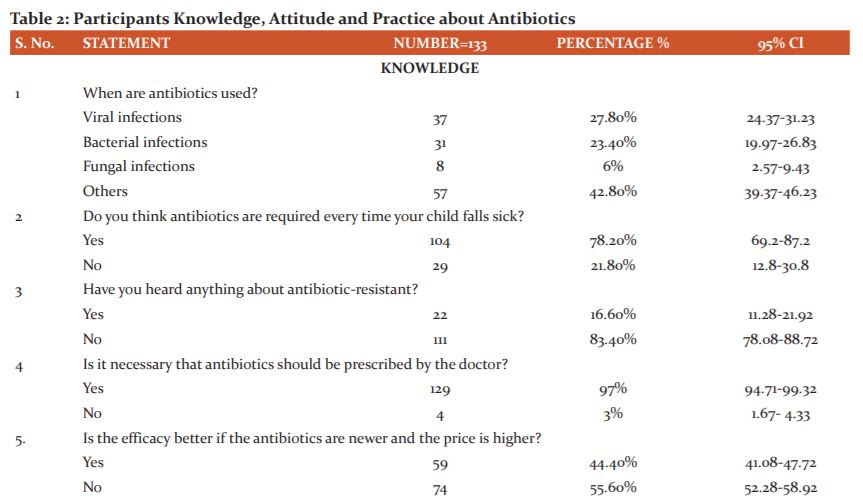
Out of the total, nearly 1/4th (23.4%) of parents knew antibiotics were used against bacterial infections, while 27.8% of parents thought it is used against viral infections, and 42.8% thought it can be used in all conditions. The majority (78.2%) of Parents also preferred antibiotics whenever their child fell sick without knowing that it is used only against bacterial infections. Moreover, only 16.6% of parents knew about the term antibiotic resistance. Nearly 2/3rd of the parents (72%) felt that antibiotics do not cause any harm after excessive use. The majority (96%) of the participants said that they complete the course duration of antibiotics as prescribed by the doctor and 60% of the parents say they never used leftover antibiotics for their child from the previous prescription. 44.4% of the parents thought that the efficacy is better if the antibiotics were newer and costlier. The majority of the people didn’t know about the adverse effects of antibiotic use but some people who knew said it causes diarrhoea (37%), and skin rashes (20%) respectively [Table 2].
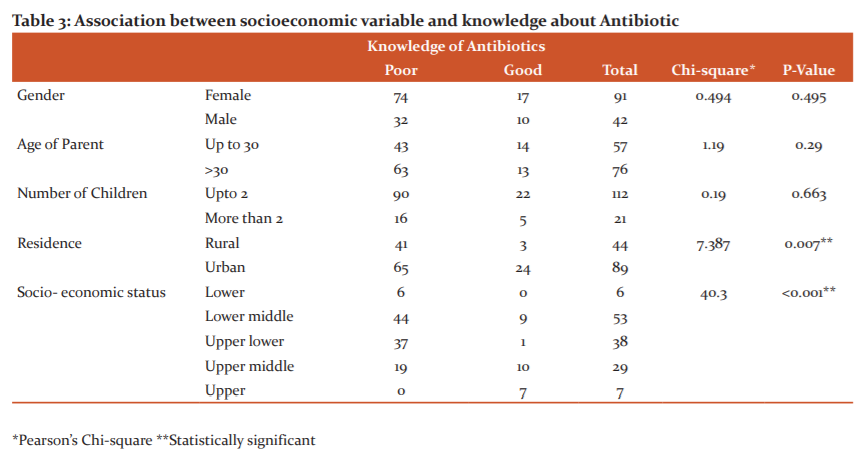
Based on their responses to all the questions in this study, the respondents were classified into having good knowledge (>50% correct responses) and poor knowledge (<50% correct responses). We found that only about 23.6% of the parents had a good knowledge of antibiotics. While calculating chi-square to find out the association between knowledge of Antibiotics and study variables, we found a significant association (p<0.05) for residence (i.e., rural or urban) and socioeconomic status with knowledge on antibiotics.
