IJCRR - 13(12), June, 2021
Pages: 155-159
Date of Publication: 22-Jun-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Effect of Physiotherapy Treatment in Early Postpartum Period after Lower Segment Caesarean Section (LSCS)
Author: Purvi Patel, Mansi Shah, Lata Parmar
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: The immediate postpartum period is more challenging for mothers who have had a caesarean delivery. The pain presented after a caesarean section makes the recovery difficult and delays the mother's mobility. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of Physiotherapy treatment on Pain by VAS, Difference in PEFR and functional mobility by \"time up and go\" scale and on cadence. Method: Mothers with lower segment caesarean section (LSCS) eligible to participate in the study were divided into two groups; routine nursing care only as to date was the practice. The experimental exercise group was given fixed physiotherapy protocol from postoperative (POD) 1 up to the day of discharge. The severity of pain was assessed with the visual analogue scale on POD 1 and the day of discharge and functional mobility was to be assessed with the \"time up and go\" scale and cadence on the day of discharge. Peak expiratory flow rate was taken op Pod 1 and day of discharge. Result: There was a significant reduction in VAS at rest and movement within the group (P0.05). There was a significant difference in mean PEFR at the day of discharge within and between the group (P0.05). Conclusion: Early Postpartum physiotherapy was found to be beneficial in both the active patient group and also in the group where education and demonstration were given.
Keywords: Early ambulation, LSCS, PEFR postpartum, Physiotherapy after caesarean section, Physiotherapy after childbirth, Post�partum pain
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Pregnancy is a long and very special journey for women.1 Term pregnancy has traditionally defined as a duration of 10 lunar months or 9 calendar months and 7 days since the first day of the last menstrual period.2,3 There are two types of delivery for birth: vaginal delivery and caesarean delivery. With an incidence of around 25%, lower segment caesarean section (LSCS) becomes the most common abdominal surgery in the world performed on females.4
Births by caesarean sections, many of them unnecessary, have started to increase, globally. India has the highest annual rate for CS among all the East Asian countries which were 7.1% in 1998 and increased up to 16.7% in recent years.5,6
A C-section is performed for the safety of the child and mother which might be at the risk of vaginal delivery is performed (emergency CS) or there is the chance of any danger to the baby or mother with vaginal delivery (planned CS).7,8 The most common reasons for a C-section are fetal distress, prolonged labour, breech presentation, multiple gestations, previous section and CS on demand.4-10 The lower abdominal transverse incision is adequate for the vast majority of caesarean operations. It has the advantages of cosmetic approval and minimal risk of postoperative complication.11,12
Post-natal care is necessary to ensure that no complications have developed in the woman after childbirth. The immediate postpartum period even more challenging for mothers who have had a caesarean delivery and most often occurs in the hospital setting, where the majority of women remain for approximately 2 days after a vaginal delivery and 3-5 days after caesarean delivery. The pain presented after a caesarean section makes the recovery difficult and delays the mothers' mobility.12,13,14
Postpartum physiotherapy assessment can identify postural and structural weaknesses arising from the pregnancy, delivery, or postpartum conditions. Physiotherapy management should be comprised of ergonomics and education as the key components for women after childbirth. Exercise has been proven to be beneficial during pregnancy as well as in the post-partum period for up to 24 weeks. Postpartum exercise improves aerobic fitness, high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol levels, insulin sensitivity, and psychological well-being. Physical activity during postpartum is both a recommended and an essential contributor to maternal health. Physiotherapists instruct women in transverses abdominus, multifidus, and pelvic floor co-activation, which strengthens core stability and is beneficial in the prevention and treatment of back pain.15-18
