IJCRR - 13(14), July, 2021
Pages: 41-46
Date of Publication: 20-Jul-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Clinical Profile and Prognosis of Community-Acquired Pneum
Author: Ranjith Kumar GK, Eshwarappa P, Rashmi GK, Nagabhushana S
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Pneumonia is a disease known to mankind from ancient ages, Despite the availability of potent antibiotics, community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) remains a common and serious illness with significant morbidity and mortality, both in developing and developed countries. In the present study, we studied the occurrence, causes, clinical features and management issues of CAP. Aims: To study the clinical, bacteriological, and radiological profile of CAP admitted in malnad area of south India. Material and Methods: The study is conducted on 100 CAP patients admitted to various medical wards of the Mc Gann Hospital attached to Shimoga institute of medical sciences, Shimoga. From June 1st, 2019 to January 30th 2020. a detailed history was taken of all the patients and a thorough physical examination was done. blood is collected for analysis of CBC, Sr Creatinine, RBS, sputum Microscopy for Gram stain, Ziehl-Neelsen (Z-N) stain, Sputum culture is done, Chest radiograph (postero-anterior views) taken. Result: There were 67 males and 33 females. The average age is 54.4 \? 14.57 years. The majority of these patients belong to the age group >50 years (68%). Smoking (45%), COPD (33%) and Diabetes mellitus (14%) are the commonest associations. Commonest symptom is cough(99%), fever(90%) followed by expectoration 87(87%) followed by dyspnoea(52%). Streptococ�cus pneumonia (40%) infection is seen in the majority. Klebsiella pneumonia in 30(30%) and GBM in 11(11%). Lobar pneumonia seen in 66(66%), Bronchopneumonia seen in 33(33%). Right lower lobe involvement is seen in 52 (52%) next common is multilobar involvement 29(29%). Conclusion: The study concluded that pneumococcus found to be the most common organism causing pneumonia in our setup. There is an increased incidence of Gram-negative organism (Klebsiella pneumoniae) is seen in our hospital. Clinical features (cough, sputum, breathlessness) are seen in all age group of patients. Ageing predisposes to a higher risk of respiratory tract infection in individuals with smoking-related lung diseases and COPD. Our observations will also be useful to monitor the trends of CAP in the population of the region and will help the physicians to start rational empirical treatment for patients with CAP.
Keywords: CAP, Sputum, Cough, Pneumonia, Smoking, Gram-negative organism
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Pneumonia is a disease known to the Human race from antiquity. Pneumonia defines as “This is an acute inflammatory reaction of the pulmonary parenchyma that can be caused by various infective and noninfective origin.1
Even with the availability of a wide variety of antibiotics,2 community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) remains a very common and lethal illness with quite a significant morbidity and mortality, in all the continents of the world. Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in persons aged over 60 years,3 with incidence and mortality rates increasing with growing age.4 Hospital admission is the greatest burden from pneumonia in terms of severity and health-care costs. Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) is a common disease with an incidence of about 20- 30% in developing countries to an incidence of 3-4% in developed countries.5
Even though definite data is lacking, pneumonia remains a leading cause of death in our country.6 The mortality rate of the pneumonia patient, who is being treated as an outpatient (mild disease) is low, in the range of 1-5%, but among patient who requires admission to ICU is approaches 25%.7-10 With the beginning of the antibiotic era, the mortality rate decreased and remained in a constant state. Despite the progress made in the diagnosis of pneumonia, it takes a few days that to in tertiary care centres, to identify the causative micro-organism in the blood or sputum samples and the aetiology of many patients with CAP remains uncertain.2 To make correct therapeutic decisions, physicians need reliable data on the prevalence of different etiological agents in the patients “locality,” in addition to the clinical, laboratory, and radiological finding.7
Because the relative frequency of etiological agents differs in different geographical areas. There are many studies conducted to explain its clinical,
Microbiological agents and radiographic features in different population groups, whether these studies can be applied to our population is a real issue to be answered. Because of this, we needed a study on community-acquired pneumonia in our locality, and by doing this study we can help in the early detection of disease, and clinical, bacteriological, and radiological profile of CAP admitted in our geographical area can be known.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study is conducted on 100 consecutive patients admitted in various medical wards of the Mc Gann Hospital attached to Shimoga institute of medical sciences, Shimoga. From June 1st, 2019 to January 30th 2020.
