IJCRR - 13(14), July, 2021
Pages: 28-34
Date of Publication: 20-Jul-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A Comparative Study of Two Manual Technique on Triceps Surae Muscle Flexibility in Working Females Wearing High Heels
Author: Ahmed H, Alqhtani R, Alshahrani A, Mughal M Y, Khan A R
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objective: This study aimed to observe the influence of two manual techniques in improving the flexibility of the triceps surae muscle in working females wearing high heels. Methods: This study is based on a pretest-posttest experimental control group design, which included forty-five working females wearing high heels. All the participants were assigned randomly into three groups A, B and C. Group A received a hot pack treatment for 20 minutes followed by a Muscle Energy Technique (MET) which was repeated four times (10-second contraction, 5-second relaxation). Group B received a hot pack intervention for 20 minutes followed by static stretching which was repeated five times (30-second hold, 15-second rest between each repetition). Group C received only a hot pack intervention for 20 minutes. Active ankle dorsiflexion range of motion (ADFROM) on day 1 pre-intervention (baseline) and post-intervention on Day 1, 3, 5 and 8 was taken as an outcome measure. Results: For the variable ADFROM, the data analysis showed insignificant differences (p0.05) against control group C, though an insignificant difference (p< 0.05) between them at Day 5 post-intervention and the Day 8 follow-up, respectively. Conclusion: This study concluded that both manual techniques are equally effective in improving the flexibility of the triceps surae muscle in working females wearing high heels.
Keywords: Flexibility, Muscle Energy Technique, Static stretching, Triceps surae muscle. Footwear, Manual therapy
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, wearing high heels is a fashion followed by around 40 to 70% of women in the world.1An average height of a high-heeled shoe is approximately 10cm while the height of a low-heeled or flat-soled shoe range between 0-4cms. Moreover, a high-heeled shoe has a narrow toe holder and a stiff heel cap that projects anteriorly2 with an excessive plantar curvature.3
Most women acknowledge that wearing high-heeled shoes provides a sense of self-esteem and intellectual well-being, which makes this type of footwear popular. However, some researchers have reported that the use of these shoes has subsequently had an adverse effect on different body structures. 4,5,6
Studies suggested that the use of high heels can contribute to the incidence and progression of knee pain,7,8 an increased predisposition toward degenerative knee osteoarthritis 8,9, low back pain due to increased spinal curvature 10,11 and changes in gait pattern, such as walking speed and mobility.12-15
Studies established that the practice of wearing high-heeled shoes for an extended period increases plantar flexion and leads to decreased triceps surae muscle extensibility and decreased ankle joint range of motion. this can lead to Achilles tendinitis, gastrocnemius strain, and plantar fasciitis.4,5
As a result, calf muscle stretches are commonly prescribed in an attempt to increase ankle joint dorsiflexion and to reduce the symptoms of such disorders.16-21 Physical therapists are using a wider approach of interventions to maintain and increase flexibility, reduce joint stiffness, avoid dysfunction and deformities resulting from muscle contractures. This includes moist heat packs, ultrasonic therapy, constant passive motion, stretching, MET, or a combination of these methods.22,23,24
The stretching technique used and widely accepted proved to be beneficial in increasing flexibility22. Similarly, athletes used the stretching to elongate the muscle-tendon unit (MTU) at the end range of motion and holding that stretch for up to one minute before relaxing, and then repeated this stretch several times.25-29
Apart from static stretching, MET is also used to improve muscle flexibility. It is a manual technique that has been described as a gentle form of manipulative therapy effective for restoring movement deficits of both the spine and extremities. It is considered to be effective in elongation of shortened/contractured muscle, strengthening of muscles, draining of fluids, and improving the ROM of a restricted joint. While osteopaths and other manual therapists use MET extensively, there is insufficient research aiding and validating its theories and use to explain the effects of MET.24, 30 Furthermore, many studies have reported on the effectiveness of MET and the contract-relax technique in increasing flexibility of the hamstring muscle.31-34
The results of the above-mentioned studies are more or less conflicting, so this study aims to establish the effectiveness of MET and static stretching in increasing the muscle flexibility of the triceps surae and also to investigate which technique is more effective.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Participants
A different subject pretest-posttest experimental control group design was selected for testing the hypothesis and data was collected. An active ADFROM was taken as the outcome measure to establish the effect of the two manual techniques. Forty-five working females wearing high heels were recruited for this study. The study was approved by the institutional review board of the integral institute of allied health sciences and research at integral university (RRC-2016-04). All the participants were recruited from the Outpatient Physiotherapy Department IIMSR, Lucknow. The criteria for inclusion were working females wearing high heels, age 20-30 years having triceps surae muscle tightness with active dorsiflexion ROM < 20o. Subjects were excluded if they had hypermobility of the ankle joint, skin diseases, wounds, neurological problems, circulatory problems and metal implants in the leg or foot.
