IJCRR - 13(14), July, 2021
Pages: 101-106
Date of Publication: 20-Jul-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Comparison of Caries Assessment Spectrum and Treatment Needs (Cast) Index with Def Index in Measuring Dental Caries Among Three to Six-Year-Old School Children: A Descriptive Cross-Sectional Survey
Author: Vemagiri Charan Teja, KS Uloopi, C Vinay, Ch Anusha, P Brahmanna Chowdary, JT Pavithra
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Widely used def index for the assessment of caries around the world, is facing criticism on various limitations. WHO, ICDAS II and puff/PUFA indices had their own merits and demerits. Furthermore, the caries assessment indices documented in the literature does not cover the total caries spectrum. That necessitated the development of a comprehensive but realistic caries assessment index called the \"Caries Assessment Spectrum and Treatment Needs (CAST) index.\" Objective: To compare CAST and def indices in measuring dental caries among 3-6-year-old school children in and around Bhimavaram town, Andhra Pradesh, India. Methods and Material: A single examiner conducted a descriptive cross-sectional survey among 898, 3-6-year-old school children at randomly selected schools. Caries experience was recorded in a structured proforma using CAST and def indices. Descriptive statistical analysis was done. Inter and intragroup comparison were made by Kruskal Wallis ANOVA and Mann Whitney U tests respectively. Correlation between def and CAST indices was explored by Spearman's rank correlation coefficient. Results: Caries prevalence with CAST index (45.7%) was marginally higher compared with def index (44.7%). No significant difference was found between mean deft scores measured with CAST and def index (p=0.87). The high statistically significant difference in mean def scores with def index and the def component of CAST index for 3, 4, 5 and 6-year age groups was observed (p< 0.001). A strong correlation in measuring dental caries (p< 0.001)and a similar percentage of agreement for application (98.5%) was observed between both indices. Conclusion: No significant difference was found in measuring caries experience indicating the similarity between CAST and def indices in quantifying dental caries. CAST index provides more detailed information on caries prevalence, experience and severity compared with def index.
Keywords: CAST index, Def index, Dental caries, Caries prevalence, Correlation coefficient, ICDAS index
Full Text:
Introduction:
Dental indices are widely used for quantifying dental caries.1 Amongst numerous indices available, DMFT and def indices1 are commonly used. However, the paradigm shift in curative to preventive dentistry2 and management protocols led to the development of new indices named International Caries Detection and Assessment System (ICDAS),3Pulpal involvement-Ulceration-Fistula-Abscess (PUFA/pufa)4and Pulpalinvolvement-Root Sepsis (PRS)4 indices. But none of these indices gained attention globally.2,3
No index available described the total picture of caries progression which is beneficial for epidemiological surveys.5 So, to visualize the entire caries spectrum, Caries Assessment Spectrum and Treatment Needs (CAST) index were developed which unfolds caries in an increasing level of severity.6
A paucity of literature is evident regarding the characteristics of the CAST index, its diagnostic precision and its reliability for use in different populations. Hence the present study was designed with a primary objective to compare the CAST index with def index in measuring dental caries among 3-6-year-old school children. The secondary objective was to measure the complete range of carious lesions using the CAST index. It was null hypothesised that CAST index was inferior to def index in detailing the caries spectrum while the alternate hypothesis was kept as CAST index gives a more detailed picture of dental caries than the def index
Material and Methods:
The present descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted among 3-6-year-old school children in and around Bhimavaram, Andhra Pradesh, India between December 2014 to July 2015 for eight months. The study was approved by the Institutional Ethical Review Board (IEC/IRB NO: VDC/IEC/2014-16). The purpose and nature of the study were explained and prior permission from school authorities and a written informed consent from their parents were obtained. Selection of schools was done randomly based on the availability of children with only fully erupted deciduous dentition on the day of examination. Children with erupted first permanent molar, congenitally missing teeth and who require special health care needs were excluded from the study.