INCLUSION CRITERIA:
Adult patient aged between 15 to 90 years in diagnosed as having Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP).
New or progressive chest infiltrates on chest X-ray with at least one of the following features:
1. Fever (temperature >37.7°C)
2. Purulent sputum
3. Cough (H/O <14 days)
4. Leukocytosis (WBC >11,000/cumm).
EXCLUSION CRITERIA:
-
Age less than 15 years,
-
Hospital-acquired pneumonia
-
Aspiration pneumonia
-
H/O pulmonary infarction, pulmonary tuberculosis, immune-compromised.
METHODS:
One hundred patients admitted in Mc Gann district Hospital attached to Shimoga institute of medical sciences, Shimoga having Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) fulfilling the above criteria were taken into the study after taking consent from all the patients. Every patient's detailed clinical history and examination was done and routine investigations were done for all patients. Chest X-ray PA view is taken. Sputum microscopy and culture are done. Other tests like 2D-Echocardiography, Ultrasound abdomen were done where ever required. Every patient is evaluated in detail to arrive at a possible etiological diagnosis.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was done using the Chi-square test. the p-value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
The statistical software SPSS 11.0 was used for the analysis of the data.
RESULTS
Demographic Data: The study group consisted of 100 patients, among whom
67 were males and 33 were females. They were studied from June 1st, 2019 to January 30th 2020. The male to female ratio is 2:1.
The age of patients ranges from 15 to 85, with the mean age 54.4 ± 14.57 years. Most patient 68 (68%) of CAP were elderly belong to >50 years age group ( Fig 1).
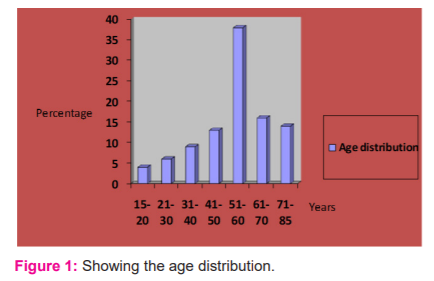
Incidence of symptoms
Cough was the most common symptom present in (99%) patients, followed by fever (90%), dyspnea (52%), expectoration (87%), fatigue (45%) and chest pain (15%). Other less common findings are haemoptysis (7%), cyanosis (5%). Chest pain was more common in younger than elderly age group patients.
In the study, chronic obstructive airway disease was the most common (33%), predisposing conditions. Other were cardiovascular disorders (14%), diabetes mellitus (DM) (14%), Cerebrovascular accident (5%), and chronic liver disease (3%). Among habits, smoking was the most commonly noted in (45%) patient, followed by alcoholism in (12%) patients. Maximum smokers and drinkers were elderly belong to > 50 years age group.
Bacteriological incidence in percentage.
Streptococcus pneumonia(40%), Klebsiella pneumonia(30%), Staphylococcus aureus(15%), Gram-negative bacilli(11%), Haemophilus influenza(6%).
The etiological diagnosis was made possible only in 55 (45.8%) cases. The isolation of organisms done by sputum culture in 44 (36.7%), and by blood culture in 11 (9.1%). The commonest causative organism isolated was Pneumoccocus 20 (36.4%) followed by Klebsiella pneumonia 16 (29%), Staphylococcus aureus 11 (20%), Haemophilus influenzae and Gram-negative bacilli 8 (14.5%).
