IJCRR - 13(14), July, 2021
Pages: 107-112
Date of Publication: 20-Jul-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Treatment-seeking Behaviour of Diabetes Patients of Meerut, Uttar Pradesh During Lockdown Phase of Covid 19 Pandemic
Author: Parashar Pawan, Sharma Saurabh, Bansal Rahul, Kumar Deepak, Ahmad Sartaj, Nasser Kaynat
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Uncontrolled T2DM (Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus) has emerged as one of the major risk factors for mortality in patients with COVID-19. The National lockdown has produced various lifestyle and health behaviour changes among diabetic patients. Aim: The present study was done to assess the treatment-seeking behaviour of diabetic patients during the lockdown phase of the Covid 19 pandemic in Meerut city. Methods: A descriptive cross-sectional study was done by using a predesigned, pre-validated online questionnaire. The study was conducted among conveniently selected 190 follow up T2DM patients from urban and rural health practice area of the community medicine department of a private medical college of Meerut, U.P. Simple descriptive tables and Chi-square test was used for statistical analysis. Results: During the lockdown phase, 110(57.9%) patients decreased physical activity whereas 68 (35.8%) patients did not follow dietary restrictions However, 159 (83.7%) of the patients were taking pharmacological treatment regularly. There was a significant association between the regularity of treatment and variables like education, occupation, total monthly income, residence, cost of treatment and blood test frequency. The diabetic patients faced the problem of the availability of physicians for consultation (38.9%) during the lockdown. Conclusion: The lockdown did not have much adverse effect on the regularity of treatment. The regularity of treatment was significantly associated with a sociodemographic profile and health awareness of diabetes patients. The patients had problems in following maintaining a healthy lifestyle during the lockdown. The patients had problems in assessing affordable healthcare during the lockdown.
Keywords: Covid 19, India, Lockdown, Treatment seeking behaviour, Type 2 Diabetes
Full Text:
Introduction:
After the COVID-19 epidemic, the Indian Government initiated a nationwide lockdown from March 25, 2020, and continued till 31st May 2020. The lockdown was imposed in India to prevent the spread of Covid 19 among people. During the lockdown phase, people stayed inside their homes, except for carrying out essential activities. The government initiated unlock phase from June 1st 2020 gradually in which activities were permitted in areas other than containment zones in a phased manner.1 However, very few relaxations were given in the Meerut district due to the high number of Covid 19 cases during unlocking phase.
During this pandemic, uncontrolled T2DM (Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus) has emerged as one of the risk factors for COVID-19 patients mortality. According to estimates, the prevalence rate of diabetes in urban areas of India is9% whereas the prevalence rate of diabetes in rural areas of India is 3%.2,3India has 65 million adults of age ≥20 years with diabetes. India has the largest number of people with diabetes in the world and is considered as Diabetic Capital of the world.2,3
T2DM is a lifestyle disorder in which proper lifestyle play important role in its management. Reports from various countries showed that the sudden lockdown and unlock phase has disrupted the physical activity, sleep, employment mental and emotional well-being of many individuals.4 Another study revealed that income, expenditure and accessibility to the healthcare of people were reduced due to lockdown in Kerala.5 There was disruption of healthcare services and the loss of continuum of care of diabetic patients during lockdown which could negatively impact on health-seeking behaviour of diabetes patients.6However, the exact impact of these disruptions on the treatment-seeking behaviour of T2DM patients during the lockdown phase in Meerut, Uttar Pradesh is not known. Therefore, the present study was conducted to study the lifestyle and treatment-seeking behaviour of diabetes patients during the lockdown in Meerut District, Uttar Pradesh. The study also tried to analyze various health-related challenges faced by diabetes patients during the lockdown in Meerut District, Uttar Pradesh.
