IJCRR - 13(13), July, 2021
Pages: 108-113
Date of Publication: 05-Jul-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Collagen Based vs Conventional Dressing in the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcer-A Comparative Study
Author: Mishra T, Mishra J, Panigrahy R, Baral P, Patra GT, Murmu D
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Diabetic Mellitus (DM) currently affects approximately 8.3 percent of the population in the United States and more than 79 million individuals are pre-diabetic. Of the many complications of DM, Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) remain a serious and challenging one to deal with. Many treatment modalities have been tried since time immemorial. As the technology and research have advanced, the treatment of DFUs has also seen many changes and the use of collagen dressings in DFUs remains one of them. Aims: Comparison between conventional dressings and collagen dressings in DFUs, to know the effectiveness of collagen dressing, its safety and effectiveness in controlling wound infection. Methodology: A prospective study was undertaken with 100 diabetic foot ulcer patients who presented to surgery OPD between 2018 and 2020. Out of the 100 patients, 50 patients were subjected to collagen dressings and 50 patients to conventional dressing. Results: Complete wound healing was seen in 42 (84%) out of 50 patients treated with collagen dressings while only 31 patients (62%) achieved complete wound healing when treated with conventional dressing. This reduced the need for skin grafting in patients treated with collagen dressings as compared to conventional dressings (16% vs 38%). Conclusion: Collagen dressing accelerates wound healing in patients with DFUs thereby reducing the duration of hospital stay and also decreases the need for split-thickness skin grafting. Through our research, we conclude that conventional dressings are better when compared to conventional dressings.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus, Diabetic foot ulcer, Collagen dressings, Chronic wounds, Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
A serious and frequent complication of diabetes mellitus (DM) is diabetic foot ulcer (DFU), which raises treatment costs significantly DM currently affects approximately 8.3 per cent of the population in the United States and more than 79 million individuals are pre-diabetic.1,2 And among people with diabetes (PWD), 12%-25% have a lifetime chance of developing a foot ulcer.3,4,5 The human foot is a remarkable mirror of the systemic diseases it harbours.
In recent years, several new treatment methods, such as growth factors, extracellular matrix materials, bioengineered human skin, hyperbaric oxygen and collagen dressing, have been developed to promote wound healing in DFU. Biological dressings such as collagen, provide a suitable physiological interface between the ulcer and the environment and it also prevents the ulcer’s bacterial contamination. In the successful completion of adult wound healing, collagen, the body's most abundant protein, plays a vital role. Collagen is identified as an endogenous material that forms an essential structural element in connective tissue and is of special significance to the skin. The significance of collagen in wound healing has been known for several years for the basic explanation that during wound healing, the scar formed is made of collagen fibers.6During the body's protein scaffolding, collagen creates molecular diversity.7
The present study contrasts the effectiveness of collagen dressing with commonly used dressing materials such as normal saline and liquid povidone-iodine moistened gauze dressings in DFU management.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
STUDY DESIGN - Prospective study.
METHOD OF COLLECTION OF DATA
-
Source of data – This study is conducted in the Department of General Surgery at the Institute of Medical Sciences and SUM Hospital, Kalinga Nagar, Bhubaneshwar, over 2 years.
-
Sample size – Sample size of 100 patients fulfilling the inclusion criteria will be a part of this study,
-
The clinical study will be through questionnaires and investigation reports.
-
Ethical Clearance No – DMR/IMS.SH/180102
INCLUSION CRITERIA:
EXCLUSION CRITERIA:
-
Patients with other foot ulcers without diabetes.
-
Patients with known hypersensitivity to any of the dressing components.
-
Patients with conditions that may interfere with wound healing (e.g.- chronic liver or renal disease, connective tissue disorder, immune system disorder, major nutritional deprivation, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus)
-
Patients who are not willing to participate in the study.
METHOD
A total of 100 patients admitted in surgery wards of IMS and SUM Hospital between June 2018 and June 2020, with the clinical picture showing Diabetic Foot Ulcer were selected for the study. After explaining the procedure of the study, written informed consent was taken before enrolment into the study.