Early ambulation is one of the very important parts of extensive postoperative care. That indicates that along with other exercises, the patient should be mobilised out of bed as soon as possible. A supervised programme within the first 24 hours is best and this should be reinforced every two hours by the team. Effective postoperative pain relief is also important to allow the patient to mobilize early.16,19
Several studies evaluated the effects of physiotherapy management in early post-CS patients and found that physiotherapy can improve the well-being of females after childbirth by improving productivity and quality of life in the early stage of post caesarean section.20,21,22 In India however there are several hospitals where such services are yet to be provided. The present study was undertaken to identify the benefits of physiotherapy post LSCS.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
This interventional study was approved by SVIEC. Every consecutive mother who had undergone LSCS and was willing to participate in the study was recruited with the approval of the Obstetrician. Mothers with cardiac, respiratory, musculoskeletal or neurological problems and who were suffering from major pregnancy complication like severe anaemia, pregnancy-induced hypertension, and postpartum haemorrhage were excluded from the study. Participants were explained about the study and a written informed consent form was taken. Mothers eligible to participate in the study were divided into two groups by even and odd method. One control group and one was the experimental group. A total of 29 patients were recruited in the study. Out of which 14 were in the control group and 15 were in the experiment group. The Control group was verbally educated and demonstrated physiotherapy along with routine nursing care as to date was the practice. The experimental group underwent a structured physiotherapy programme from post-operative (pod) 1 up to the day of discharge in form of Assisted active and active movements of the limbs like ankle toe movements, leg slides, movement around the bed, bottom lift techniques using crook lying, gentle exercises, such as pelvic rock, knee rolls from side to side, abdominal contraction on expiration, gluteal contractions, pelvic tilt exercises and ambulation. Each exercise was performed 5-10 times. Ergonomic training was also given such as comfortable breastfeeding positions, sitting and lying on the bed, walking, elimination of urine, excretion of bowel material, diet, self-care and attention to the newborn.23,24,25
The severity of pain was assessed with a visual analogue scale (VAS) on pod 1 and the day of discharge and functional mobility was assessed with the “time up and go scale”,26 and cadence by pedometer on the day of discharge. Peak expiratory flow rate was taken on pod 1 and the day of discharge.
Statistical analysis
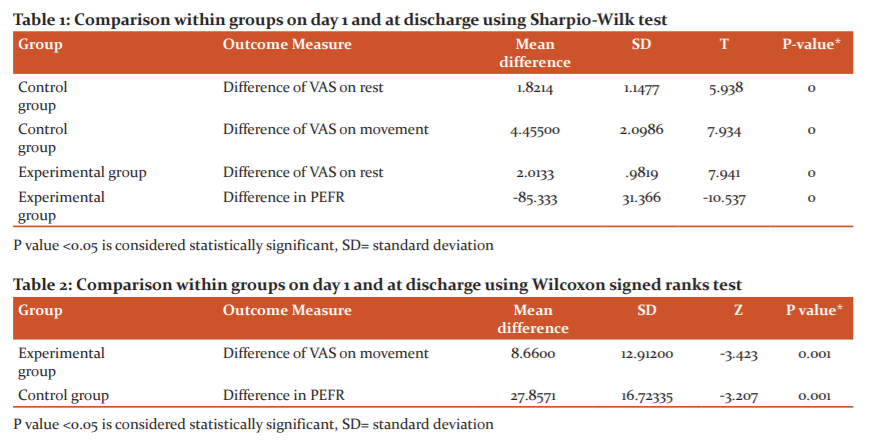
To check normality assumption descriptive statistics, normality plot, and Shapiro Wilk test was obtained for all data, it was found that PEFR at baseline in the control group and VAS on movement in the experimental group did not satisfy normality assumptions whereas all other parameters satisfied the normality assumptions. Therefore non-parametric test was carried out for PEFR at baseline in control and VAS on movement in the experimental group. A parametric test was carried for all other variables. The same type of normality check was done for difference (pre to post) of PEFR and VAS between the control and experimental group. It was seen that only VAS on movement difference in the experimental group was not satisfying normality assumptions and this variable was dealt with non-parametric and the rest of all with a parametric test.
RESULT
All data were entered into a Microsoft Excel sheet. Collected data were analysed using SPSS and STATA software. Descriptive statistics including mean, standard deviation (SD), and confidence interval (CI) were obtained.
