IJCRR - 13(13), July, 2021
Pages: 18-23
Date of Publication: 05-Jul-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Comparison of Photographic and Visual Method for Tooth Shade Selection Using Two Shade Guides: A Clinical Research to Improve Shade Communication
Author: Bhandari AN, Bulbule NS, Bhatt V, Bhatlekar T, Mondal S, Amit K Jagtap
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aims and Objectives: To evaluate shade of maxillary central incisor visually, digitally by using a smartphone camera and graphic software and calculating the percentage of correct shade matching comparing both the methods using two different shade guides. Materials and Methods: A total of 45 participants were selected from the outpatient department of prosthodontics. The maxillary central incisor chosen had no history of any congenital or acquired deformities, restoration or structural defect. The shade for the same tooth was selected using two shade guides by conventional visual method, digitally by using a smartphone camera and graphic software for computer shade matching and the percentage of correctness between two was calculated. The agreement between both the results was compared and subjected to statistical analysis. Results: The results showed that when both the methods were compared with each shade guide i.e. Vita Classic Shade guide was found to be statically insignificant (p value=0.933) and with Vitapan 3D Master Shade guide was also found to be statistically insignificant (p value=0.825).Though the study showed close clinical relation for shade matching done visually when compared with the digital method the amount of correct shade matching was about 66.66% and 60% for Vita Classic Shade guide and Vitapan 3D Master Shade guide respectively. Conclusion: It was concluded that digital photography when combined with visual shade matching, can prove to be an effective method for shade communication thus improving the final esthetic qualities of restoration.
Keywords: Shade guide, Visual method, Digital method, Esthetic restoration, Colour science, Shade selection
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION:
We all know that the success of restorative dentistry which is a combination of art as well as science is based on its functional as well as esthetic results. So, correct shade matching becomes a challenging aspect in esthetic and restorative dentistry.
Though colour research has shown that the shade guides have very little representation of colour space of natural dentition but are still used for assessment and communication of colour of teeth in dentistry.1
Chairside colour matching with help of shade guides is subjective and tough due to different observer interpretation and environmental factors like the human eye, age, emotions, experience, colour blindness. There has always been a difference in the shade matching done visually by different observers due to all of these factors.2, 3
To make a restoration look natural, the selection of shade can be done either visually or by instrumental methods. But, the most common and traditional approach of selection of shade is visually through the use of a prefabricated shade guide. As shade guides are visual support for selecting shades and are defined as the collection of shade tabs, organized by colour (hue, chroma and value) which are used to suit the colour of the natural tooth.4
Instruments like computerized colourimeters and spectrophotometers have been developed to describe dental colours digitally. They may yield high stable results but do not have high accuracy.5They evaluate tooth colour by measuring the amount and spectral composition of reflected light on the surface of the tooth .5
But these contact type instruments may have several disadvantages like limiting area of measurement on the tooth surface, edge loss of light due to translucency of tooth, measure flat surfaces instead of translucent surfaces on curved teeth.3
Digital cameras and imaging systems are substitute for contact-type colour measurement instruments and have been used widely in dentistry. Digital photographs not only help in communication amongst clinicians and technicians but also help in precisely knowing the morphology of teeth, colour distribution as well as intraoral conditions.6
As we all know that smartphones have become universal devices and their applications to the clinician have also improved. Photographs from smartphones can be used for referencing colour shade matching for tooth and also help in easy communication between technicians and dentists.6
Also to improve the accuracy of shade selection procedures, the use of Vitapan 3D-Master tooth shade guide can be done.1
Therefore, this study was designed to compare the shade of maxillary central incisor by two shade guides and by two different techniques-visual method and digital (using smartphone camera graphic software) for computerised shade matching and calculate the measure of correctness between both the methods.
MATERIALS AND METHODOLOGY:
A sample of size forty-five cases in each group, satisfying the inclusion criteria was chosen. After obtaining the required approval from the Scientific and Ethics Committee of the Institution with ref no. DYPDCH/IEC/123/125/19, forty-five (n=45) patients were randomly selected from the outpatient department of prosthodontics.
Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
-
Missing maxillary anterior teeth
-
Any congenital or acquired dental deformity, structural defects in anterior teeth
The observer viewed the patient at the eye level so that colour sensitive part of the retina was used for about 10 seconds which reduces the chances of fatigue of the retina. A time interval of 10 minutes between uses of two shade guides was kept .1
The clinical area for shade matching was standardized accordingly for shade selection4:
-
Remove bright colours from the visual field
-
If participants were found wearing heavy makeup we need to remove it.
-
Shade selection was done in daylight (noon) and near the window.
-
Shade selection was done on the middle third portion of the maxillary central incisor.
The chronological sequence followed in the study:
-
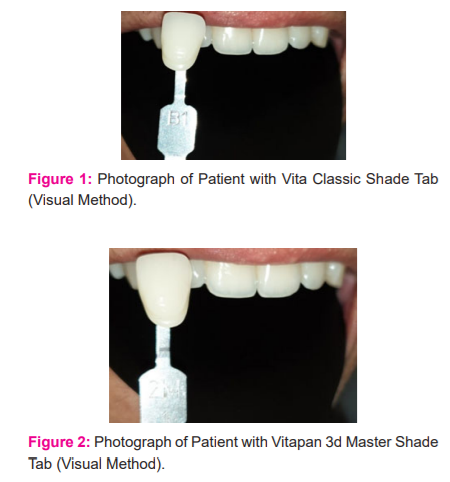
Shade selection was done on the tooth using Vitapan classical shade guide which is hue based where chroma increases within the groups (A-D).4 (Figure 1)
-
The shade tab was placed at the same relative edge position adjacent to the maxillary central incisor under the lip.4
-
The distance of the operator from the patient was about 25-30 cm.4
-
After each shade selection, relaxation of eyes was done by observing a neutral grey card before the next trial.4
-
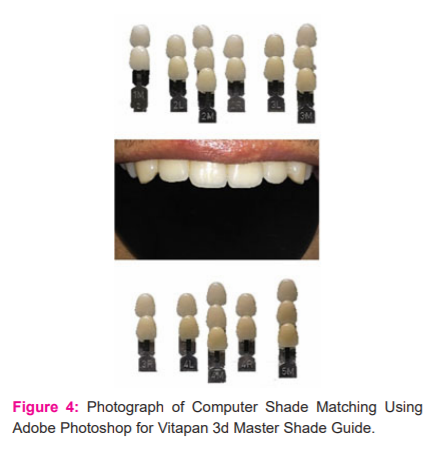
Shade selection using VITA tooth guide 3D- Master shade guide was done in a similar procedure by the operator as for the Classic shade guide but since it is value-based; selection of shade was completed by selecting each component of colour i.e., firstly by determining value, secondly by selecting Chroma (vertically) and then the hue of the tooth(horizontally).4 (Figure 2)
-
The digital method made use of a smartphone camera to take the image of the teeth which was adjusted at the level of the patient’s occlusal plane. The distance between the smartphone camera and teeth will be kept constant about 16-20 cm by use of a measuring scale and tripod stand. The images were taken by smartphone camera by auto features .3
-
The images of both shade guides were captured by using a smartphone camera at the dental clinic against a contrasting background.
-
The images were then transferred to the computer by connecting the phone to the computer in JPEG format.
-
The images were processed by using Adobe Photoshop (7.0) program by moving the shade from their screen position to the incisor position for matching the colour.
-
The magnetic lasso tool was used to delineate the area on the central incisor whose shade has to be decided. The magic wand tool next to it was used to eliminate reflection on the tooth surface.