Concerning Socioeconomic status, the lower-middle and upper-middle-class had more knowledge than the other classes. Other variables like gender, age of the parents, and number of children in the family did not have statistical significance with antibiotics knowledge [Table:3]
DISCUSSION
Knowledge of antibiotics and their resistance is known to be less, currently to the general public in India as well globally. Anyone of any age or country antibiotic resistance affects everyone. Though antibiotic resistance occurs naturally, it is the misuse of antibiotics in humans that is speeding this process.10 But because of the relaxed laws in India and other developing countries, it is somewhat easy to obtain antibiotics without prescription (over-the-counter drugs), and hence, antibiotics misuse is common by people.11,12This study presents several observations concerning antibiotic use, levels of knowledge, and understanding of the problem of antibiotic resistance.
The results on the understanding of the respondents' knowledge clearly show a high level of misunderstanding. Only about 23 % of the participants had good knowledge of Antibiotics. Similar findings were reported in China where 39% of the parents had a good knowledge of Antibiotic use.13 On the contrary, a study was done in Norway where more than half of the participants had good knowledge of Antibiotics.14
Also evident from this study is that only 23.4% of parents were aware that antibiotics are used against bacterial infections and are not effective against viruses. The majority 42.8% of parents thought that antibiotics could be used for any conditions and also thought that antibiotics were effective against viruses. Several studies also report similar findings.13-15 A possible reason could be that while counselling, doctors use ‘Germs’ as a common word for indicating pathogens, rather than specifically mentioning bacteria. Also, as mentioned by Rousounidis et al.people don’t have the knowledge to differentiate bacteria and viruses and hence, believe that antibiotics are effective against any infection. 16
The lack of knowledge regarding antibiotic resistance was evident because only 16.6% of parents were aware of antibiotic resistance. The majority of the parents didn’t know about antibiotic resistance but interestingly few of them know that excessive use of antibiotics may harm the child 28%. In contrast, a study done by Chinnasami et al. showed respondents had more knowledge about resistance.17 Parents with more than one child had some knowledge about antibiotic usage and the consequences of using it from their personal experience when they used to give it to their first child. 96% of parents follow the duration of antibiotics as prescribed by the doctor in our study. Higher rates of compliance were also reported by Vanderberg et al. and Hoppe et al. in Germany with nearly 70 % compliance.18,19 Similarly, Rasheena et al.showed that 64% of respondents followed doctors' advice.20 In general, compliance was better whenever a single dose per day was advised as opposed to multiple doses in a day. Additionally, some antibiotic suspensions are flavoured with the essence which is more appealing to children during consumption. Knowledge of antibiotics and their resistance must be required for parents, otherwise, we may see an increase in community-acquired infections.21
CONCLUSION
The present study found that the majority of parents lack knowledge of antibiotics use and its resistance. Without the proper knowledge, they misuse antibiotics with excessive use. We need to invest more time in educating and creating awareness regarding the judicial use of antibiotics and to check unprescribed dispensing of antibiotics. Strategies for effective communication among parents and physicians to ensure patients' knowledge about antibiotics and tell them its excessive use causes consequences and to advise to reduce self-medication practices with antibiotics.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references to this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/ editors/publishers of all those articles, journals, and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Disclosure of funding sources
Not applicable.
Financial disclosure
The author has no sources of funding or other financial disclosures concerning the above article.
Informed Consent
Proper Informed Consent was taken from all participants before initiation of the study and Confidentiality was maintained.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Contribution of the Authors
(1) Conception and design of the study, acquisition, and entry of data (2) analysis and interpretation of data, manuscript writing (3) Drafting the article, revising it critically for important intellectual content & Proofreading.
Table 1: Demographic characteristics of the participants


References:
-
Adedeji WA. The treasure called antibiotics. Ann Ib Postgrad Med. 2016; 14:56–57.
-
Laxminarayan R, Duse A, Wattal C, Zaidi AK, Wertheim HF, Sumpradit N, et al. Antibiotic resistance-the need for global solutions. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13(12):1057-98.
-
Desai AJ, Gayathri GV, Mehta DS. Public’s perception, knowledge, attitude and behaviour on antibiotic resistance–a survey in Davangere city, India. J Prev Med Holistic Health. 2016;2(1):17-23.
