IJCRR - 13(12), June, 2021
Pages: 99-106
Date of Publication: 22-Jun-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Formulation Development and Evaluation of Polyherbal Suspension of Some Medicinal Plants
Author: Sachin M. Mahajan, Dheeraj T. Baviskar
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: World Health Organisation promoting the application of traditional medicinal plant in the form of herbal formulation in various countries. Aim: The present investigation was focused on the development and stability study of polyherbal suspension produced from alcoholic extracts of selected medicinal plant. Methodology: Three suspensions Polyherbal formulation-A, Polyherbal formulation-B, Polyherbal formulation-C of different concentration of Sodium Carboxy Methyl Cellulose 0.7%, 1.4%, 2.0% respectively formulated and evaluated to accelerated stability for 3 months. Result: Polyherbal formulation-C exhibited pleasant appearance and texture; there were no changes in sedimentation, flow rate, pH, viscosity and other physiochemical parameters. Quality control parameters like phytochemical and High-Performance Thin Layer Chromatography were also done on the developed polyherbal formulation. It reveals the presence of various phytoconstituents. All the quality control parameters in formulated suspension are stable and acceptable. Conclusion: It is concluded that suspension of ethanolic extracts of Curcuma caesia, Citrullus lanatus, Evolvulus alsinoide, Gymnema sylvestre, Tinospora cordifolia, Caesalpinia bonduc, Withania coagulants formulated in combinational therapy could be effective and safe for use.
Keywords: Polyherbal formulation, Suspension, Quality Evaluation, Stability testing, Heavy metal test, Microbial limit test, HPTLC fingerprinting
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION:
The oral route of drug administration is one of the oldest methods of administrating drugs for systemic effects. In general, the parenteral route is not readily used for the self-administration of Medicines. The majority of medicine used to produce systemic therapeutic effects are probably given by the oral route.1, 2 Polyherbal formulations are the product of nature, they are comparatively cheaper, eco-friendly and readily available than Modern drugs. Their better affordability and greater accessibility account for increasing demand globally, particularly in rural areas and some developing countries, where costly modern treatments are not available. The scientific advancement carries with its developments in Polyherbal formulations through the study of diverse phytoconstituents and the discovery of helpful medicinal herbs combinations that work synergistically to exert a therapeutic effect. Almost, they bring out satisfactory effect and safety making them one of the highly selected drugs of choice.3,4 Ayurvedic herbal formulations were also administered preferentially by oral route.
Liquid forms of drugs contain certain limitation, but public demand or expectations are tremendous for such formulations. Moreover, some formulations are more effective in a liquid form and are used commonly by young children’s or the adult to overcome difficulty in swallowing solid oral dosage forms. Most of the orally administered herbal formulations belong to the liquid dosage form of drug or drug combination. Designing and developing oral liquid herbal formulations is to date a challenge in modern pharmaceutics.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant Materials
The plant material required for the present study the selected plant material was collected from the hills of Satpuda Mountains especially from the hills of Toranmal and from the forest of Boradi. Plant materials which are collected with the help of the traditional healers of Toranmal such as the whole of the plant of Evolvulus alsinoides, seeds of Citrullus lanatus (Thumb) Matsumura, leaves of Gymnema sylvestre (Retz.) R. Br. Ex Roem and Schut, (Asclepidaceae) (Bedki Pal), stems of Tinospora cordifolia (Gulvel), seeds of Caesalpinia bonduc L. Roxb. (Caesalpiniaceae) (Sagargota), fruits of Withania coagulance Dunal (Solanaceae) paneer Ke Phool), rhizomes of Curcuma caesia Roxb (Zingiberaceae) purchased from the local market. After collection of the plant material was sent to Prof. Dr. D.A. Patil, Department of Botany, S.S.V.P. Sanstha's Dr. P.R. Ghogere Science College, Dhule and properly authenticated. After collection and authentication of the plant material was subjected to shade drying and pulverization. All the chemicals required for the present study were analytical grade.