Types of pneumonia according to Chest X?ray findings in patients with CAP
Lobar pneumonia seen in 66%, Bronchopneumonia seen in 28%, Interstitial pneumonia in 5%, Pleural effusion seen in 10% of patients ( Fig. 2).
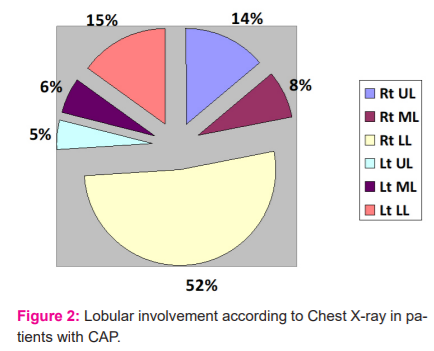
(UL-Upper Lobe, ML-Middle Lobe, LL-Lower Lobe)
The right lower lobe of the lung is most commonly involved in CAP (P < 0.0001).
Bilateral lung involvement is seen in 19.8% of chest X-ray. Multiple lobes involvement is seen in 29 (29%).
There is no relation between the area of lung involvement and causative organism.
Prognostic factors and Mortality
Duration of stay varied from 3 days to 23 days (10±7). Sepsis is seen in 17%. Lung abscess 4%, Pneumothorax 3%, Pleural effusion 30%, Respiratory support 45% (in the form of oxygen received by 33% patients, NIV in 7%, invasive ventilation in 5%). The death occurred in 7 patients. Sepsis and respiratory failure is the cause in 6, one had a myocardial infarction.
DISCUSSION
Age/Sex Incidence
In the study, 100 patients were observed, and the majority of patients 67 (67%) were males in comparison to the female population which were 33 (33%). The male to female ratio is 2:1. The mean age of patients was 54.4 ± 14.57 years. 68 (68%) belong to > 50 years of age group. It is well-documented that pneumonia incidence rises sharply with extremes of age ( Table 1).11,12
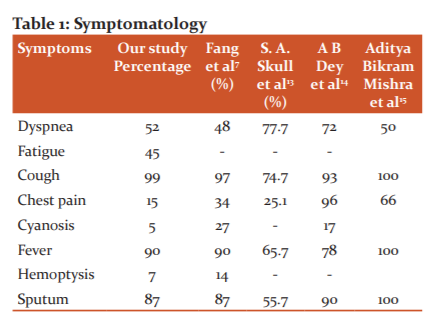
The most common symptom is Fever. Most of the symptoms presentations correlate with other studies.
Fever in 90 (90%), cough in 99 (99%) and expectoration in 87 (87%) patients. Other symptoms were shortness of breath in 52 (52%), pleuritic chest pain in 15 (15%), hemoptysis in 7 (7%), altered sensorium in 3, nausea, vomiting and lose motions in 2 and abdominal pain in 3 patients. This fact supported by some Indian and Western studies ( Table 2).7,16,17
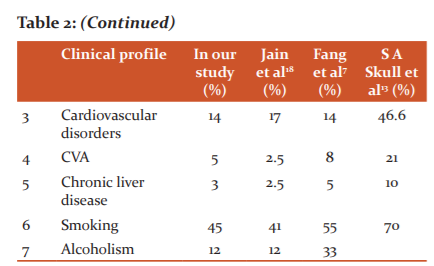
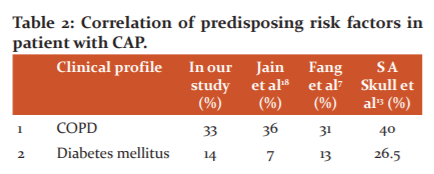
This is the well-established fact that the majority of predisposing risk factors like cigarette smoking, alcoholism, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, (COPD), coronary artery disease, etc., similar in all most studies. It is more common in middle-aged and elderly predominantly in males. This is by the earlier studies like Jain et al.,18 Fang et al.,7 S A Skull et al.13
The most common identified risk factor was smoking (45%), COPD (33%), cardiovascular diseases (14%), followed by DM (14%) and alcoholism (12%), there are many mechanisms which change regional and systemic respiratory antimicrobial immune function which causes respiratory infection. that is proved beyond doubt. These factors are not different in our locality, India or around the world.4,16,17,19.