Procedures
All the participants were selected based on the above criteria. Before participation, the whole procedure was explained to the subjects and informed consent was given and signed by them. Then, all the participants were randomly assigned into three equal groups A, B and C. The experimental group's A and B received a hot pack intervention plus MET and a hot pack intervention plus static stretching, respectively. Control group C received the hot pack intervention only. Data collected at baseline (pre-intervention Day 1), and post-intervention Days 1, 3, 5 and 8.
Assessment of ankle ROM
For goniometric measurements of ankle dorsiflexion ROM, a standard tape measure was used to ensure that the participants were positioned prone on the testing table with their lateral malleolus nine inches beyond the table’s edge. Then, the researchers marked the 5th metatarsal head, the base of the 5th metatarsal, fibular head, and lateral malleolus with a permanent marker. The moving arm of the goniometer was placed at the lateral border of the foot, while the fixed part of the goniometer was placed along the long axis of the fibula to lie at the centre of the axis of rotation at the lateral malleolus. To establish the reliability of ROM measurements, readings were taken thrice, and their mean used for analysis.
Interventions
Hot pack
The patient was comfortably positioned in prone lying on a plinth and a hot pack was placed over the triceps surae muscle for 20 minutes. This was carried out on both experimental and control groups for five consecutive days.
Static stretching
In order to stretch the calf muscle, the participant was asked to place their forearms against the wall with their forehead resting on their hands. Participant stood barefoot between two to three feet away from a solid wall, placed the testing foot perpendicular to and facing the wall, the opposite leg placed on the ground with the knee bent and the foot in front of the body. The testing limb was placed straight out behind the body, keeping the knee straight and the heel flat on the ground. Once the subject became comfortable, they were instructed to lean forward at the hips until they felt a stretching sensation in their calf muscle. Each stretch was held for a duration of 30 seconds35, 36. This was repeated five times in a single session for five consecutive days.
Muscle energy technique
The participant lay in a supine position with feet extending over the edge of the plinth while the knees were kept straight. For the right leg MET, the therapist held the tested Achilles tendon with the right hand just above the heel to keep the heel in the palm of their right hand. The therapist’s left hand was placed so that the fingers rested on the dorsum of the foot. Then, the barrier was assessed and the muscle was kept in a comfortable position, in the mid-range away from the restriction barrier. The participant was instructed to exert an effort (approx. 20% of maximal contraction) of available strength towards the plantar flexion, against unyielding resistance, with appropriate breathing i.e. inhale as they built up the isometric contraction, holding the breath for 10 seconds during the contraction, and then exhaling as they slowly loosened the contraction. This was followed by a rest period of five seconds to ensure complete relaxation before re-commencing the stretch. Then the tissue was held for 10 sec. in the slight stretch to enable a slow lengthening of the tissue. This was repeated four times in a single session for five consecutive days.
Statistical methods
A computer software package SPSS.inc was used for the statistical analysis of the data. Baseline demographic data of subjects, including age and sex, were descriptively summarized and statistically analysed. The ADFROM, as a dependent variable measured on Day 1 (pretest data is represented as PREROM1, posttest data is represented as POSTROM1), on Day 3 (Pretest data is represented as PreROM3, posttest data is represented as POSTROM3), on Day 5 (Pretest data is represented as PREROM5, posttest data is represented as POSTROM5), and after two days follow-up on Day 8 (represented as follow-up).
