IJCRR - 13(12), June, 2021
Pages: 174-178
Date of Publication: 22-Jun-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Psychological Impact of the Covid - 19 Pandemic on Health Professionals
Author: Rosa PS, Hernan MS, Eduardo MS
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: The coronavirus pandemic nowadays is one of the most important challenges for health professionals, since, during this situation, many of them are under pressure regarding their physical and mental health. Objective: The objective is to determine the psychological impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on health professionals, which it will allow observing what psychological impact exists on health professionals from different Hospitals and Health Centers of Lima - North. It is a descriptive and cross-sectional design, the population is made up of 100 health professionals from different hospitals and health centers in North Lima. Results: The psychological impact on health professionals from different hospitals and health centers in North Lima, of the 100 health professionals participating in the research work, 42.0% of health professionals have a medium psychological impact, 33% have a low psychological impact and 25% have a high psychological impact. Conclusions: It is concluded that the health professional must be adequately trained and oriented for the activities of care for patients who have the disease since programs must be specified in which professionals can access and be able to adapt to the reality that is happening to not perform the attentions of inadequate way.
Keywords: COVID – 19, Health personnel, Mental health, Pandemic
Full Text:
Introduction
The consequences of the rapid expansion of the coronavirus (COVID - 19), worldwide, has had an impact on society, generating fear and concern both in the population and in health professionals, for which the World Health Organization (WHO) in terms of public and professional mental health maintains that the psychological impact has generated increased stress and anxiety in health professionals because they are available in first-line care against this disease.1
Also, in our country, the COVID-19 disease has potentially exposed the population and health professionals, generating negative effects on them, such as stress, worry, fear that they may be infected, they are factors that predispose the population but that in health personnel alters the quality of care for patients.2
The COVID – 19 pandemic today is one of the most important challenges for health professionals, since, during this situation, many of them are under pressure regarding their physical and mental health-compromising their physical and mental well-being,3 however, in the health professional is not only altered physical and mental health due to this disease, also the quality of care that health professional performs during its working hours is altered.4,5
Also, health professionals are not only under high pressure to work day by day fighting in the first line of care for the (COVID - 19), but they are also highly exposed to being at risk of contagion of the COVID-19, due to inadequate protection, frustration, discrimination, isolation and interacting with patients with negative thoughts about their health, all this has repercussions on the health professional causing physical and mental exhaustion.6,7
The psychological impact caused by the virus has generated fear for those who may be the carriers of the virus and therefore, they can transmit it to their family if they continue working, therefore many of the workers have resigned leaving a burden of excessive work to other health workers where there is a probability that they due to the high demand for care, may be carriers of this disease,8since being continuously in contact with COVID-19 patients makes the mental health of health professionals can relapse and can be infected by the decrease in their physical and mental well-being and that can be affected in the medium and long term while the pandemic is still present.9
In Spain, after declaring a state of sanitary emergency, a situation of increased stress was seen, a work burden of the health professional, while research was carried out to observe the degree of psychological impact that health professionals had with pictures of depression, anxiety, stress, and insomnia in a population of 421 health professionals where 46.7% of the professionals surveyed presented stress pictures, 37% presented anxiety pictures, 27.4% presented depression pictures and the 28.9% presented insomnia.10
In the research work carried out in Saudi Arabia, it was observed that 582 health workers surveyed, the degree of anxiety presented by health workers for Coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) is higher than in the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) or seasonal influenza, where 41.1% are more anxious and concerned about COVID-19, 41.4% are anxious and concerned about MERS-CoV and COVID-19, and 17.5% are more anxious, concerned, and stressed about the MERS-CoV outbreak at the hospital, therefore, the health workers were in a degree of anxiety in such a way that they thought that the infection would not only reach them but also their relatives.11
In the research work carried out in Singapore, it was mentioned that health workers have a higher prevalence of contracting anxiety, stress, and depression, especially nursing professionals since they are in the first line of care and are in contact with the patient every time because they do not have relevant information about this disease that allows them to know how to act appropriately and also have the necessary protective equipment and infection control measures to counteract it.12
The objective of the research work is to determine the psychological impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on health professionals, 2020, which it will allow observing what psychological impact exists on health professionals from different Hospitals and Health Centers of Lima - North. This study is important since it will provide relevant and real data about the mental vulnerability that health professionals have as the first line of action against this disease.