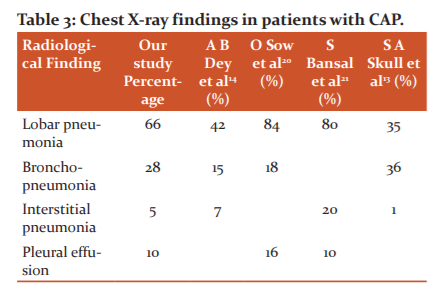
The radiological data in our study showed a predominance of lobar pneumonia in 66 (66%) patients followed by bronchopneumonia in 28 (28%) and interstitial pneumonia in 5 (5%) patients. Radiological information from our study emphasized by similar studies done by O Sow et al.20 Bansal et al.21 Chest X-ray showing infiltrates is necessary to establish the diagnosis of pneumonia. However, it cannot differentiate between bacterial and nonbacterial pneumonia (Table 3).
Chest X-ray pattern of patients with CAP
In our study shows a significant correlation with Jain et al study. Right lower lobe involvement is commonly similar to Jain et al.18 studies. Maybe because this lobe has straight communication with the trachea. Organisms in more number get lodged in this lobe ( Table 4).
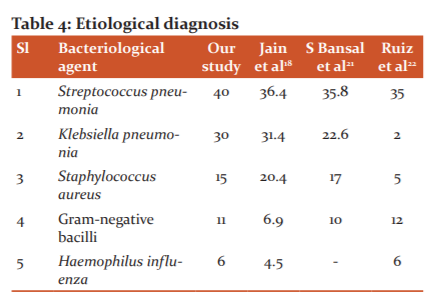
In a study, the microbial diagnosis of CAP was confirmed only in 40% of patients. This could be due to the limited use of laboratory tests, error in sample collection. Results of our study showed close resemblance to the study by Ruiz et al.22 In our study, we only used sputum and blood culture as diagnostic tools to identify the culprit organism that causes pneumonia. 32 (32%) isolated by sputum, and 8 (8%) by blood culture. But the fact is that even with the use of extensive laboratory testing and various invasive procedures, etiological confirmation could be achieved only in 45-70% of patients.2,23 The most common isolated pathogen was S. pneumonia accounting for 40%. Next common was K. pneumonia which accounts for 30% this followed by S. aureus, and other Gram-negative bacilli 15%, 11%, respectively (Gram-negative bacilli includes H. influenzae, Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter, Escherichia coli, Enterobacter, Citrobacter accounting 6%, 1%, 1%, 1%, 1%, 1% respectively). In the previous 3 decades many studies done in our nation showed the predominance of gram-negative organisms in culture-positive samples .24-27 there is more number of culture-positive Gram-negative bacteria in this study compared to studies were done in other nations ( Table 5).28


The prognosis outcome of CAP in our study is 7% mortality and 93% recovery rate. Joint ICS/NCCP (I) guidelines published in the year 2012 mentioned that mortality rates across India vary from 3.3% to 11%32. Duration of stay is almost similar to most of the studies with 3 to 4 days for mild cases, 10-15 days for severe diseases requiring ICU admission. Complication like lung abscess, pleural effusion, pneumothorax and sepsis varies with other studies, this can be explained by different organisms affecting, their antibiogram and use of different antibiotics and also patient immunity status. Most of the mortality is seen in diabetics, old age, anaemic and malnourished people.
CONCLUSIONS
The study is conducted on 100 consecutive patients admitted in various medical wards of the Mc Gann Hospital, Department of Medicine attached to Shimoga institute of medical sciences, Shimoga. From June 1st, 2019 to January 30th 2020. to know the incidence and prevalence of etiological organisms in CAP in our area, clinical features, and to know the relation between the involvement of a particular lung area with the causative etiological organism.