Preparation of extracts
Air-dried coarsely powdered plant materials of were defatted petroleum ether; extracted with ethanol using soxhlet apparatus. All the ethanolic extracts were concentrated, dried and lyophilized.5
Formulations
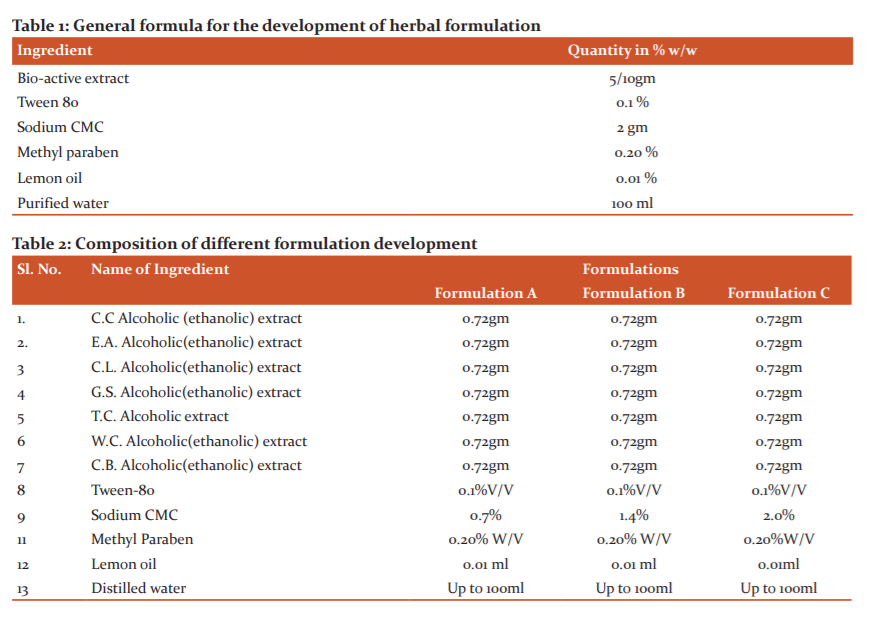
The dried lyophilised ethanolic extracts of Curcuma caesia, Citrullus lanatus, Evolvulus alsinoide, Gymnema sylvestre, Tinospora cordifolia, Caesalpinia bonduc, Withania coagulance were taken for the preparation of 100 ml of Suspension. (Table 1).
Preparation of Polyherbal Suspension Dosage Form
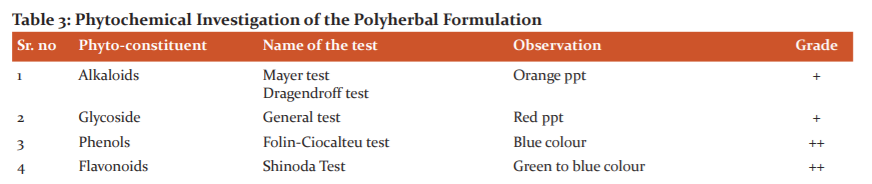
The formulae for preparing 100 ml of a suspension of extracts of Curcuma caesia, Citrullus lanatus, Evolvulus alsinoide, Gymnema Sylvestre, Tinospora cordifolia, Caesalpinia bonduc, Withania coagulance was as shown in Table 1.They were taken in the ratio of 1:1:1.6,7 Suspension was prepared by using various bioactive extracts of selected plant materials trituration method in mortar and pestle by using the suitable suspending agent of Tween 80 and Sodium carboxy methyl cellulose (CMC) along with other excipients. The dried extracts were mix in water and the additives likeTween-80, Sodium CMC. The suspending agent, sodium CMC in the aqueous medium containing selected preservatives was added in mortar and pestle along with ethanolic extracts of selected plant material with continuous triturating. Three possible formulations of Suspension viz. Polyherbal formulation-A, Polyherbal formulation-B and Polyherbal formulation-C were prepared by using 0.7%, 1.4%, 2.0% aqueous Sodium C.M.C solution respectively. Finally, by addition of purified water by continuous trituration in suspension brought up to the final volume to get the uniform product. All three possible forms of suspension of extracts of Curcuma caesia, Citrullus lanatus, Evolvulus alsinoide, Gymnema Sylvestre, Tinospora cordifolia, Caesalpinia bonduc, Withania coagulance were then subjected to evaluation as per standards (Table 2).
