IJCRR - 13(12), June, 2021
Pages: 82-87
Date of Publication: 22-Jun-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Comparison of Colour Stability of Three Types of Provisional Prosthodontic Materials in Coffee and UV Light - an In vitro Study
Author: Sejal Narendrakumar Shah, Govind Lal Meena, Tarun Kumar Singh, Manish Kumar, Sankalp Agnani
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Provisional prosthodontic materials provide pulpal protection by covering the prepared tooth structure, providing thermal insulation, and preventing leakage by forming an intimate seal with the prepared tooth during the fabrication of the definitive prosthesis. Aims and Objectives: To compare colour stability of provisional restoration to provide an initial esthetic shade match and then to remain colour-stable during its period of service. Material and Methods: A total of 90 disc-shaped specimens (10 \? 0.1mm by 1 \? 0.05mm) will be fabricated with three commercially available provisional prosthodontic materials: Methyl Methacrylate Resin (RR Rapid Repair, Dentsply), Methyl Methacrylate Resin (RR Cold Cure, DPI), Methyl Methacrylate Resin (Acrylic-R, Asian). Ten specimens of each material will be randomly selected and immersed individually in coffee (37\?C) for 20 days or exposed to UV irradiation for 1 hour time respectively. Colour will be measured with a colourimeter before and after the immersion or UV exposure. Colour change (?E) will be calculated and data will be analysed by 1-way ANOVA and the Tukey multiple comparisons test (\a =0.05). Results: In 3 types of provisional restorative material, Asian provisional restorative material shows the highest colour difference and least colour stability. Integrity provisional restorative material sample shows the lowest colour difference and highly colour stable. Comparison of mean of colour change by coffee and UV light shows that coffee caused more colour change than UV light. Discussion and Conclusion: Discolouration of provisional materials in fixed prosthodontics may lead to patient dissatisfaction and additional expense for replacement. The stainability of the various materials is not just related to the chromogens but also to the chemical composition of the materials that are being tested.
Keywords: Colour stability, Provisional Prosthodontic material, Esthetics, Coffee, UV light
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Achieving optimum esthetics has been one of the goals in Prosthodontics. In this changing world, appearance is important. A provisional restoration is a transitional restoration that provides protection, stabilization and function before the fabrication of a definitive prosthesis. It may also be used to determine the esthetics, functional and therapeutic effectiveness of a treatment plan.1
The provisional restoration may be required to be placed in the patient’s mouth for a few days to few weeks. A fixed or removable dental prosthesis or maxillofacial prosthesis is designed to enhance esthetics, stabilization and/or function for a limited period, after which it is to be replaced by a definitive dental or maxillofacial prosthesis.
While the provisional restoration is in use, it is prone to discolouration due to its contact with various pigments present in the food and this does adversely affect the esthetics of the patient. Thus, the colour stability of the material becomes an important criterion for the selection of the provisional restorative material. It is used in the anterior region for esthetics and masticatory function in the posterior region.
Various studies have been done on the effect of various food colourants on colour stability of provisional restorative materials.1-4
Today, there are several new provisional materials available that differ in their chemical composition and curing methods thus having different physical properties. Thus, there is a need to comparatively analyse the colour stability of these materials.5,
AIMS AND OBJECTIVES
The aims and objectives of the study are:
-
To evaluate the effect of selected food colourant (consumed by the Indian population) on the colour stability of the provisional restorative materials.
-
To evaluate the effect of coffee and UV light on the colour stability of the provisional restorative materials.
-
To compare the colour stability of three commercially available provisional restorative materials in coffee and UV light.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
The effect of two media coffee and Ultraviolet (UV) light was investigated on the colour of three different types of provisional restorative materials. This prospective, in-vitro study was conducted in the Department of Prosthodontics and Crown and Bridge, Tatyasaheb kore dental college and research centre Kolhapur Maharashtra and Department of Chemical Engineering in Dattajirao Kadam Technical Education Society (DKTE) engineering institute rajwada Maharashtra.
The colour stability was measured using a spectrophotometer with the measurements being taken in the International Commission on Illumination (CIELAB) colour system.
The methodology will be discussed under the following headings:
-
Specimen fabrication
-
Staining solution preparation
-
Colour measurement
-
Statistical analysis
-
Specimen fabrication:
A total of 90 disc-shaped specimens (10 mm in diameter by 1 mm in thickness) were prepared from each material using similar shade groups using stainless steel die. This size of the specimen allowed ease of manipulation and polishing to approximately 1.0 ± 0.5 mm, which is generally the thickness of the material at the facial and the occlusal surfaces.