Analysis was conducted using one-way ANOVA and post-hoc (Bonferroni’s test) analysis with the level of significance, α, set at 0.05. The paired t-test was used for the analysis within the groups, set ting the confidence interval and the level of significance, α at 95% and 0.05, respectively.
RESULTS
This study was designed to check the comparative effects of MET and static stretching on improving the flexibility of triceps surae among working females wearing high heels. 45 working females who wear high heels were evaluated for the study and their age, weight, height and BMI were recorded. Demographic details with their means and standard deviations are presented in Table 1.
Between-group analysis
The mean and standard deviation details of between-group analyses showed in table 2. The pretest reading i.e. PREROM1 for all the three groups was statistically insignificant (p=.136). On comparing Group A and Group B, the PREROM1 is insignificant (p=.710). Similarly, PREROM1 values for Group A and Group C were insignificant statistically (p=.144) and again when Group B was compared with Group C for PREROM1, the values were insignificant (p=1.00) as shown in table 3.
The posttest reading on Day 1 i.e. POSTROM1 for all the three groups was also statistically insignificant (p>0.05). Further post-hoc analysis revealed insignificant differences (p>0.05) between Groups A and B (p=1.00), Groups A and C (p=.063), and Groups B and C (p=.359).
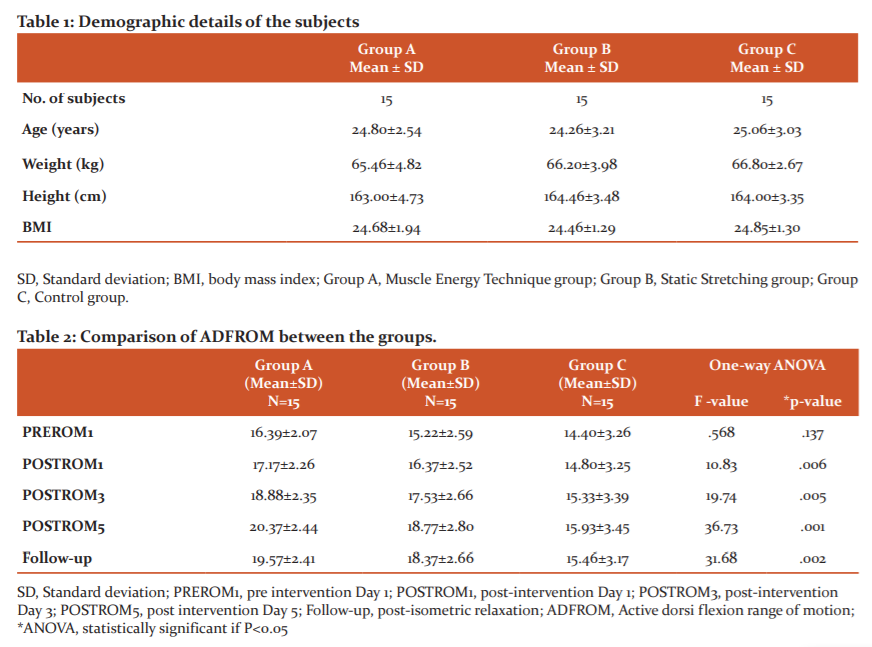
On Day 3, i.e. at POSTROM3, a significant difference was found (p= .005) between Groups A, B and C (Figure 1). However, post-hoc analysis revealed an insignificant difference between Groups A and B (p= .596) and Groups B and C (p=.120), but there was a significant difference between Groups A and C (p=.004) as shown in table 3.
On day 5, i.e. POSTROM5, a significant difference (p<.05) was also found between the Groups A, B and C. Further, post-hoc analysis revealed a significant difference between Groups A and C (p=.000), Groups B and C (p=.033), but an insignificant difference between Groups A and B (p=.427) as shown in table 3.