Phytochemical investigation of the polyherbal formulation.8
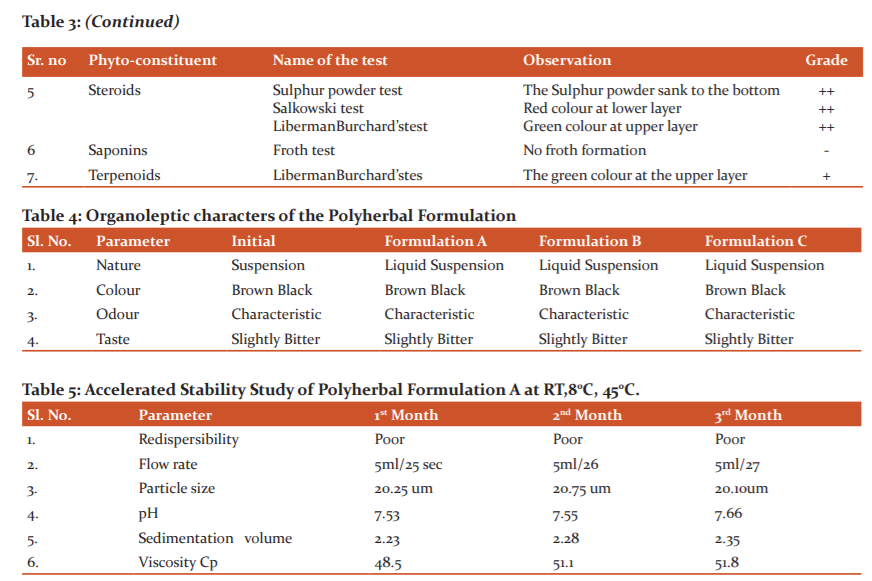
Phytochemical analysis of polyherbal formulation was carried out and it reveals the presence of alkaloids, Steroids, terpenoides, glycosides, flavonoids, phenolic compounds etc. (Table 3).
QUALITY PARAMETERS OF POLYHERBAL SUSPENSION.9.10,11
The organoleptic characters of the Polyherbal Suspension were evaluated by using the following parameters colour, odour, taste and texture etc. (Table no.4).
Accelerated stability studies
The accelerated stability studies were carried out for polyherbal formulations (Polyherbal formulation-A, Polyherbal formulation-B and Polyherbal formulation-C) of bioactive constituents at 8°C, room temperature and 45°C±2 at 75%±5 humidity. The stability of polyherbal suspension was studied for three months. The different parameters such as pH, sedimentation volume, re-dispersibility were studied for all the formulation at 1st, 2nd and 3rd months.
-
Sedimentation volume:
The sedimentation volume is the ratio of the ultimate height of the sediment to the initial height of the total suspension as the suspension settles in a cylinder under appropriate standard conditions. It was evaluated by keeping a measured volume of suspension in a graduated cylinder in an undisturbed state for a certain period and note that the volume of the sediment is expressed as ultimate height.
-
Redispersibility
The suspension was allowed to settle in a measuring cylinder. The mouth of the cylinder was closed and was inverted through 180º and the number of inversions necessary to restore a homogeneous suspension was determined.
-
Rheology
The time required for each suspension sample to flow through a 10 ml pipette was determined by the apparent viscosity by using the equation.
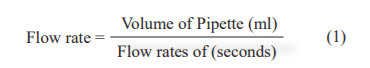
-
pH
The pH of the suspension was determined by using a pH meter (Eutech).
-
Particles size analysis:
The distribution of particle size in suspension is an important aspect of its stability. Particle size distribution was carried out by using optical microscopy in dilute suspensions.
Determination of Microbial limit test:
A microbial limit test was performed as per I.P 2014. 12
Determination of Heavy metal
Heavy metals such as lead, cadmium and arsenic were estimated for Polyherbal formulation C at Nutralytica research centre as per the protocol of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry ICP-MS (Agilent 7700e) with an autosampler (ASX-500).
High-Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HPTLC) of polyherbal formulation C
Preparation of Sample for HPTLC determination. 13, 14, 15
10.0 g of polyherbal formulation (suspension) C was weighed accurately in a 100 ml conical flask; 30 mL of water was added and mixed thoroughly. The solution was transferred carefully in a 250 mL separating funnel and 50 mL of ethyl acetate was added in the funnel and was shaken carefully for 10 min. After complete separation of layers, the upper ethyl acetate layer was filtered through the Whatman filter paper. Extraction was repeated four times more and ethyl acetate fraction was collected into the same round-bottomed flask. The organic fraction was evaporated under a vacuum. The dry residue obtained from fractionation was dissolved in 5 ml of ethanol and transferred quantitatively into a 10 ml volumetric flask which is further applied for HPTLC determination after making it up to the mark.