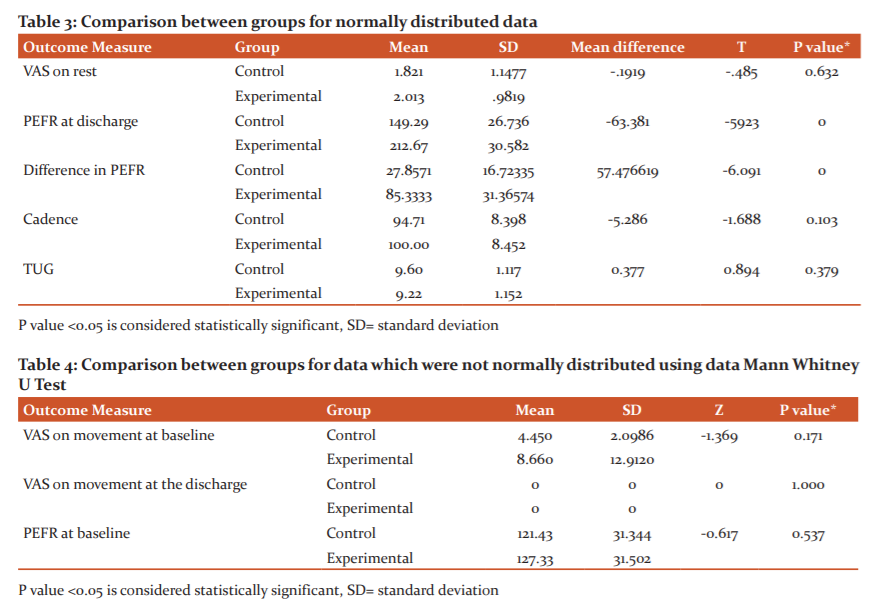
Table 1 shows VAS at rest in both the groups and VAS on movement in the control group was significantly reduced (P<0.01). Also, PEFR in the experimental group was significantly increased (P<0.01). There was also a significant decrease in VAS on movement in the experimental group and an increase in PEFR in the control group as shown in table 2. Table 3 shows the difference between the two groups was not statistically significant for VAS on rest, cadence and TUG whereas there was a significant difference for PEFR at the time of discharge and a difference of PEFR pre and post physiotherapy. There was no significant difference in VAS on movement at baseline and at the time of discharge between the two groups. PEFR at baseline also shows no significant difference as shown in table 4.
DISCUSSION
In the present study, a total of 29 patients who underwent LSCS has recruited the study (14 in the control group and 15 in the experiment group).
The control group comprised of participants who were just verbally educated and demonstrated physiotherapy (earlier this was also not done effectively and in some case, few instructions by nurses may have been given) whereas the experiment group received a structured physiotherapy programme to help prevent venous stasis, joint stiffness and peripheral oedema have been recommended and used.23,24,25
Encouragement of deep breathing exercises to keep lungs well ventilated, to decrease the risk of mucus accumulation and increase the venous return also have recommended and used in the literature.21,23,24,25 Physical activity can be resumed as soon as physically and medically safe. There are no published studies to indicate that, in the absence of medical complications, rapid resumption of activities will result in adverse effects.15
Lígia de Sousa et al., “concluded Post caesarean section pain commonly rated as moderate leads to limitations of physical activities for sitting down, standing up, and walking.[19] In the present study also the women rated their pain as moderate (mean VAS movement at 1st day in the control group 4.450, and in the experimental group 8.660) in activities like sitting down, standing up, walking.
