IJCRR - 13(13), July, 2021
Pages: 149-153
Date of Publication: 05-Jul-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Morphogenesis of Ureter in Human Fetuses: A Histological Study in North India
Author: Kaur Harmeet, Naik Shishir Kumar, Minakshi
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The contribution of anatomist and pathologist into the knowledge of the developmental and maturational changes in the human fetal ureter has been significant and play an essential vital role in the development of features. Ureter The ureters in neonates and infants can be anatomically and functionally so severely compromised as to warrant the various congenital terms That's why Microsectional study of the ureter has been a dynamic stair that can contribute to understanding congenital diseases such as agenesis, hypoplasia and dysplasia etc. Aim: My study has brought to light numerous insight into the fine structure of the ureter, with specific embryological highlights with cytologic and physiologic considerations. Materials and Methods: The study was conducted in the Department of Anatomy, JNUIMSRC, Jaipur. Thirty aborted human fetuses between 8- 38 weeks of gestational age with no obvious congenital anomalies were obtained from the Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology after taking consent of parents following approval from the Institutional Ethical Committee Result: Before 12 weeks there is only mesenchymal tissue appear after that mature histological appearance increase with gestational age in the craniocaudal direction. Conclusion: We are now able to better explain several microstructure-function relationships of the ureter in health and disease.
Keywords: Crown-rump length, Fetal ureter, Itravesical, Juxtavesical
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION:
Developmental road map and maturational changes in the human fetal ureter has been playing an essential vital role in the identification of normal and abnormal development of human features. The groundbreaking work of Satani,1 and Stein and Weinberg 2 clearly showed that the ureter displays morphologic plasticity, physiologic accommodation, and anatomic change under different conditions, e.g., physiological function, stress, obstruction, and ageing.
There are three layers in the ureter from outside inwards they are the transitional epithelium, then comes the smooth muscle layer and then it is continued by the adventitia.3
All these develops around the fourth week of intrauterine life. The ureteric bud develops and forms the majority of the collecting part of the kidneys.4
The ureteric bud is a primordial structure giving rise to the ureter, renal pelvis, calyces and collecting tubules. The ureteric wall is highly permeable at an early stage (5 mm CRL). Its lumen becomes obliterated later at (13-22mm CRL) which is subsequently recanalized. Both events begin at intermediate levels of the ureter and proceed cranially and caudally. 5 Two fusiform enlargements appear at the lumbar and the pelvic levels of the ureter at the 5th and 9th months of intrauterine life respectively which is responsible for the ureteric constrictions at its upper end and another as it crosses the pelvic brim. A third narrowing is always present at its lower end and is related to the growth of the bladder wall. Felix W has stated that after the 4 and 5 months of fetal life the ureter no longer is a straight tube of uniform calibre but shows two dilatations in the lumbar and pelvic regions respectively. 6,7 The ureteric wall is highly permeable at an early stage (5 mm CRL). Its lumen becomes obliterated later at (13-22mm CRL) which is subsequently recanalized. Both events begin at intermediate levels of ureter and proceed cranially and caudally. Two fusiform enlargements appear at the lumbar and the pelvic levels of the ureter at the 5th and 9th months of intrauterine life respectively which is responsible for the ureteric constrictions at its upper end and another as it crosses the pelvic brim. A third narrowing is always present at its lower end and is related to the growth of the bladder wall. Felix W has stated that after the 4 and 5 months of fetal life the ureter no longer is a straight tube of uniform calibre but shows two dilatations in the lumbar and pelvic regions respectively. The terminal part of the ureter perfectly continues with the intramural part. One should understand that the muscle fibres and the fibroelastic fibres run longitudinally. There is a fine balance in the formation of the ureter and deviation leads to functional problems.7 One of the most common birth defects seen in the foetus is related to the urinary tract.8
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
The present study carried out in the Department of Anatomy, JNUIMSRC, Jaipur. It was based on microscopic examination of ureteric tissue of 30 human features. Ureter procured from different gestational ages ranging from 8 to 40 week of fertilization with no obvious abnormalities on macroscopic inspection. After studying its external morphology tissue samples were taken from proximal, middle and distal regions of the ureter then fixed in 10% formalin and later processed in paraffin wax. 5-7µ sections were prepared and stained with hematoxylin and eosin.