Procedure
Before starting the analysis, HPTLC (CAMAG Linomat 5) plates were cleaned by predevelopment with methanol by ascending method. HPTLC plate was immersed in a CAMAG glass chamber (20 cm × 10 cm). Apply 10μl of Test solution on a precoated silica gel GF254 HPTLC plate (E. Merck) which was used as stationary phase, mobile phase Toluene: ethyl acetate: formic acid (7:3:1) and of uniform thickness of 0.2 mm. along with 10μl ethanolic extracts of each plant prepared in a concentration of 1mg/1ml. Develop the plate in the solvent system to a set distance. The plate was visualised under UV 254 nm and photo documentation was done. The plate was scanned at 254 nm wavelength.
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
It was observed that all these three formulation Polyherbal formulation-A, Polyherbal formulation-B and Polyherbal formulation-C have similar organoleptic characteristics such as liquid in nature, brownish-black slightly yellowish-green shade in colour, slightly bitter taste.
In Polyherbal formulation –A it was observed that, sedimentation volume ranging from (2.26-2.37), PH slightly alkaline pH (7.52-7.82), viscosity (48.0-52.2) rapid flow rate (25sec-27sec) per 5 ml of formulation and particle size observed around (20.25um-20.10um) (Table:5).
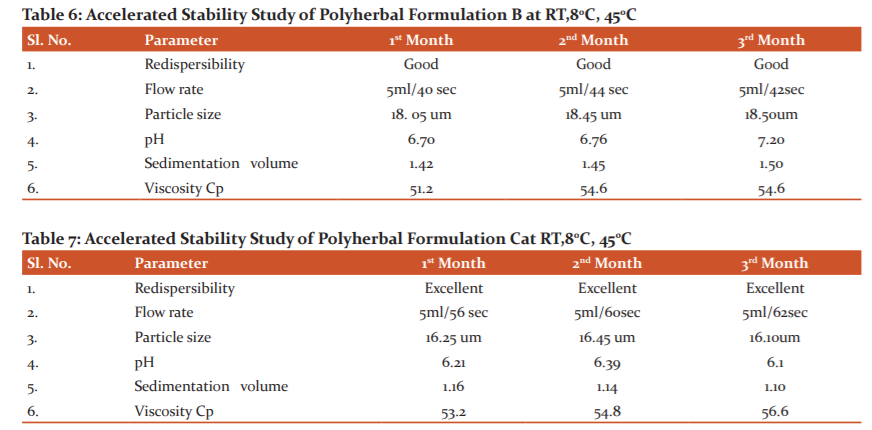
In Polyherbal Formulation –B it was observed that sedimentation volume reduced to ranging from (1.43- 1.52) as compared to Polyherbal formulation-A due to the increase in the concentration of Sodium C.M.C. it also affects the viscosity (51 centipoise to 56.2 centipoise), alkaline pH (6.68-7.40), increase in viscosity decrease the flow rate of formulation (40sec-44sec) per 5 ml of formulation and particle size observed around (20.25um-20.10um) (Table:6).
Polyherbal Formulation-3 formulation appears like brownish-black slightly yellowish-green shade in colour with characteristic odour and texture at room temperature (RT) and 45ºC. The suspension had a pleasant appearance and texture at different temperature and did not exhibit any change. As shown in the resulting pH of the suspension is 6.34 throughout storage, it does not show any appreciable changes. Viscosity centipoise and flow rate 56, 60 and 62 seconds per 5 ml indicating satisfactory rheological behaviour of formulated suspension. There were no noticeable changes in sedimentation volume as time increases because it is near to 1 which is the acceptable limit (Table no. 7).