On Day 8 i.e. FOLLOW-UP, a significant difference was found (p<.05) between Groups A, B and C. Further, post-hoc analysis revealed a significant difference between Groups A and C (p=.002), Group B and C (p=.033), but an insignificant difference between Groups A and B (p=.837) as shown in table 3.
Within-group analysis
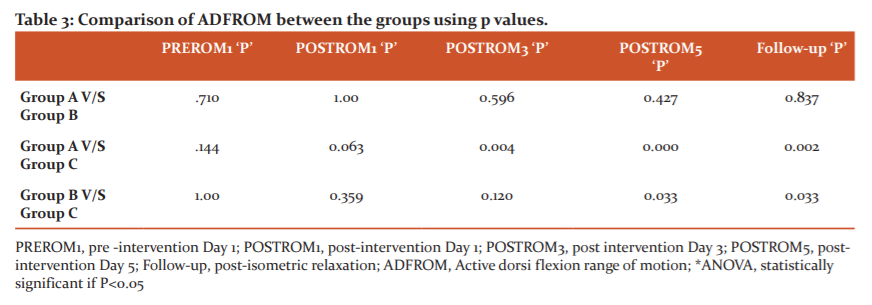
On comparing the values between pretest and posttest (PREROM1-POSTROM1) reading on Day 1, a significant difference (p<0.05) was found in all three groups (Figure 2). The participants in Groups A, B and C showed an improvement in their mean scores at 0.78 ±0.19, 1.15 ±0.07, and 0.40 ±0.01 respectively.
On comparing the values between the pretest and the posttest (PREROM3-POSTROM1) reading on Day 3, a significant difference (p<0.05) was found in all three groups. The participants in Groups A, B and C showed an improvement in their mean scores at 0.93 ±0.12, 1.07 ±0.07, and 0.40 ±0.24, respectively.
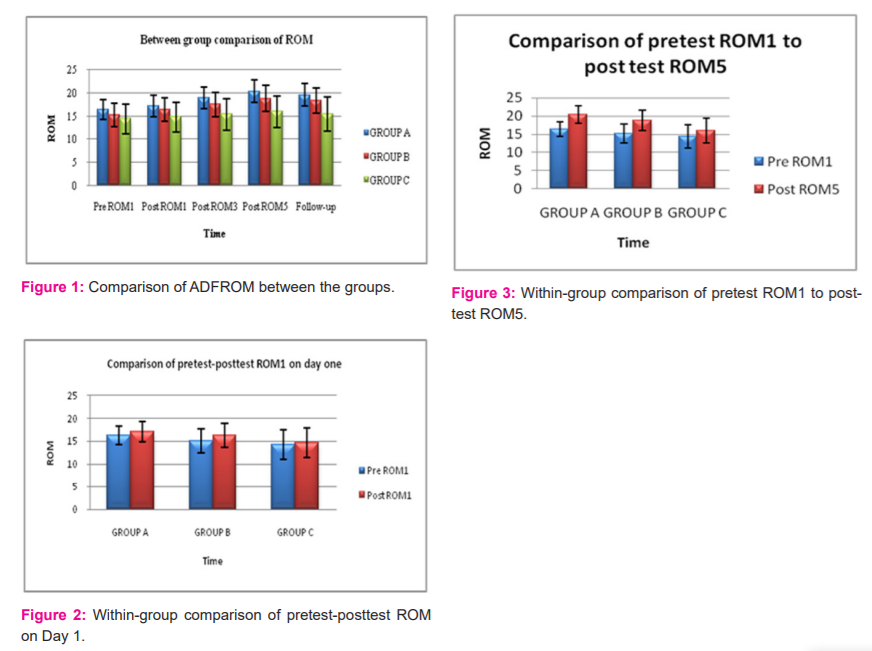
On comparing the values between pretest and posttest (PREROM5-POSTROM1) reading on Day 5, further, a significant difference (p<0.05) was found in all three groups (Figure 3). The participants in Groups A, B and C showed an improvement in their mean scores at 3.98±0.37, 3.55±0.21, and 1.53 ±0.19, respectively.