Gestational age, sex and crown-rump length were noted. The abdomen was opened by a midline incision extending from the xiphisternum to the pubic symphysis (FIG .1) Tissue samples of 3-5 mm thickness were collected from both ureter in transverse planes from the abdominal, pelvic, juxtavesical and intramural parts and fixed in 10% formalin separately for 24-48 hours. Tissues were processed and paraffin blocks prepared. 5-7µ thick sections were cut and stained with haematoxylin and eosin. Some slide stained with Masson’s trichrome. All studied under the light microscope.
RESULT
The structures of the different parts of the ureter were observed histologically in 30 human fetuses ranging from 8 weeks to 38 weeks. Special emphasis was given to the developing muscular layer and the epithelium.
Group I (6-11 weeks)
At 8th and 9th week, the developing ureter depicted no muscular tissue in its wall. Instead, it consisted of mesenchymal tissue only. The upper part of the ureter was dilated to form the pelvis. At 10 weeks multiple narrow spaces were observed in the middle 1/3 of the developing ureter which seemed that the canalization process had been initiated. The lining epithelium was not observed to line these spaces. The periphery of the ureter was covered by a very thin layer of connective tissue arranged regularly. Sections of the ureter at the 11th week depicted a distinct lumen lined by 5-6 layered epithelium whose cells were polygonal in shape and appeared vacuolated. The surface of the epithelium was thickened and 2-3 shallow mucosal folds were observed. The mesenchymal tissue was very thin and arranged spirally around the lining epithelium which in turn was covered by a layer of loose connective tissue. The juxtavesical part of the ureter showed mesenchymal tissue surrounding the epithelium at the 11th week.
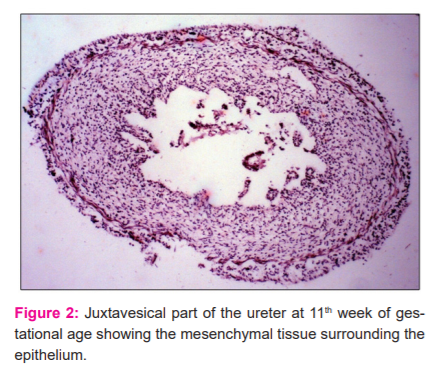
The epithelium was 2-3 layered thick and transitional. No epithelial folds were observed (FIG 2). The intravesical part opens in the posterior wall of the bladder by an oblique. The intravesical part showed a 3 layered transitional epithelium whose cells were polygonal in shape and depicted no muscular tissue in its wall.