Methodology
A cross-sectional study was conducted among diabetic patients residing in the field practice area of the community medicine department of Subharti medical college, Meerut. The study protocol was approved by the Institute Ethics Committee (Approval No. SMC/UECM/2020/119/95). A total of 190 follow up patients with T2DM (Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus) residing in the field practice area of the department of community medicine a Subharti medical college, Meerut were selected conveniently for conducting the study. The patients were included by conveniently sampling as randomization was not possible due to lockdown. The follow-up case of T2DM of the age group of 18-75 years having valid email or WhatsApp number were included in the study. The diabetes patients, who were critically ill, were excluded from the study. Patients with gestational diabetes mellitus were also excluded from the study.
A predesigned, pre-validated close-ended online questionnaire was developed to determine treatment-seeking behaviour among diabetes patients. The various sociodemographic indicators like age, sex, education, residence, occupation, total monthly income, family type and family history and health awareness variables like addiction, dietary habit, body mass index (BMI), frequency of blood sugar investigations, cost of treatment were included in the questionnaire. The patients who were taking pharmacological treatment either oral hypoglycemic or through insulin injections or both, from a public or private clinic or hospital regularly were categorized under regular treatment. The patients who were not taking pharmacological treatment not regularly were categorized under irregular treatment.7,8The patients were allowed to fill in multiple responses about reasons of irregularity of treatment (if applicable), lifestyle changes and problems faced during lockdown by them. The data was collected from July 2020 to September 2020. For statistical analysis, the data was entered and analyzed using the statistical package SPSS Version 20. Results were tabulated in percentages, mean, standard deviation. A Chi-square test was applied to test the significance. P-value of < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results:
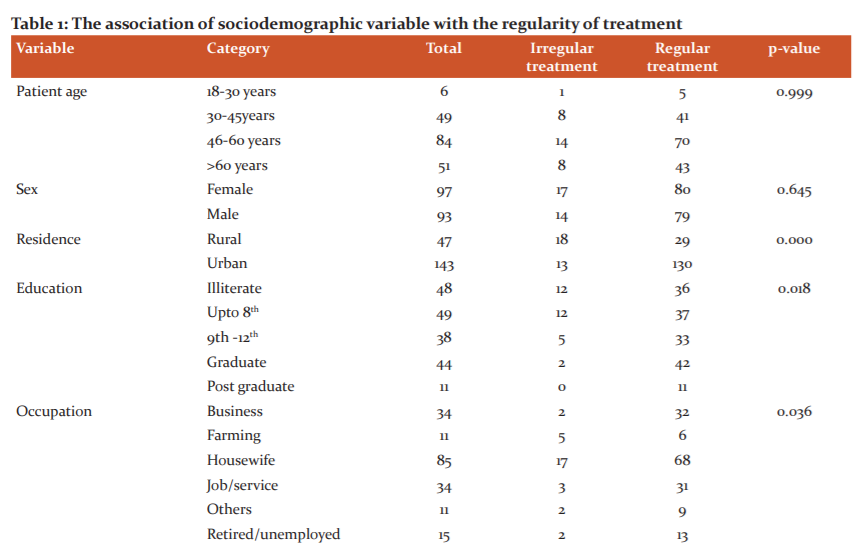
The sociodemographic characteristics of diabetic patients are described in Table 1. In our study, 51 patients were above 60, 84 patients of age group 46-60 years, 49 patients belonged to 30-45 years and the rest 6 were below 30 years. The male patients were 97 whereas the female patient was 93. The most of patients (143) were living in urban areas whereas only 47 patients were living in rural areas. Illiterate study subjects were 48 (25.3%) where graduate diabetic patients were 44(23.2%). In the occupation category, maximum diabetic patients were housewives followed by business and service. The family status of 113(59.5%) patients was joint whereas the family status of 77(40.5%) patients was nuclear. The family history of 99 (52.1%) patients was positive whereas the rest of the patients had a negative family history. The various other sociodemographic variables and association of these variables with the regularity of treatment is shown in Table 1. The association between regularity of treatment and sociodemographic variables like residence, education, occupation, total monthly income, family type and family history was found statistically significant with p-value 0.000, 0.018, 0.036, 0.000, 0.026,0.000 respectively. The association between regularity of treatment and sociodemographic variables like age and sex was not found statistically significant with p-value 0.999, 0.645 respectively.