-
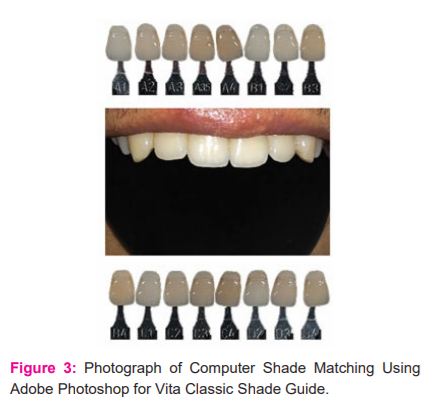
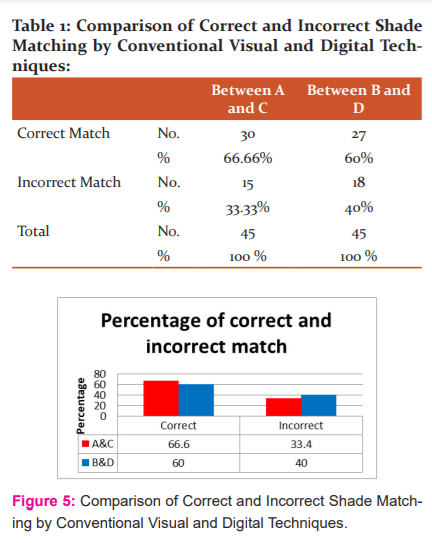
The image of the selected tooth was matched with digital images of both the shade guides (Figure.3 and Figure .4)
-
The selected shade by the operator by using both techniques were assessed and compared.

RESULTS AND STATISTICAL ANALYSIS:
In this study shade matching of maxillary central incisor was done visually with both shade guides. Also, a comparison between visual and digital shade matching by making use of a smartphone camera and two shade guides was done.
Testing of data analysis: Data analysis was done with Mann Whitney U test
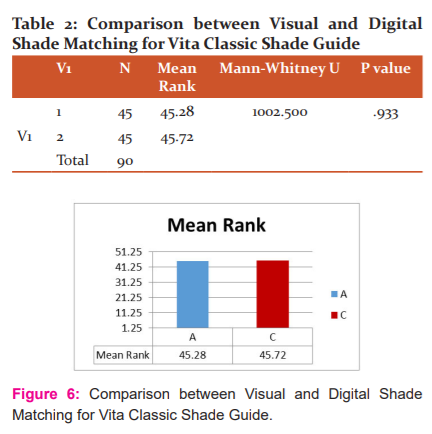
It was found that digital shade matching using smartphone camera was statistically different from conventional visual shade matching with 66.66% correctly matched shade for VITA CLASSIC SHADE GUIDE and 60% correctly matched shade for VITA 3D MASTER SHADE GUIDE (table no-1 and Figure no- 5)
Comparison between visual and digital shade matching for vita classic shade guide:
The mean rank of shade matching done visually (A) was about 45. A 28 and shade matching done digitally (C) was about 45.7A 2 for VITA CLASSIC SHADE GUIDE. Though the clinical significance of relation was seen amongst A and C, the p-value was about 0.933 which considered being statistically insignificant (Table no- 2 and Figure no-6).
Comparison between visual and digital shade matching for vita 3 d master shade guide:
The mean rank of shade matching done visually (B) was about 44.9A 2 and shade matching done digitally (D) was about 46.08 for VITA 3 D MASTER SHADE GUIDE. Though the clinical significance of relation was seen amongst A and C, the p-value was about 0.825 which considered being statistically insignificant (Table no-3 and Figure no-7). Though statically insignificant, the mean rank values for A and C (45.A 28 and 45.7A 2) were found to be much closer in comparison to B and D (44.9A 2 and 46.08) which suggests a better relation for VITA CLASSIC SHADE GUIDE as compared to VITA 3 D MASTER SHADE GUIDE visually and digitally.
DISCUSSION:
One of the most common failures of esthetic dentistry is the lack of correct shade matching which maybe because of the clinician’s inability to match the shade or miscommunication with the technician or inability of the technician to reproduce it.
Due to various combinations in hue, value, chroma in teeth it may be difficult to communicate this to the technician.