Group II (12-14 weeks)
Histological sections studied at the 12th week demonstrated that the basal cells of the lining epithelium were smaller than the superficial cells and rested on a thin and extremely undulating basement membrane. The superficial cells appeared dome-shaped with large oval nuclei. Mucosal folds were observed to be more prominent. Deep to the transitional epithelium single tapered cells were evident in 2-3 rows which were characterized by eosinophilic cytoplasm and elongated nuclei. These cells were the precursors of the smooth muscle cells (Fig.3)
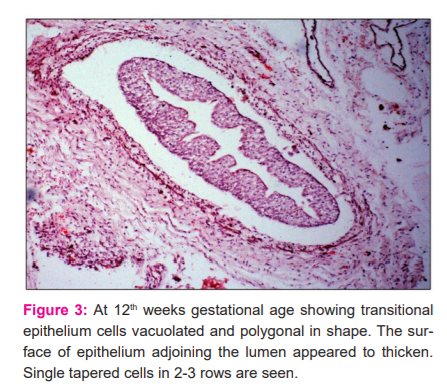
Such cells were deficient on the peripheral adventitious coat which contained a few blood vessels. The juxtavesical ureter at this stage had a very thin epithelium and a lamina propria containing darkly stained mesenchymal cells. The epithelium was still 3 layered. During the 13th week, the nuclei of the lining transitional epithelium became more conspicuous with well-defined nucleoli in certain places. The smooth muscle cell precursors were arranged circularly in 3-4 rows. These cells appeared more matured with the increase in its length and a deeper stained eosinophilic cytoplasm which were closely apposed to each other. The density of these cells was observed to be increased in the consecutive 14th week. However, sections from the lower 1/3 of the ureter during this period depicted scattered smooth muscle cell precursors which appeared to mature in the deeper layers closer to the lining transitional epithelium. It was also observed that in the juxtavesical ureter the superficial cells of the lining epithelium were polygonal with large oval nuclei. This was surrounded by a thin layer of smooth muscle cell precursors which were arranged circularly in 3-4 rows. The intramural part presented no muscular tissue in its wall.
Group III (15-17 weeks)
In this group sections of the ureter taken from the lumbar region showed a well-formed transitional epithelium with deep folds. The muscular coat comprised of 4-5 layers of smooth muscles spirally arranged and closely apposed to each other. Broadband of lamina propria consisting of connective tissue separated the muscular coat from the epithelium. The adventitious coat was also well-formed containing blood vessels. However, sections of the ureter from its lower 1/3 did contain the transitional epithelium but the folds were not well marked till the 16th week. The smooth muscles which were spirally arranged in the muscular coat appeared to come closer to each other at intervals during the 17th week (Fig.4). Observations on the juxtavesical part showed similar features but were delayed in development.
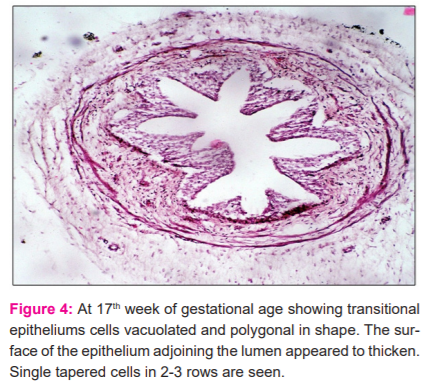
Group IV (18-24 weeks)
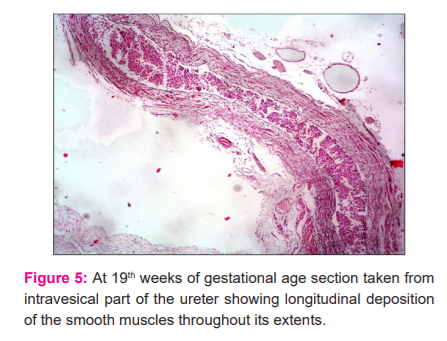
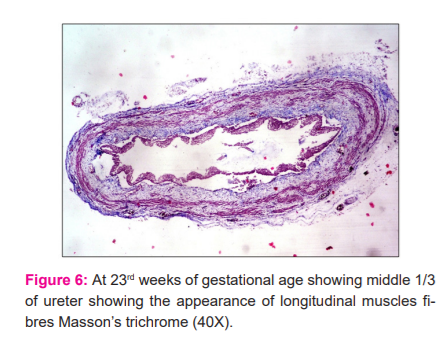
Sections of the ureter from the lumbar regions depicted that the individual muscle fibres in the circular muscle coat became gradually closer to each other to form thicker muscle bundles. At 23 weeks the inner longitudinal muscle coat became slightly visible at focal areas in sections. At 24 weeks this layer could be well demonstrated. Sections from the lower 1/3 of the ureter showed a delayed development in comparison to the middle 1/3 (Fig.5). The transitional epithelium further progressed in development by the increase in the number of layers to 7-8 and increase in the number of mucosal folds giving the shape of a typical star-shaped lumen. An increase in thickness of the adventitious coat was also observed with an increase in its vascularity. Sections observed from the intramural parts of the ureter demonstrated that muscle precursors arranged longitudinally were just observed at the 19th week (Fig.6) which became well differentiated at the 21st week. These longitudinal muscle fibres were observed with the superficial trigonal muscle at this stage also.