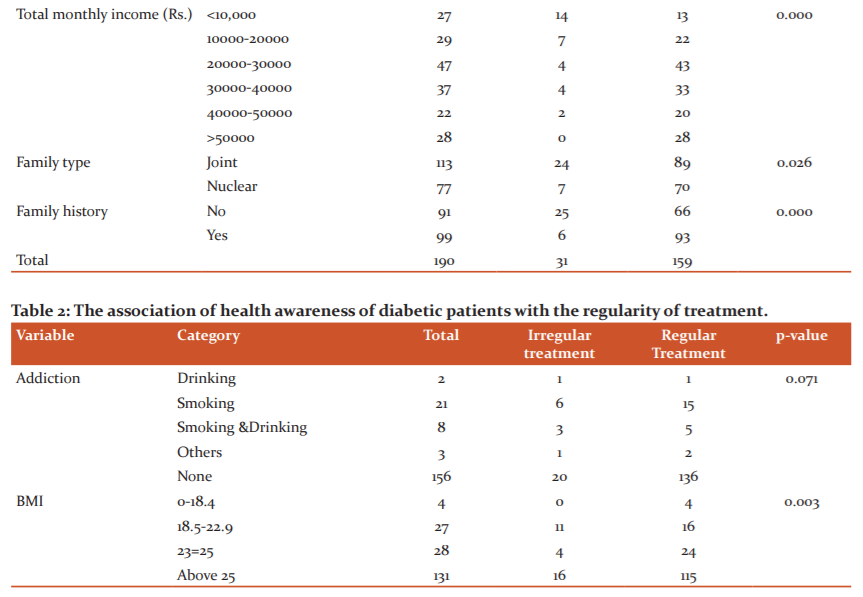
Table 2 depicted the association of health awareness of diabetic patients with the regularity of treatment. In our study, 156 (82.1%) patients had no addiction. Regarding BMI, 68.9% of patients had BMI >25.0 whereas 14.7% had BMI between 23.0-24.9. The no vegetarian dietary habit was practised by 82(43.2%) patients whereas vegetarian dietary habit was practised by 108 (56.8%) patients. The blood sugar was investigated in more than one month time by 88 (46.3%) patients whereas 53 (27.9%) investigated blood sugar monthly and was investigated by the rest of the patients in less than one month time. The average cost of a maximum number of patients (117) was between Rs.1000-5000. The various other personal attributes of diabetic patients and the association of these variables with the regularity of treatment are shown in Table 2. The association between regularity of treatment and variables like BMI, the frequency of blood sugar investigation, the monthly cost of treatment was found statistically significant with p-value 0.003, 0.000, 0.000 respectively. The association between regularity of treatment and variables like addiction and the dietary habit was not found statistically significant with p-value 0.071, 0.151 respectively.