And the study concluded that Pneumococcus is the most common causative micro-organism in CAP, but there is an increase in the incidence of Gram-negative bacterial infection particularly by Klebsiella pneumonia is seen in our malnad area. Typical symptoms (cough, sputum,
breathlessness) were common in both young and elder age group patients, Ageing predisposes to a higher risk of respiratory tract infection in individuals with smoking-related lung diseases and debilitating non-respiratory diseases. Our observations will also be useful to monitor the trends of CAP in the population of the region and will help the physicians to start rational empirical treatment for patients with CAP.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study is supported by many in data collection: Nursing staff, Interns, staff of the department of medicine, SIMS Shimoga. We thank each and everybody.
Conflict of interest: nil. Source of funding: nil
Authors contribution
Dr Ranjith kumar G K. had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Dr Rashmi Gk, Dr Eshwarappa, Dr Nagabhushana S contributed substantially to the study design, data analysis and interpretation, and the writing of the manuscript.
References:
-
Seaton A, Seaton D, Leich AG. Crofton & Douglas’s. Respiratory Diseases. 5th ed., Vol. 1. Ch. 13. New Delhi: Wiley; 2008. p. 356-429.
-
Ishida T, Hashimoto T, Arita M, Ito I, Osawa M. Etiology of community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized patients: A-3-year prospective study in Japan. Chest 1998; 114 : 1588-93.
-
Niederman MS, Ahmed QAA. Community-acquired pneumonia in elderly patients. Clinics in Geriatric Medicine 2003; 19: 101–120. 2. Loeb M. Pneumonia in older persons. Clin Infect Dis. 2003; 37: 1335–1339.
-
Garibaldi RA. Epidemiology of community-acquired respiratory tract infections in adults. Incidence, aetiology, and impact. Am J Med. 1985;78:32-7.
-
Diwakar T N, Ravish KS, Hussain ZG. Comparative study of pneumonia severity index and curb65 in assessing the severity of community-acquired pneumonia. J Evol Med Dental Sci. 2013; 2(8):836-850.
-
Kulpati DDS, Khastgir T. Reappraisal of cases of pneumonia. J Assoc Physicians Ind. 1988; 36: 660-64.
-
Fang GD, Fine M, Orloff J, Arisumi D, Yu VL, Kapoor W, et al. New and emerging etiologies for community-acquired pneumonia with implications for therapy. A prospective multicentre study of 359 cases. Med (Baltimore).1990;69:307-16.
-
Marrie TJ, Durant H, Yates L. Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization: a 5-year prospective study. Rev Infect Dis. 1989;11:586-99.
-
Torres A, Serra-Batlles J, Ferrer A, Jiménez P, Celis R, Cobo E, et al. Severe community-acquired pneumonia. Epidemiology and prognostic factors. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991;144:312-8.
-
Pachon J, Prados MD, Capote F, Cuello JA, Garnacho J, Verano A. Severe community-acquired pneumonia: aetiology, prognosis, and treatment. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990;142:369-73.
-
Vilar J, Domingo ML, Soto C, Cogollos J. Radiology of bacterial pneumonia. Eur J Radiol. 2004;51:102-13.
-
Siegel RE, Halpern NA, Almenoff PL, Lee A, Cashin R, Greene JG. A prospective randomized study of inpatient IV. Antibiotics for community-acquired pneumonia. The optimal duration of therapy. Chest. 1996;110:965-71.
-
Skull SA, Andrews RM, Byrnes GB, Campbell DA, Kelly HA, Brown GV et al. Hospitalized community-acquired pneumonia in the elderly: an Australian case-cohort study. Epidemiol. Infect. 2009; 137, 194–202.