The DPI, Asian, and Integrity provisional restorative material were directly added with the monomer polymer ratio given by the manufacturer in the stainless steel die (1:1.3) with petroleum jelly as the separating medium and allowed to cure for 30 min.
It is supplied in an automix system. The die was coated with petroleum jelly. The automix system was then used to dispense the material into the die carefully to avoid void formation. The stainless steel slab was placed on the material to allow uniform thickness and the discs were removed after 4 min.
Once polymerisation is over, the specimens were removed from the die and were polished. Specimens were polished using a 15 sec. application of pumice applied with moist muslin wheel. A single individual polished all the specimens to avoid intra variation. 7,8
The specimens were divided into groups of nine, with ten samples each. The discs were randomly picked and serially-numbered using an acrylic bur.
-
Staining solution preparation:
For the evaluation of the colour stability, the specimens were immersed in coffee for 20 days and exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light for 1-2 hours. The coffee was prepared by using a standardized method.
The specimens of each type were divided into nine groups with ten specimens in each group. Ten specimens of each group were immersed in coffee for 20 days. The samples were immersed at 37° C in an incubator to simulate the temperature of the oral environment. Ten specimens of each group were exposed to Ultraviolet light (UV) for 1-2 hours. They were evaluated for the colour change before and after the immersion or UV exposure. 9,10
-
Colour measurement:
For the measurement of colour, the specimens were removed from the staining solution and cleaned using an ultrasonic cleaning device. The specimens were then wiped clean dry using an absorbing tissue paper. Thereafter, the specimens were subjected to spectrophotometric analysis.
The spectrophotometer used was a reflectance spectrophotometer – Premier Colour scan. The specimens were placed on a clean surface. The aperture of the spectrophotometer was placed and the reading was taken, which was recorded on the computer.
Values of the colour change were recorded in the CIELAB colour system. The CIELAB colour system is an approximately uniform colour space with coordinates for lightness, namely, white-black (L*), redness – greenness (a*) and yellowness – blueness (b*). The L, a and b values of each specimen was measured 3 times, and a mean of each was calculated.
The colour difference was calculated from the means using the following formula:
DE = (DL2 + Da2+ Db2)1/2
Where, DL, Da, Db denotes the values of the samples before and after the immersion or UV exposure, DE is the colour difference between the samples before and after the immersion or UV exposure. Readings were taken of three randomly selected areas of the discs and the mean was calculated. All data recordings were taken by the same investigator to minimise inconsistency of the technique. 11
-
Statistical analysis:
The statistical analysis of the data obtained was done using the Statistical Package for Social Scientists (SPSS) computer software for windows version XP. This program provides the descriptive summary statistics and statistical technique applied in the study. The results were then analysed using ANOVA analysis, paired test for intragroup comparisons. 12
RESULTS
The purpose of this study was to determine the colour stability of 3 provisional restorative materials before and after immersion in coffee, and exposure to UV light.
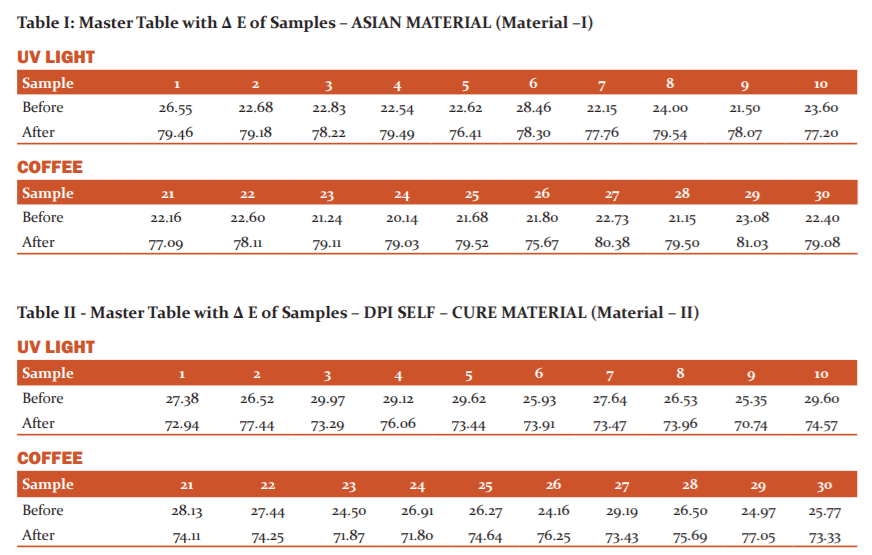
Table I shows the master table with DE values of 90 Asian provisional restorative material samples. It shows the highest colour difference and the least colour stable.