In the present research, the depression, anxiety, and stress scale (DASS-21) will be used as the data collection instrument. The data collection was processed through the survey of health professionals from different Hospitals and Health Centers of Lima - North, the data to be entered was carried out in a data matrix that will be designed in the statistical program IBM SPSS Statistics Base 25.0, it proceeded to its corresponding analysis, which will allow to better process data to make statistical tables so that they can be described and interpreted in results and discussions, respectively.
This study is important since it will observe in the health professional the mental quality, due to the difficulties present in the global crisis by the coronavirus pandemic, where the health professional has not have been adequately trained or prepared to face this disease.
Methodology
Research type and Design
The present study, due to its characteristics, the way of collecting data and measurement of the variables involved is a quantitative approach. As for the methodological design, it is a non-experimental, descriptive, cross-sectional study.13
Population and Sample
The population is made up of 100 health professionals from different hospitals and health centers in North Lima - Peru.
Inclusion Criteria
Health Professionals including doctors, nursing graduates, and nursing technicians who are directly in contact with patients infected with COVID – 19.
Health Professionals who signed the consent informedACTA N°036-2020-CE/UMA UNIVERSIDAD MARIA AUXILIADORA.
Exclusion Criteria
Those health professionals who are not directly in contact with patients infected with COVID – 19 are excluded.
Technique and Instrument
The technique used was the survey, using the questionnaire or data collection instrument DASS-21, which aims to measure the psychological impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on health professionals.
The depression, anxiety, and stress scale (DASS-21), each of the three DASS scales contain 14 elements, divided into subscales of two to five elements with similar content. The 3 scales are the physical, mental and environmental levels of the person. It consists of four response alternatives, 0 "not at all", 1 "sometimes", 2 "much of the time" and 3 "most of the time" that serve to rate the degree to which each state has experienced during the last week. To obtain the final score of the DASS-21, the total score obtained must be multiplied by two (data x2).1.4
Place and Application of the Instrument
The survey carried out to measure the psychological impact on health professionals was carried out at different Hospitals and Health Centers in North Lima.
To start the data collection process, it was coordinated with health professionals such as Doctors, Nursing Graduates, and Nursing Technicians from the Essalud Marino Molina Hospital, Sergio E. Bernales Hospital, Lanfranco la Hoz Hospital, Villa Norte Health Center, and San Martin Confraternidad Health Center to be participants of the research work, although there were limitations to carry out the work because not all health personnel was available to be in the present research work.
Results
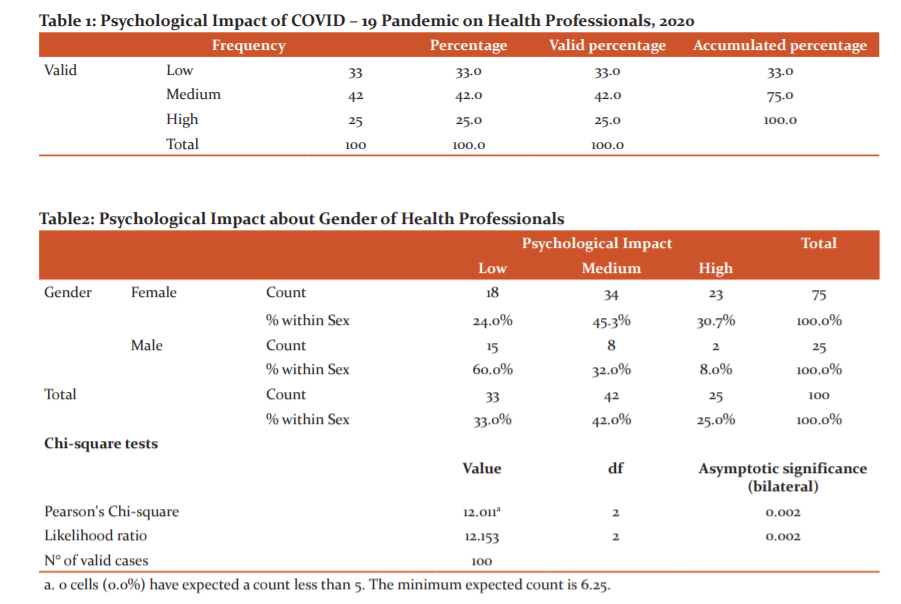
In Table 1, 100 health professionals participating in the research work, 42.0% of health professionals have a medium psychological impact, 33% have a low psychological impact and 25% have a high psychological impact.