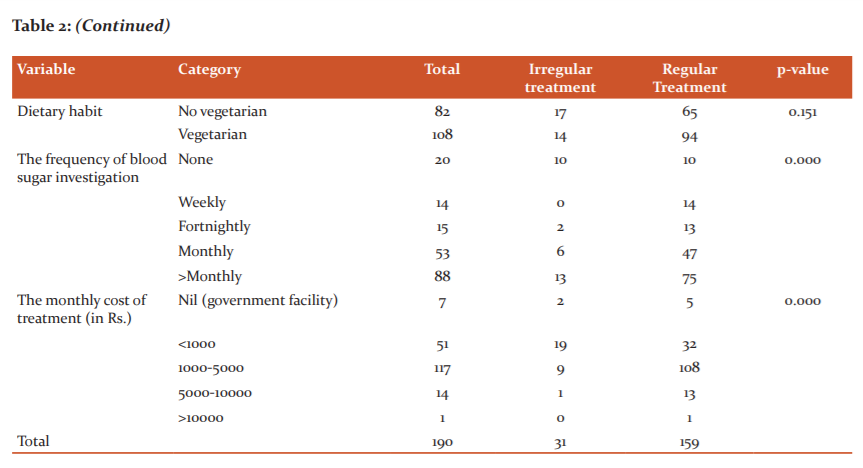
In our study, 159 (83.68%) patients were taking pharmacological treatment regularly whereas 31(16.32%) patients were not taking pharmacological treatment regularly. Table 3 depicted various reasons regarding the irregularity of treatment. The most common reason for irregularity were financial constraints, lack of support from family members and carelessness. The carelessness included reasons like forgetfulness and lack of time etc. The lockdown was considered as the main reason for irregularity by7 (3.68%) patients.
Fig 1 depicted that only 7(3.68%) patients increased physical activity or exercise during lockdown whereas 110(57.89%) patients decreased their physical activity. 89 (46.84%) patients followed dietary restrictions whereas 68 (35.79%) patients did not follow dietary restriction due to lockdown. The increase in yoga/meditation activity was observed by 14 (7.37%) patients and a decrease in yoga/meditation activity was observed by 7(3.68%) patients. Only 13(6.84%) patients observed no effects of lockdown on their lifestyle.
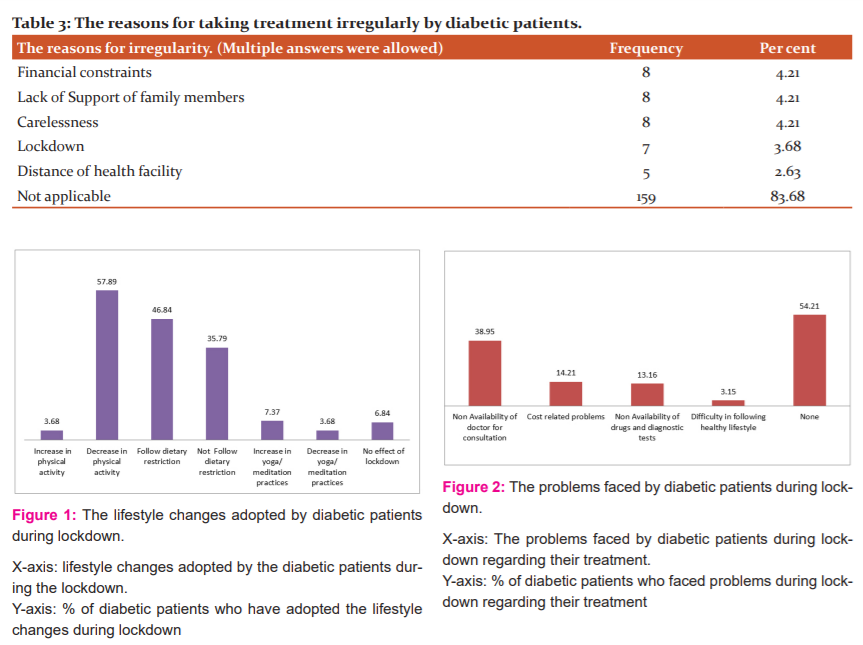
Fig 2 depicted that 103(54.21%) did not face any problem regarding the treatment of diabetes during the lockdown. However,74(38.95%) diabetic patients faced problems regarding the availability of a doctor for consultation. The problems regarding the availability of drugs and diagnostic tests were faced by 25(13.16%) patients. The cost-related problems were faced by 27 (14.21%) patients. Only 6 (3.15%) patients considered that following a healthy lifestyle during lockdown was a problem.