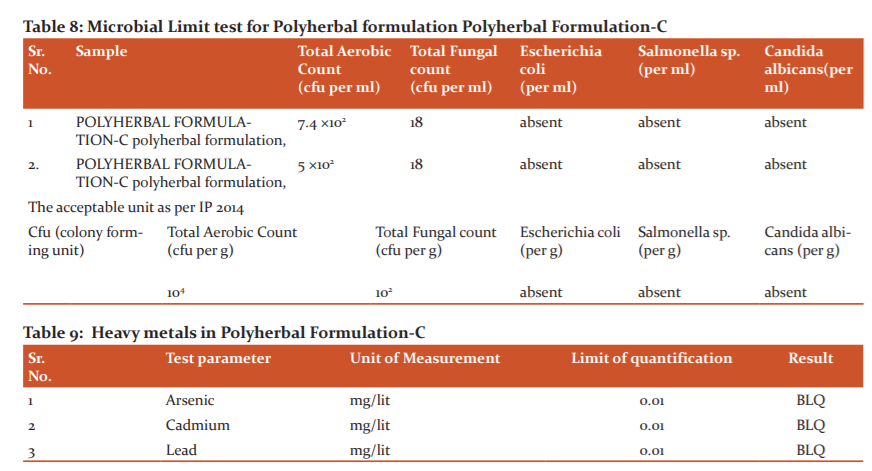
To assess the standard and shelf life of the herbal formulation total aerobic bacterial count was performed. Unintentional contamination, like fungal contamination throughout the production stage, may cause deterioration in safety and quality as the risk of mycotoxin production, particularly aflatoxin, could arise mutagenic, carcinogenic, teratogenicity, neurotoxic, nephrotoxic, and immunosuppressive activities For the evaluation of microbial contamination, total aerobic count, Total Fungal count, Escherichia coli, Candida albicans and Salmonella spp. the count was determined as per Indian Pharmacopoeia. It was observed that Polyherbal Formulation-C there is presence of TAC (7.4 and 5x102) cfu, TFC (18) cfu, and absence of Escherichia coli, Salmonella and Candida albicans which is within limits of standardization parameters (Table no-8).
WHO recommends that raw material obtained from medicinal plants which are used for the finished products may be scrutinized for the presence of heavy metals. World health organization set up the limits 1.0, 0.3, and 10 parts per million (ppm) of toxic metals like Arsenic, Cadmium, and Lead. During growth, development, collection transformation and processing of medicinal plants are mostly contaminated. During the development of dosage form, heavy metals enter into the body through plant material and accumulate in different organs and de channelized the normal functions of the central nervous system, liver, lungs, heart, kidney, brain and produce serious health problems such as damage to the kidneys, symptoms of chronic toxicity, liver damage and renal failure.