On comparing the values between posttest readings for Day 5 and Day 8 (FOLLOWUP- POSTROM5), a significant decrease (p<0.05) in ADFROM was noted in all three groups. The mean decrease in Groups A, B, and C were noted as 0.80±0.03, 0.40±0.14 and 0.47 ±0.28, respectively.
DISCUSSION
The available literature on the role of different techniques on improving the flexibility of muscles revealed a confusing picture yet to prove which one is the best, either MET or SS, to serve this purpose. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate and evaluate the efficacy of MET and SS on improving the flexibility of the triceps surae muscle in working females wearing high heels and to establish which would be better to use in the long run.
The results of our study demonstrate that both MET and SS are effective methods to improve triceps surae muscle flexibility when compared to the control group. The results further suggest that both techniques are equally effective in improving flexibility as there is no significant difference between the MET and SS groups.
There has been no previous study to check the efficacy of MET on improving the flexibility of the triceps surae muscle in working females wearing high heels so there is no data or results for comparison. Many studies have focused on muscles such as the hamstring triceps surae as well as muscles in the cervical and lumbar regions in healthy populations with no criteria for wearing high heels. Neurophysiological or biomechanical changes or an increase in stretch tolerance have been considered to be responsible for the increased flexibility of the muscle/viscoelastic tissue.37 Some studies have speculated on the neurological mechanisms which may increase the range of motion of a joint after application of MET; however, there is little research to substantiate these theories. Ahmed et al concluded that increase cervical range of motion of a joint after application of MET38. Kuchera attributed the effectiveness of MET to the inhibitory Golgi tendon reflex that may be activated during isometric contraction of the muscles, which is claimed to produce a stretch on the Golgi tendon organs and a reflex relaxation of the muscle.35
The therapeutic action of MET can be understood through static stretching to the mechanical component of the muscle. Resting tension of the muscle is upheld by myofibrils and the range of motion is subject to viscoelastic elements of the connective tissues. As the constant stretch is applied over a viscoelastic structure, the myofibrils become detached and the force of material is decreased, resulting in an increased range of motion. Both Halbertsma et al., and Magnusson et al., reported that an increase in the extensibility of the muscle was achieved through increasing applied torque. Therefore, they concluded that elongation of muscle length could be achieved through a constant application of torque over a viscoelastic tissue. 36
Although both MET and SS focuses on non-contractile viscoelastic components, MET places more emphasis on the contractile component which causes post isometric relaxation of the muscle via the Golgi tendon.
As described earlier, there is no comparative study on triceps surae muscle flexibility in working females wearing high heels, though the following studies support the above findings. Feland J B et al 2001found that a contract-relax PNF technique (like MET) is slightly more effective than static stretching in acute flexibility gains in hamstrings muscle groups. 37Bruce R E et al 1986 discovered that the contract-relax -and antagonist-contract method is more effective than a contract-relax method, while contract-relax is more effective than static stretching in increasing the bent-knee ankle dorsiflexion range of motion 41. The finding of our study suggested that there was no difference between muscle energy technique and static stretching which concurs with other studies that have similar results. Ahmed et al discovered that MET and static stretching had similar benefits in improving hamstring flexibility.38,39,40
Additional research is needed to evaluate the extensibility of muscle groups covering other joints such as hamstrings or quadriceps femoris muscles. MET may be compared with other techniques like eccentric training in improving triceps surae flexibility. Additional factors need to be examined in working females wearing high heels, such as the type of job and the level of pressure at work. Future research should also investigate the effectiveness of different prevention and intervention measures on triceps surae muscle flexibility.
CONCLUSION
This study examined the effects of MET and SS on triceps surae muscle flexibility in working females who wear high heels. The findings of this study reveal that both MET and SS techniques are effective in improving the flexibility of the triceps surae muscle. However, MET has more advantage over SS in terms of feasibility and effectiveness when compared with conventional treatment (hot pack) in improving the flexibility of the triceps surae muscle in working females wearing high heels. Since this study included only healthy women, future studies are warranted to examine the effects of these manual techniques on the flexibility of the triceps surae muscle in women with heel pain or other foot problems such as flat feet. Future study should also evaluate the impacts of triceps surae muscle flexibility on the gait pattern and balance in women who wear high heels.