For analysis, the patients were divided into two groups i.e., Group A (Collagen Dressing group) and Group B (Conventional Dressing group). The patients were numbered serially from one to a hundred in the study group. The patients bearing odd study group serial numbers were subjected to Collagen dressing with collagen granules (BioFil) and the patients bearing even study group serial numbers were subjected to Conventional dressing (Normal saline & betadine).
In both the groups data regarding characteristics of ulcers such as size, edge, floor characteristics, slough, granulation tissue, pathogenic organisms and wound swab or pus culture sensitivity results were noted and analysed. Wound swabs were taken, first at the time of admission, at the end of the 2nd and 4th week of treatment and also when specifically required. Fasting blood sugar and 2hr PPBS were done every three days interval and result noted. Before applying the dressing, the affected area was thoroughly cleaned for removal of external contamination and infected wounds were debrided properly. Both groups were subjected to antibiotic treatment based on pus culture sensitivity reports.
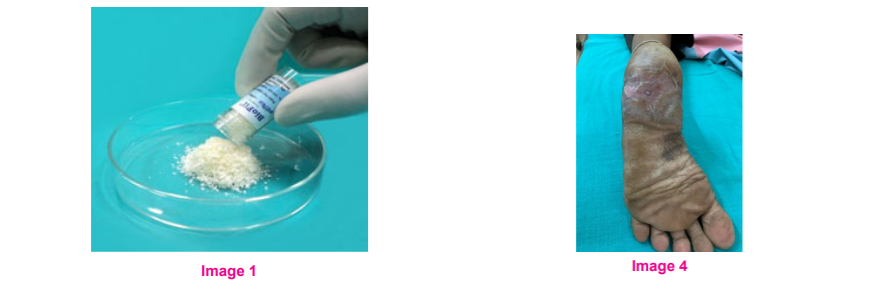
In Group A i.e., "Collagen dressing group" collagen granules were sprinkled over the diabetic foot ulcer after appropriate debridement of slough and necrosed tissue. The wound was then covered with a moist dressing. Initially, the dressing was changed on alternate days or earlier if there is soakage of the dressing, subsequently, the dressings were spaced every three or four days, depending upon the wound condition. Before sprinkling the collagen granules, the wound bed was thoroughly cleaned and the collagen sprinkled over the raw area of the ulcer. Dressing with collagen was continued till the wound heals or for 6 weeks. If by the end of 6 weeks, the DFU had not healed then the patient was considered for split-thickness skin grafting (SSG).
In Group B i.e., "Conventional dressing group" isotonic sodium chloride and liquid povidone iodine moistened gauze were applied over wound area and covered with gauze bandage and tapes. The conventional dressings were changed every alternate day or earlier if the dressing was soaked till the wound heals or for 6 weeks. If by the end of 6 weeks, the DFU had not healed then the patient was considered for split-thickness skin grafting (SSG).
The patients in both groups were studied for six weeks. After the completion of six weeks, those patients who had not achieved complete wound healing were subjected to split-thickness skin grafting (SSG).
Results of this study were noted in terms of the number of dressings required, achieving a sterile wound, time is taken for healthy granulation, complete wound healing and needs for SSG. Both groups were followed till discharge and its results noted. The patients were followed up for three months after discharge and any morbidity or mortality factors recorded.
RESULT
Out of the 100 patients in the study, 72 were male and 28 were female. (Table – 1)
In the above study, most of the patients (56%) were found to be in the age group of 51 – 65 years. The mean age of patients in the collagen and the conventional group were 61.26 ± 12.22 and 59.60 ± 10.31 respectively. (Table – 1)
The size of the ulcers ranged from 2 cm2 to 18 cm2 in both the study groups. Most of the patients (56%) were having ulcer size between 1 cm2 to 6 cm2. (Table 2)
The average size of ulcer in collagen and the conventional groups were 6.46 cm2 and 7.24 cm2 respectively. (Table 2)
Most of the patients with DFUs presented in the 2nd week (8-14 days) of them developing the ulcer. It was also observed that larger ulcers were comparatively of longer duration in onset in both the study groups. (Table 3)
In the collagen dressing group significantly a greater number of ulcers (P=0.027) became sterile (66%) as compared to the conventional dressing (44%) group at the end of two weeks of the study period as shown by their swab culture reports. (Table 4)
*Fisher’s exact test is applied as one cell has a value less than 5.