-
Selvaraj K, Chinnakali P, Majumdar A, Krishnan IS. Acute respiratory infections among under-5 children in India: A situational analysis. J Nat Sci Biol Med. 2014 Jan;5(1):15.
-
Zahreddine L, Hallit S, Shakaroun S, Al-Hajje A, Awada S, Lahoud N, et al. Knowledge of pharmacists and parents towards antibiotic use in paediatrics: a cross-sectional study in Lebanon. Pharm Pract (Granada). 2018;16(3):1194.
-
Nair M, Tripathi S, Mazumdar S, Mahajan R, Harshana A, Pereira A, et al. “Without antibiotics, I cannot treat”: A qualitative study of antibiotic use in Paschim Bardhaman district of West Bengal, India. PloS one. 2019;14(6): e0219002.
-
Raja KC, Dharshanram R, MenakaV, Kumar PDM. Knowledge, Attitude and Practice of Self-Medication Among Patients Visiting A Dental Hospital in Chennai- A Cross-Sectional Study. Int J Recent Sci Res. 2018; 9(10): 29395-29398.
-
Choo SJ, Chang CT, Lee JCY, Munisamy V, Tan CK, Raj JD, et al. A cross-sectional study on public belief, knowledge and practice towards antibiotic use in the state of Perak, Malaysia. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2018; 12:960-969.
-
Mitsi G, Jelastopulu E, Basiaris H, Skoutelis A, Gogos C. Patterns of antibiotic use among adults and parents in the community: a questionnaire-based survey in a Greek urban population.Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2005;25(5):439-43.
-
Chandy SJ. Consequences of irrational use of antibiotics. Indian J Med Ethics. 2008;5(4):174-5.
-
Blenkinsopp A, Bradley C. Over the Counter Drugs: Patients, society, and the increase in self-medication. Bri Med J. 1996 Mar 9;312(7031):629-32.
-
Agarwal S, Yewale VN, Dharmapalan D. Antibiotics use and misuse in children: A knowledge, attitude and practice survey of parents in India. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015;9(11): SC21SC4.
-
Yu M, Zhao G, Lundborg CS, Zhu Y, Zhao Q, Xu B. Knowledge, attitudes, and practices of parents in rural China on the use of antibiotics in children: a cross-sectional study. BMC Infect Dis. 2014;14(1):112.
-
Waaseth M, Adan A, Røen IL, Eriksen K, Stanojevic T, Halvorsen KH, et al. Knowledge of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance among Norwegian pharmacy customers - a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):66.
-
ElongEGA, Ebongue OC, Penda IC, Nga NE, MpondoME,Moukoko ECE. Knowledge, practices and attitudes on antibiotics use in Cameroon: Self-medication and prescription survey among children, adolescents and adults in private pharmacies. PLoS One. 2019;14(2): e0212875.
-
Andreas R, Vassiliki P, Adamos H, Sotiria P, Maria T, George S, et al. Descriptive study on parents’ knowledge, attitudes and practices on antibiotic use and misuse in children with upper respiratory tract infections in Cyprus. Int J Environ Res Public Hea. 2011; 8:3246–62.
-
Chinnaswamy B, Sadasivam K, Ramraj B, Pasupathy S. Knowledge, attitude and practice of parents towards antibiotic usage and its resistance. Int J Contemp Pediatrics. 2016; 1:256-61.
-
Vandenberg C, Niswander C, Carry P, Bloch N, Pan Z, Erickson M, et al. Compliance With a Comprehensive Antibiotic Protocol Improves Infection Incidence in Pediatric Spine Surgery. J Pediatr Orthop. 2018;38(5):287-292.
-
Hoppe JE, Blumenstock G, Grotz W, Med C, Selbmann HK. Compliance of German pediatric patients with oral antibiotic therapy: results of a nationwide survey. The Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1999;18(12):1085-91.
-
Shamsher R, Sudhir S, Nuwara H, Knowledge, attitude and practice of parents regarding antibiotic use in children. Int J Contemp Pediatrics 2019; 6:2282-6.
-
Basu R, Rao R, Sarkar A, Kongbrailatpam B. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility pattern of extended-spectrum Beta-Lactamase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from respiratory samples in a South Indian Tertiary Care Hospital. Int J Cur Res Rev 2013;5(19):81-87.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License