Conflict of interest: Nil
Source of Funding: Nil
Author contributions:
Conceptualization: Ahmed H, Alqhtani R, Alshahrani A, Mughal M Y and Khan A R
Data curation: Khan A R
Formal analysis: Ahmed H and Alshahrani A
Methodology: Ahmed H and Mughal M Y
Project administration: Alqhtani R
Supervision: Alshahrani A
Writing – original draft: Ahmed H
Writing – review & editing, Ahmed H, Alqhtani R, and Khan A R
All authors contributed to the final version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to express their Gratitude's to the ministry of education and the deanship of scientific research – Najran University – Kingdom of Saudi Arabia for their support. The authors are also grateful to the Deanship of Research at integral university for the approval of this project.
References:
-
Nadège KF, Jean-Marie F, Mansourou LM, Polycarpe G, Gabriel AY, Sophia L. Wearing high heel shoes during gait: kinematics impact and determination of comfort height. Am J Life Sci. 2015 Feb 15;3(2):56-61.
-
Stephens MM, Sammarco GJ. Heel pain: shoes, exertion, and Haglund's deformity. The Physic Sportsmed. 1992 Apr 1;20(4):87-95.
-
Schwartz RP, Heath AL. Preliminary findings from a roentgenographic study of the influence of heel height and empirical shank curvature on osteoarticular relationships in the normal female foot. J Am Pod Med Ass.. 1959 Sep 1;41(6):1065-76.
-
Cowley EE, Chevalier TL, Chockalingam N. The effect of heel height on gait and posture: a review of the literature. J Am Pod Med Ass. 2009 Nov;99(6):512-8.
-
Cronin NJ, Barrett RS, Carty CP. Long-term use of high-heeled shoes alters the neuromechanics of human walking. J Appl Phys. 2012 Mar 15;112(6):1054-8.
-
Chien HL, Lu TW, Liu MW. Effects of long-term wearing of high-heeled shoes on the control of the body's centre of mass motion about the centre of pressure during walking. Gait Post. 2014 Apr 1;39(4):1045-50.
-
Mika A, Oleksy ?, Mika P, Marchewka A, Clark BC. The influence of heel height on lower extremity kinematics and leg muscle activity during gait in young and middle-aged women. Gait Posture. 2012 Apr 1;35(4):677-80.
-
Kerrigan DC, Todd MK, Riley PO. Knee osteoarthritis and high-heeled shoes. The Lancet. 1998 May 9;351(9113):1399-401.
-
Kerrigan DC, Johansson JL, Bryant MG, Boxer JA, Della Croce U, Riley PO. Moderate-heeled shoes and knee joint torques relevant to the development and progression of knee osteoarthritis. Arch Phys Med Rehab. 2005 May 1;86(5):871-5.
-
Barton CJ, Coyle JA, Tinley P. The effect of heel lifts on trunk muscle activation during gait: a study of young healthy females. J Electromy Kines. 2009 Aug 1;19(4):598-606.
-
Nam SJ, Kim MJ, Yim SJ, Oh DW, Park HJ, Kim CY. Influence of walking speed on electromyographic activity of the rectus abdominis and erector spinae during high-heeled walking. J Back Musc Rehabil. 2014 Jan 1;27(3):355-60.
-
Alkjær T, Raffalt P, Petersen NC, Simonsen EB. Movement behaviour of high-heeled walking: how does the nervous system control the ankle joint during an unstable walking condition? PloS one. 2012 May 16;7(5):e37390.
-
Tiberio D. The effect of excessive subtalar joint pronation on patellofemoral mechanics: a theoretical model. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1987 Oct;9(4):160-5.