Before the original research, the investigator was trained and calibrated for two weeks, recording “def” and “CAST” indices under the guidance of the staff in charge to assess the intra examiner variability. The investigator had first carried out an oral examination on twenty subjects with dental caries. Then the same subjects were reexamined after two days and the results of two examinations were compared to assess intraexaminer variability. The Cohen’s kappa coefficient (K) value for intraexaminer agreement for both the indices was established at 0.93 (95% Confidence interval (CI = 0.791 -0.968), Z=1.96), (p<0.001) and the percentage of agreement for application of indices by the investigator was about 98.5%.
Based on the prevalence (46.21%) obtained in the pilot study, the minimum sample size was estimated to be around 398 using the formula (Z2α/2 x p × (1-p)) / E2 taking 95% confidence interval for which the value of Z2α/2 = 1.96 and marginal error 0.05. However, considering the CAST index can estimate a range of carious lesions and based on the availability of children from schools in and around Bhimavaram during the study period, 898 school children of various socio-economic status were allocated into the study by simple random sampling (lottery) method. Ten per cent of the sample was re-examined to assess intra examiner variability and found to be having good agreement (K=0.917).
The clinical examination was performed at pre-decided dates under sufficient daylight making children sit in an upright position with a plane mouth mirror and WHO periodontal probe under strict aseptic conditions. The data regarding caries experience was recorded in a specially designed proforma. The examination was limited to ten subjects per day and the average time spent for each child was approximately 15 minutes. Children who required any invasive dental procedures were referred to college for the needful.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was done using IBM Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) Ver.17.0 software. The intraexaminer reliability was determined by the unweighted Cohen’s kappa coefficient values. The Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient (r) explored the correlation between the “def” index and the “CAST” index. Inter and intragroup comparisons were made using Kruskal Wallis ANOVA and Mann Whitney U tests respectively. For all the tests, the p-value was set ≤ at 0.05.
Results:
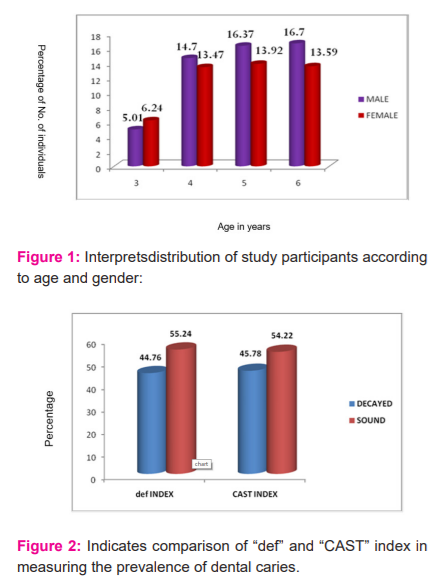
Around 898 school children, 474 males (52.78%) and 424 females (47.22%) with a mean age of 4.79 years were examined in the present study. Both age and gender show almost equal in their distribution. (Figure 1) The unweighted kappa value for intraexaminer consistency of measuring dental caries with def and CAST indices was established at 0.93 (95% Confidence interval (CI = 0.791 -0.968), Z=1.96). The spearman rank correlation coefficient showed a highly significant strong agreement between CAST and def indices for all age groups (p<0.001). (Table 1)
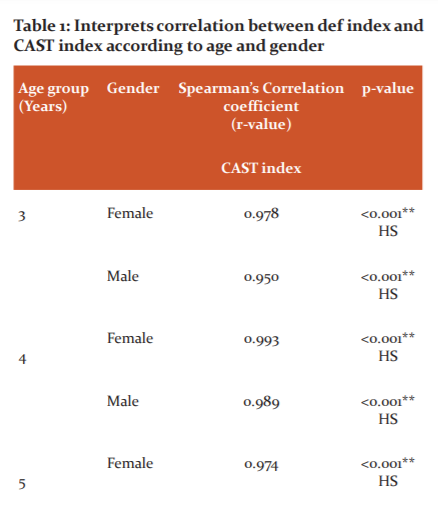
The CAST index presented 45.7% caries prevalence among the study subjects which was marginally higher and statistically insignificant (p=0.87) compared with the deft index (44.7%). (Figure 2)
The difference observed on the comparison of the overall mean score for the d, e, and f component of the CAST index (2.19 ± 3.30) with def index (2.16 ± 3.30) was statistically insignificant (p= 0.87). (Table 2)
A significant increasing trend of the mean deft score was observed in both the indices as the age increased from three to six years (Table 2). However, intergroup comparison of mean def scores of different age groups between both the indices showed no significant difference (p=0.819 for 3 years, p=0.913 for 4 years, p=0.937 for 5 years, p=0.874 for 6 years) (Table 2).