Discussion
The regularity of the treatment
In our study, the regularity of the treatment was practised by 83.7 % which was similar to findings of various other studies.7-10 Another study also revealed that during lockdown drug adherence was not a problem for most diabetic patients.11The regularity of treatment was comparatively better in urban, educated and patients have high monthly income and patients belonging to nuclear families (Table 1). Another study also supported our findings that patient education and socioeconomic status played a very important role in compliance with medical treatments in diabetic and hypertensive patients.12,13 These studies also revealed that health awareness was an important pillar of prevention and management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Similar to the findings of these studies, the current study found that addiction, BMI and frequency of blood sugar investigation had a significant association with the regularity of treatment.
The reasons for irregularity of drug treatment were cost of treatment and accessibility of health facility. Similar reasons for not taking treatment regularly were reported in a study done on Malasia.8 The income of many families was reduced and many health centres and private clinics were not accessible during the lockdown which resulted in the irregularity of treatment in many patients.
The carelessness was also the important reason for the irregularity of treatment in our study. Another study also observed that forgetfulness due to work was the main reason for drug non-compliance in diabetic and hypertensive patients.13 The lockdown was considered as the main reason for the lesser number of diabetes patients. Thus, we can conclude, lockdown did not have much adverse effect on the regularity of drug treatment of diabetic patients.
Problems faced by diabetic patients during lockdown
In our study, 38.95% of patients faced problems in consultation with physicians. Similar to the finding of a study from South India.14 The main reason behind the availability of physician was that most of the government health facilities were engaged in management of Covid 19 Pandemic. The accessibility to the private health sector was also lower during lockdown In Meerut city. Therefore, measure like the use of telemedicine for consultation of Diabetes patients should be adopted. Our study also observed that the availability of drugs and diagnostic tests, financial resources for diabetes treatment were problems for a minority of patients. Likewise, a study from AIIMS Bhopal observed that regularity of pharmacological treatment, availability of drugs and diagnostic tests and cost of drugs were not constraints for the majority of patients during the lockdown in India.11
In our study, the patients could not follow a healthy lifestyle. 110(57.89%) patients decreased their physical activity. 89 (46.84%) and 68 (35.79%) patients did not follow dietary restriction due to lockdown. An increase in yoga/ meditation practices was done by only 7.37% Another study from AIIMS Bhopal observed similar findings that adherence to a healthy lifestyle posed problems to the patients during the lockdown. The increase in yoga/ meditation was practised by fewer patients.11 In contrast to this, the diabetic patients were able to maintain diet and exercise schedule as usual.6,15 These finding suggested that more metacentric studies should be conducted to study the effect of lockdown on the lifestyle of diabetic patients. These findings also suggest that there is a need for counselling for diabetic patients for maintaining a healthy lifestyle during the lockdown as diet and physical exercise or yoga are also important components of prevention and management of Diabetes.16,17
Conclusion:
The lockdown had not much adverse impact on the regularity of pharmacological treatments among diabetic patients. The health awareness, socioeconomic status of diabetic patients played important role in the regularity of diabetic treatment during the lockdown. However, the non-pharmacological part or lifestyle management was ignored by diabetic patients during the lockdown. Only some patients were able to maintain physical activity and diet plan during the lockdown. Therefore, diabetes patients should be counselled for adopting a healthy lifestyle in future despite lockdown or any other such restrictions. The diabetic patients faced problem in consultation with physicians for their treatment during the lockdown. This problem provides us with an opportunity to adopt measures like telemedicine in our health system for the prevention and management of diabetes patients.
Acknowledgement:
The Authors acknowledge the diabetic patients who had truly given their views regarding treatments seeking behaviour been in the study. The authors also acknowledge the efforts of health workers of the urban health training centre (UHTC), rural health training centre (RHTC) of the medical college who played important role in the data collection during the study. The authors also acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Prior publication: Nil
Funding Support: Nil
Conflicts of interest: Nil
Permissions: Nil
Individual Author Contribution: All authors contributed equally in the every part of the study.