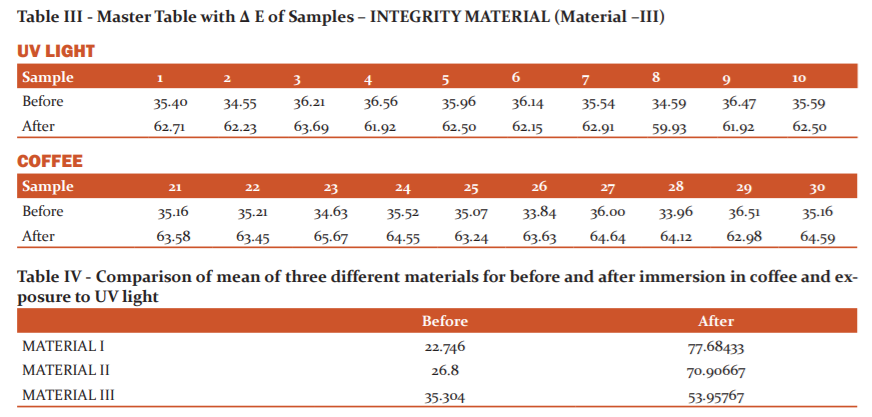
Table II shows the master table with DE values of 90 DPI – self-cure provisional restorative material samples. It shows the significant colour difference in coffee and UV light.
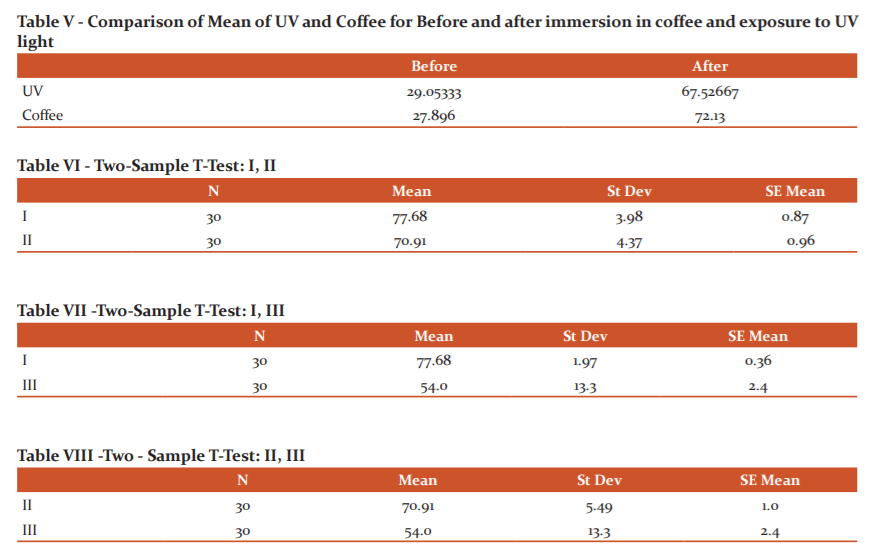
Table III shows the master table with DE values of 90 Integrity provisional restorative material samples. It shows the lowest colour difference and highly colour stable.
Table IV and Graph I shows the comparison of the mean of three different materials for before and after immersion in coffee and exposure to UV light. The material I & II shows significant colour change compared to Material III.
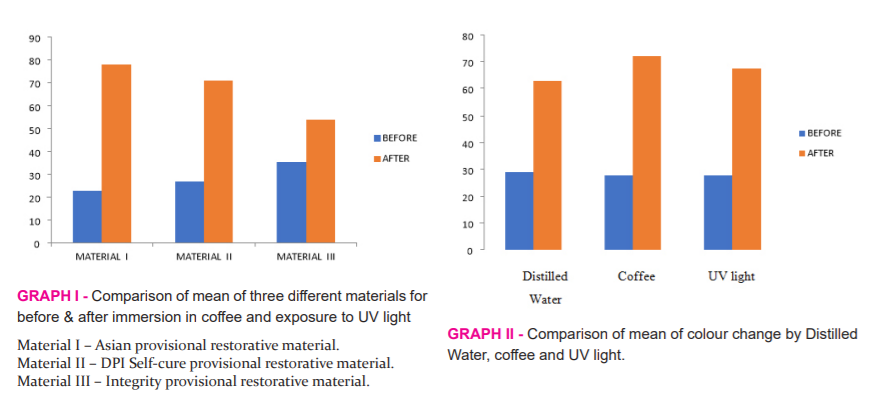
Table V and Graph II show the comparison of mean colour change by coffee, distilled water and UV light. It shows that coffee caused more colour changes compared to UV light.