Group V (25-38 weeks)
Observations carried out in this group revealed further maturation of the layers of the ureter. The outer longitudinal coat was first observed in the lower 1/3 at the age of 30 weeks in focal areas adjoining the adventitious layer. The various layers of the ureter observed till the age of 38 weeks showed continued but delayed maturation. Sections of the fetal ureter in lumbar regions depicted that the individual muscle fibres in the circular pattern ,coat became gradually closer to each other to form thicker muscle bundles. The longitudinally arranged muscle fibres in the intramural part were seen to become thicker in this group (Fig. 7).

Discussion :
It is necessary for correlation with its development in increased gestational age and pathological changes for normal functioning of the urinary system in fetal life. In the present study during the 8th week, the epithelium was the only component that could be distinguished histologically in the wall of the ureter. During the 11th week, a distinct lumen lined by a 5-6 layered epithelium whose cells were polygonal in shape and appearing vacuolated was observed. The surface of the epithelium was thickened with the presence of 2-3 shallow mucosal folds. The mesenchymal tissue was very thin and arranged spirally around the lining epithelium which in turn was covered by a layer of loose connective tissue. Throughout the study sections of the ureter taken from the middle 1/3 showed a well-formed transitional epithelium with deep folds although sections from the lower 1/3 and upper 1/3 of the ureter showed delayed development and the folds were not well marked till the 16th week in comparison to the middle 1/3. A broad layer of lamina propria consisting of vascularized connective tissue separated the muscular coat from the epithelium. The epithelium in the juxtavesical and intramural parts of the ureter at this stage was only 2-3 layered thick and transitional. The superficial cells of the lining epithelium were polygonal with large oval nuclei. Tacciuoli M et al also reported in their study that the development of muscle coat and epithelium was observed earlier in the lumbar part of the ureter but developed slightly later in a craniocaudal direction.11,12
Satan's report1 observations indicated that fewer polynuclear cells are found in the urethral epithelium and that the size of each cell is smaller than that of the bladder.
Walker7 found that at around the 16th to 17th day of embryonic life of the mouse both binucleate cells and polyploid nuclei become obvious in the superficial layers of the urinary bladder. these observations point to the early observations of Satani.1 Significant positive linear relationships exist between a gestational week and distal and intravesical ureteral wall thickness of the mesenchymal and smooth muscle growth to the length of the intravesical ureter in fetuses.13,14
In the present study, no muscular tissue could be depicted in the wall of the ureter till the 9th week. Precursors of muscle primordium were observed during the 10th and 11th week of gestation in its wall. Deep to the lamina propria spindle-shaped muscle cells were evident in 2-3 rows characterized by eosinophilic cytoplasm and elongated nuclei during the 12th week in the middle part of the ureter. Throughout the entire study, the lower 1/3 of the ureter was observed to possess a delayed development in comparison to the middle 1/3. At 23 weeks the inner longitudinal muscle coat became slightly visible at focal areas in sections stained with Masson’s Trichrome. At 24 weeks this layer could be well demonstrated. Tacciuoli M et al reported a similar observation that the ureter in fetuses of 12 -14 weeks demonstrated single tapered cells overlying the loose connective tissue of the lamina propria in the lumbar region.11 The development of these smooth muscles proceeded in a craniocaudal direction.11,12 On the contrary, Matsuno T et al. observed that the differentiation of the ureteral musculature commenced from the renal pelvis and the upper part of the ureter at the 12th week which proceeded distally.13