In Table 2, the psychological impact about the gender of health professionals is related, which was determined with the Pearson chi-square test (X2). The level of significance of the test obtained a value of 6.25 (p> 0.05) (X2 = 12.011; d.f = 2). Therefore, a dissociation hypothesis is not rejected, which is why it verifies that there is no relationship between the psychological impact and the gender of health professionals. Therefore, it can be observed that in the female sex 34 (45.3%) present a medium psychological impact, 23 (30.7%) medium psychological impact, and 18 (24%) low psychological impact, as for the male sex 15 (60%) present a low psychological impact, 8 (32%) medium psychological impact and 2 (8%) high psychological impact.
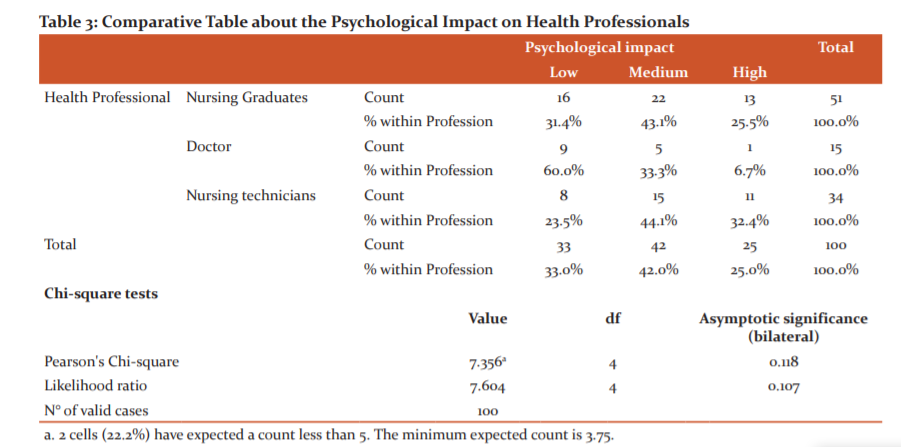
In Table 3, the psychological impact is related according to the type of health professional, which was determined with Pearson's chi-square test (X2). The level of significance of the test obtained a value of 3.75 (p> 0.05) (X2 = 7.356; d.f = 4). Therefore, an association hypothesis is not rejected, for which there is statistical data that verifies the relationship between the psychological impact and the type of health professionals. It can be seen that 100 health professionals participating in the research work, 43.1% of Nursing Graduates have a medium psychological impact, 31.6% have a low psychological impact and 25.5% have a high psychological impact, in Doctors, 60.0% have a low psychological impact, 33.3% have a medium psychological impact and 6.7% have a high psychological impact, in Nursing Technicians, 44.1% present a medium psychological impact, 33.0% present a low psychological impact and 25.0% present a high psychological impact.
Discussions
This study raises the issue of psychological impact from the point of view of the promotion of mental health on health professionals, in which it seeks to contribute to programs that benefit the professional with the necessary capacity to face this disease, promoting the ability to adapt and make the right decisions so that they can provide adequate care in patients prone or infected by the coronavirus.
These obtained results reflect the crucial role of health professionals during a pandemic, making them more susceptible to presenting symptoms of anxiety, stress, and depression, because health systems are not adequate to be able to provide care effectively, in addition to the fact that the health professionals are afraid of getting this disease and that they may infect their relatives once they are at home. In the same way, M. Temsah et al.,11 maintain that health professionals as the first line of care for COVID-19 are more likely to contract pictures or symptoms of depression, anxiety and stress, as a result of the amount of attending patients.
Many of the factors that cause anxiety, depression, and stress are linked to workload, excessive work hours and overtime shifts due to lack of personnel, affect the health professional because they must adapt to the situation and high demand of the population that is having this disease; therefore, health professionals are not in optimal conditions to carry out an effective work that allows care to be carried out correctly. In the same way, Tan B. and collaborators,12 stating that the factors that affect health professionals to contract symptoms of depression, anxiety and stress are the long working hours, the high demand of patients due to COVID - 19, and the excessive workload they present due to lack of personnel.
In addition to the conditions where the care is carried out, they do not have the necessary equipment from both the same health establishment and the health professional who cannot acquire the appropriate protective equipment for such care, therefore they are at risk of getting this disease if they do not have adequate protection, which is interpreted by Walton M. et al.3 who argue that the lack of biosafety equipment, inadequate care conditions, and equipment that does not predispose the health facility are the risk that compromises the health professionals to contract COVID - 19.