-
Dey AB, Nagarkar KM, Kumar V. Clinical presentation and predictors of outcome in adult patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Nat Med J Ind. 1997; 10(4):169-172.
-
Mishra AB, Behera GB. Community-Acquired Pneumonia, Detection and Prevention– A Hospital-Based Descriptive Study. Int J Contemporary Med Res. 2016; 3(4), April:1127-1129.
-
Shah BA, Singh G, Naik MA, Dhobi GN. Bacteriological and clinical profile of Community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized patients. Lung Ind. 2010;27:54-7.
-
Bansal S, Kashyap S, Pal LS, Goel A. Clinical and bacteriological profile of community-acquired pneumonia in Shimla, Himachal Pradesh. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2004;46:17-22.
-
Jain SK, Jain S, Trikha S. Study of Clinical, Radiological, and Bacteriological Profile of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Hospitalized Patients of Gajra Raja Medical College, Gwalior, Central India. Int J Sci.2014; 2( 6):96-100.
-
Arbo MD, Snydman DR. Influence of blood culture results on antibiotic choice in the treatment of bacteremia. Arch Intern Med. 1994;154:2641-5.
-
Sow, Frechet, Diallo, Soumah, Conde, Diot, Boissinot, Lemarie. Community-acquired pneumonia in adults: a study comparing clinical features and outcome in Africa (Republic of Guinea) and Europe (France). Thorax. 1996;51:385-388.
-
Bansal S, Kashyap S, Pal LS, Goel A. Clinical and Bacteriological Profile of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Shimla, Himachal Pradesh. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2004; 46: 17-22.
-
Ruiz, Ewig, Marcos, Martinez, Arancibia, Mensa et al. Etiology of Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Impact of Age, Comorbidity, and Severity. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160:397–405.
-
Lieberman D, Schlaeffer F, Boldur I, Lieberman D, Horowitz S, Friedman MG, et al. Multiple pathogens in adult patients admitted with community-acquired pneumonia: A one-year prospective study of 346 consecutive patients. Thorax. 1996;51:179-84.
-
Ailani RK, Agastya G, Ailani RK, Mukunda BN, Shekar R. Doxycycline is a cost-effective therapy for hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Arch Intern Med. 1999;159:266-70.
-
Almirall J, Morató I, Riera F, Verdaguer A, Priu R, Coll P, et al. Incidence of community-acquired pneumonia and Chlamydia pneumonia infection: A prospective multicentre study. Eur Respir J. 1993;6:14-8.
-
Amsden GW. Pneumococcal macrolide resistance – Myth or reality? J Antimicrob Chemother. 1999;44:1-6.
-
Berntsson E, Lagergård T, Strannegård O, Trollfors B. Etiology of community-acquired pneumonia in out-patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986;5:446-7.
-
Basi SK, Marrie TJ, Huang JQ, Majumdar SR. Patients admitted to hospital with suspected pneumonia and normal chest radiographs: Epidemiology, microbiology, and outcomes. Am J Med. 2004;117:305-11.
-
Mbata GC, Chukwuka CJ, Onyedum CC, Onwubere BJC, Aguwa EN.: Role of complications of CAP on the outcome of the illness. Ann Med Health Sci Rese. 2013;3( 3):365-369.
-
Peyrani P, Forest W. Arnold, Bordon J, Furmanek S, Carlos M et al. Incidence and Mortality of Adults Hospitalized With Community-Acquired Pneumonia According to Clinical Course. Chest. January 2020; 157(1):34-41.
-
Lamb A, Patil AH. Management and outcome of community-acquired pneumonia: hospital-based study, Int J Res Med Sci. 2018 Jul;6(7):2271-2274.
-
Gupta D, Agarwal R, Aggarwal AN, Singh N, Mishra N, Khilnani GC, et al. Guidelines for diagnosis and management of community-and hospital-acquired pneumonia in adults: Joint ICS/NCCP(I) recommendations. Lung Ind. 2012;29: S2:27-62.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License