The primordia of the smooth muscles in the juxtavesical and intravesical parts of the ureter were just recognizable during the 19th week of fetal life. They were arranged longitudinally in the intramural part. These primordial cells became well-differentiated in sections of the 21st week. The longitudinal muscle fibres were observed to blend with the superficial trigonal muscle of the urinary bladder. It consists of a juxta and intravesical segments with the latter having an oblique course through the bladder wall. Matsuno et al. observed that the intramural part of the ureter consisted of purely longitudinal muscle fibres.13 They were found to appear much later during the 17th week in comparison to the appearance of the muscle fibres in the proximal parts of the ureter. In contrast, the orientation of the ureteral musculature in the proximal parts was spiral. The longitudinal muscle fibres of the intravesical part became continuous with the periureteral sheath. On the other hand, Tacciuoli et al. reported that both longitudinal and oblique muscle fibres were present in the intravesical part of the ureter between 22 and 24 weeks.14 Most of these fascicles were present on the medial side of the intramural ureteric wall and some reached the mucous membrane of the bladder to terminate around the ureteric orifice.11
Conclusion:
Canalization of the Ureter was first observed to be initiated at the age of 10 weeks. The lining transitional epithelium was 5-6 layered thick with vacuolated and polygonal cells. The mucosa was lined by mesenchymal tissue. Single tapered muscle cells replaced the surrounding mesenchymal tissue at 12 weeks. The number of mucosal folds also increased. It was observed during this time that the lumbar part of the ureter showed the earliest developmental changes which proceeded in a craniocaudal direction. At 23 weeks the inner longitudinal muscle coat was observed in the middle 1/3. The intravesical part of the ureter depicted smooth muscles arranged longitudinally.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: Nil.
SOURCE OF FUNDING: Self-funded.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTION:
-
Dr Kaur Harmeet: Principal Investigator
-
Naik C Shishir kumar: Principal investigator, Research methodology.
-
Dr Minakshi: Principal Investigator.
References:
1. Satani Y. Histological study of the ureter. J Urol.1919; 3:247.
2.Stein J, Weinberg SR. A histologic study of the normal and dilated ureter. J Urol. 1962; 87:33-38.
3.Ross MH, Pawlina W . Histology A Text and Atlas, 6th edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2010; 280-282
4.Moore KL, Persaud TV. The Developing Human- Clinically oriented embryology, 5th ed. University of Michigan : Ishiyaku. 1993; 244-246
5.Standring S. Urogenital System. Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 40thedn. Churchill Livingst. 2008;.1225-1259.
6.William J. Larsen. Human Embryology. 3rd edn. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19106: Chur chill Livingst. 2001; 265-313.
7. Felix W. The development of the urogenital organs. Man Hum Embry. 2012;3:752–979.
8. Woodburne RT. The Ureter Ureterovesical Junction and Vesical Trigone. Anat Rec. 1965; 151: 243-250.
9.Smith D, Lau L, Khan B, David A, Jerry L Congenital variations in mucomuscular development of the ureter. BJU Int. 2002; 90:130–134.
11.Tacciuoli M, Lotti T, de Matteis A, Laurenti C. Development of the smooth muscle of the ureter and vesical trigone: histological investigation in human fetus. Eur Urol. 1975; 1(6): 282-286.
10.Walker BE. Polyploidy and differentiation in the transitional epithelium of mouse urinary bladder. Chromo Soma 1957; 9:105: 1958.
12.Schoenwolf GC, Bleyl SB, Brauer PR, Francis-West PH. Larsen's Human Embryology. Development of urogenital system. Churchil livingst. 2009; 4: 479-497.
13.Matsuno T, Tokunaka S, Koyanagi T. Muscular development in the urinary tract. J Urol. 1984; 132(1):148-52.
14.Oswald J, Brenner E, Deibl M, Fritsch H, Bartsch G, Radmayr C. Longitudinal and thickness measurement of the normal distal and intravesical ureter in human foetuses. J Urol. 2003; 169:1501.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License