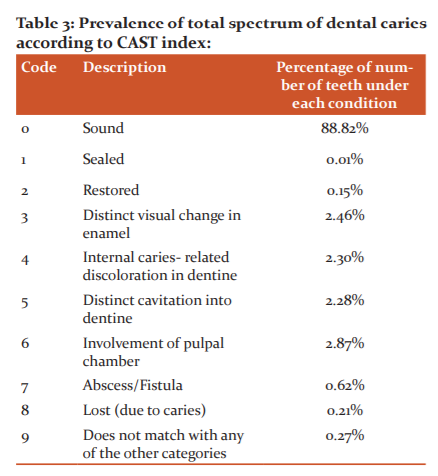
Table 3 shows the results of the CAST index recording criterion. Around 88.2% of the examined teeth were found to be sound whereas 2.46% presented a distinct visual change in enamel. 2.30% and 2.28% of teeth had non cavitated and cavitated dentinal lesions, respectively. The teeth with pulpal involvement and with abscess formation were 2.87% and 0.62% respectively. Sealed tooth component was 0.001% and 0.65% of examined teeth represented restored (0.15%), lost (0.21%) and other components (0.27%) of the index.


Discussion:
Data collected by dental indices is reliable and helps in the prevention and treatment of dental caries.6 Since eight decades, the def (decayed extracted and filled teeth) index has been frequently used for caries measurement of primary teeth in a given population.1,2 However, it fails in recording the early white spot lesions thereby underestimating the prevalence and severity of caries lesions.1 Therefore, its use is only limited to those populations who have high caries prevalence.2 Nevertheless, assessing carious lesions in both enamel and dentine has become vital in recent times.7
To combat the changing ideology to minimal invasive dentistry, the Caries Assessment Spectrum and Treatment Needs (CAST) index which describes the complete range of carious lesions hierarchically was developed. 8,9 Although the CAST index was validated for face content and construct,7 a few studies are reported in the literature regarding its usage in populations of different age groups and backgrounds in various countries. Hence the present study was designed.
The present study included three to six-year age group children because the primary dentition eruption completes by around 33±6 months and also it was difficult to get a large sample at a single place below three years.10
the def index was compared since it is most frequently used for dental caries quantification in primary dentition.1,2Examination and cavitation confirmation were done by WHO periodontal probe as the children are very young.3,8 Furthermore, the child’s cooperation with the examination, in turn, a positive dental behaviour was achieved. Besides, the literature reveals the usage of the explorer probe disrupts the surface layer and prevents the possibility of re-mineralization. 11,12
The study reveals the caries prevalence was marginally higher with CAST index (45.7%) compared to def (44.7%) similar to Baginska J et al. and de Souza et al. studies.13,14 CAST index records initial enamel decalcifications while def index ignores them thus underestimating the prevalence rate.11High caries prevalence in the present study population was also in similarity to that reported in Brazil (46%) in 2000,15 Nigeria(40%) in 1985,16 Aurangabad (47.8%) in 1992 .17
The kappa coefficient and Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient values in the present study revealed a perfect intro examiner reliability and a strong correlation in measuring dental caries between CAST and def indices for all the age groups and both genders. This was in agreement with the study conducted by Baginska J et al. 13
No significant difference was found in overall mean deft scores and deft scores for different age groups indicating that caries prevalence and experience recorded by CAST and def indices were similar for all age groups. This result coincides with that of de Souza et al. 14
The mean deft scores were significantly different between different age groups with CAST (0.86, 1.60, 2.15 and 3.27) and def (0.79, 1.58, 2.17 and 3.22) indices which suggest an increase in caries experience as the age increases with both the indices. A similar finding was also reported by Das et al. and Shankar et al. 18,1
CAST index criterion presents 0-9 codes in a hierarchical pattern of caries progression, out of which code 3, 4 and 5 reports carious experience representing enamel, non cavitated and cavitated dentinal caries respectively. The remaining six show the sealed (code 1), restored (code 2), caries severity (code 6 and 7) and lost/missing status (code 8).2
In the present study, a high proportion of children having teeth with pulpal involvement (2.87%) was observed implying that the availability of dental treatment services in the present population is lower. This in turn led to the high incidence of caries severity (0.62%). High enamel caries lesions (2.46%) indicate the requirement of immediate restorations, dental health education and continuous follow up. Furthermore, codes 4 and 5 percentage (4.76%) depict a portrait of the amount of curative care required for the school children. Lack of awareness among parents could be known by the low proportion of sealants (0.01%) and restorations (0.15%) in the present study population.