Heavy metals such as lead, cadmium and arsenic were estimated for Polyherbal formulation C at Nutralytica research centre and it was found to be below the level of quantification as per standardization parameters (Table no.9).
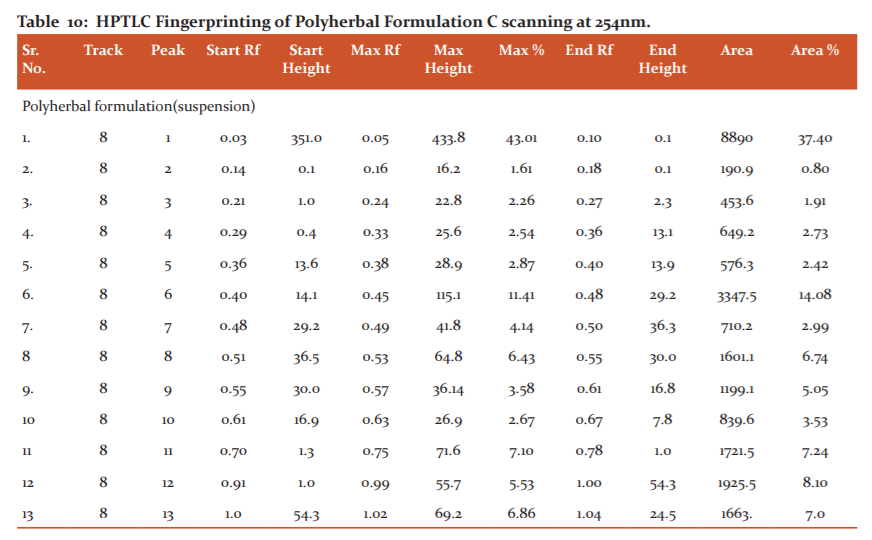
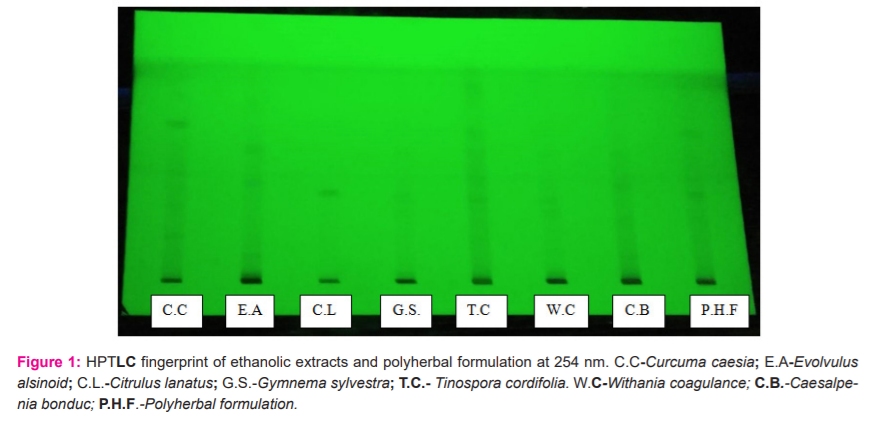
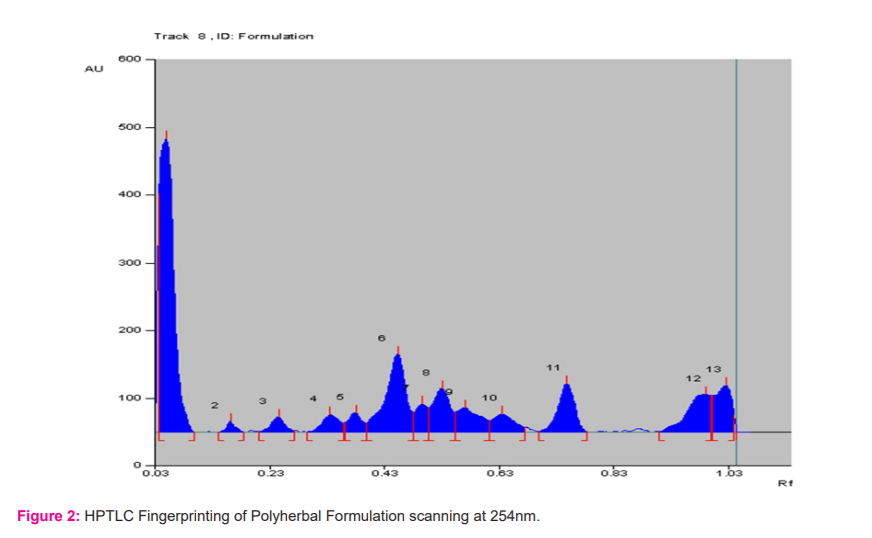
Investigation of the ethanolic extracts of the polyherbal formulation revealed the presence of phenols, flavonoids, tannins, terpenoids, steroids, glycosides and alkaloids whereas saponin was absent in the formulation as mentioned in alkaloids, etc. Fingerprinting analysis of the phytoconstituents present in Polyherbal formulation-C (Suspension) was carried out by using the HPTLC method. The results of the analysis are concluded in (Table 10) and Fig.(1 2).
The scanning done at wavelength 254 nm showed a total of thirteen bioactive compounds with Rf values 0.10,0.18, 0.27,0.36, 0.40, 0.48, 0.50,0.55, 0.61, 0.67, 0.78 with percentage peak area 37.40, 0.80, 1.91,2.73,2.42,14.08, 2.99, 6.74, 5.05, 3.53, 7.24, 8.10, 7.00 respectively. Out of the thirteen compounds, the compounds with Rf values 0.10, 0.48, 0.55, 0.61, 0.78, 0.83, were found to be predominant with peak area percentage in the range of 5.23 to 37.40. The maximum peak area percentage observed was 37.40 for the compound with the Rf value of 0.10. The HPTLC fingerprint analysis confirmed that the formulation possesses many phytoconstituents.