Regarding gender, we can interpret that the female sex is the one that presented a medium psychological impact; therefore, it can be interpreted that as a woman the mental health aspect is more compromised than the men since as being emotional and sentimental, they tend to decrease the capacity mental than in males. Santamaría M. and collaborators10, sustain that women are the ones with the highest levels of anxiety and stress during the COVID-19 pandemic because their mental health is unbalanced and they feel fear and concern about being infected at the moment to attend patients with COVID - 19, and thus is a predisposition to increase their levels of anxiety and stress.
It is recommended that the headquarters where health professionals work provide adequate training for the management of patients with COVID - 19.
It is recommended to look for strategies that allow health professionals to maintain their optimal mental health to provide quality care in COVID-19 positive patients.
A psychological intervention strategy planning is recommended for health professionals through telemedicine care.
The limitation in the present research work was the access to carry out virtual surveys to health professionals since as professionals in the first line of care against COVID-19, they did not have time to be in the study or be able to develop the survey.
This research study will benefit future research on the main topic since in our country there have not been many studies on the psychological impact generated by COVID-19 on health professionals.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the psychological impact caused by the COVID-19 pandemic has produced a broad and substantial effect that can be long-lasting over time, negatively affecting health professionals, since they must be adequately trained and oriented for the activities of care for patients who get the disease since programs must be specified in which professionals can access and be able to adapt to the reality that is happening if proper care is not performed.
It is concluded that there is no hypothesis of an association between the psychological impact of the sex of health professionals.
It is concluded that there must be programs that support the mental health of professionals who are on the first line of care for COVID - 19.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding Source
This research work doesn’t have Funding Sources
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals, and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Author’s Contributions
Rosa PS: Conceived and designed the analysis, wrote the paper, analysis tools, and translation.
Hernan MS: Collected the data, Performed the analysis.
Eduardo MS: Contact the people for the survey-taking.
References:
1. Organización Mundial de la Salud. Mental health and COVID-19.. OMS. 2020.
2. Medina R, Jaramillo L. El COVID-19: Cuarentena y su Impacto Psicológico en la población. Scielo, núm. 1.Recuperado el 16 de Agosto del 2020. Scielo. 2020;1:1–12.
3. Walton M, Murray E, Christian M. Mental health care for medical staff and affiliated healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic. Eur Hear J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2020;9(3):241–7.
4. Muñoz C, Rumie H, Torres G, Villarroel K. Impacto en la salud mental de la(del) enfermera(o) que otorga cuidados en situaciones estresantes. Cienc Y Enferm . 2015;21(1):45–53.
5. Xiao X, Zhu X, Fu S, Hu Y, Li X, Xiao J. Psychological impact of healthcare workers in China during COVID-19 pneumonia epidemic: a multi-centre cross-sectional survey investigation. J Affect Disord. 2020;274:405–10.
6. Lozano A. Impacto de la epidemia del Coronavirus (COVID-19) en la salud mental del personal de salud y en la población general de China. Rev Neuropsiquiatr. 2020;83(1):51–6.
7. Blake H, Bermingham F, Johnson G, Tabner A. Mitigating the psychological impact of covid-19 on healthcare workers: A digital learning package. Int J Environ Res Public Health [Internet]. 2020;17:2997.
8. Chew N, Lee G, Tan B, Jing M, Goh Y, Ngiam N, et al. A multinational, multicentre study on the psychological outcomes and associated physical symptoms amongst healthcare workers during COVID-19 outbreak. Brain Behav Immun. 2020; 21:113–116.
9. Batalla D, Campoverde K, Broncano M. El impacto en la salud mental de los profesionales sanitarios durante la COVID-19. Rev Enfermería y Salud Ment. 2020;16:17–25.
10. Santamaría M, Etxebarria N, Rodriguez I, Albondiga J, Gorrochategui M. Impacto psicológico del COVID-19 en una muestra de profesionales sanitarios españoles. Rev Psiquiatr Salud Ment. 2020;1–13.
11. Temsah M, Al-Sohime F, Alamro N, Al-Eyadhy A, Al-Hasan K, Jamal A, et al. The psychological impact of COVID-19 pandemic on health care workers in a MERS-CoV endemic country. J Infect Public Health. 2020; 3(8): 829-832.
12. Tan B, Chew N, Lee G, Jing M, Goh Y, Yeo L, et al. Psychological Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Health Care Workers in Singapore. Ann Intern Med. 2020;16(4): 542-546.
13. Fernández C, Baptista P. Metodología de la Investigación. 6ta ed. México: Mc Graw-Hill/Interamericana.. 2015. 1–634 .
14. Lovibond A. Depression Anxiety Stress Scale (DASS-21). Psychology Foundation of Australia. Sydney - Australia. 1995
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License