Quantification of deft scores from the CAST index is possible which infers that caries prevalence and experience recorded with the CAST index can be compared with the def index and other caries assessment criteria.7 Furthermore, reporting of progression of caries on a single tooth can be possible with CAST but not with def index.14 In addition, the CAST index details initial distinct visual changes in enamel as well as non cavitated and cavitated dentinal lesions based on which appropriate treatment plan can be designed which was not possible with def index. For collecting complete caries prevalence and experience in a population, the CAST index is advantageous because deft scores do not have to be complemented with pufa/PUFA index as that with the def index.5
Measurement of dental caries with both CAST and def indices was found to be similar in the present study population. CAST coding criterion will differentiate preventable and restorable carious lesions, which were just recorded as cavities in epidemiological studies to date with def index. Furthermore, the CAST index also details the untreated caries consequences which were omitted using the def index. 2,3,4
Despite immense training, the intraobserver bias may occur since only a well-trained eye can visualise caries in the superficial brilliance of the enamel even while using an air syringe. Hence, the investigator might have underestimated the actual caries status as caries was diagnosed entirely on visual examination. Moreover, the relative lack of discolouration of an early lesion would have also contributed to the underestimation of caries by the investigator.
Certain limitations about the CAST codes observed during the present study also need to be addressed such as where should a carious tooth with developmental disturbance of enamel and dentin is to be coded. The investigator moreover finds difficulty in distinguishing dentinal caries lesions with cavitation just only on visual discolouration without the radiographs especially in proximal regions. It was also observed that code 8 can be misinterpreted as tooth loss should be recorded exclusively on proper history and tooth can be lost due to various other reasons such as periodontal problems, trauma, orthodontic reasons etc. Furthermore, code 9 doesn’t detail what other dental disease conditions apart from dental caries has to be included. Time consumed for recording caries experience with CAST codes in comparison with a def index will also be a challenge if used in epidemiological research.
CAST index was more advantageous and delivered a detailed picture of caries experience than the def index in the primary dentition of the present study population thus satisfying the alternate hypothesis. However, further studies with equally distributed sample size in different populations of the globe need to be carried out for the acceptance of CAST as a reliable index.
Conclusion:
Based on the findings from this cross-sectional study, the following conclusions were drawn.
-
Dental caries prevalence and experience measured with CAST index was marginally higher compared with def index but the difference was statistically not significant.
-
Similar caries experience was provided by both CAST and def indices for different age groups.
-
CAST index has the potential for detecting the whole spectrum of dental caries more precisely compared with the def index.
Acknowledgements: Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Sources of Financial support: None
Conflict of Interest: None
Authors’ Contribution: All the six authors had contributed to the data collection, manuscript concept,
preparation, analyzing and writing the discussion.
References:
-
Shankar S, Naveen N, Kruthika M, Vinay S, Shaikh H. Comparison of def index with Nyvad's new caries diagnostic criteria among three to six years old children in a school at Bangalore city. Indian J Dent Res. 2012; 23:135-139.