Table VI shows the intragroup comparison of Asian (Material – I) and DPI self-cure (Material –II) provisional restorative materials. It shows that material II is better than the material I.
Table VII shows the intragroup comparison of Asian (Material – I) and Integrity (Material –III) provisional restorative materials. It shows that material III is better than the material I.
Table VIII shows intra group comparison of DPI self-cure (Material –II) and Integrity (Material –III) provisional restorative materials. It shows that material III is better than material II.
DISCUSSION
One of the important things to consider is that restoration must not only satisfy function but also the esthetics. In fixed prosthodontics, a provisional restoration is given until the permanent restoration is fabricated. Colour stability can govern the selection of materials when a long period of service is anticipated. The materials should be esthetically acceptable and colour stable. Discolouration of provisional materials in fixed prosthodontics may lead to patient dissatisfaction and additional expense for replacement.13 The degree of color change can be affected by several factors including incomplete polymerization, water sorption, diet and oral hygiene.14
The stainability of the various materials is not just related to the chromogens but also to the chemical composition of the materials that are being tested.
The discolouration of resin-based materials can be caused by various factors. According to Hersek et al. 15, one of the factors involves the discolouration of the resin material itself, such as alteration of the resin matrix and the interface of the matrix and fillers. The cause of chemical discolouration has been attributed to the change of oxidation of the amine accelerator, oxidation in the structure of the polymer matrix and oxidation of unreacted pendant methacrylate groups.16
However, there is another threshold regarding the stability of the materials. This threshold justifies the clinical acceptability of the stained materials. The upper limit of acceptability in subjective visual evaluations has been confirmed by Um and Ruyter17 who suggested that a perceptible discolouration must be referred to as acceptable up to a Value DE =3.3, while Guler et al18 have stated that a value of 3.7 should be considered as visually perceptible. The colour measurement was done using a reflectance spectrophotometer that incorporates 10 – degree observer, 45- degree illumination, with light provided by a pulsed xenon arc lamp.
Changes in optical properties within the materials could have been responsible for the colour change. Studies demonstrated lower water sorption for composite materials with high filler content (low resin content) compared with materials with lower filler content. Highly cross-linked resins were also shown to exhibit less water sorption. It is unknown from the manufacturers or the literature whether any differences exist in water sorption or filler content and the amount of cross-linking between the methyl/ethyl methacrylate and the bis-acryl methacrylate-based resins. Additional research is necessary to validate such a hypothesis. 17
Conversely, DE values for bis-acryl methacrylate were significantly lower than methyl/ethyl methacrylate after immersion in coffee. Mechanisms explaining how UV radiation affects the colour stability of acrylic resins have been proposed. It was suggested that the oxidation of residual unreacted carbon double bonds (C=C) in the polymerized resins may promote the production of yellowing compounds.18,19
In a study conducted by Jyoti et al, it was found that nano-composite denture teeth are highly polished table, stain and impact-resistant material. 20
SUMMARY
A provisional restoration is required to be worn till the final restoration is fabricated. The provisional restoration should not undergo colour change during the period it is worn. The colour change of the material may occur as a consequence of the consumption of chromogenic food.
With the advent of newer materials being introduced at a rapid pace, a need was felt to compare and evaluate the colour stability of the provisional materials in coffee and UV light.
Three commercially available provisional restorative materials with different chemistry and curing methods were chosen.
CONCLUSION
Provisional restoration is an important part of fixed prosthodontic treatment. The provisional restoration, while it is in use by the patient, is prone to discolouration with various types of food colourants. Thus colour stability of the materials used in the provisional restoration is an important property.
The present investigation aimed at evaluating the colour stability of provisional restorative materials before and after immersion in distilled water, coffee for 20 days & ultraviolet light (UV) for 1-2 hours using spectrophotometric analysis was done to evaluate the colour change.