In the present study, VAS at rest and movement of the control group on day 1 and discharge was significantly reduced (P<0.01). VAS at the rest of the experimental group on day 1 and discharge were significantly reduced (P<0.01).VAS on the movement of the experimental group on day 1 and at discharge shows a significant decrease in VAS (P=.001). Several studies also conclude that the physiotherapy program in the early post-caesarean period reduces incisional pain.27-30
It has been recommended that women must be helped to experiment to find comfortable positions for feeding, relaxation and sleep, using pillows. Pain relief can occur rapidly if the mother’s weight is advantageously redistributed. It is also theoretically possible that the muscle activity triggers the pain gait mechanism and may also stimulate the production of endogenous opiates.21,23
The present study found that PEFR amongst both the control and experimental group was significantly lesser than normal values of the same age group. One study with regards to PEFR quotes support from various other studies that PEFR progressively increases with advancing gestational age. Though Different measurement devices, differences in the timing of each measurement, differences in how the study is conducted, and differences in statistical methods may in part explain these differing findings and conclusions concerning changes in PEFR during pregnancy.30
They explain their findings on a mechanical basis, pointing out the effect of uterine enlargement and maternal weight gain and that the women in their study were of mixed ethnicity. Further, the author also quotes Puranik et al. who measured PEF with a portable flow meter in an Indian population and found PEFR to decline throughout pregnancy. They attribute their findings to inadequate nutritional status and developing muscular weakness because of poor socioeconomic status in the studied population. The observations of that study would not apply to all populations because of variations in ethnic, social, and economic conditions. Hence, further studies would be warranted in different populations.30
CONCLUSION
In the present study, the PEFR difference on day 1 and the day of discharge in the control group showed a significant increase (P=.001). PEFR difference on day 1 and the day of discharge in the experimental group also showed a similar significant increase (P<0.01). Also, there was a significant difference in mean PEFR on the day of discharge in the experimental group (P<0.01) as compared to the control. Thus it has been seen that physiotherapy given post-partum both structured and/or education in the present study was found to be effective.
In conclusion, there was significant pain reduction within both groups. There was a significant increase in PEFR within the group and between the groups while other parameters showed no difference between groups. There was no difference between TUG & cadence. The study confirms the benefit of physiotherapy in both the active patient group and also in the group where education and demonstration were given.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors thank the Department of obstetrics & gynaecology of Sumandeep Vidyapeeth. The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTION
P.P. - Drafting the article, critical revision of the article
M.S. - Data collection, data analysis and interpretation
L.P. - Conception of the work, final approval of the version to be published
SOURCE OF FUNDING
NIL
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
References:
-
Dash MB, Selvi S. Effectiveness of Infrared Rays on Wound Healing among Caesarean Section Mothers at Puducherry. Am. J. Nurs Res. 2013;1(1):43-6.
-
Cameron EC, Maehle V, Reid J. The effects of early physical therapy intervention for very preterm, very low birth weight infants: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Pediatr Phys Ther. 2005 Jul 1;17(2):107-19.
-
Fleischman A, Oinuma M, Clark S. Rethinking the definition of “Term Pregnancy”, Am J Gynaecol Obstet. 2010 July; 116- 136.
-
Sreevidya S, Sathiyasekaran BW. High caesarean rates in Madras (India): a population-based cross-sectional study. BJOG. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2003 Feb 1;110(2):106-11.
-
Cantwell R, Clutton-Brock T, Saving Mothers’ Lives: Reviewing maternal deaths to make motherhood safer: 2006-2008. Bio J Obst Gynecol . 2011 Mar;111(1):1-203.
-
Rudman A, Waldenström U. Critical views on postpartum care expressed by new mothers. BMC Health Serv Res. 2007 Dec 1;7(1):178.
-
Mukherjee SN. Rising cesarean section rate. J Obstet Gynecol India. 2006 Jul 1;56(4):298-300.
-
Mangesi L, Hofmeyr GJ. Early compared with delayed oral fluids and food after caesarean section. Cochr Database System Rev. 2002(3).
-
Dube JV, Kshirsagar NS. Effect of planned early recommended ambulation technique on selected post caesarean bio-physiological health parameters. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014 Jan 1;3(1):41-8.
-
Oh HE, Lee YS, Shim MJ, Kim JS. Effects of a postpartum back pain relief program for Korean women. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm 2007 Mar 1;37(2):163-70.