In the present study, the aim was to check the reliability of shade matching based on digital imaging of tooth and shade tab by using a smartphone camera by comparing it with the conventional visual method of shade matching by making use of two different shade guides by making use of graphic software in colour analysis.
It was observed that digital shade matching in comparison to the conventional visual shade matching provided a reliability of 66.6% and 60% for VITA CLASSIC and VITAPAN 3D MASTER Shade guide respectively.
The mean rank of shade matching done visually was about 45. 28 and shade matching done digitally was about 45.72 for VITA CLASSIC SHADE GUIDE. Though the clinical significance of relation was seen amongst A and C, the p-value was about 0.933 which considered being statistically insignificant.
Similarly, the mean rank of shade matching done visually was about 44.92 and shade matching done digitally was about 46.08 for VITA 3 D MASTER SHADE GUIDE. Though the clinical significance of relation was seen amongst A and C, the p-value was about 0.825 which considered being statistically insignificant.
In a study conducted by Miyajiwala et al.13, when a comparison of shade matching between the visual and spectrophotometric methods was done, the coefficient of agreement (using Kappa coefficient) was checked. Results revealed a fair agreement between the shades as determined by these two methods with (Kappa coefficient = 0.204).
A study conducted by Ihab A. Hammad1which evaluated the effects of 2 shade guides on the interrater repeatability of prosthodontists concerning shade selection stated that interrater repeatability of prosthodontists was significantly higher than that of general practitioners when Vita Lumin Vacuum shade guide was used in comparison to Vita 3 D Master which had higher intrarater repeatability in general practitioners.
A study conducted by Amit V Naik et al. 2 compared the interoperator variability in shade matching by visual techniques using two shade guides which stated that Vitapan 3D- Master shade guide was better than the Vitapan Classical shade guide in reducing the interoperator colour differences.
A study conducted by Rapti M Dahane et al. 4which studied the comparison between two operators in shade selection by visual techniques using VITA tooth guide 3-D Master and VitapanClassical shade guide stated that there was about 14% interpersonal variability in Vitapan classical shade guide and about 23% in Toothguide 3-D master. This shows that VITA Toothguide 3D - Master showed higher interpersonal variability than Vitapan classical shade guide.
None of the studies above could alone prove to be successful in determining the accurate shade of tooth using only one technique.
The digital method made sure that both the tooth and shade guide could be viewed on the same screen and shades could be moved around, placed adjacent to or even overlap with the tooth to be matched. It makes use of black background to eliminate the scattering lights in the images.
In this study, the use of a smartphone camera for digital shade matching using graphic software provided a new method of colour matching to an operator as well as laboratory technician even in absence of actual shade guides. In cases, where the clinician may find it cumbersome to match a single shade tab to the tooth, a prescription can be made combining several shades from different tabs.
The different areas on the tooth can be related to these tabs. Making use of digital images will allow the technician to evaluate different tabs of shades about different areas on the tooth. This may help the technician to apply his experience to develop restoration that matches the patient’s natural tooth.
This method may also improve computer link communication instead of receiving tooth colour as shade number. The digital images can also be sent via the internet to the laboratory and technician who can match tooth colour on the screen.
Certain shortcomings were seen because of lack of use of colour corrected lights, environmental illumination, lack of familiarity with the digital photo imaging software and in a clinical setup, the surface texture of tooth, a wide variety of shade tabs available. So there was comparatively less relation between digital and visual shade matching for VITAPAN 3 D Master shade guide in comparison to the VITA CLASSIC Shade guide.
This study opens up new horizons for the advanced scientific approach to colour matching in dentistry. Furthermore, the colour match of restorations fabricated using shades suggested by the digital photography technique should also be investigated.
CONCLUSION:
Within limitations of this study, we can conclude that,
1. The reliability of shade matching by conventional visual shade matching and digital shade matching using a smartphone camera and graphic software were about 66.66% and 60% for VITA CLASSIC and VITAPAN 3 D MASTER Shade guide respectively.