Within the limitations of the study, the following conclusions can be drawn:
-
Integrity material showed the least colour change after immersion in distilled water, coffee for 20 days and exposure to ultraviolet light (UV) for 1-2 hours.
-
Asian material showed the maximum colour change after immersion in distilled water, coffee for 20 days & ultraviolet light (UV) for 1-2 hours.
-
DPI Self-Cure material showed significant colour change after immersion in distilled water, coffee for 20 days & ultraviolet light (UV) for 1-2 hours.
-
Coffee caused the maximum discolouration on the first day, while distilled water caused the least discolouration. Ultraviolet light (UV) showed colour change greater than distilled water but less than coffee.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: Authors acknowledge the enormous help received from the authors whose articles are cited and included in references to this manuscript.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: NIL
ETHICAL CLEARANCE: Not required (In- Vitro Study)
PATIENT CONSENT- Not required (In- Vitro Study)
FINANCIAL SUPPORT- NIL
References:
-
Criptin BJ, Caputo AA. Colour stability of temporary restorative materials. J Prosthet Dent. 1979;42:27-33.
-
Khan Z, von Fraunhofer JA, Razavi R. The physical properties of a visible light-cured temporary fixed partial denture material. J Prosthet Dent. 1988;60:543-5.
-
Koumjian JH, Firtell DN, Nimmo A. Colour stability of provisional materials in vivo. J Prosthet Dent. 1991;65:740-2.
-
Scotti R, Mascellani SC, Forniti F. The in vitro colour stability of acrylic resins for provisional restorations. Int J Prosthodont. 1997;10:164-8.
-
Robinson FG, Haywood VB, Myers M. Effect of 10% carbamide peroxide colour of provisional restoration materials. J Am Dent Assoc. 1997;128:727-31.
-
Hoshiai K, Tanaka Y, Hiranuma K. Comparison of new auto curing temporary acrylic resin with some existing products. J Prosthet Dent. 1998;79:273-7.
-
Yannikakis SA, Zissis AJ, Polyzois GL, Caroni C. Colour stability of provisional resin restorative materials. J Prosthet Dent. 1998;80:533-9.
-
Lang R, Rosentritt M, Leibrock A, Behr M, Handel G. Colour stability of provisional crown and bridge restoration materials. Br Dent J. 1998;185:468-71.
-
Ergun G, Mutlu – sagesen L, Ozkan Y, Demirel E. In vitro colour stability of provisional crown and bridge restoration materials. Dent. Mater J. 2005;24:342-50.
-
Bagheri R, Burrow MF, Tyas M. Influence of food simulating solutions and surface finish on susceptibility to staining of aesthetic restorative materials. J Dent. 2005;33:389-98.
-
Haselton DR, Diaz – Arnold AM, Dawson DV. Colour stability of provisional crown and fixed partial denture resins. J Prosthet Dent. 2005; 93:70-5.
-
Guler AU, Yilmaz F, Kulunk T, Guler E, Kurt S. Effects of different drinks on stainability of resin composite provisional restorative materials. J Prosthet Dent. 2005; 94:118-24.
-
Hayashi H, Maejima K, Kezuka K, Ogushi K, Kono A. In vitro study of discolouration of composite resins. J Prosthet Dent. 1974; 32:66-9.
-
Gross MD, Moser JB. A colourimetric study of coffee and tea staining of four composite resins. J Oral Rehabil. 1977; 4:311-22.
-
Hersek N, Canal S, Uzan G, Yildiz F. Colour stability of denture base acrylic resins in three food colourants. J Prosthet Dent. 1999; 81:375-9.
-
Douglas RD. Colour stability of new-generation indirect resins for prosthodontics application. J Prosthet Dent. 2000; 83:166-70.
-
Um CM, Ruyter IE. Staining resin-based veneering materials with coffee and tea. Quintessence Int. 1991; 22:377-86.
-
Sham SK, Frederick C, Chai CJ, Law D, and Chow TW. Colour stability of provisional prosthodontic materials. J Prosthet Dent. 2004; 91:447-52.
-
Christensen GJ. Making provisional restorations easy, predictable and economical. J Am Dent Assoc. 2004; 135:625-7.
-
Jyoti K, Kumar R, Seshan S. A study on evaluation of surface roughness and the anti-staining propensity of nano-composite denture teeth.Int J Curr Res Rev. 2014; 06(07): 52-57.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License