-
Mathai M, Hofmeyr GJ, Mathai NE. Abdominal surgical incisions for caesarean section. Cochr Database System Rev. 2013(5).
-
Dutta DC, Textbook of obstetric, Central Publication, fifth edition,64,318, 590-597
-
Bailey BA. Partner violence during pregnancy: prevalence, effects, screening, and management. Int. J. Women's Health. 2010;2:183.
-
Patnaik VV, Singla RK, Bansal VK. Surgical incisions—their anatomical basis Part IV-abdomen. J Anat Soc India. 2001;50(2):170-8.
-
Watson ED, Oddie B, Constantinou D. Exercise during pregnancy: knowledge and beliefs of medical practitioners in South Africa: a survey study. BMC pregnancy child. 2015 Dec 1;15(1):245.
-
Fawcett J, Aber C, Weiss M, Haussler S, Myers ST, King C, et al. Adaptation to cesarean birth: Implementation of an international multisite study. Nurs Sci Quart. 2005 Jul;18(3):204-10.
-
Stepan H, Kuse-Föhl S, Klockenbusch W, Rath W, Schauf B, Walther T, Schlembach D. et al. Diagnosis and treatment of hypertensive pregnancy disorders. Guideline of DGGG (S1-Level, AWMF Registry No. 015/018, December 2013). Geburtshilfe und Frauenheilkunde. 2015 Sep;75(09):900-14.
-
Torkan B, Parsay S, Lamyian M, Kazemnejad A, Montazeri A. Postnatal quality of life in women after normal vaginal delivery and caesarean section. BMC pregnancy child. 2009 Dec 1;9(1):4.
-
Sousa LD, Pitangui AC, Gomes FA, Nakano AM, Ferreira CH. Measurement and characteristics of post-cesarean section pain and the relationship to limitation of physical activities. ActaPaulista de Enfermagem. 2009 Dec;22(6):741-7.
-
Adeniyi AF, Ogwumike OO, Bamikefa TR. Postpartum exercise among Nigerian women: issues relating to exercise performance and self-efficacy. ISRN Obstet Gynecol. 2013;2013.
-
Ç?takKarakaya ?, Yüksel ?, Akbayrak T, Demirtürk F, Karakaya MG, Ozyüncü Ö, et al., “Effects of physiotherapy on pain and functional activities after Cesareandelivery”, Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2012 Mar:285(3):621-627.
-
Dube J, Kshirsagar N, Durgawale P. Effect of planned early ambulation on selected postnatal activities of post-caeserean patients. Int J Health Sci Res. 2013;3(12):112-8.
-
Postnatal care in the first-week guideline; Clinical Protocols and Guideline, Version 1, September 2010
-
Caesarean Section: NICE clinical guideline; Royal College of Obstetrician and Gynecologist,2nd Edition, November 2011;174-176.
-
Jill Mantle, Physiotherapy in Obstetrics and Gynecology, Second edition; 212-238
-
Thomas J, Paranjothy S. The national sentinel caesarean section audit report. National Sentinel Caesarean Section Audit Report. 2001.
-
Kayman-Kose S, Arioz DT, Toktas H, Koken G, Kanat-Pektas M, Kose M, et al. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) for pain control after vaginal delivery and cesarean section. J. Matern. Fetal Neonat Med. 2014 Oct 1;27(15):1572-5.
-
Binder P, Gustafsson A, Uvnäs-Moberg K, Nissen E. Hi-TENS combined with PCA-morphine as post caesarean pain relief. Midwifery. 2011 Aug 1;27(4):547-52.
-
Navarro CN, Pacheco MC. Transcutaneous electric stimulation (TENS) to reduce pain after cesarean section. Ginecologiay obstetricia de Mexico. 2000 Feb;68:60-3.
-
Grindheim G, Toska K, Estensen M, Rosseland L, Changes in Pulmonary function during pregnancy: a longitudinal cohort study. Bri J Obste Gynec,1471-2011.03158
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License