-
Malik A, Shaukat MS, Qureshi A. Prevalence of dental caries using novel caries assessment index; CAST. J Dow Uni Health Sci. 2014; 8(1): 7-10.
-
Baginska J, Rodakowska E, Wilczynska-Borawska M, Jamiolkowski J. Index of clinical consequences of untreated dental caries (pufa) in the primary dentition of children from north-east Poland.Adv Med Sci. 2013; 58(2): 442-447.
-
Tiwari S, Dubey A, Singh B, Avinash A. Clinical consequences of untreated dental caries evaluated with the pulpal involvement- roots-sepsis index in the primary dentition of school children from the Raipur and Durg districts, Chhattisgarh State, India. Med Princ Pract. 2015; 24:184–188.
-
Baginska J, Rodakowska E, Milewski R, Kierklo A. Dental caries in primary and permanent molars in 7-8-year-old school children evaluated with Caries Assessment Spectrum and Treatment (CAST) index. BMC Oral Health. 2014; 14:74.
-
de Souza AL, Leal SC, Chaves SB, Bronkhorst EM, Frencken JE, Creugers NHJ, et al. The Caries Assessment Spectrum and Treatment (CAST) instrument: construct validation. Eur J Oral Sci. 2014; 122:149-153.
-
Frencken JE, de Souza AL, van der Sanden WJM, Bronkhorst EM, Leal SC. The Caries Assessment Spectrum and Treatment (CAST) instrument. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2013; 41:117–123.
-
Phansopkar S, Hegde-Shetiya S, Devadiga A, Agrawal D, Mahuli A, Mittal-Mahuli S, et al. Face and content validation of caries assessment spectrum and treatment index among few subject matter experts in India. Int J Dent Health Concern. 2015; 1(1):13-18.
-
De Souza AL, Bronkhorst EM, Creugers NHJ, Leal SC, Frencken JE. The Caries Assessment Spectrum and Treatment (CAST) instrument: its reproducibility in clinical studies. Int Dent J. 2014; 64(4):187-194.
-
Agarwal D, Sunitha S, Reddy CVK, Machale P. Early childhood caries prevalence, severity and pattern in 3-6-year-old preschool children of Mysore city, Karnataka. Pesq Bras Odontoped Clin Integr. 2012; 12 (4): 561-565
-
Simratvir M, Moghe GA, Thomas AM, Singh N, Chopra S. Evaluation of caries experience in 3-6-year-old children, and dental attitudes amongst the caregivers in the Ludhiana city. J Indian Soc PedodPrev Dent. 2009; 27(3):164-169.
-
Singh S, Vijayakumar N, Priyadarshini HR, Shobha M. Prevalence of early childhood caries among 3to 5yearold preschoolers in schools of Marathahalli, Bangalore. Dent Res J. 2012; 9(6):710-714.
-
Baginska J, Rodakowska E, Kierklo A. Status of occlusal surfaces of first permanent molars in 6 to 8yearold children evaluated by the CAST and DMF indices.Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2014; 15(2):107-112.
-
De Souza et al., Leal SC, Bronkhorst EM, Frencken JE. Assessing caries status according to the CAST instrument and WHO criterion in epidemiological studies. BMC Oral Health. 2014; 14:119.
-
Dini EL, Holt RD, Bedi R. Caries and its association with infant feeding and oral health-related behaviour in 3 to 4yearold Brazilian children. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2000; 28(4):241-248.
-
Milnes AR. Description and epidemiology of nursing caries. J Public Health Dent 1996; 56(1):38-50
-
Ali YA, Chandranee NJ, Khan A, Khan ZH. Prevalence of dental caries in nursery school children of Akola city. J Indian Soc PedodPrev Dent. 1996; 16(1):21-25.
-
Das D, Misra J, Mitra M, Bhattacharya B, Bagchi A. Prevalence of dental caries and treatment needs in children in coastal areas of West Bengal. Contemp Clin Dent. 2013; 4:482-487.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License