-
GREENFIELD B. Evaluation of Overuse Syndrome. Biomech Foot Ankle. 1996:201-3.
-
Root ML. Normal and abnormal function of the foot. Clin Biomech. 1977;2(5):314.
-
Porter D, Barrill E, Oneacre K, May BD. The effects of duration and frequency of Achilles tendon stretching on dorsiflexion and outcome in painful heel syndrome: a randomized, blinded, control study. Foot Ankle Int. 2002 Jul;23(7):619-24.
-
Glick JM. Muscle strains: prevention and treatment. Physic Sports Med. 1980 Nov 1;8(11):73-7.
-
Hubley-Kozey CL, Stanish WD. Can stretching prevent athletic injuries. J. Musculoskel. Med. 1990;7(3):21-31.
-
Bandy WD, Irion JM, Briggler M. The effect of static stretch and dynamic range of motion training on the flexibility of the hamstring muscles. J Orthop Spor Phys Ther. 1998 Apr;27(4):295-300.
-
Youdas JW, Krause DA, Hollman JH, Harmsen WS, Laskowski E. The influence of gender and age on hamstring muscle length in healthy adults. J Orthop Spor Phys Ther. 2005 Apr;35(4):246-52.
-
Kisner C, Colby LA, Borstad J. Therapeutic exercise: foundations and techniques. Fa Davis; 2017 Oct 18.
-
Cameron MH. Physical agents in rehabilitation: from research to practice. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2012 Oct 12.
-
Chaitow L, Crenshaw K. Muscle energy techniques. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2006.
-
Wilson GJ, Elliott BC, Wood GA. Stretch shorten cycle performance enhancement through flexibility training. Medic Sci Spor Exercise. 1992 Jan 1;24(1):116-23.
-
Halbertsma JP, van Bolhuis AI, Göeken LN. Sport stretching: effect on passive muscle stiffness of short hamstrings. Arch Phys Med Rehab. 1996 Jul 1;77(7):688-92.
-
Evetovich TK, Nauman NJ, Conley DS, Todd JB. Effect of static stretching of the biceps brachii on torque, electromyography, and mechanomyography during concentric isokinetic muscle actions. J Stren Condit Res. 2003 Aug 1;17(3):484-8.
-
Greenman PE. Principles of manual medicine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2003.
-
Wallin D, Ekblom B, Grahn R, Nordenborg T. Improvement of muscle flexibility: a comparison between two techniques. Am J Sports Med. 1985 Jul;13(4):263-8.
-
Gribble PA, Guskiewicz KM, Prentice WE, Shields EW. Effects of static and hold-relax stretching on hamstring range of motion using the flexibility LE1000. J Sport Rehab. 1999 Aug 1;8(3):195-208.
-
Youdas JW, Krause DA, Egan KS, Therneau TM, Laskowski ER. The effect of static stretching of the calf muscle-tendon unit on active ankle dorsiflexion range of motion. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2003 Jul;33(7):408-17.
-
Muir IW, Chesworth BM, Vandervoort AA. Effect of a static calf-stretching exercise on the resistive torque during passive ankle dorsiflexion in healthy subjects. J Orth Spor Phys Ther. 1999 Feb;29(2):106-15.
-
Waseem M, Nuhmani AH, Ram CS, Agarwal A, Begum SH, Ahmad F, Ahmad SH. A comparative study of the Impact of Muscle Energy Technique and Eccentric Training on Popliteal Angle: Hamstring Flexibility In Indian Collegiate Males. Serb J Spor Sci. 2010;4(1):41-6.
-
Ahmed H, Jarrar MA, Ahmed R, Alqhtani R, Alshahrani A. Effect of Post-Isometric Relaxation and Laser on Upper Trapezius Trigger Point Pain in Patients with Mechanical Neck Pain. Nig J Clin Pract. 2020 Dec 1;23(12):1660.
-
Ahmed H, Miraj M, Katyal S. Effect of muscle energy technique and static stretching on hamstring flexibility in healthy male subjects. Ind J Phys Occ Ther. 2010 Jul;4(3):32-6.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License