Of the DFUs treated with collagen, 94% had sterile wound swab culture at the end of 4 weeks while only 76% of the DFUs wounds were sterile in the patients treated with conventional dressing at the end of 4 weeks. (Table 4)
Of the DFUs treated with collagen, 42 patients (84%) had sterile wound swab culture at the end of 6 weeks (P =0.013) while only 31 patients (62%) of the DFUs wounds were sterile in the patients treated with conventional dressing at the end of 6 weeks. (Table 4)
Of the DFUs treated with collagen, 16% required SSG while 38% of the DFUs wounds required SSG in the patients treated with conventional dressing. (Table 4)
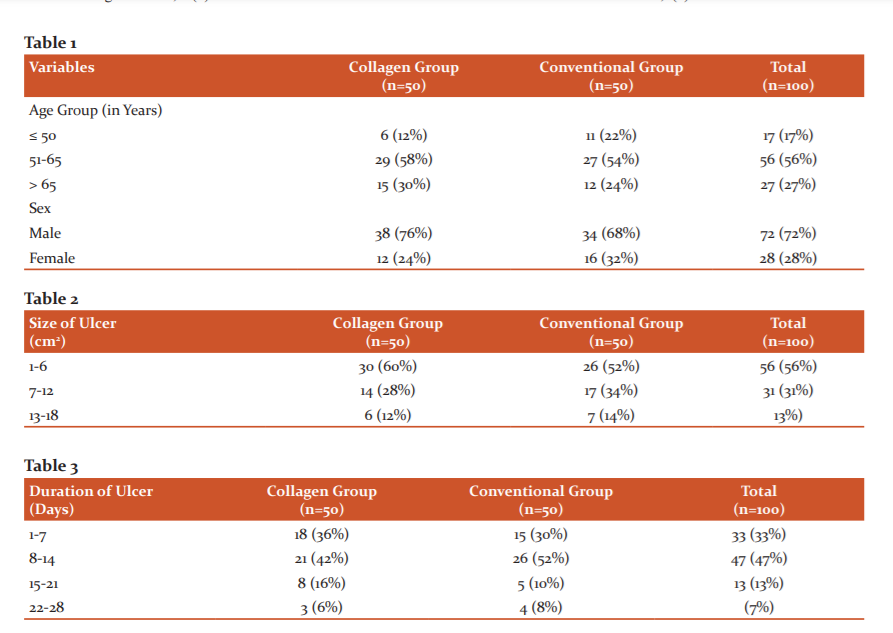
In the collagen group, most of the patients required 5 or fewer no of dressings whereas in the conventional group most of the patients required 6 to 10 numbers of dressings. (Figure 1)
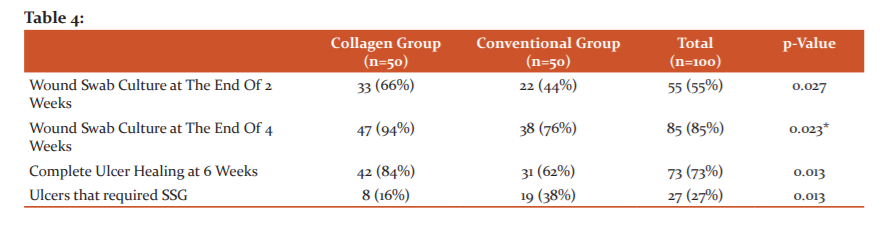
Most of the DFUs in the collagen group developed healthy granulation tissue within 10 days of starting of dressing (72%) while the development of healthy granulation tissue in the conventional group was significantly delayed (P < 0.001). (Figure 2)
DISCUSSION
Collagen is an important component of wound healing. Wounds tend to stall in the inflammatory phase due to a number of factors such as local tissue ischemia, bioburden, necrotic debris, recurrent trauma etc. increasing their chronicity. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) is one of the key components found to be elevated in chronic wounds. Not only do increase MMPs degrade non-viable collagen, but also viable collagen. In addition, fibroblasts in chronic wounds may not secrete tissue inhibitors of MMPs (TIMPs) at the levels needed to regulate the function of MMPs. This prevents the stage necessary for cell migration from forming and further prevents extracellular matrix (ECM) and granulation tissue from forming. By acting as a 'sacrificial substrate' at the wound site, collagen-based wound dressings help solve the issue of increased levels of MMPs. The breakdown products of collagen are chemotactic agents for different cells necessary for the formation of granulation tissue. Dressings based on collagen are also capable of removing wound exudates and preserving a moist wound environment.