References:
1.Ahmed WN, Arun CS, Koshy TG, Nair A, Sankar P, Rasheed SA et al. Management of diabetes during fasting and COVID-19eChallenges and solutions. J Fam Med Prim Care 2020;9(8):3797e806.
2. India State-Level Disease Burden Initiative Diabetes Collaborators. The increasing burden of diabetes and variations among the states of India: The Global Burden of Disease Study 1990?2016. Lancet Glob Health. 2018;6:e1352?62
3. Kumar P, Agarwal N, Singh CM, Pandey S, Ranjan A, Kumar D. Diabetes and quality of the life-a pilot study. Int J Med Sci Public Health. 2016;5:1143-7.
4. Ammar A, Trabelsi K, Brach M, Chtourou H, Boukhris O, Masmoudi L et al. Effects of home confinement on mental health and lifestyle behaviours during the COVID-19 outbreak: insights from the ECLB-COVID19 multicentre study. Biol Sport. 2021;38(1):9e21.
5. Sujathan PK, Azad P. Social impact of lockdown in Kerala: a case study (April 25, 2020). Available at SSRN:https://ssrn.com/abstract=3587603.
6. Ghosh A, Arora B, Gupta R, Anoop S, Misra A. Effects of nationwide lockdown during COVID-19 epidemic on lifestyle and other medical issues of patients with type 2 diabetes in north India [Published online ahead of print, June 2020]. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2020;14(5):917e20.
7. Bhosale S, Pawar AT, Kumar KD. Healthcare-seeking behaviour among diabetic patients in Kozhikode, Kerala. Int J Med Sci Public Health. 2017;6(10):1524-7.
8.Abidin SI, Sutan R, Shamsuddin K. Prevalence and determinants of appropriate health-seeking behaviour among known diabetics: Results from a community-based survey. Adv Epidemiol. 2014;10(11):58-86.
9. Mookambika RV, Nelson SB, Ashok VG. A study on diabetic care among diabetic patients in a tertiary care health centre. Int J Contemp Med Res. 2016;3(10):3091-2.
10. Mangaiarkkarasi A, Nitya S, Ali RM, Ramaswamy S. A study to assess the knowledge, attitude and practice about diabetes among diabetic patients in Pondicherry. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci. 2012;3(4):1185-96.
11. Joshi R, Atal S, Fatima Z, Balakrishnan S, Sharma S, Joshi A. Diabetes care during COVID-19 lockdown at a tertiary care centre in India. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.2020 Aug;166:108316.
12.Tabassum N, Rao RL. A study on adherence to therapy among hypertensives in urban slums of Hyderabad. Int J Health Sci Res. 2017;7:180?6.
13.Kotian SP, Waingankar P, Mahadik VJ. Assessment of compliance to treatment of hypertension and diabetes among previously diagnosed patients in urban slums of Belapur, Navi Mumbai, India. Indian J Public Health. 2019;63:348-52
14.Olickal JJ , Chinnakali P, Suryanarayana BS, Ulaganeethi R, Kumar SS, Saya GK. Effect of COVID19 pandemic and national lockdown on persons with diabetes from rural areas availing care in a tertiary care center, southern India. Diab Metab Syndr: Clin Res Rev.2020; 14: 1967e-1972
15. Nachimuthu S, Vijayalakshmi R, Sudha M, Viswanathan V. Coping with diabetes during the COVID - 19 lockdown in India: results of an online pilot survey. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2020;14(4):579e82.
16. Kumar D, Ahmad S, SharmaS. A review article on relation between metabolic syndrome, general wellbeing and yogic lifestyle. Subharti J of Interdisciplinary Research 2019; 2( 2) :5-10.
17. Sahay BK. Role of Yoga in Diabetes. J Assoc PhysiciansIndia. 2007;55:121-6.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License