2. Digital method of taking photographs using smartphone camera can be used as an aid to visual shade matching using shade tabs to enhance shade communication between technician and dentist
3. The use of digital images in shade matching allows technicians to view variations, surface texture and tooth colour and improve shade communication.
4. Considering the technological advancement in the current & future world, digital photographs with advanced features will play a significant role in giving a life-like appearance to prosthetic restorations. It will also save the clinical & laboratory time for the operator & technician to visualising the actual shade rather than interpreting the conveyed shade.
5. Currently ceramic shades are in conjunction with the shade tabs in the shade guide but with the use of technological advancements, we can expect the introduction of the mobile apps to record the correct shade & do the auto-matching of the same with shades of ceramic. This will help us to produce more lifelike restorations.
6. Use of technology for better results is the need of the hour& digital methods of shade selection in form of digital photographs can be an adjunct along with the manual shade guides in recording the correct shade. This technological advantage even though demands financial support but can be an incomparable asset if combined with the conventional method of shade selection with the shade guide
AUTHORSHIP STATEMENT:
All persons who meet authorship criteria are listed as authors and have participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for the content, including participation in the concept, design, analysis, writing, or revision of the manuscript. All authors revised and gave final approval for the version submitted.
Conflict of Interest: Nil
Source of Funding: Nil
Acknowledgement: Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
-
Hammad IA.Intrarater repeatability of shade selections with two shade guides. J Prosthet Dent. 2003;89:50-3.
-
Naik AV, Jurel SK, Pai RC.Interopertor variability in shade matching for restoration with two shade guides.Int J Con Den. 2011 Jan;2(1).
-
Bayindir F, Kuo S, William M. Johnston, Wee A G. Coverage error of three conceptually different shade guide systems to the vital unrestored dentition. J. Prosthetic Dent. 2007; 98(3):175-84.
-
Dahane TM, Gupta R, Godbole SR, Pakhan AJ, Sathe S.Interoperator Variabilty in Shade Selection using two shade guides .Int J Prosthod Restor Dent. 2017;7(4):124-128.
-
Paravina R, Stankovi D, Aleskov L, Mladenovic D, Risti K. Problems in standard shade matching and reproduction procedure in dentistry. Uni Dent Con. 1997 May; 4(1);12-16.
-
Tam W-K, Lee H-J. Accurate sh. ade image matching by using a smartphone camera. J Prosthodont Res. 2016;71(41): 281.
-
Basavanna RS, Gohil C, Shivanna V. Shade selection. Int J Oral Health Sci. 2013; 3:26-31
-
Kuzmanovic´ D, Lyons KM. Tooth shade selection using a colourimetric instrument compared with that using a conventional shade guide. New Zeala Dent J. 2009; 105:131–4.
-
Alomari M, Chadwick R G. Factors influencing the shade matching performance of dentists and dental technicians when using two different shade guides. Brit Den J. 2011; 1-7.
-
Llena C, Lozano E, Amengual J Forner L. Reliability of Two Color Selection Devices in Matching and Measuring Tooth Color. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2011; 12(1):19-23.
-
Çapa N, Malkondu O, Kazazog? LU, Çal?kkocaog? lu S. Evaluating factors that affect the shade-matching ability of dentists, dental staff members and laypeople. J Ame Dent Ass. 2010; 141(1):71-76.
-
Mangal K, Dhamande M, Sathe S, Godbole S, Patel R .: An overview of the implant therapy: The esthetic approach. Int J Cur Res Rev. 2021; 13 (02):106-112.
-
Miyajiwala JS, Kheur MG, Patankar AH, Lakha TA. Comparison of photographic and conventional methods for tooth shade selection: A clinical evaluation. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2017;17:273-81. https://www.j-ips.org/text.asp?2017/17/3/273/212742.
-
Kulkarni P, Bulbule N, Kakade D, Hakepatil N. Radiographic Stents and Surgical Stents in Implant Placements: An Overview. Int J Curr Res Rev. 2019;11(12): 11-15.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License