Collagen is a biological material that facilitates wound healing through the deposition and arrangement of freshly formed fibres and granulation tissue in the wound bed, providing a suitable wound healing environment.8When sprinkled over a wound, collagen granules facilitate angiogenesis and also strengthen the healing processes of the body.9,10 This serves as a mechanical help, reducing oedema and loss of fluid from the ulcer site, promoting the movement of fibroblasts into the ulcer and increasing the granulation tissue metabolic activity.11 Collagen dressings can be applied to wound easily and has the added benefit of preventing bleeding.
In a wound-healing analysis performed by Veves et al. 276 DFU patients were divided into two comparable groups of the patients, of which the ones treated with Promogran- collagen/oxidized regenerated cellulose dressing- 51 (37.0%) had full wound closure compared to 39 (28.3%) control (moistened gauze) patients after 12 weeks of care, but this disparity was not statistically significant (p value= 0.12).12 This study demonstrated collagen dressings having a significant advantage over conventional dressings in terms of wound healing rates. Compared to conventional dressing groups, we also observed a significant difference in the number of wounds that reached full closure at the end of six weeks in the collagen dressing group (p-value = 0.013). Also, a significantly lesser number of DFUs treated with collagen dressing required SSG as compared to conventional dressing (p-value = 0.013). The need for SSG in a DFU can thus be avoided by collagen dressing.
In a similar study done by Onkar et al. on 120 patients, 60 patients suffering from wounds of varied aetiology were given collagen dressing and the other 60 patients were subjected to conventional dressing methods.13 Significant difference was found in sterile wound swab culture status (p value= 0.03), at 2 weeks and 4 weeks (p value= 0.04), average healthy granulation tissue time taken (p value= 0.03) and in the number of patients required to undergo split-thickness skin grafting (p value= 0.04) in between the two study groups. (Table 5)
For 8 weeks, the Onkar et al. study was performed and 87% of the wounds treated with collagen dressing had more than 75% wound closure compared to 80% with conventional dressing (p-value = 0.21). This study also shows that the number of patients in the collagen dressing group who need SSG is significantly lower than in the conventional dressing group (p-value = 0.04).
Harish Rao et al. compared collagen and conventional dressings in 100 patients with foot ulcers of chronic variety due to diabetes or burn injuries.14 Out of the 100 patients, 75 patients were treated with collagen dressing while the remaining were subjected to conventional dressing. Compared to moistened gauze, the study showed a substantially higher rate of wound healing with collagen dressing. The patients with collagen dressing required a healing time of 4.63±1.18 weeks which was significantly lower than the patients receiving conventional dressing (7.79±1.61 weeks). SSG was needed only in 64.47% of the patients undergoing collagen dressing as opposed to 100% in the patients treated with conventional dressing, which is significant. No adverse events were reported in either of the groups. The study concluded that collagen dressing is reliable and effective for the treatment of chronic foot ulcers, decreasing healing time, SSG demand and follow-up time significantly.
The role of collagen is well known in promoting wound healing in chronic wounds, but there are only a few studies on the use of collagen as a dressing material for DFUs. Therefore, the findings of the present study are promising by showing that the use of collagen dressing has a major advantage in DFU healing compared to conventional dressing. However, the DFUs should be debrided and cleaned before the use of collagen dressing. Suitable antibiotics should be administered based on the wound swab culture reports if there is evidence of local wound infection.
Limitations of the Present Study
-
Each patient was under treatment for only 6 weeks.
-
The wound was studied in only 2 dimensions, the depth of the wound was not taken into consideration.