CONCLUSION
The present investigation revealed the presents of bioactive compounds such as phenolic, flavonoids, terpenoids, steroids, alkaloids and glycoside in the polyherbal formulation. The HPTLC fingerprint analysis confirmed that the polyherbal formulation possesses many phytoconstituents
Liquid dosage forms have the upper hand over solid dosage form in children and elder people due to them overcome the problem of swallowing. In Ayurveda, most of the formulations are developed in liquid form and mostly in combination with more than two crude drugs. Pharmaceutical suspension is one of the most trusted and acceptable formulations among another oral dosage form because of flexibility, ease of administration, easy swallowing in the administration of the drug. The polyherbal suspension was prepared by using lyophilized ethanolic extracts of selected plants by trituration method using a suitable suspending agent and other excipients.
There are noticeable changes were observed in sedimentation, viscosity and other physicochemical parameters after performing stability studies at variable temperature with different concentration of Sodium CMC. As per the result of accelerated stability studies of Polyherbal suspension A, B, and C it concludes that as we increase the concentration of Sodium C.M.C. gradually there is an increase in viscosity of the formulation, decreases the flow rate of formulation simultaneously. It also affects sedimentation volume and PH of the suspension. There were no noticeable changes in the organoleptic and physicochemical properties of the polyherbal formulation. In Polyherbal Formulation-C all the stability parameters are stable acceptable, and optimum at variable temperature.
ABBREVARTION
HPTLC: High performance thin layer chromatography;
CMC: carboxy methyl cellulose; Rf: retention factor;
nm: nanometer;
cfu: colony forming units;
TAC: Total Arabic count;
TFC: Total Fungal count;
ICP-MS: inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry;
UV: Ultra Violet;
RT: room temperature;
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest
SOURCE OF FUNDING
Nil
ETHICAL APPROVAL
Not Applicable
Present work is carried out under the supervision of Dr. Dheeraj T Baviskar and Manuscript preparation was prepared by Mr. S.M. Mahajan along with experimental work.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I am highly grateful to the Nutralytica research centre for performing the heavy metal detection test.
References:
-
Ansel HC, Allen LV. Pharmaceutical dosage forms and drug delivery systems, 7th edition, Lippincott, 2000; 347-56.
-
Aulton ME, Pharmaceutics: The Science of Dosage form. Churchill Livingstone, 1996, 304.
-
Subramani P, Gan ST, Sokkalingam A, Dhanaraj. Polyherbal Formulation: Concept of Ayurveda. Pharmac Rev. 2014; 8(16): 73–80.
-
Shinde JS, Khurde SS, Suchita LS, Chavan SS. Hulmajge SB. Need of polyherbal formulations and its standardization: A Review. World J Pharm Pharmac Scien.2016; 5(11):526-533.
-
Mukherjee PK. Quality Control of Herbal Drugs. New Delhi: Syndicate Binders; 2002.
-
Dandagi PM, Patil MB, Mastiholimath VS, Gadad AP. Development and evaluation of a hepatoprotective polyherbal formulation containing some indigenous medicinal plants. Ind J Pharm Sci Mar-Apr 2008;70(2):265-8.
-
Pandey VN, Rajagopalan. An effective ayurvedic hypoglycemic formulation. J Res Ayur Siddha. 1995; 16:1-14.
-
Khandelwal KR. Practical Pharmacognosy Technique and Experiments. Nirali Prakashan, 15th edition, 2006; 25.1-26.6.
-
Jain NK, Sharma SN. Textbook of Professional Pharmacy, Vallabh Prakashan, New Delhi, 3rd ed, 1994, 228.
-
Stability studies an overview of ICH guidelines for drug products: Natalie McClure, Matrix Pharmaceutical Inc. 1997.
-
Mahato RI. Pharmaceutical dosage forms and drug delivery. Boca Raton: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis group. 2007.123-133.
-
Microbial contamination in non-sterile products, (2.2.9), Volume I, Indian Pharmacopoeia, 2014; 38-50.
-
Stahl E. Thin Layer Chromatography – A Laboratory Hand Book. Second Edition. New York: Springer International Student Edition; 1969:311-471
-
Wagner H, Baldt S, Zagainski EM. Plant Drug Analysis. Germany: Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg; 1994:149-355.
-
Shanthi A, Radha R. pre-formulation Assessment: the fruit of Cuminum cyminum, Linn. Int J Curr Res Rev.2011;3(6):49-57.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License