-
The researcher and the patient have not been blinded, thereby raising the likelihood of bias.
-
This study didn’t include an important issue of the cost of collagen dressing and whether collagen dressing is economically better than conventional dressing.
-
While SSG was required for the significantly smaller number of subjects in the “collagen group” (8 compared to 19 in the “conventional group”), this was based on the results of a small sample size.
CONCLUSION
Collagen dressing, when compared to Conventional dressing with betadine, normal saline, gauze pad & bandage -
-
Accelerates wound healing and thereby reduces the hospital stay.
-
Gives a better sterile cover to the ulcer.
-
Decreases the need for skin grafting.
-
Reduces the morbidity suffered by the patients.
-
When collagen was put over the DFU, there were no adverse effects or reactions seen.
In terms of the completeness of chronic ulcer recovery, collagen dressing offers substantially better outcomes than traditional dressings.
Through our research, we were able to demonstrate that collagen dressing is better compared to conventional dressings, taking into account the early development of granulation tissue, early sterile wound swab culture and the decreased need for split-thickness skin grafting.
Thus, we recommend the use of collagen as a routine in Diabetic foot ulcers of small and medium size. Therefore, it is important to acknowledge the findings of the present research that, collagen-based dressings can prevent the need for future skin grafting in a significant number of cases of DFUs, but at the same time it is prudent to appreciate that more randomised controlled trials including a larger number of patients are needed to firmly establish this form of therapy as a suitable option in the treatment of DFUs.
Acknowledgement- We are grateful to Siksha 'O' Anusandhan (Deemed to be University) for their constant support and encouragement.
Conflicts of Interest- Nil.
Source of funding- Nil.
References:
1. Lipsky BA. A report from the international consensus on diagnosing and treating the infected diabetic foot. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2004;20(SUPPL. 1):68–77.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Fact Sheet: National Estimates and General Information on Diabetes and Prediabetes in the United States, 2011. Atlanta, GA, USA: Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2011.201(1):2568-25689
3. Huang Y, Cao Y, Zou M, Luo X, Jiang Y, Xue Y, Gao F. A comparison of tissue versus swab culturing of infected diabetic foot wounds. Intl J Endocrinol. 2016 Jan 1;2016.
4. May K. Preventing foot ulcers. Aust Prescr. 2008; 31:94–96.
5. Andersen CA, Roukis TS. The Diabetic Foot. Surg Clin North Am. 2007;87(5):1149–1177.
6. Sai KP, Babu M. Collagen based dressings - A review. Burns. 2000;26(1):54–62.
7. Botham KM, Murray RK. The extracellular matrix. Harper’s Illustrated Biochemistry. 27th edition. 2006; 545-548.
8. Nataraj C, Ritter G, Dumas S, Helfer FD, Brunelle J, Sander TW. Extracellular wound matrices: Novel stabilization and sterilization method for collagen-based biologic wound dressings. Wounds. 2007;19(6):148–156.
9. Park SN, Lee HJ, Lee KH, Suh H. Biological characterization of EDC-crosslinked collagen-hyaluronic acid matrix in dermal tissue restoration. Biomaterials. 2003;24(9):1631–1641.
10. Lazovic G, Colic M, Grubor M, Jovanovic M. The application of collagen sheet in open wound healing. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2005;18(3):151–156.
11. Motta G, Ratto GB, De Barbieri A, Can heterologous collagen enhance the granulation tissue growth? An experimental study. Ital J Surg Sci. 1983;13(2):101-108.
12. Veves A, Sheehan P, Pham HT. A randomized, controlled trial of Promogran (a collagen/oxidized regenerated cellulose dressing) vs standard treatment in the management of diabetic foot ulcers. Arch Surg. 2002;137(7):822–827.
13. Singh O, Gupta S, Soni M, Moses S, Shukla S, Mathur R. Collagen dressing versus conventional dressings in burn and chronic wounds: A retrospective study. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2011;4(1):12.
14. Harish Rao A. A comparative study between collagen dressings and conventional dressings in wound healing. Int J Collab Res Intern Med Public Heal. 2012;4(5):611–623.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License